Motion Graphs
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
There are ___ types of graph that can represent motion
5
5 types of graph that can represent motion:
Distance-time, displacement-time, speed-time, velocity-time, acceleration-time
On a distance-time graph, slope equals:
Speed
On a distance-time graph, the y-intercept equals the:
Initial position
On a distance-time graph, a straight (diagonal) line represents a:
Constant speed
On a distance-time graph, a curved line represents an:
Acceleration
On a distance-time graph, the slope can be zero/positive/negative/all
Zero or positive
On a distance-time graph, why can the slope be only zero/positive?
Distance is a scalar quantity
On a distance-time graph, a zero slope (horizontal line) represents a state of:
Rest
On a distance-time graph, what does the area under the curve represent?
Meaningless
On a displacement-time graph, slope equals:
Velocity
On a displacement-time graph, the y-intercept equals the:
Initial position
On a displacement-time graph, a straight (diagonal) line represents a:
Constant velocity
On a displacement-time graph, a curved line represents an:
Acceleration
On a displacement-time graph, a positive slope represents motion in the positive/negative direction
Positive
On a displacement-time graph, a negative slope represents motion in the positive/negative direction
Negative
On a displacement-time graph, a zero slope (horizontal line) represents a state of ______
Rest
What does the area under the curve of a displacement-time graph represent?
Meaningless
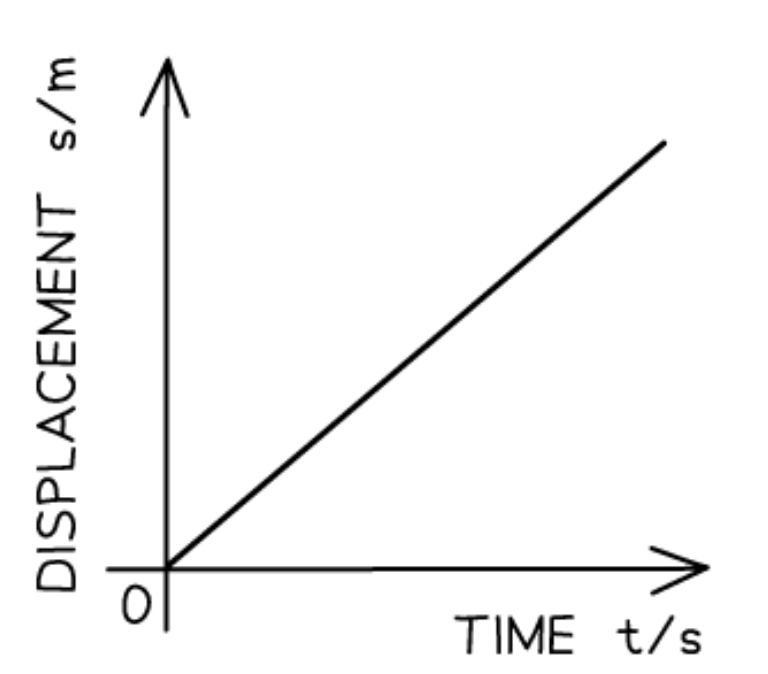
Displacement-time graph for constant velocity:
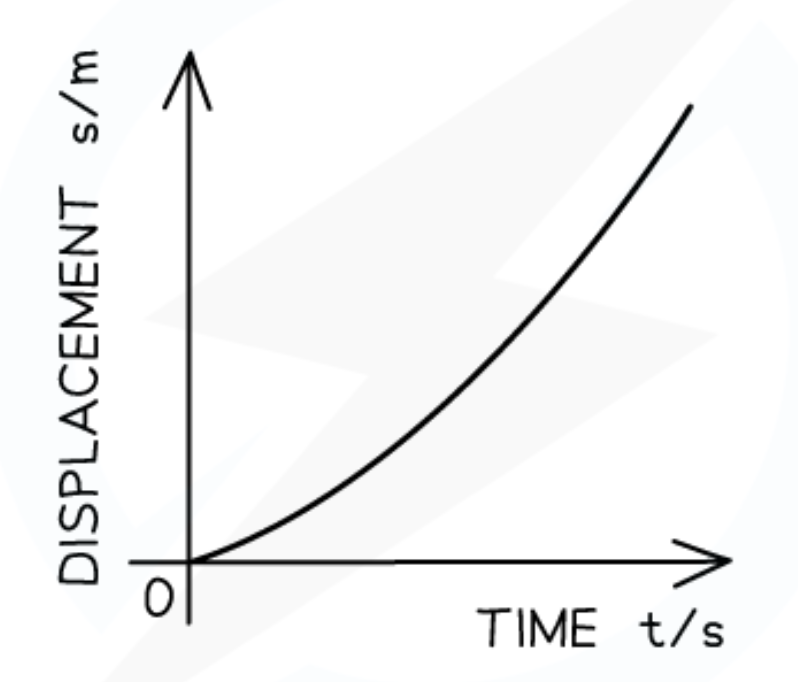
Displacement-time graph for velocity increasing at a constant rate:
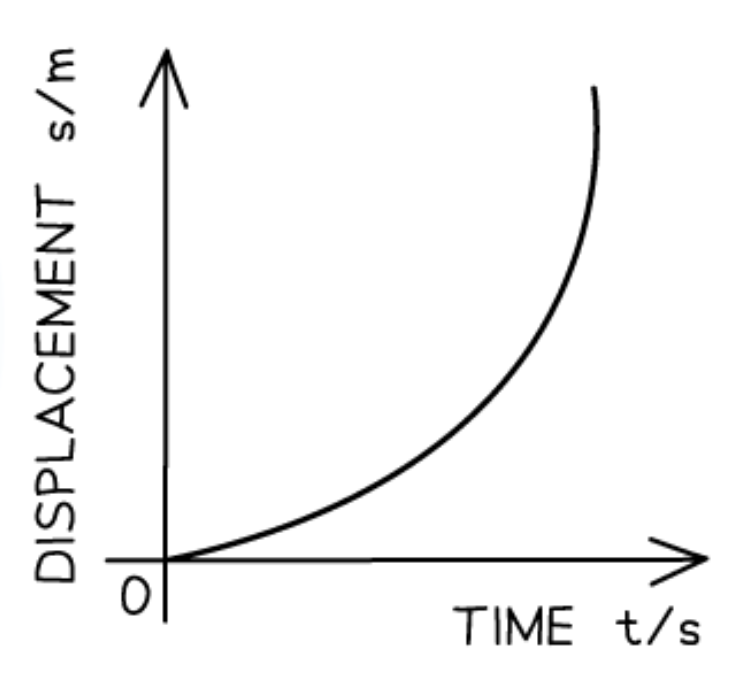
Displacement-time graph for velocity increasing and acceleration increasing at a constant rate:
The displacement-time graph for constant velocity is a:
Straight diagonal line
The displacement-time graph for acceleration is a:
Curve
On speed-time graphs, slope equals:
Acceleration
On speed-time graphs, the y-intercept equals:
Initial speed
On speed-time graphs, a straight line represents:
Uniform acceleration
On speed-time graphs, a curved line represents:
Non-uniform acceleration
On speed-time graphs, a positive slope represents an increase/decrease in speed
Increase
On speed-time graphs, a negative slope represents an increase/decrease in speed
Decrease
On speed-time graphs, a zero slope (horizontal line) represents motion with:
Constant speed
On speed-time graphs, the area under the curve equals the:
Distance travelled
On velocity-time graphs, slope equals:
Acceleration
On velocity-time graphs, y-intercept equals:
Initial velocity
On velocity-time graphs, a straight line represents:
Uniform acceleration
On velocity-time graphs, a curved line represents:
Non-uniform acceleration
On velocity-time graphs, a positive velocity and positive slope represents an increase/decrease in velocity in the positive/negative direction
Increase, positive
On velocity-time graphs, a positive velocity and negative slope represents an increase/decrease in velocity in the positive/negative direction
Decrease, positive
On velocity-time graphs, a negative velocity and positive slope represents an increase/decrease in velocity in the positive/negative direction
Increase, negative
On velocity-time graphs, a negative velocity and negative slope represents an increase/decrease in velocity in the positive/negative direction
Decrease, negative
On velocity-time graphs, a zero slope (horizontal line) represents motion with:
Constant velocity
On velocity-time graphs, the area under the curve equals the:
Displacement
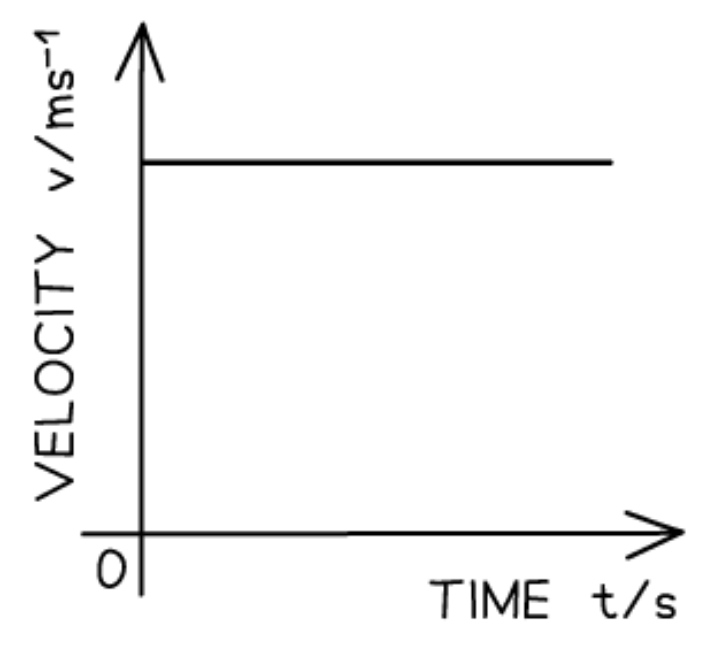
Velocity-time graph for constant velocity:
Velocity-time graph for increasing velocity:
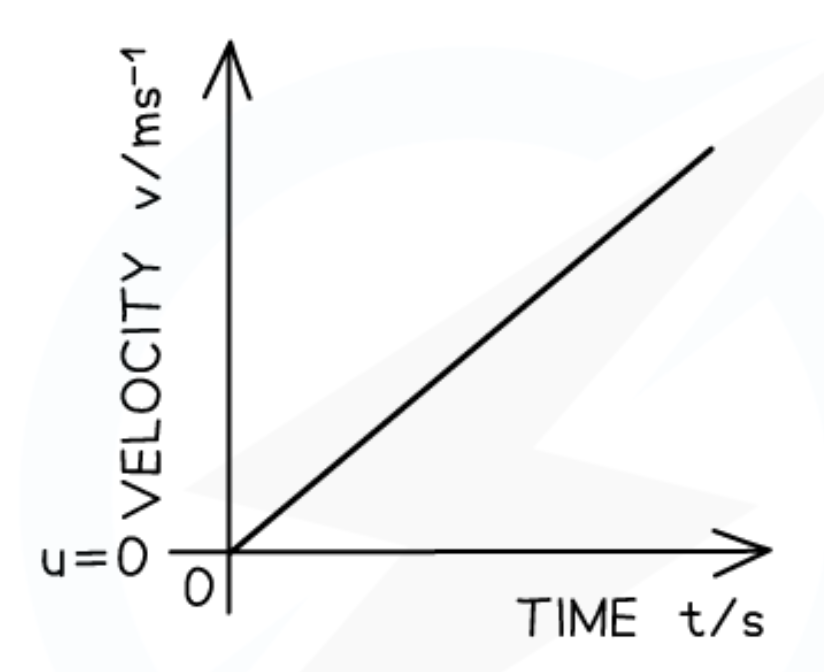
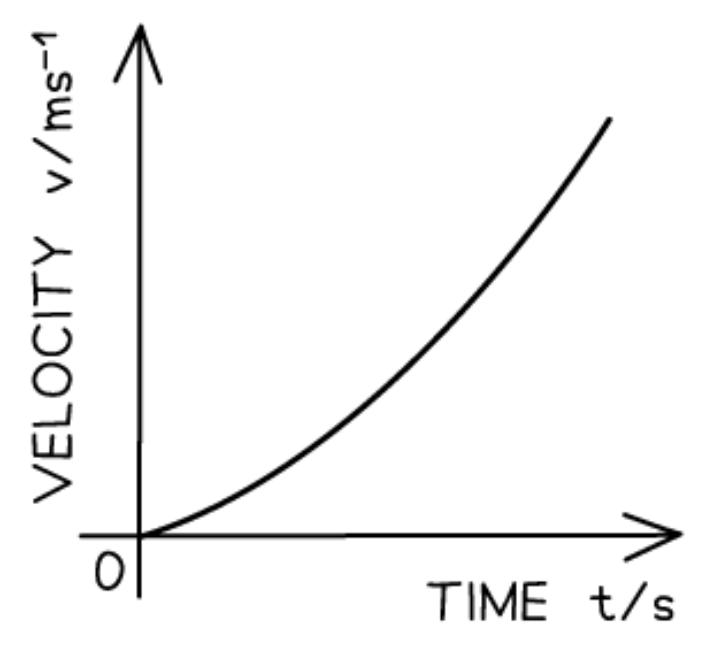
Velocity-time graph for increasing acceleration:
The velocity-time graph for constant velocity is a:
Straight horizontal line
The velocity-time graph for acceleration is a:
Straight diagonal line
The velocity-time graph for increasing acceleration is a:
Curve
On an acceleration-time graph, the slope equals:
meaningless
On an acceleration-time graph, the y-intercept equals the:
Initial acceleration
On an acceleration-time graph, a zero slope (horizontal line) represents an object undergoing:
Constant acceleration
On an acceleration-time graph, the area under the curve equals the:
Change in velocity
Acceleration-time graph for constant velocity:
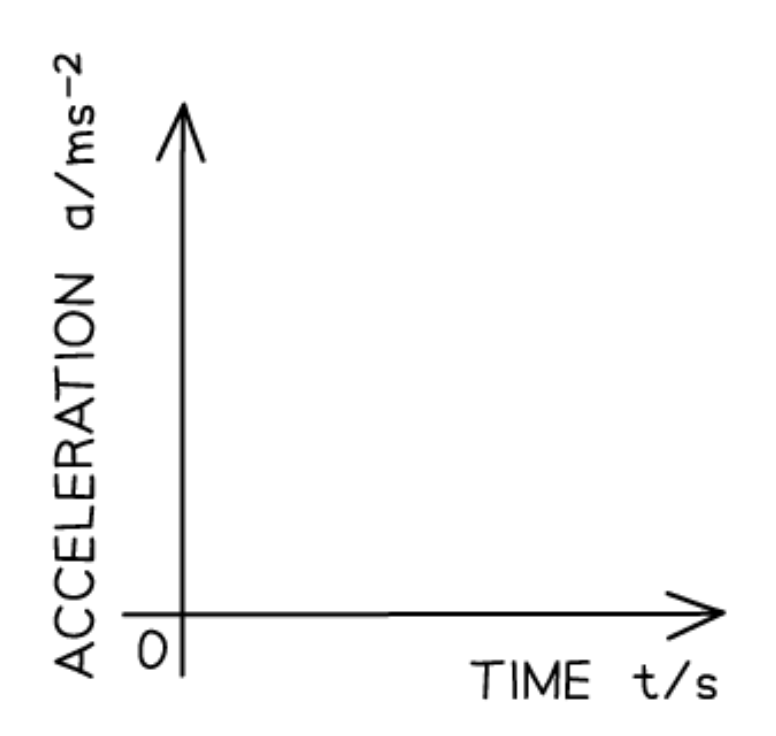
Acceleration-time graph for increasing velocity:
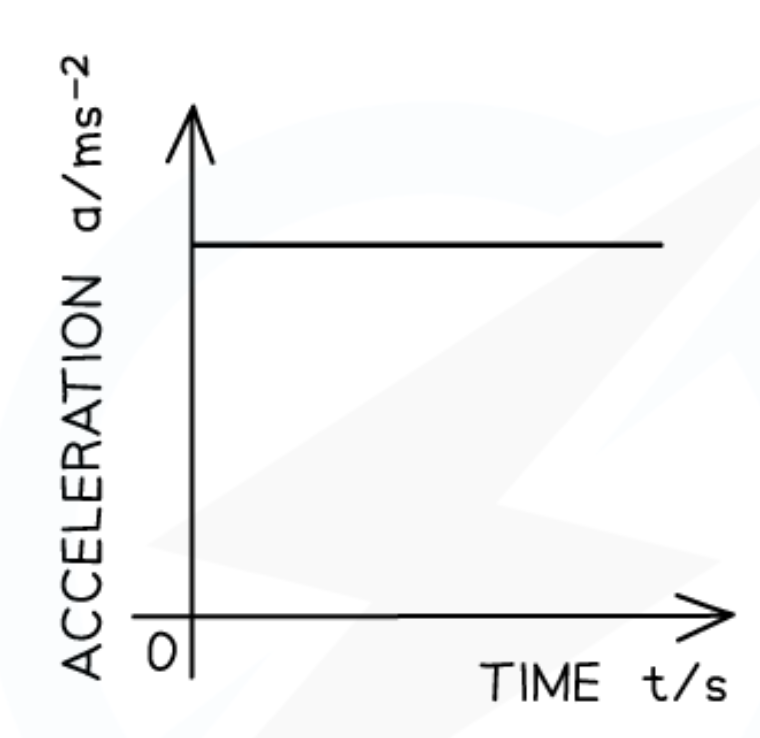
Acceleration-time graph for increasing acceleration:
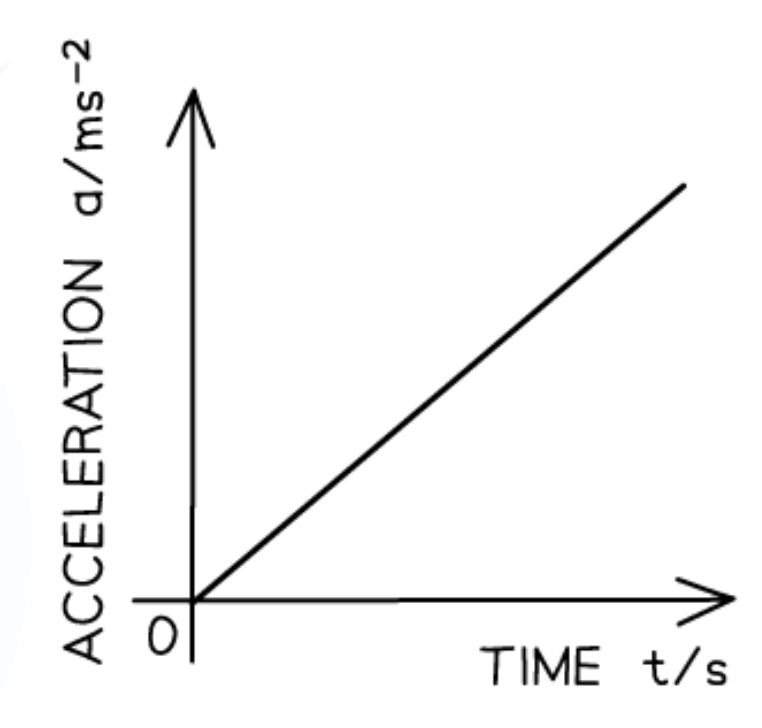
The acceleration-time graph for constant velocity is:
Blank
The acceleration-time graph for increasing velocity is a:
Straight horizontal line
The acceleration-time graph for increasing acceleration is a:
Straight diagonal line
Always check the ______ when dealing with graphs
Axes
The differences between distance-time graphs and displacement-time graphs, and speed-time graphs and velocity-time graphs are:
Subtle but important