Industrial Revolution
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
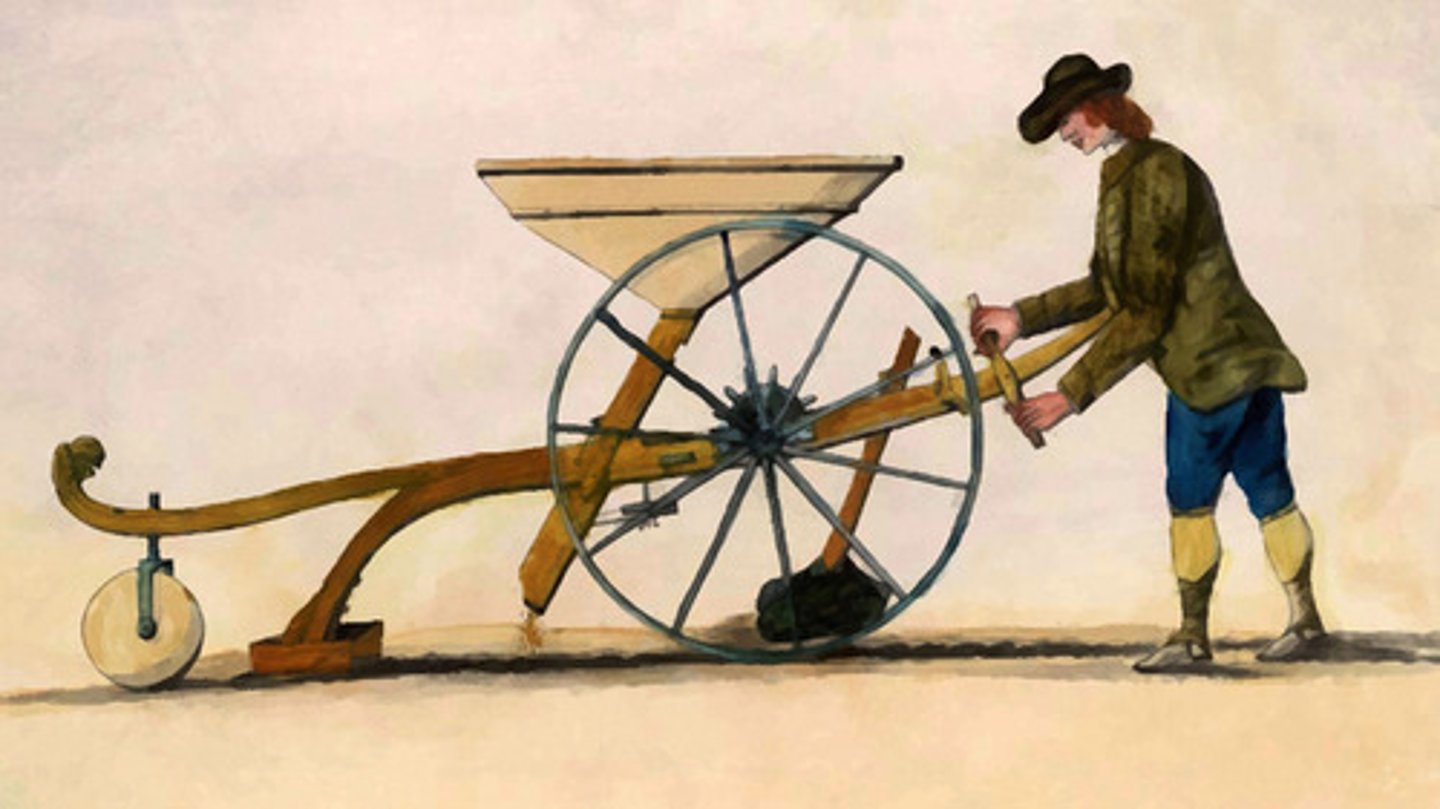
Agricultural Revolution
A time when new inventions such as the seed drill and the steel plow made farming easier and faster. The production of food rose dramatically. Also known as Agrarian Revolution.
Enclosure Movement
Practice of fencing or enclosing common lands into individual holdings. Small tenant farmers couldn't afford the land so pushed people to the cities to find work.

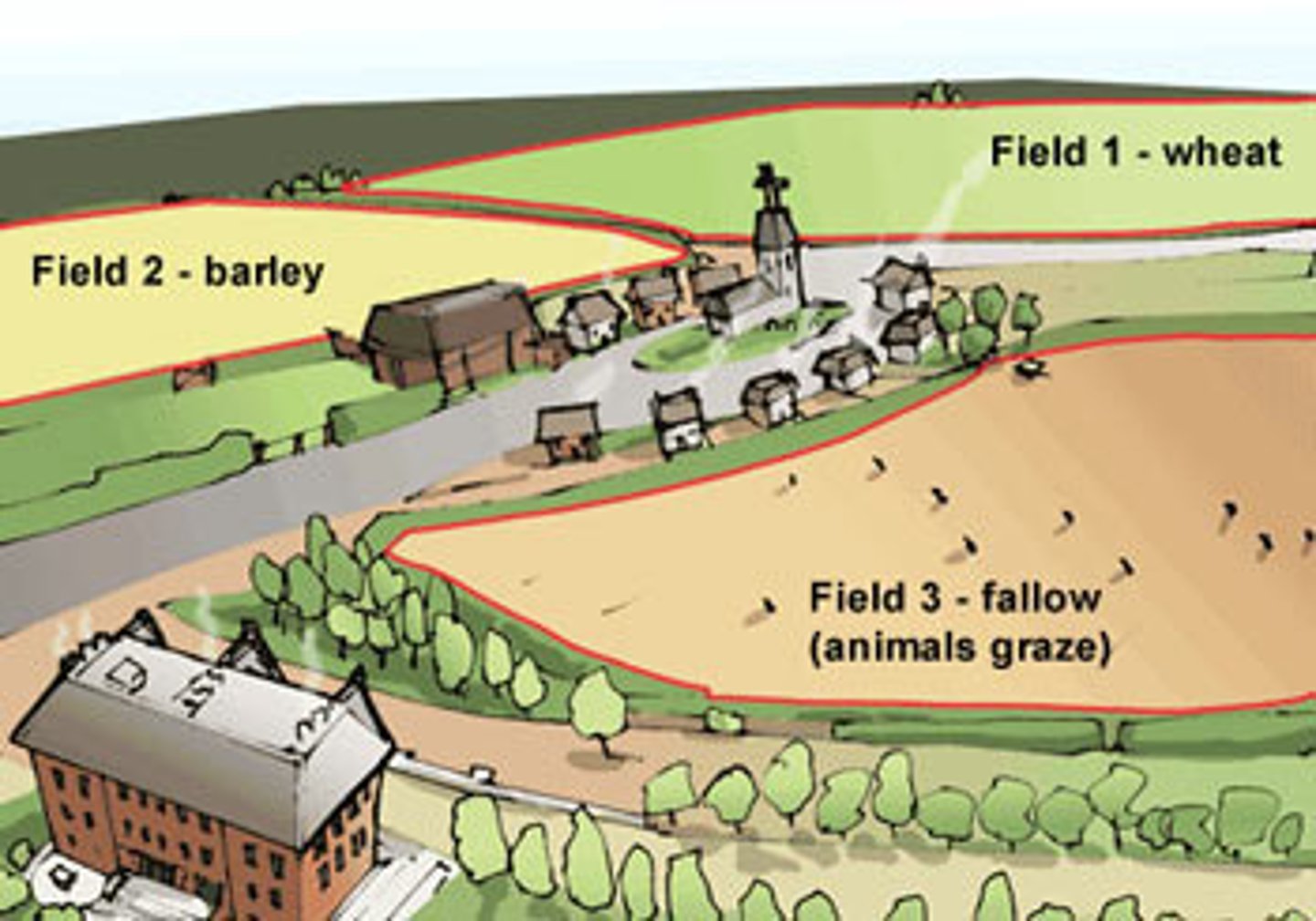
crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil.
Domestic System
Early industrial labor system in which workers produced goods at home.

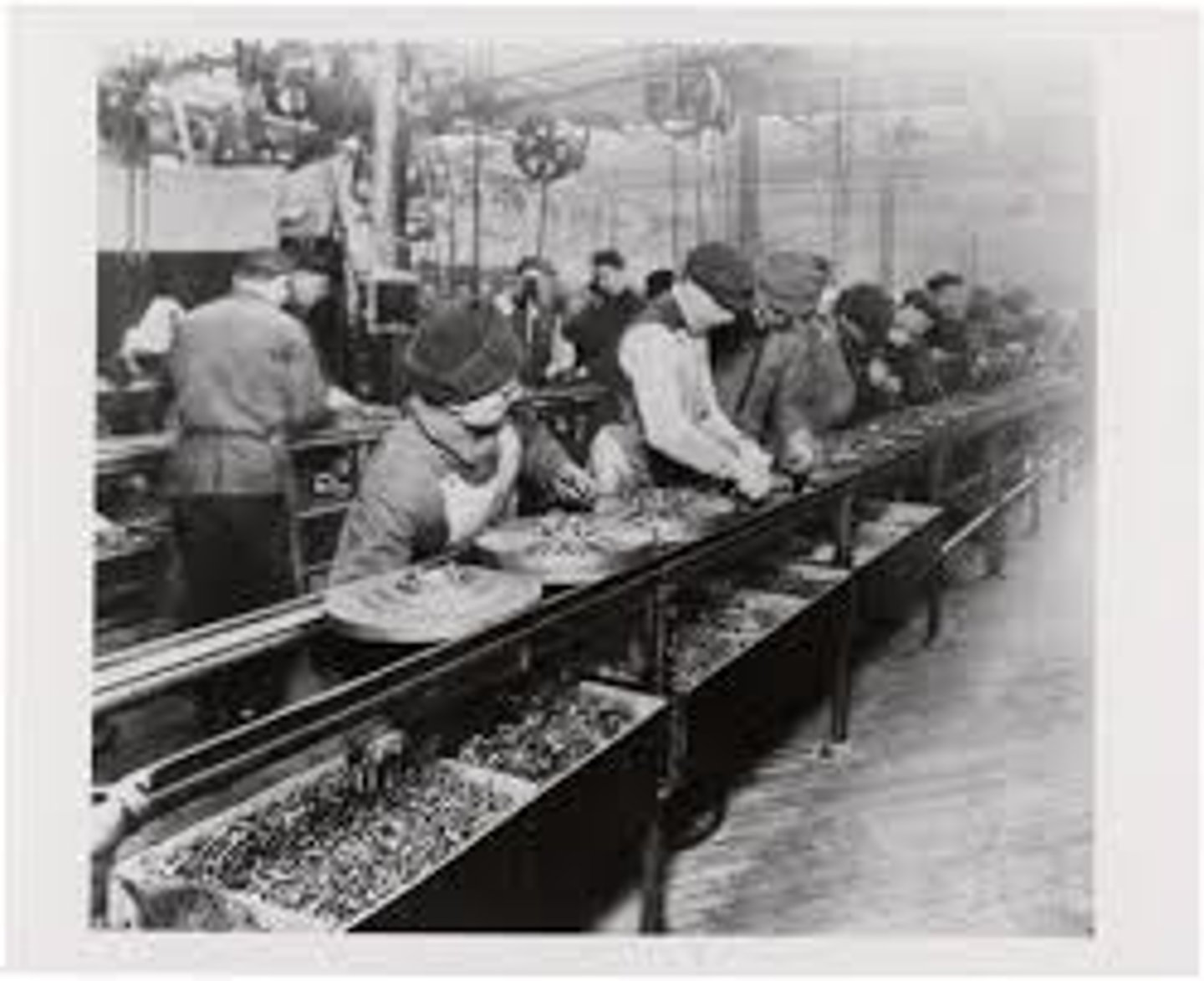
assembly line
In a factory, an arrangement where a product is moved from worker to worker, with each person performing a single task in the making of the product.

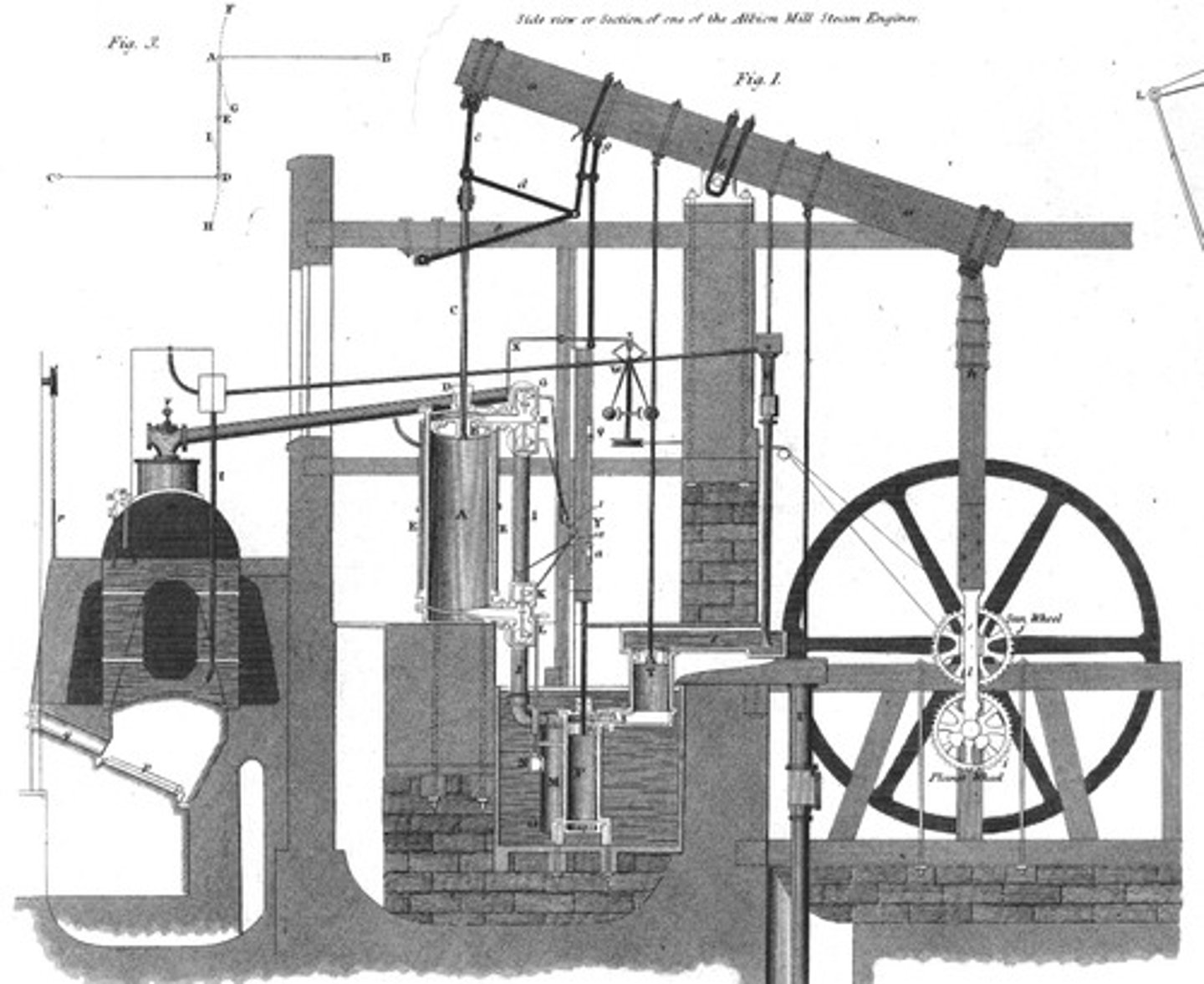
Steam Engine (James Watt)
invented by James in mid 1700s, powered by steam and coal that could pump water from mines three times as quickly as previous engines.
Entrepreneur
A person who organizes, manages, and takes on the risks of a business.
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban (city) settlements.

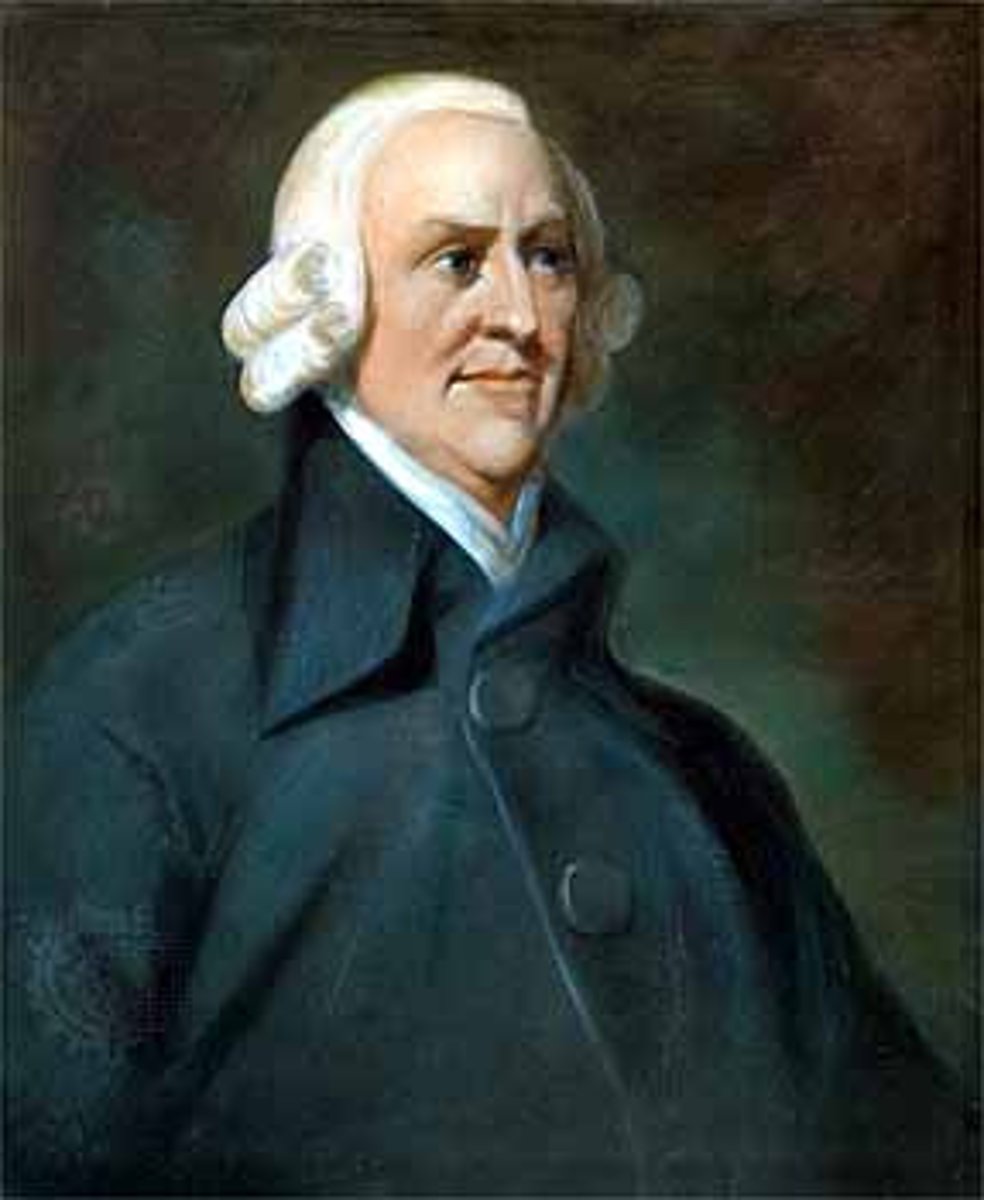
Adam Smith
Scottish philosopher and a pioneer of political economics. Seen today as the father of Capitalism. Wrote "The Wealth of Nations" (1776).

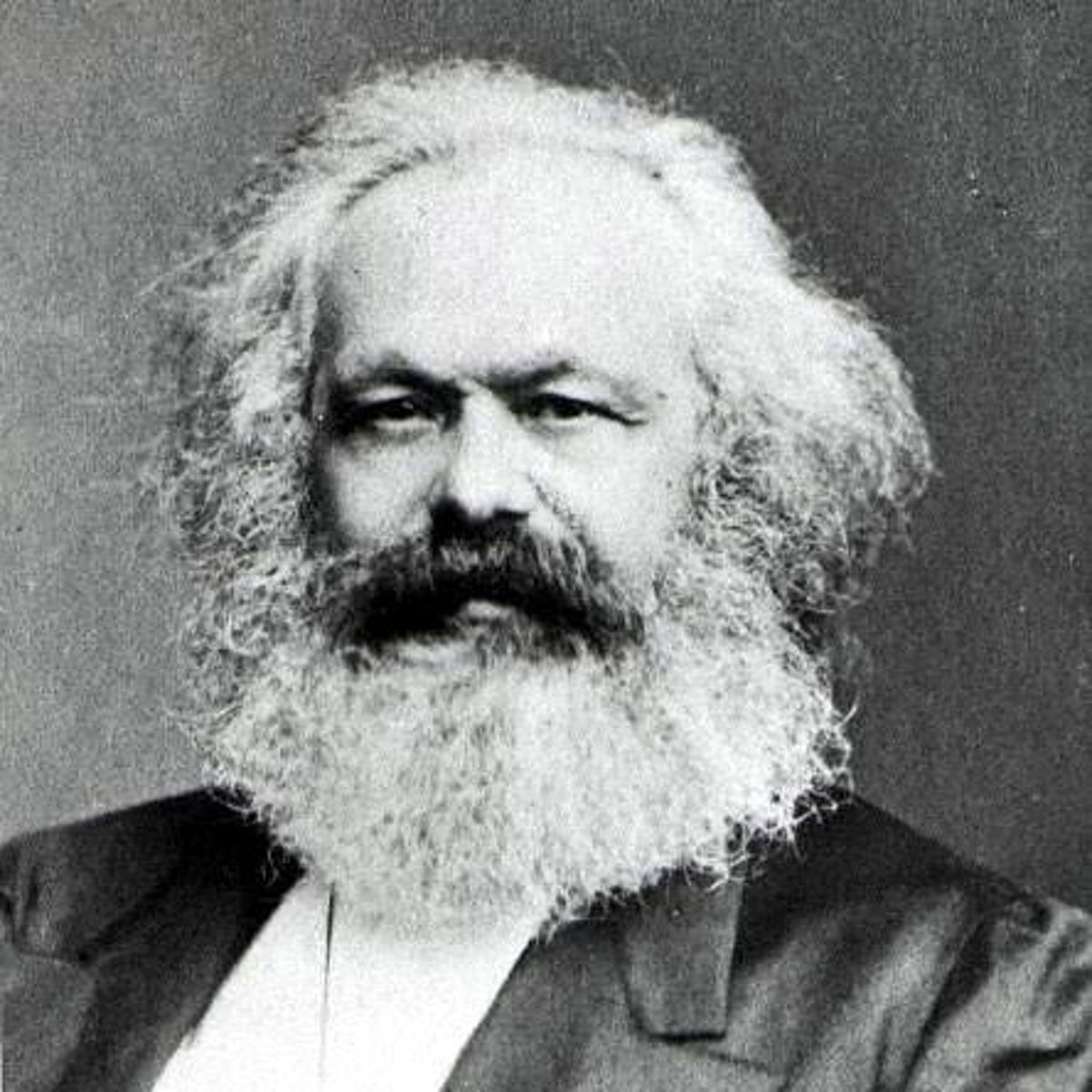
Karl Marx
19th century philosopher, political economist, sociologist, humanist, political theorist, and revolutionary. Often recognized as the father of communism. Believed in a classless society.

Laissez-faire
Idea that government should play as small a role as possible in economic affairs.

Capitalism
an economic and political system in which a country's trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state.
Socialism
the people as a whole rather than private individuals would own and operate the means of production.
Communism
A theory or system of social organization based on the holding of all property in common, actual ownership being ascribed to the community as a whole or to the state.
Monopoly
Complete control of a product or business by one person or group.

Social Darwinism
The belief that only the fittest survive in human political and economic struggle.
Sadler report
A report on child labor conditions that led to new laws against child labor because of bad working conditions.
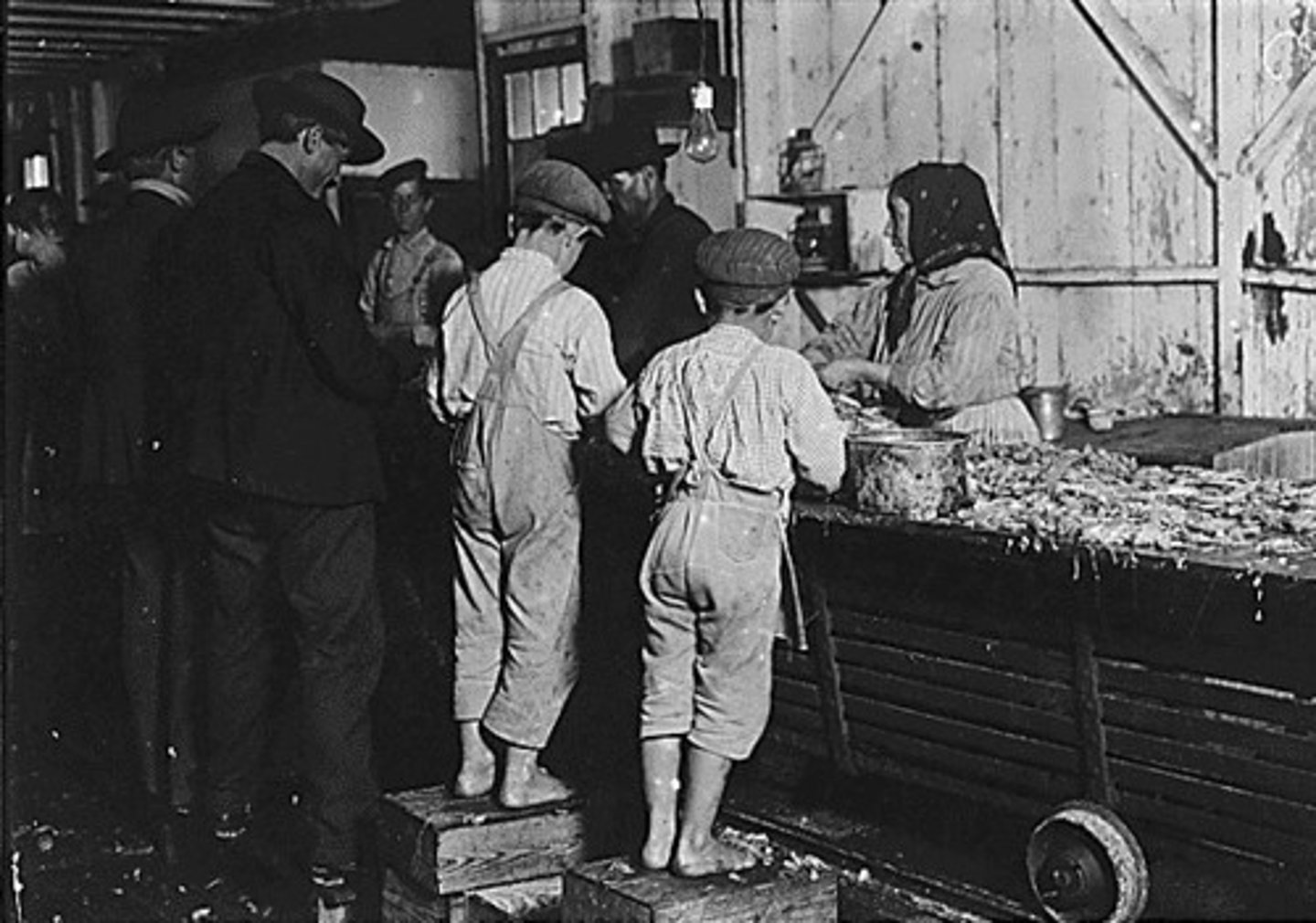

labor union
An organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members

Causes of the Industrial Revolution
1. Agricultural Revolution
2. Population Explosion
3. Energy Revolution

Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain?
1. Natural Resources & Geography
2. Labor & Capital
3. Entrepreneurs & Inventors
4. Favorable climate for Business
Innovations of the Industrial Revolution
Steam Engine
Less-expensive & better quality iron
Medical advancements - IE. anesthesia
Seed Drill
New sources of energy - using natural resource (IE. coal, water)
Cotton gin
Spinning Jenny
Flying Shuttle
Effect of the increase in population from the Industrial Revolution
Rapid urbanization-as small downs became busy industrial centers, labor & people were greatly changed.
1. Major benefits for entrepreneurs
2. New middle class - clean, pleasant neighborhoods
3. Poor lived in crowded, unsanitary tenements
Positive Results of the Industrial Revolution
Labor Unions form
More job opportunities & more goods available - lower prices.
Chances for social mobility & higher standards of living.
New technology
Communication & transportation
Cities
Expanded trade, education, mid class, role of women
Medicine
Negative Results of the Industrial Revolution
Harsh conditions in factories & mines - unsafe, long hours, low wages, women & children
Growth of Big Business & monopolies - negative for competition
Living Conditions - pollution, disease, fire
How did Parliament respond to the problems in Britain caused by the Industrial Revolution?
Many reforms, Acts, Bills, etc to work toward women's suffrage & worker's rights