Module 7: Earthquakes & Volcanoes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is stress in rocks?
What causes it?
How does stress lead to faults?
Stress is any force applied to a rock
Tectonic activity
Magma moving into crust
Pull of gravity
When the rock finally breaks, pieces move along a fault in response to the direction of the stress
What is strength in rocks?
Strength is a rock’s ability to resist stress
How do the three directions of stress compare to the types of plate boundaries?
Tensional stress → divergent
Compression stress → convergent
Sheer stress → transform
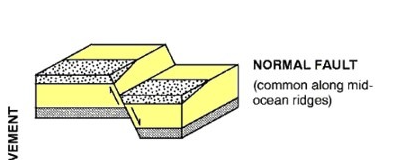
What is a normal fault, and how does it compare to the direction of stress?
Vertical movement
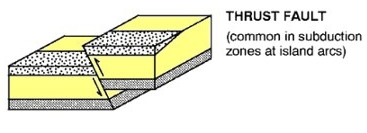
What is a revers/thrust fault, and how does it compare to the direction of stress?
Vertical movement
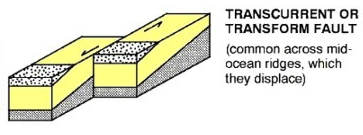
What is a transcurrent/transform fault, and how does it compare to the direction of stress?
Horizontal movement
How does elastic rebound theory explain earthquakes? Why aren’t earthquakes predictable?
When rocks accumulate stress and break, they result in earthquakes
We don’t yet have the technology to accurately predict most earthquakes
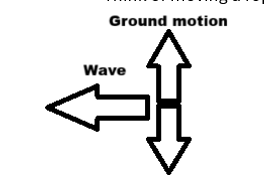
Characteristics of P-waves (5)
Fastest
High frequency, low amplitude
Travels through solids, liquids, and gases
Ground motion is same as wave’s direction
Length of p-wave is directly proportional to how far earthquake is
Characteristics of S-waves (4)
Slower than p-waves
Lower frequency, higher amplitude
Travels only through solids → can’t travel through outer core
Sheer — direction of ground motion perpendicular to wave’s direction
Characteristics of Surface waves (4)
Slowest
Causes damage
Low frequency, high amplitude
Limited to earth’s surface
How does Moment Magnitude measure the intensity of an earthquake?
It measures the amount of movement along a fault, which relates to the energy released
How do earthquakes reveal information about the interior of the earth?
Certain waves travel through certain states of matter, which can tell us what such states make up the interior of the earth
Why are each of the following three hazards associated with earthquakes?
Fire — shaking can cause objects to catch fire
Liquefaction — vibrations cause ordinarily-solid ground to flow like a liquid
Tsunami — caused from the seafloor suddenly changing shape
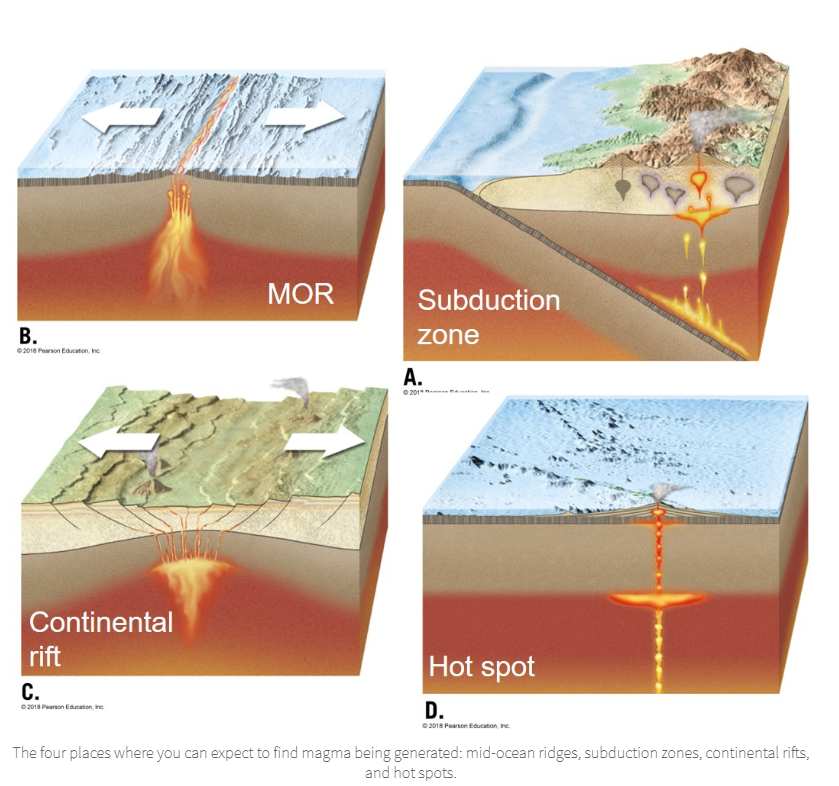
At what kinds of locations does melting occur? (4)
Mid-ocean ridge
Subduction zone
Continental rift
Hot spot
What is viscosity, and what affects the viscosity of lava?
Viscosity is how easily the lava flows
The composition and temperature of the lava affect its viscosity
Characteristics of low viscosity lava (6)
Pahoehoe
High temperature
More mafic
Effusive eruptions
Shield volcanoes
Occasional cinder cone volcano
Characteristics of high viscosity lava (5)
A’a
Low temperature
More felsic
Explosive eruptions
Stratovolcanoes/composite volcanoes
Why was the eruption of Krakatau significant? (4)
Because the effects felt were not limited to where the eruption occurred
Biggest explosion was loudest sound heard by human ears
Global av temps dropped 1.2 degrees Celsius
Unusual weather patterns for next 5 years
What are the following five volcanic hazards?
Volcanic ash — tiny, sharp rock fragments that damage machinery & lungs
Pyroclastic flow — superheated cloud of rock fragments
Lahar — muddy mix of melted ice & rock fragments
Volcanic gases — poisonous gases
Tsunami