Thyroid Gland Pharmacology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
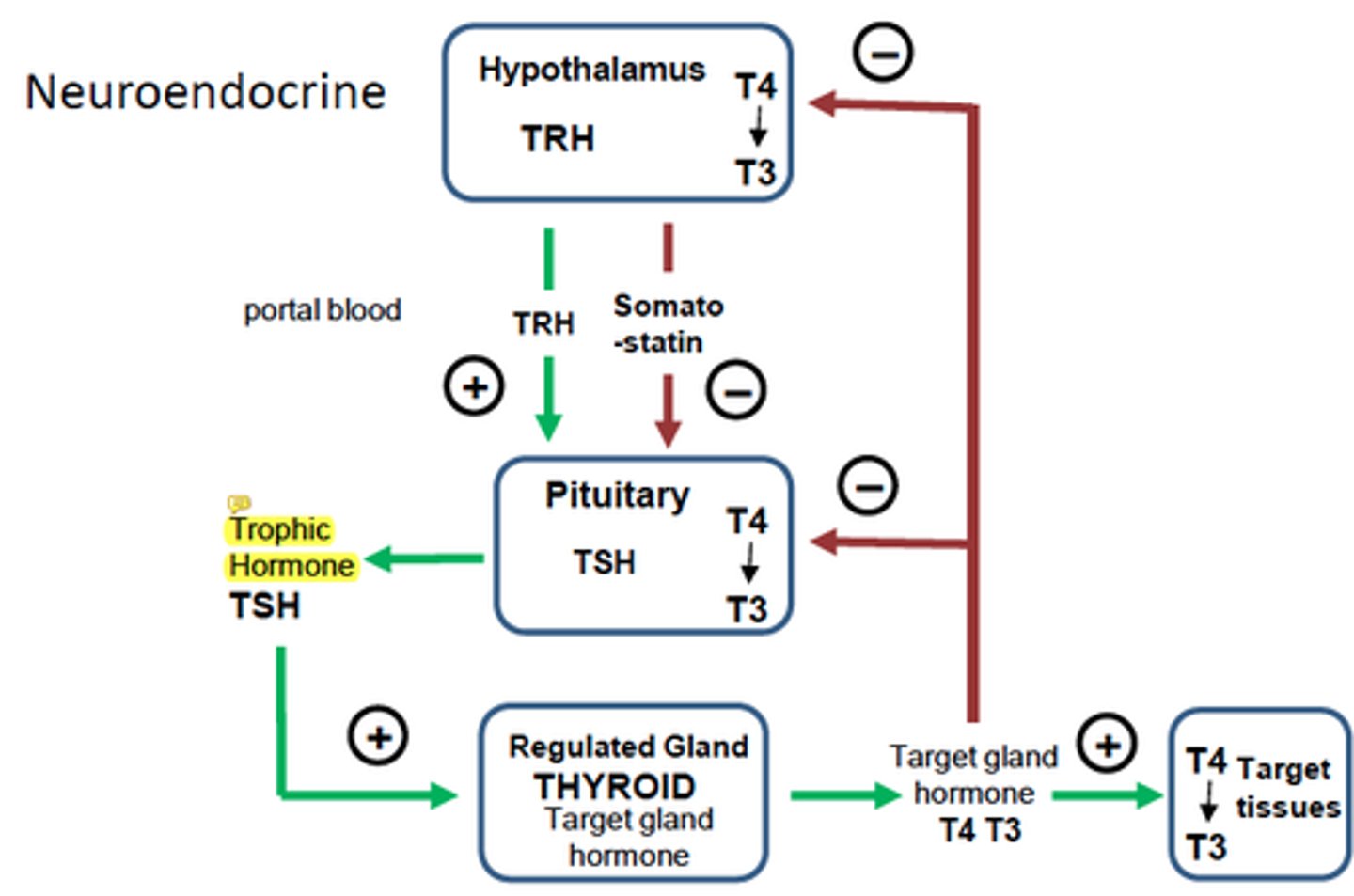
How is the secretion of thyroid hormone controlled?
What are the tests for thyroid function?
- Serum TSh
- Serum free T4
- Serum free T3
What result does each thyroid test give for hyperthyroidism?
- Decreased serum TSh
- Increased serum free T4
- Increased serum free T3
What result does each thyroid test give for hypothyroidism?
- Increased serum TSh
- Decreased serum free T4
- Decreased serum free T3
What are the forms of thyroid disease?
- Hyperthyroidism - overactivity
- Hypothyroidism - underactivity
- Goitre - enlargement
How prevalent is hyperthyroidism?
- 1.3% (more common in women than men)
- 1 in 50 women
- 1 in 500 men
How prevalent is hypothyroidism?
- 4.6% (more common in women than men)
- 40/100 women
How prevalent is goitre?
- 24.4% (more common in women than men)
What is the aetiology (cause) of hyperthyroidism?
- Graves' hyperthyroidism
- Toxic nodular goitre (single or multinodular)
- Thyroiditis (silent, subacute): inflammation
- Exogenous iodine
- Facetious (taking excess thyroid hormone
- TSH secreting pituitary adenoma
- Neonatal hyperthyroidism
What are the cardiovascular symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
- AF (atrial fibrilation)
- Shortness of breath
- Ankle swelling
What are the neurological symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
- Tremor
- Myopathy (muscle weakness)
- Anxiety
What are the gastrointestinal symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
- Weight loss
- Diarrhoea
- Increased appetite
What are the eyes/skin symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
- Sore, gritty eyes
- Double vision
- Staring eyes
- Pruritus (itching)
How many cases of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease?
- 60-80%
- Most prevalent autoimmune disorder in UK and US
What are the causes of Graves' disease?
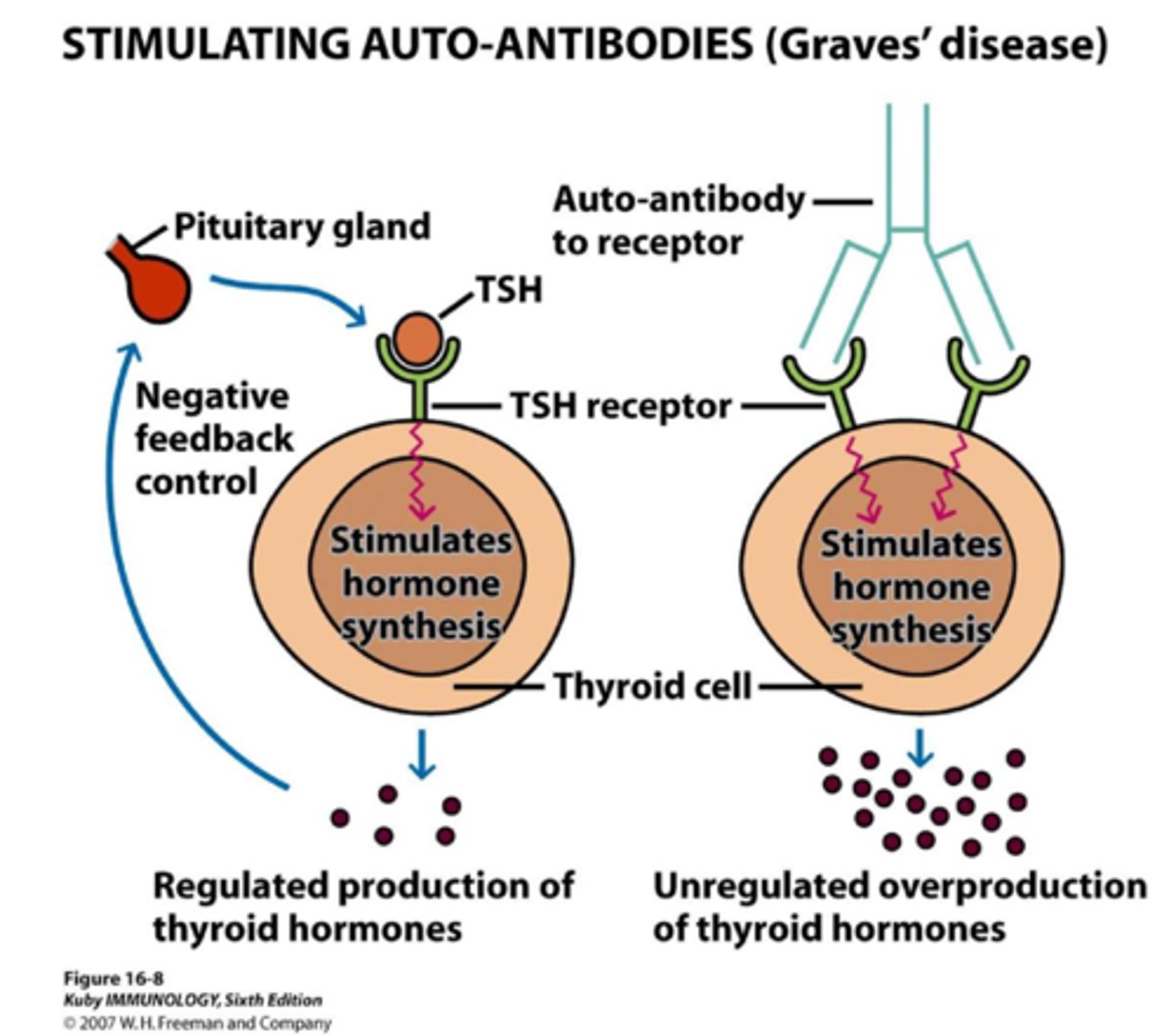
- Pathogenetic antibodies mimic TSH and bind to TSH receptor on thyroid follicular cells (Long Acting Thyroid Stimulators)
- Interplay between genetic (80%) and environmental factors (20%)
- Environmental factors - gender, stress, infection, pregnancy, drugs
Graves' disease pathogenesis
What occurs with neonatal hyperthyroidism?
- TSH-R antibodies cross the placenta
- Control hyperthyroidism in mother during pregnancy
How is hyperthyroidism diagnosed?
- Clinical features of Graves'
- Consider iodine uptake scan - GD vs thyroditis
- Consider isotope imaging - GD vs TN hyperthyroidism
- TPO abs +ve in 75% of Graves'
- TSH receptor Abs +ve in 99% of Graves'
How is hyperthyroidism treated?
- Antithyroid drugs to block hormone synthesis
- Surgical removal of thyroid
- Radioiodine (131) therapy
What are the considerations of thionamide therapy?
-> Rapid control, well tolerated
-> Side effects
- Rash (5%), joint pains (5%), sickness (5%)
- Agranulocytosis - no white blood cells, infection risk, rare, 1:1000 or less - KNOW
- Liver disease with propylthiuracil - KNOW
- Pancreatitis with carbimazole
-> Low cure rate
- 30-40% (lower in men)
When is surgery used for hyperthyroidism?
-> Used infrequently
-> Pre-treatment with antithyroid drugs
-> Indications:
- large goitre (especially if suspicion of co-existing thyroid cancer)
- Pregnancy (serious side-effects of drugs
- Pronounced ophthalmopathy
- Patient preference
What are the features of iodine-131?
- Capsule (fixed dose)
- Highly effective (85% cure) - iodine more concentrated in thyroid as that is the only place with iodide symporter
- Usually pre-treatment with drugs
- May worsen eye disease (steroids)
- Risks:
-> Hypothyroidism (~60%)
-> Cancer
-> Infertility
-> Tetratogenesis (contra-indicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding)
What are the treatment aims and prognosis of hyperthyroidism?
-> Treatment aims
- Relieve symptoms
- Restore T4 and T3 values within normal range
- Obtain long-term normal thyroid function
-> Prognosis
- 30% od patients with Graces' disease have normal thyroid function long-term following drugs
- 131-I and surgery associated with >50% risk of long-term hypothyroidism
What is the aetiology of hypothyroidism?
- Autoimmune - Hashimoto thyroiditis (TPO and Tg antibodies - genetic predisposition)
- After treatment for hyperthyroidism
- Subacute/silent thyroiditis
- Iodine deficiency
- Congenital (thyroid agenesis/enzyme defects)
What are the causes and symptoms of hashimoto thyroditis?
- Body produces TPO and Tg antibodies which damage thyroid follicular cells
- Inflammation and goitre/swelling
- Fibrosis and shrinkage
What is the main source of iodine in diet?
- Milk and dairy products
What are the cardiovascular symptoms of hypothyroidism?
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Heart failure
- Pericardial effusion
What are the gastrointestinal symptoms of hypothyroidism?
- Weight gain
- Constipation
What are the skin symptoms of hypothyroidism?
- Myxoedema
- Rash on legs
- Vitiligo
What are the neurological symptoms of hypothyroidism?
- Depression
- Psychosis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
What is Levothyroxine?
- Synthetic T4
- 33 million tablets prescribed in UK annually
- Goal of therapy is to restore patients to euthyroid state and to normalise serum TSH concentrations (best marker of thyroid status in primary hypothyroidism)
- Long half-life - takes 6 weeks to reach steady state levels
What is the prevalence of goitre?
- Wickham survery
- Palpable goitre - 8.6% (women - 12.1%, men - 4.5%)
- Visible goitre - 6.9%
What is the significance of thyroid nodules?
- May cause thyroid dysfunction
- May cause compression
- Need to exclude thyroid cancer
- Prevalence of malignancy is 4-6.5%
- Independent of nodule size
- Malignancy risk in incidentalomas remains controversial
- Risk of PET-positive thyroid nodule - 27%
How common is thyroid cancer?
- Rare
- Less than 10% of nodules selected for surgery
- 1% of all new malignancies diagnosed in UK (2016-2018)
- 20th most common cancer
- Important to select those with thyroid cancer
How are thyroid nodules investigated?
1) Assessment of thyroid function
2) Assessment of thyroid size
3) Assessment of thyroid pathology
What occurs during the assessment of thyroid function?
- Serum TSh
- Serum free T4, serum free T3
- (thyroid antibodies)
What occurs during the assessment of thyroid size?
- Symptoms
- X-ray thoracic inlet
- CT or MRI of neck
- Respiratory flow loop
- Barium swallow
What occurs during the assessment of thyroid pathlogy?
- Radionuclide scanning
- Ultrasound scanning
- Fine needle aspiration
What occurs in thyroid ultrasound scanning?
- Differentiation of solid from cystic nodules
- Differentiation of single from multiple nodules (superior to palpation)
- Criteria suggestive of malignancy (irregular margin, calcifications, solid, increased blood flow)
- Guidance of fine needle aspiration
What is used for differentiated thyroid cancer?
- External beam DXT
- Chemo RX
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor Rx