Blood and Heart
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Six general functions of blood?
Transport, Immune component, clotting, temperature regulation, pH (Proteins, RBCs), and osmotic fluid distribution
3 determinants of blood plasma osmolarity
sodium concentration, RBC, and plasma protein (albumin created by the liver)
polycythemia
elevated RBC
Average blood volume
5 Liters
Three main proteins in the blood
albumin, globulins, fibrinogen
Components of blood
Plasma: protein(7%), water (91%), other solutes (2% i.e. waste, nutrients ions, etc.); Cells: Platelets, White blood cells, RBCs
Function of the 5 main white blood cells (WBCs) found in blood?
protect the body from infections
granulocyte vs agranulocyte
Granulocytes contain visible granules that can be used to attack foreign cells or alert other immune system cells
Agranulocytes do not contain visible granules, serving to either eat pathogens through phagocytosis or alert other cells about the infection.
Hematopoiesis
Blood cell production
Cytokines
Chemicals released by the immune system communicate
Erythropoiesis: Location and stimulator
red bone marrow and EPO from kidneys/liver
Typical life span of RBC
~120 days (no nucleus)
Hematocrit def. and gender percentatges
% of blood samples that are RBCs; Men: 42-52%, Women:37-48%
How does respiratory illnesses like emphysema or chronic bronchitis impact hematocrit levels?
Decreased oxygen from the respiratory system results in increased EPO production leading to a increased hematocrit
Effects of polycythemia versus anemia
Polycythemia: increased RBC, viscosity, Blood volume, and decreased heart rate (HR);
Anemia: decreased RBC, viscosity, blood volume, and increased HR
Causes of Hypoxia
decreased RBC count, Decreased hemoglobin, Decreased Oxygen availability
Effect of emphysema on RBC count
decreased oxygen access->increased EPO synthesis->increased RBC count->polycythemia
Components of Hemoglobin complex
Heme(4 and contains iron that oxygen binds with) and globin (2 alpha and 2 beta)
Shape of red blood cell
biconcaved disc
Sickle cell
HbS results from one amino acid difference in beta chain; result is aggultination (clumping), poor oxygen capacity, and hemolysis
Other components needed for erythropoiesis
EPO, Iron, B12, folic Acid, Vitamin C, Copper
Iron Deficiency Anemia
anemia resulting when there is not enough iron to build hemoglobin for red blood cells
Where RBCs go to die
RBCs cannot die in circulation because Hb will clog kidneys ; thus, consumed and broken down by macrophages in spleen and liver.
disposal proticol for broken down RBCs
Old red blood cells in spleen/broken down. Amino Acids/Iron return to red bone marrow while bilirubin is transported to liver to be excreted as bile. If liver cannot break down bilirubin, the chemical build ups in blood→result in jaundice.
jaundice
accumulation of yellow pigmented bilirubin in the blood that results in the skin and eyes developing a yellow pigment
Hemostasis
balancing clotting when injured and not clotting when no damage is present
Steps in forming a clot
vascular spasm->platelet plug->coagulation->clot retraction->thrombolysis
Vascular spasm
smooth muscles contract and platelets release serotonin that stimulate vasoconstriction
platelet plug formation
Damaged tissues release vWF to alert platelets. Recruited platelets release cytokines to alert more platelets to and the process continues until the damage site is covered in a soft plug of platelets loosely held together.
Coagulation
Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin by Thrombin and forms a hard blood clot
Two primary types of Coagulation amplification cascades that leads to blood clot
Extrinsic pathway(damage through the wall of a blood vessel or surrounding tissue) and Intrinsic pathway (damage within the vessel itself)
Important steps in the Coagulation amplification cascade
extrinsic and intrinsic factors and calcium->activate Prothrombin activator-> convert prothrombin to thrombin-> convert fibrinogen to fibrin
3 main steps in thrombolysis
healed tissue releases tPA which activates plasminogen converting it to Plasmin that then breaks down fibrin
chemicals that inhibit clot formation
antithrombin(liver) and heparin(mast cells and basophils)
emolus
traveling clot
deep vein thrombosis
formation of a blood clot in a vein deep in the body, most commonly the leg
stroke
Damage to the brain from interruption of its blood supply, often due to a blood clot.
cause of heart attack
clot blockage of coronary arteries
heart is housed inside
pericardial cavity made up of visceral pericardium(epicardium) and parietal pericardium
Systole/diastole
contraction and empties/relaxation and filling
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
cardiac muscle contains intercalated discs creating a network or branching cells to enable electrical signal transmission.
Location that electrical signal transfers from cardiac cell to adjacent cells
gap junctions
autorhythmic
heart beat without central nervous system control
Effects of ANS modulation
SNS=increase HR while PSNS (vagus)=decreased HR. PSNS is more in control at rest and sets our base rate at about 72 beats per min.
Which electrical signal=mechanical events?
Depolarization=systole; Repolarization=diastole
Flow of electrical depolarization across the heart.
SA node generate action potential->depolarizes both atriums->collects at atrioventricular node->travels down septum through the AV bundle to AV bundle branches->traverses apex to base through Purkinje fibers along the external wall of each ventricle
Times for electrical conduction in heart
Depolarization of atria (50msec); Pause (100msec) ventricles fill; ventricle myocardium depolarize (200msec)
arrhythmia
any irregular rhythm
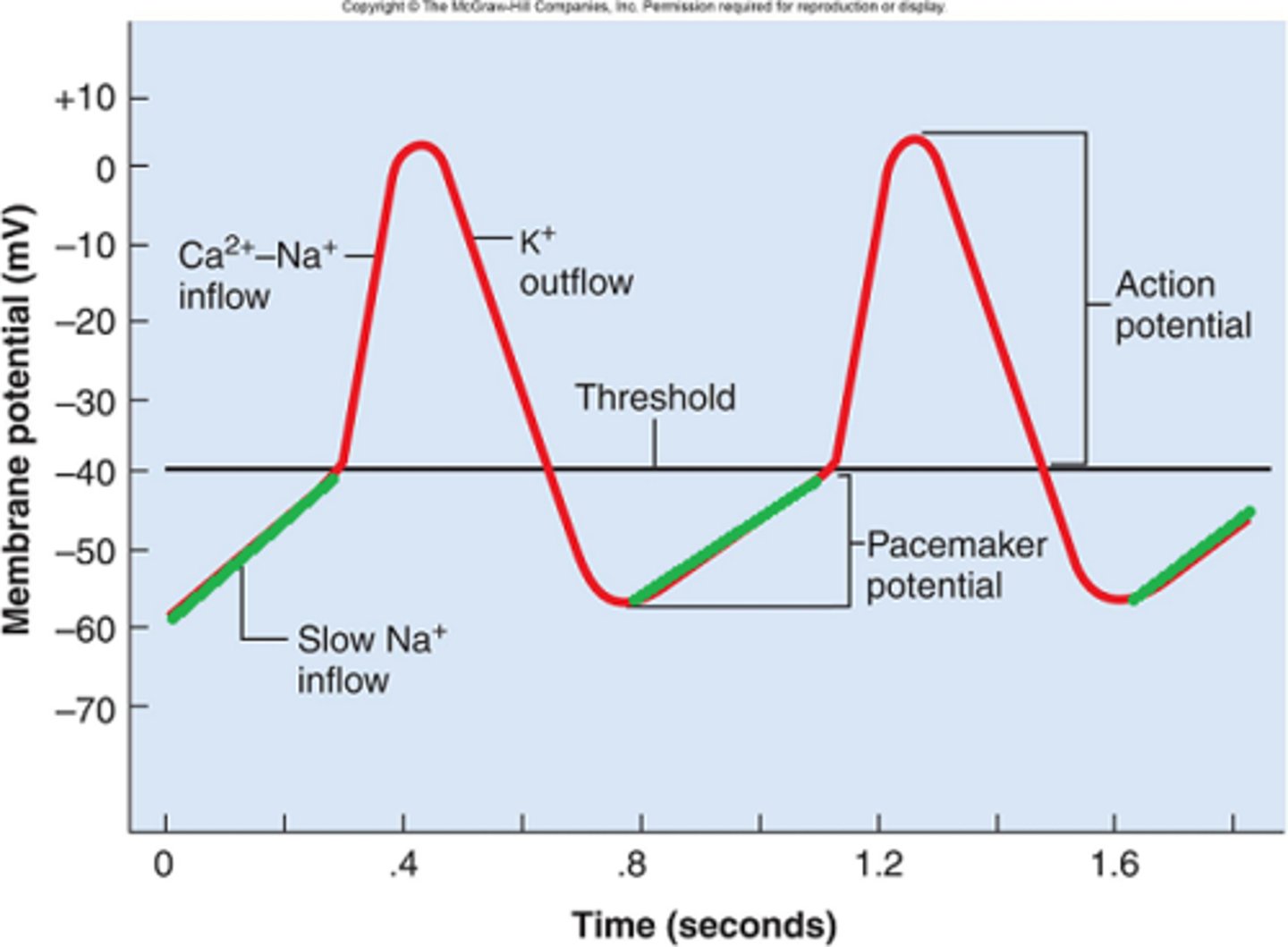
The cause of slow steady depolarization of cardiac pacemaker cells
sodium slowly flows in the cell eventually reaching threshold
Parts of a cardiac contractile cells electrophysiology graph
0-1. Depolarization
2. Plateau
3. Repolarization
4. Resting Membrane potential
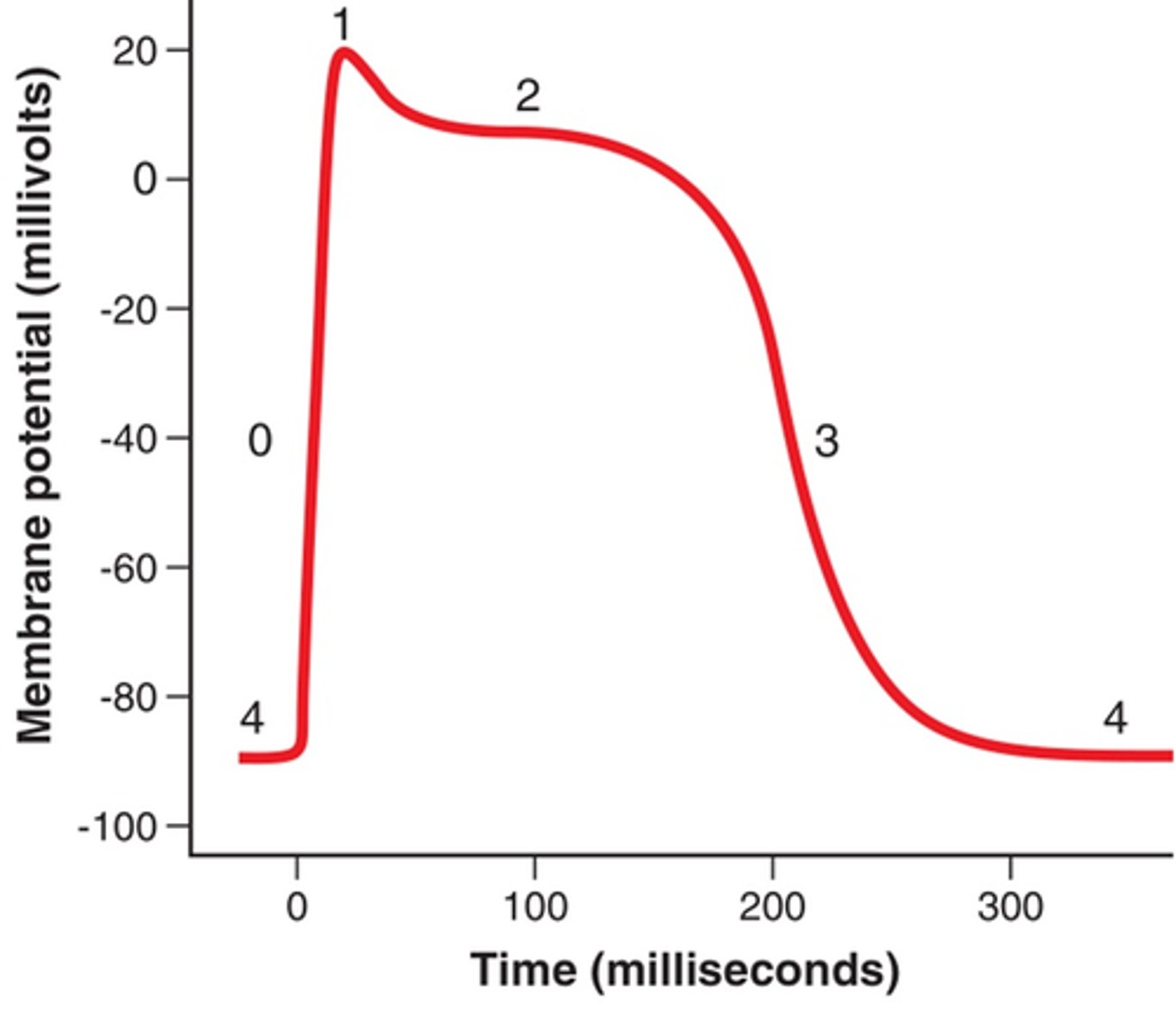
purpose of plateau phase
lengthens cardiac action potential (slightly slows heart rate to allows heart to fill with blood)
Ejection Fraction (EF)
Stroke volume/end diastolic volume
pressure in the left ventricle/right ventricle and pressure needed to over come to move through a valve
LV=120mmHg overcome 80mmHg in Aorta
RV=25mmHg overcome 10mmHg in the pulmonary trunk
cardiac output
volume of blood pumped per minute; CO=HR X Stroke Volume
Variables influencing heart rate
ANS: SNS (EPI and NE) increases HR while PSNS(Ach) decreases HR; fitness level, presence of ions and their concentrations
An effect that increases HR is...
positive chronotropic effect
An effect that decreases HR is...
negative chronotropic effect
An effect that decreases heart contractility is...
negative ionotropic effect
An effect that increases heart contractility is...
positive ionotropic effect
General limit to heart rate
230 bpm because of the refractory period of SA node
Variables that influence stroke volume
Preload: amount of stretch on wall of ventricle; Contractility: hearts ability to contract with force; Afterload: force against which a heart has to pump to eject blood
How preload influences stroke volume
increase in Blood volume and/or EDV->increases stroke volume
How contractility influences stroke volume
increased contractility->increased stroke volume
How afterload influences stroke volume
increased afterload->decreased stroke volume
Determinants for EDV
Length of diastole and venous return
How does ventricular stretch impact stroke volume
the more blood the ventricle receives the more it will stretch and the more blood that it will push as it rebounds through contraction.
universal blood donor
O- because it does not have surface antigens A, B, or Rh
universal blood recipient
AB+ because it does not have antibodies for A, B, or Rh
where doe the thumping sounds come from when you listen to your chest
The first sound is the AV closing and the second is the SL valves closing
4 primary stages of the cardiac cycle
Ventricular filling, isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, and isovolumetric relaxation.
what is occurring during ventricular filling
Atrial pressure is greater than ventricle pressure so blood is forced through opening the tricuspid and bicuspid into the ventricles
what is occurring during isovolumetric contraction
Ventricle pressure is greater than atrial pressure so the tricuspid and bicuspid close (first heart sound) and blood flow from the atria is halted.
Blood is not ejected from the ventricles at this point because ventricle pressure is not greater than the pulmonary trunk and aorta pressure; their semilunar valves remain closed.
what is occurring during ventricular ejection
ventricle pressure is greater than the pulmonary trunk and aorta pressures; their semilunar valves open to let blood flow to the lungs and body.
Atria are repolarizing and accepting blood again. Tricuspid and bicuspid are closed.
what is occurring during isovolumetric relaxation
Pressure in the ventricles decreases as it progresses through diastole and repolarizes. Decrease pressure causes the semilunar valves of the pulmonary trunk and aorta to shut (second heart sound).
Atria continue through diastole filling with blood until the SA node triggers another action potential. Tricuspid and bicuspid are closed.
Parts of an electrocardiogram
P wave, QRS complex, T wave
The P wave of an ECG represents
atrial depolarization
The QRS wave of an ECG represents
ventricular depolarization (atria repolarization is masked/hidden)
The T wave of an ECG represents
ventricular repolarization
Identify the primary waves of an ECG
P, QRS, and T waves
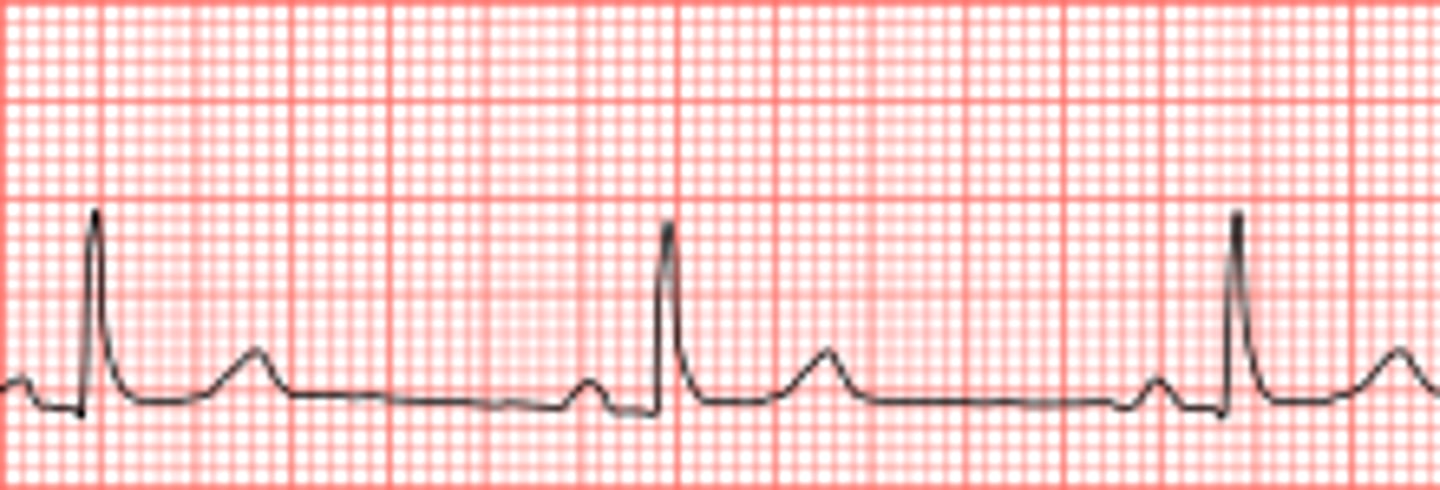
Tachycardia vs. Bradycardia
tachycardia= rapid pulse over 100 bpm
bradycardia= slowed pulse under 60 bpm