CCNA 200-301 Official Cert Guide Part 3
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
In a LAN, which of the following terms best equates to the term VLAN?
a. Collision domain
b. Broadcast domain
c. Subnet
d. Single switch
e. Trunk
Broadcast domain
Imagine a switch with three configured VLANs. How many IP subnets are required, assuming that all hosts in all VLANs want to use TCP/IP?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
e. You cannot tell from the information provided
3
Switch SW1 sends a frame to switch SW2 using 802.1Q trunking. Which of the answers describes how SW1 changes or adds to the Ethernet frame before forwarding the frame to SW2?
a. Inserts a 4-byte header and does change the MAC addresses
b. Inserts a 4-byte header and does not change the MAC addresses
c. Encapsulates the original frame behind an entirely new Ethernet header
d. None of the other answers are correct
Inserts a 4-byte header and does not change the MAC addresses
Imagine that you are told that switch 1 is configured with the dynamic auto parameter for trunking on its Fa0/5 interface, which is connected to switch 2. You have to configure switch 2. Which of the following settings for trunking could allow trunking to
work? (Choose two answers.)
a. on
b. dynamic auto
c. dynamic desirable
d. access
e. None of the other answers are correct.
on
dynamic desirable
A switch has just arrived from Cisco. The switch has never been configured with any VLANs, but VTP has been disabled. An engineer configures the vlan 22 and name Hannahs-VLAN commands and then exits configuration mode. Which of the following are true? (Choose two answers.)
a. VLAN 22 is listed in the output of the show vlan brief command.
b. VLAN 22 is listed in the output of the show running-config command.
c. VLAN 22 is not created by this process.
d. VLAN 22 does not exist in that switch until at least one interface is assigned to
that VLAN.
VLAN 22 is listed in the output of the show vlan brief command.
VLAN 22 is listed in the output of the show running-config command.
Which of the following commands identify switch interfaces as being trunking interfaces: interfaces that currently operate as VLAN trunks? (Choose two answers.)
a. show interfaces
b. show interfaces switchport
c. show interfaces trunk
d. show trunks
show interfaces switchport
show interfaces trunk
In a switch that disables VTP, an engineer configures the commands vlan 30 and shutdown vlan 30. Which answers should be true about this switch? (Choose two answers.)
a. The show vlan brief command should list VLAN 30.
b. The show running-config command should list VLAN 30.
c. The switch should forward frames that arrive in access ports in VLAN 30.
d. The switch should forward frames that arrive in trunk ports tagged with VLAN 30.
The show vlan brief command should list VLAN 30.
The show running-config command should list VLAN 30.
The show interfaces g0/1 trunk command provides three lists of VLAN IDs. Which items would limit the VLANs that appear in the first of the three lists of VLANs?
a. A shutdown vlan 30 global command
b. A switchport trunk allowed vlan interface subcommand
c. An STP choice to block on G0/1
d. A no vlan 30 global command
A switchport trunk allowed vlan interface subcommand
What are some common reasons for choosing to create VLANs?
■ To reduce CPU overhead on each device, improving host performance, by reducing the
number of devices that receive each broadcast frame
■ To reduce security risks by reducing the number of hosts that receive copies of frames
that the switches flood (broadcasts, multicasts, and unknown unicasts)
■ To improve security for hosts through the application of different security policies per
VLAN
■ To create more flexible designs that group users by department, or by groups that work
together, instead of by physical location
■ To solve problems more quickly, because the failure domain for many problems is the
same set of devices as those in the same broadcast domain
■ To reduce the workload for the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) by limiting a VLAN to a
single access switch
When you are using VLANs in networks that have multiple interconnected switches, what must be used between switches?
VLAN trunking
When using VLAN trunking, what does the trunking protocol cause the switch to use?
VLAN tagging
What is VLAN tagging?
The sending switch adds another header to the frame before sending it over the trunk.
In VLAN tagging, what does the extra trunking header include?
VLAN identifier (VLAN ID)
What is a VLAN identifier (VLAN ID)?
so that the sending switch can associate the frame with a particular VLAN ID, and the receiving switch can then know in what VLAN each frame belongs.
What are the two VLAN Trunking Protocols?
IEEE 802.1Q
ISL
What is Inter-Switch Link (ISL)?
Created before IEEE 802.1Q by Cisco, A proprietary protocol. Cisco doesn't even support ISL anymore
What is IEEE 802.1Q?
The popular trunking protocol, the industry standard.
802.1Q tag each frame with the VLAN ID, what else does 802.1Q insert?
extra 4-byte 802.1Q VLAN header into the original frame's Ethernet header
Cisco switches break the range of VLAN IDs (1-4094) into two ranges, what are they?
normal range
extended range
What range can ALL switches use?
All switches can use normal-range VLANs with values from 1 to 1005.
Only some switches can use extended range, what is the rule for extended range?
it depend on the configuration of the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
What are the ranges for Extended Range?
1006 to 4094
What are the four parts of the 802.1Q Tag?
Type, Priority, Flag, VLAN ID
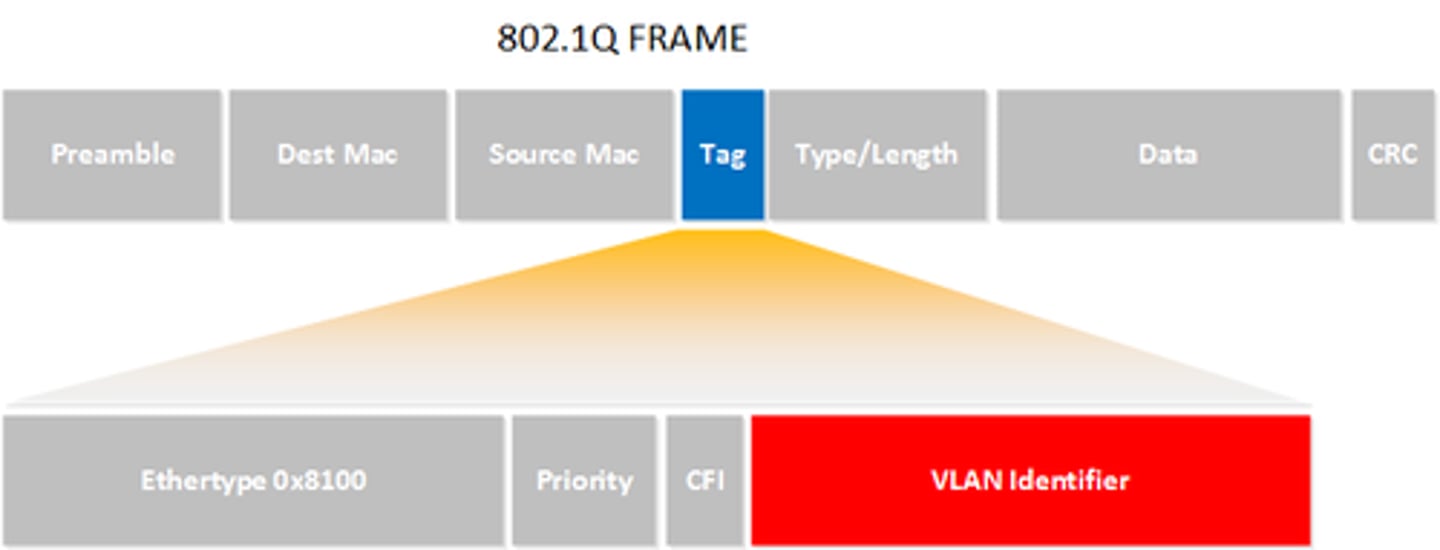
What are the Trunking Administrative Mode Options with the switchport mode Command?
Access
Trunk
Dynamic Desirable
Dynamic Auto
What is VTP transparent mode?
One of three VTP operational modes. Switches in transparent mode can configure VLANs, but they do not tell other switches about the changes, and they do not learn about VLAN changes from other switches.
What is a Trunk
In campus LANs, an Ethernet segment over which the devices add a VLAN header that identifies the VLAN in which the frame exists.
What is Trunking
Also called VLAN trunking. A method (using either the Cisco ISL protocol or the IEEE 802.1Q protocol) to support multiple VLANs, allowing traffic from those VLANs to cross a single link.
What is Trunking administrative mode
The configured trunking setting on a Cisco switch interface, as configured with the switchport mode command.
What is Trunking operational mode?
The current behavior of a Cisco switch interface for VLAN trunking
What is a VLAN
A group of devices, connected to one or more switches, with the devices grouped into a single broadcast domain through switch configuration. VLANs allow switch administrators to separate the devices connected to the switches into separate VLANs without requiring separate physical switches, gaining design advantages of separating the traffic without the expense of buying additional hardware.
What is a VTP
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) A Cisco-proprietary messaging protocol used between Cisco switches to communicate configuration information about the existence of VLANs, including the VLAN ID and VLAN name.
What is a Layer 3 Switch
A LAN switch that can also perform Layer 3 routing functions. The name comes from the fact that this device makes forwarding decisions based on logic from multiple OSI layers (Layers 2 and 3).
What is a Trunk Interface?
A switch interface configured so that it operates using VLAN trunking (either 802.1Q or ISL).
What is a Data VLAN?
The data VLAN is also called as user VLAN because it is designed only for user-generated data.
What is voice VLAN?
A VLAN defined for use by IP Phones, with the Cisco switch notifying the phone about the voice VLAN ID so that the phone can use 802.1Q frames to support traffic for the phone and the attached PC (which uses a data VLAN).
What is a native VLAN?
The one VLAN ID on any 802.1Q VLAN trunk for which the trunk forwards frames without an 802.1Q header.
What is a Default VLAN?
A reference to the default setting of 1 (meaning VLAN ID 1) on the switchport access vlan vlan-id interface subcommand on Cisco switches, meaning that by default, a port will be assigned to VLAN 1 if acting as an access port.
What is a Static Access Interface?
A LAN network design term, synonymous with the term access interface, but emphasizing that the port is assigned to one VLAN as a result of static configuration rather than through some dynamic process.
What are the options for the Switchport command?
access Always act as an access (nontrunk) port
trunk Always act as a trunk port
dynamic desirable Initiates negotiation messages and responds to negotiation messages to dynamically choose whether to start using trunking
dynamic auto Passively waits to receive trunk negotiation messages, at which point the switch will respond and negotiate whether to use trunking
What are the Expected trunking results based on the configuration of the switchport mode command
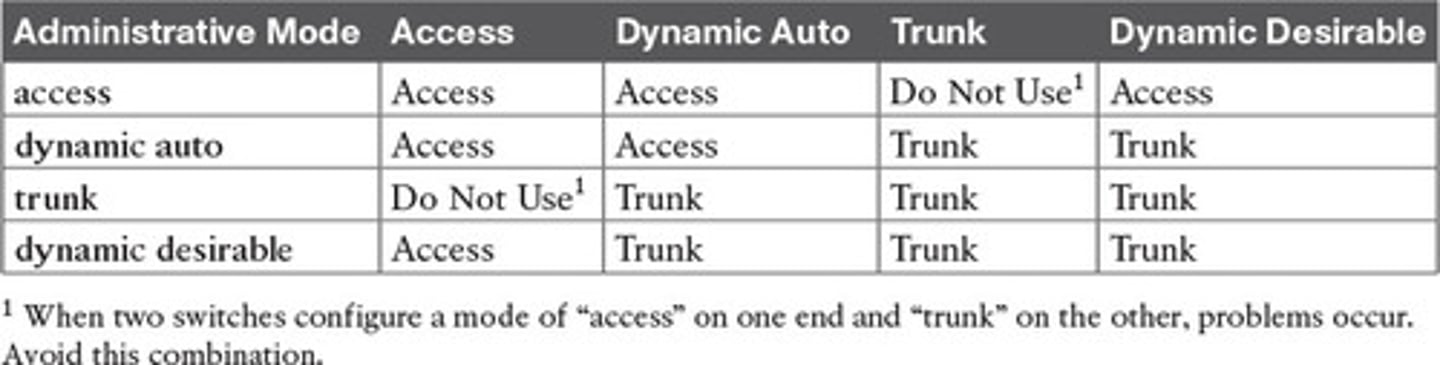
What are the Administrative Modes of Trunking Operations
Access
Dynamic Auto
Trunk
Dynamic Desirable
What combination should you avoid when in Administrative Mode of Trunking?
When two switches configure a mode of "access" on one end and "trunk" on the other, problems occur. Avoid this combination.
Expected Trunking Operational Mode Based on the Configured Administrative Mode of access
Access Dynamic Auto Trunk Dynamic Desirable
Access Access not used Access
Expected Trunking Operational Mode Based on the Configured Administrative Mode of Dynamic Auto
Access Dynamic Auto Trunk Dynamic Desirable
Access Access Trunk Trunk
Expected Trunking Operational Mode Based on the Configured Administrative Mode of trunk
Access Dynamic Auto Trunk Dynamic Desirable
Not used Trunk Trunk Trunk
Expected Trunking Operational Mode Based on the Configured Administrative Mode of dynamic desirable
Access Dynamic Auto Trunk Dynamic Desirable
Access Trunk Trunk Trunk
When configuring IP Telephony Ports on Switches, what are the most important items to remember
Configure these ports like a normal access port to begin: Configure it as a static access port and assign it an access VLAN.
Add one more command to define the voice VLAN (switchport voice vlan vlan-id).
Look for the mention of the voice VLAN ID, but no other new facts, in the output of the show interfaces type number switchport command.
Look for both the voice and data (access) VLAN IDs in the output of the show interfaces type number trunk command.
Do not expect to see the port listed in the list of operational trunks as listed by the show interfaces trunk command
What is the process of troubleshooting VLANs and VLAN Trunks?
Step 1. Confirm that all VLANs are both defined and active.
Step 2. Check the allowed VLAN lists on both ends of each trunk to ensure that all VLANs intended to be used are included.
Step 3. Check for incorrect trunk configuration settings that result in one switch operating as a trunk, with the neighboring switch not operating as a trunk.
Step 4. Check the native VLAN settings on both ends of the trunk to ensure the settings match.
When running the show interfaces trunk command, it creates three separate lists of VLANs, each under a separate heading. What are they.
In descending order
Vlans allowed on trunk
Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
What does the list Vlans allowed on trunk contain?
VLANs 1-4094, minus those removed by the switchport trunk allowed command
What does the list Vlans allowed and active in management domain contain?
The first list, minus VLANs not defined to the local switch (that is, there is not a vlan global configuration command or the switch has not learned of the VLAN with VTP), and also minus those VLANs in shutdown mode
What does the list Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned contain?
The second list, minus VLANs in an STP blocking state for that interface, and minus VLANs VTP pruned from that trunk
Which of the following port states are stable states used when STP has completed convergence? (Choose two answers.)
a. Blocking
b. Forwarding
c. Listening
d. Learning
e. Discarding
Blocking
Forwarding
Which of the following bridge IDs wins election as root, assuming that the switches with these bridge IDs are in the same network?
a. 32769:0200.1111.1111
b. 32769:0200.2222.2222
c. 4097:0200.1111.1111
d. 4097:0200.2222.2222
e. 40961:0200.1111.1111
4097:0200.1111.1111
Which of the following are transitory port states used only during the process of STP convergence? (Choose two answers.)
a. Blocking
b. Forwarding
c. Listening
d. Learning
e. Discarding
Listening
Which of the following facts determines how often a nonroot bridge or switch sends an STP Hello BPDU message?
a. The Hello timer as configured on that switch.
b. The Hello timer as configured on the root switch.
c. It is always every 2 seconds.
d. The switch reacts to BPDUs received from the root switch by sending another BPDU 2 seconds after receiving the root BPDU.
he Hello timer as configured on the root switch
Which of the following RSTP port states have the same name and purpose as a port state in traditional STP? (Choose two answers.)
a. Blocking
b. Forwarding
c. Listening
d. Learning
e. Discarding
Forwarding
Learning
RSTP adds features beyond STP that enable ports to be used for a role if another port on the same switch fails. Which of the following statements correctly describe a port role that is waiting to take over for another port role? (Choose two answers.)
a. An alternate port waits to become a root port.
b. A backup port waits to become a root port.
c. An alternate port waits to become a designated port.
d. A backup port waits to become a designated port
An alternate port waits to become a root port.
A backup port waits to become a designated port
What STP feature causes an interface to be placed in the forwarding state as soon as the interface is physically active?
a. STP
b. EtherChannel
c. Root Guard
d. PortFast
PortFast
A [...] domain is the group of devices which will receive a frame with the destination MAC address FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
broadcast
An [...] port is a switchport which belongs to a single VLAN, and usually connects to end hosts like PCs.
access
Configure a switch interface to be an access port:
SW1(config-if)# [...]
switchport mode access
Configure the name of a VLAN:
SW1(config-vlan)# [...]
name name
Configure the VLAN of a switch access port:
SW1(config-if)# [...]
switchport access vlan vlan-number
Create a VLAN:
SW1(config)# [...]
vlan vlan-number
Switchports which carry multiple VLANs are called '[...] ports'.
trunk
VLANs are used to split up [...] domains.
broadcast
VLANs operate at Layer [...] of the OSI model.
2
What are the 5 VLANs that exist by default on a Cisco switch?
1, 1002, 1003, 1004, 1005
What VLAN are Cisco switch interfaces in by default?
VLAN1
Will a Layer 2 switch forward traffic between VLANs? (inter-VLAN routing)
no
802.1Q tag: The [...] field identifies the VLAN the frame belongs to.
VID
802.1Q tag: The [...] field indicates that a frame can be dropped if the network is congested.
DEI
802.1Q tag: The [...] field is use for Class of Service.
PCP
802.1Q tag: The DEI field is [...] in length.
1 bit
802.1Q tag: The PCP field is [...] bits in length.
3
802.1Q tag: The TPID field is [...] bits in length.
16
802.1Q tag: The TPID field is alway set to a value of [...]
0x8100
802.1Q tag: What does DEI stand for?
Drop Eligible Indicator
802.1Q tag: What does PCP stand for?
Priority Code Point
802.1Q tag: What does TPID stand for?
Tag Protocol Identifier
802.1Q tag: What does VID stand for?
VLAN ID
Configure the allowed VLANs on a trunk port:
SW1(config-if)# [...]
switchport trunk allowed vlan allowed-vlans
Configure the encapsulation type on a trunk port:
SW1(config-if)# [...]
switchport trunk encapsulation encapsulation-type
Configure the interface as a trunk port:
SW1(config-if)# [...]
switchport mode trunk
Configure the native VLAN on a trunk port:
SW1(config-if)# [...]
switchport trunk native vlan vlan-number
Configure the VLAN number on a router subinterface:
R1(config-subif)# [...]
encapsulation dot1q vlan-number
Display all trunk ports on the switch:
SW1# [...]
show interfaces trunk
For security purposes, it is best to change the native VLAN to an [...] VLAN.
unused
ROAS involves configuring VLAN tags and IP addresses on router [...].
subinterfaces
What does ROAS stand for?
Router on a stick
The 802.1Q tag is [...] bytes in length.
4
The 802.1Q tag is inserted after the [...] field of the Ethernet header.
Source MAC Address
The default native VLAN is VLAN [...] on all trunk ports.
1
The Extended VLAN range is [...] to [...]
1006 to 4094
The Normal VLAN range is [...] to [...]
1 to 1005
The range of usable VLANs is [...] to [...]
1 to 4094
The switch does not add an 802.1Q tag to frames in the [...] VLAN over a trunk link.
native
VLANs [...] and [...] are reserved and cannot be used.
0 / 4095
VLANs: [...] ports are known as 'tagged' ports.
Trunk