1.1 Lipids
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is the solubility of lipids
Contain hydrocarbon molecules(non polar bonds)
Insoluble in polar substances
Lipid solubility improved by combo with other molecules(eg: glycolipids, lipoproteins)
What is a triglyceride
3 fatty acids attached to one glycerol molecule
Saturated-single bonds
What is the process of forming triglycerides
Esterification(condensation reaction that forms 3 h2os
Formation of phospholipids
2 fatty acids only bonded to a glycerol molecule, 3rd one replaced by a phosphate ion(PO43-)
Solubility of phospholipids
Amphipathic(hydrophilic phosphate head, hydrophobic fatty acid tail)
Which contain more energy, lipids or carbohydrates?
Lipids due to their higher number of C-H bonds
Properties of triglycerides
Hydrolysis releases glycerol and fatty acids(which form useful respiratory substrates)
Energy storage: Lipids Insoluble→aren’t transport easily→remain in storage cells
Lots of h2o produced when lipids r respired compared to carbs(metabolic water can be used when h2o unavailable)
Insulation and protection: triglycerides stored in adipose tissue→thermal insulation and cushions organs(in animals)
Adipose tissue to store lipid(for insulation and protection)
Subcutaneous fats stored below skin
Visceral fats stored around major internal organs
Endothermic(seals and walruses)→have thick adipose tissue called blubber→helps trap heat generation by respiration
Properties of phospholipids
Membrane structure: phospholipid bilayers form cell membranes→controls movement on substances in n out of cell
Membrane fluidity: level of saturation in fatty acid tails influence membrane fluidity(for cellular function)
Saturated fatty acids properties
Straight molecules(molecules packed tightly tg)→increase melting point
Storage for animals as it’s solid at rtp
Unsaturated fatty acids properties
Doubles bonds cause kink→they cannot pack as tightly as saturated→liquid at rtp
Difference between mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids
Mono(single double bond): lower mp than saturated fatty acids
Poly(many double bonds): low mp(forms oils for storage in plants)
How do non-polar steroids pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Steroid hormones contain cholesterol→hydrocarbon region of cholesterol is non-polar

What are examples of steroid hormones
Oestradiol
Testosterone
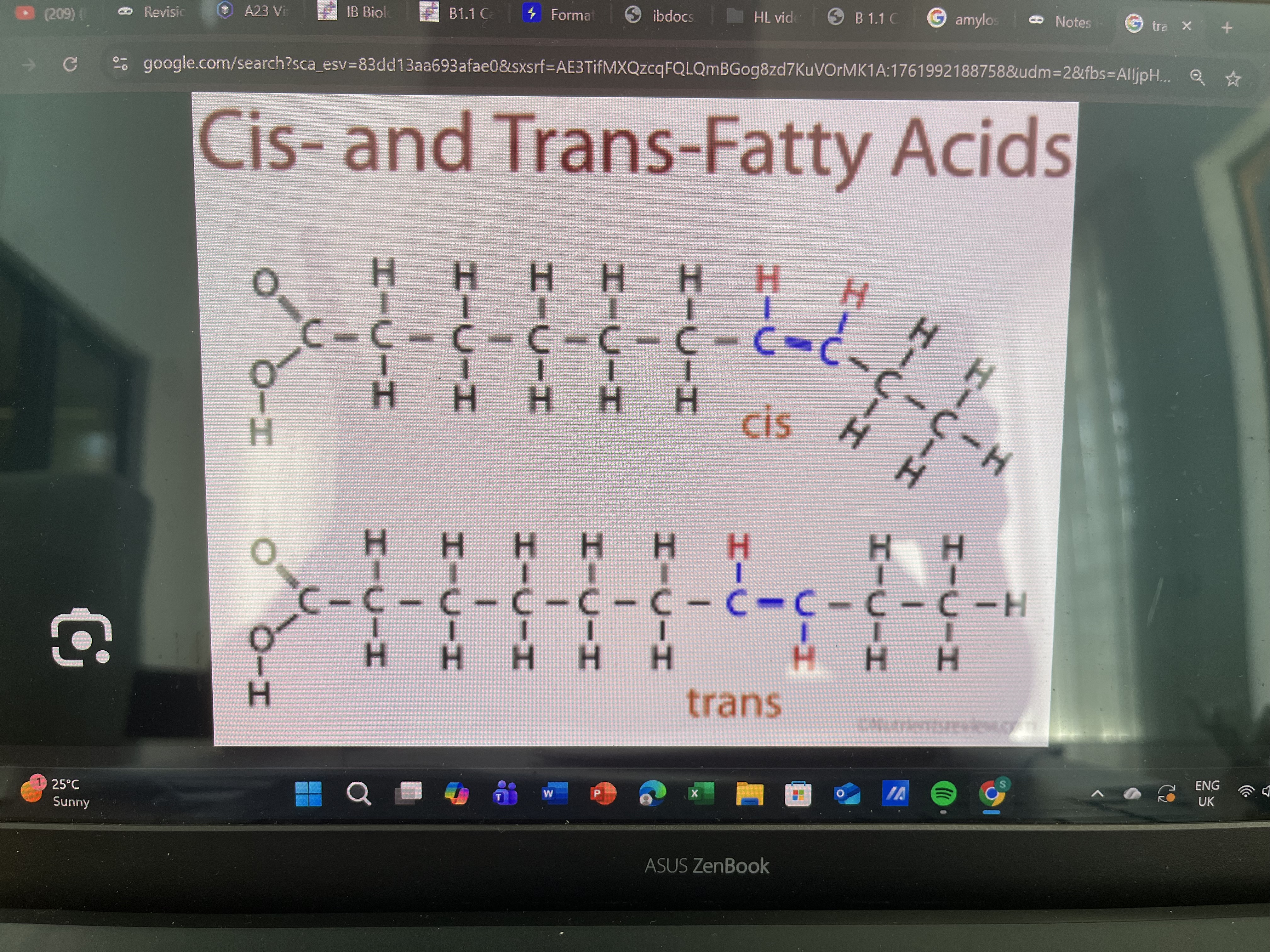
Difference between trans fat and cis fat(unsaturated)
Cis has both hydrogens on the same side→increases good cholesterol(healthy)
Trans has one hydrogen on top of one carbon and below the other carbon→increases bad cholesterol(unhealthy)
Structure of steroid
fused 4 ring structure

What are essential features of the structure of a fatty acid
Carboxyl group(COOH)
2 H on each C except the last C has 3 H(CH3)