Chapter 13, 14, 15
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
1
New cards
First Impressions
* Less Than 30 seconds to form one
* Can be very accurate but not always
* Very Persistent
* Ignore Contradictory Information
* Take long time to change “wrong impression”
* Can be very accurate but not always
* Very Persistent
* Ignore Contradictory Information
* Take long time to change “wrong impression”
2
New cards
Halo Effect
Judgement based on one characteristic of a person (negative or positive)
3
New cards
Attributions
Judgement about cause of a person’s behavior
4
New cards
Internal Attributions
An inner trait or characteristic that made them act a certain way
5
New cards
Situational Attributions
The cause of a behavior being the enviroment
6
New cards
Fundamental Attribution Error
Tendency to give other peoples behavior as internal attribution enven if situtational attribution calls for it
7
New cards
Actor-Observor Bias
We view our behavior and others very differently, situational attribution for worse behavior and internal attribution for good behavior
8
New cards
Just-World Beliefs
Good things happen to good people and bad things to bad people
9
New cards
Prejudice
Negative assessment of another person based on his/her membership to a group
10
New cards
Stereotypes
Set of traits associated with a group
11
New cards
Discrimination
Unfair behavior towards a person based on stereotyping and prejudice
12
New cards
Prejudice is Universal
* May influence how we feel about others subconciously or consciously
* May not necessarily influence how we treat them
* May not necessarily influence how we treat them
13
New cards
Reducing Prejudice
* Contact between people of equal standing
* Participation in cooperative activity
* Robber’s Cave Study
* Participation in cooperative activity
* Robber’s Cave Study
14
New cards
Reducing Prejudice
* Education
* Prejudice education and how it can influence behavior
* Brown Eyes - Blue Eyes Project
* Prejudice education and how it can influence behavior
* Brown Eyes - Blue Eyes Project
15
New cards
Attitudes
Positive or negative feeling towards objects, persons, or situation
\
* Formation
* Personal Experience
* Other’s Experience
* Operant Conditioning
\
* Formation
* Personal Experience
* Other’s Experience
* Operant Conditioning
16
New cards
Cognitive Dissonance
Uncomfortable state that occurs when behavior and attitude do not match, can be resolved through attitude change
17
New cards
Social Norms
Unwritten rules for behavior in social setting
18
New cards
Conformity
Matching your behavior or apperance to the percieved social norms
\
* Asch Line Study // Asch Conformity
\
* Asch Line Study // Asch Conformity
19
New cards
Stanford // Zimbardo Prison Study
* Volunters: White Young Men
* 2 Gaurds took their role to seriously and chaos ensues
* Femal partner asks Zimbardo to end it because he was blind to the damage
* 2 Gaurds took their role to seriously and chaos ensues
* Femal partner asks Zimbardo to end it because he was blind to the damage
20
New cards
Obedience
Do as others command
21
New cards
Compliance
Do as others want
22
New cards
Conformity
Do as others do
23
New cards
Compliance
No authority is used, you do something another person asks of you
\
* Want to be agreeable
* Want to get along
\
* Want to be agreeable
* Want to get along
24
New cards
Obedience
Compliance with the request of an authority figure
\
* Milgram Obedience Study
* Understand actions of normal people in Nazi Germany
\
* Milgram Obedience Study
* Understand actions of normal people in Nazi Germany
25
New cards
Ethics Issue Milgram // Zimbardo
* Informed consent not observed
* Listed out all actions to be committed on subjects
* Listed out all actions to be committed on subjects
26
New cards
Power of One
An individual or small group can influence a larger one
\
* Must Display
* Confidence
* Consistency
\
* Must Display
* Confidence
* Consistency
27
New cards
Social Facilitation
Observers of a performance changes the result of performance
\
* Well Practiced = Improved with audience
* Novel / Complex = Worse with audience
\
* Well Practiced = Improved with audience
* Novel / Complex = Worse with audience
28
New cards
Social Loafing
Reduce motivation and effect shown by individuals working in a group
29
New cards
Deindividuation
* Immersion of individual within a group, feels anonymous
* Leads to contrary behavior for individuals in a group
* Leads to contrary behavior for individuals in a group
30
New cards
Bystander Effect
* Large group of people = Less likely for individuals to do anything
* Diffusion of Responsibility
* Diffusion of Responsibility
31
New cards
Kitty Genoverse
* Her death led to 911 system and study of Bystander Effect
32
New cards
Proximity
Physical closeness to other person
33
New cards
Exposure Effect
Consistent exposure leads to familiarity and liking
34
New cards
Similarities
Shared values
35
New cards
Physical Apperance
* Preference for attractive faces
* Symmetrical Faces
* Effects initial attraction but is not important for long term
* Symmetrical Faces
* Effects initial attraction but is not important for long term
36
New cards
Matching Hypothesis
Matching levels of attractiveness gravitate towards each other
37
New cards
Resource Exchange
In heterosexual dating, male trades occupational status for physical attractiveness in females
38
New cards
Reciprocal Liking
Like people more when other people like us
39
New cards
Similarity
Drawn to those with similar qualities
40
New cards
Desirable Personality Traits
* Warmth
* Good sense of humor
* Social Assertiveness
* Good Communication
* Good sense of humor
* Social Assertiveness
* Good Communication
41
New cards
Relationship Maintenance
Actions and activites used to sustain the desired quality of a relationship
42
New cards
Interdependence or Social Exchange Theory
If cost for being in a relationship is lower than benefit the relationship lasts
43
New cards
Intimacy (Sternberg)
Warmth, closeness, and sharing
44
New cards
Passions (Sternberg)
Intense feeling (positive/negative), sexual desire
45
New cards
Commitment
Intent / decision to stay in relationship
46
New cards
Ultimate Type of Love
Consummate Love
* All 3 ingredients
* All 3 ingredients
47
New cards
Sternberg’s Triangular Theory
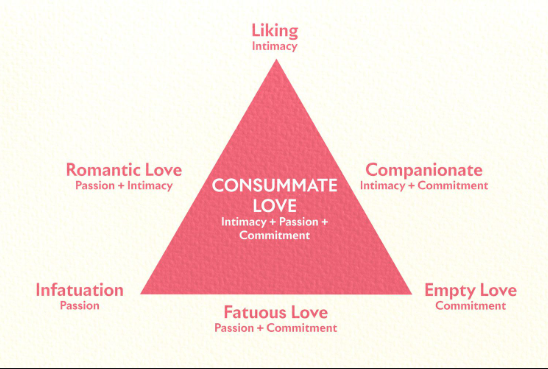
48
New cards
Criteria for Abnormal Behavior
1) Deviance
2) Maladaptive Behavior
3) Personal Distress
4) Dangerousness
2) Maladaptive Behavior
3) Personal Distress
4) Dangerousness
49
New cards
Deviance
The behavior must be significantly differnt from what society deems appopriate
50
New cards
Maladaptive Behavior
The behavior interferes with the person’s ability to function
51
New cards
Personal Distress
The behavior is troubling to the individual
52
New cards
Dangerousness
The behavior could cause harm to oneself or others
53
New cards
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
* Worried about everything and anything possible
* No clear trigger for Anxiety
* No clear trigger for Anxiety
54
New cards
Panic Attack
Not a disorder but a symptom of a possible disorder
* 10 minute peak of intense discomfort, with four or more symptoms
* Chest Pain
* Sweating
* Palpitations
* Fear of Death
* 10 minute peak of intense discomfort, with four or more symptoms
* Chest Pain
* Sweating
* Palpitations
* Fear of Death
55
New cards
Panic Disorder
* Recurring and Unexpected Panic Attacks
* Followed by 1 month or more of
* Concern about having another
* Maladaptive change in behavior to aviod Panic Attack
* Followed by 1 month or more of
* Concern about having another
* Maladaptive change in behavior to aviod Panic Attack
56
New cards
Phobias
* Unrealistic/Overexaggerated fears of an object or situation
* Clear Trigger that causes anxiety or even attack
* Aviodance behavior towards trigger
* Clear Trigger that causes anxiety or even attack
* Aviodance behavior towards trigger
57
New cards
Agoraphobia
* Fear of the marketplace, populated places
* Avoidance behavior
* Avoidance behavior
58
New cards
Social Anxiety Behavior
Social or performance situation causes anxiety or even attacks due to potiental embarrasment
59
New cards
Specific Phobia
Marked by a persistent and irrational fear of an object or situation that presents no realistic danger
60
New cards
Animal Type Phobia
Dogs, Cats, Spiders
61
New cards
Blood-Injection-Injury Type Phobia
Own blood or others, injury, and needle
* Faint on exposure
* Faint on exposure
62
New cards
Natural Enviroment Type Phobia
Heights, storms
63
New cards
Situational Type Phobia
Flying, driving over bridges
64
New cards
Anxiety Sensitivity Theory
People are more sensitive to internal physiological symptoms of anxiety and overreact with fear when they occur
65
New cards
Classical Conditioning
Acquisition of phobic fear
66
New cards
Operant Conditioning
Negative reinforcement through aviodance, person feels less anxious
67
New cards
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Obsessed with certain though, image, idea, or urges uncontrolled
* Compulsions: Repetitive behaviors or mental acts that a person feels must be performed (about an hour a day)
* Level of Insight: Does patient understand that their behavior is drastic or do they think it’s normal
* Compulsions: Repetitive behaviors or mental acts that a person feels must be performed (about an hour a day)
* Level of Insight: Does patient understand that their behavior is drastic or do they think it’s normal
68
New cards
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Must experience Level 1 trauma, actual or threatened death / injury / or sexual assault
* 14% of Combat Soilders
* Women have higher rate because of SA
* 14% of Combat Soilders
* Women have higher rate because of SA
69
New cards
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
* Depressed mood or loss of interest/pleasure
* Must last 2 weeks or longer
* 16% of population
* More common in Women, however may be caused by societal expectations
* Must last 2 weeks or longer
* 16% of population
* More common in Women, however may be caused by societal expectations
70
New cards
MDD Causes
* Biological Factors
* Genetic Disposition
* Biochemical Factors
* Cognitive Factors
* Negative Thinking
* Interpersonal Issues
* Poor social skills
* Precipitating Stress
* Pre-existing stressor in life
* Genetic Disposition
* Biochemical Factors
* Cognitive Factors
* Negative Thinking
* Interpersonal Issues
* Poor social skills
* Precipitating Stress
* Pre-existing stressor in life
71
New cards
Anxiety Disorder Causes
* Biological Factors
* Genetics
* Anxiety Sensitivity Theory
* Past Experience/Conditioning & Learning
* Classical Conditioning
* Operant Conditioning
* Cognitive Factors
* Misinterpret harmless situations as threatening
* Focus excess attention on perceived threats
* Selective recall information that seems threatening
* Genetics
* Anxiety Sensitivity Theory
* Past Experience/Conditioning & Learning
* Classical Conditioning
* Operant Conditioning
* Cognitive Factors
* Misinterpret harmless situations as threatening
* Focus excess attention on perceived threats
* Selective recall information that seems threatening
72
New cards
Manic Episode
Lasts atleast 1 week, abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive or irritable mood
* Symptom of Bipolar disorder
* Symptom of Bipolar disorder
73
New cards
Bipolar I Disorder
* Atleast one manic episodes at any point in life
* Do not need to have depression to be diagnosed
* Do not need to have depression to be diagnosed
74
New cards
Bipolar II Disorder
* Hypomanic episodes, less intense than manic
* Never had manic episode
* Needs to have depressive episodes
* Most destressing flipping back and forth between two
* Never had manic episode
* Needs to have depressive episodes
* Most destressing flipping back and forth between two
75
New cards
Bipolar Disorder Causes
* Genetic Predisposition
* VERY strongly tied to genetics
* Biochemical Factors
* Low serotonin activity
* Stress
* VERY strongly tied to genetics
* Biochemical Factors
* Low serotonin activity
* Stress
76
New cards
Suicide
Each Day
* 126 people commit
* 2,000 attempt
Women attempt 2x to 3x more often
Men 4x more likely ‘
* 78.8% of suicides are Male
* 126 people commit
* 2,000 attempt
Women attempt 2x to 3x more often
Men 4x more likely ‘
* 78.8% of suicides are Male
77
New cards
Risks of Suicide
* Previous Attempts
* Family History of Suicide
* Depression
* Substance Use
* 1/3 Alcohol in System
* 1/4 Legally Drunk
* Access to Firearms
* 5x more likely with gun in home
* Family History of Suicide
* Depression
* Substance Use
* 1/3 Alcohol in System
* 1/4 Legally Drunk
* Access to Firearms
* 5x more likely with gun in home
78
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa
* Intense fear of gaining weight or becoming fat, even though underweight
* Undue influence of body weight or shape on self-evalution
* Undue influence of body weight or shape on self-evalution
79
New cards
Restricting Type
Place severe restrictions on the quantity and type of food they consume
80
New cards
Binge-Eating/Purging Type
Consume a large amount of calories or food, then self-induce vomitting or laxiative
81
New cards
Anorexia Side Effects
* Cold intolerance
* Cardiovascular Problems
* Death
* 18-20% of people with the condition will die of it
* Cardiovascular Problems
* Death
* 18-20% of people with the condition will die of it
82
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa
* Recurrent episodes of binge eating
* Recurrent inappropriate compensatory behavior
* Vomiting
* Misuse of laxatives
* Fasting
* Occurs Regularly
* About once a week for 3 weeks
* Body image important for self-esteem
* Recurrent inappropriate compensatory behavior
* Vomiting
* Misuse of laxatives
* Fasting
* Occurs Regularly
* About once a week for 3 weeks
* Body image important for self-esteem
83
New cards
Bulimia Side Effect
* Significant and permanent loss of dental enamel
* Increase frequency of dental cavities
* Gastric Rupture
* Dependence on laxatives
* Increase frequency of dental cavities
* Gastric Rupture
* Dependence on laxatives
84
New cards
Eating Disorder Causes
* Learning Factors
* Unhealthy weight management behaviors
* Cognitive/Social Factors
* Misperception of body shape/size
* Too much importance on weight
* Need for control (Anorexia)
* Difficulty controlling negative emotions (Bulimia)
* Role of Media
* Thin ideal internalization
* Pressure to be thin in our society
* Unhealthy weight management behaviors
* Cognitive/Social Factors
* Misperception of body shape/size
* Too much importance on weight
* Need for control (Anorexia)
* Difficulty controlling negative emotions (Bulimia)
* Role of Media
* Thin ideal internalization
* Pressure to be thin in our society
85
New cards
Schizophrenia
* Significant impairment in functioning
* Continuous signs of impairment for atleast 6 months
* Continuous signs of impairment for atleast 6 months
86
New cards
Schizophrenia Cause
* Genetic vulnerability
* Neurochemical factors
* Excess activity of Dopamine
* Structural Abnormalities in Brain
* Enlarged ventricles
* Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis
* Neurochemical factors
* Excess activity of Dopamine
* Structural Abnormalities in Brain
* Enlarged ventricles
* Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis
87
New cards
Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis
Schizophrenia as being the result of a disruption of brain development
* Prenatal exposure to a flu virus
* Severe famine
* Birth trauma
* Prenatal exposure to a flu virus
* Severe famine
* Birth trauma
88
New cards
Personality Disorders
* Enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from expectations
* Pattern leads to clinically significant distress
* Pattern is stable and of long duration, onset in adolescence
* Pattern leads to clinically significant distress
* Pattern is stable and of long duration, onset in adolescence
89
New cards
Cluster A
* Schizoid
* Schizotypal
* Paranoid
* Schizotypal
* Paranoid
90
New cards
Cluster B
* Antisocial
* Borderline
* Histrionic
* Narcissistic
* Borderline
* Histrionic
* Narcissistic
91
New cards
Cluster C
* Avoidant
* Dependent
* Obsessive-Compulsive
* Dependent
* Obsessive-Compulsive
92
New cards
Cluster B
* Trouble with emotional control and trouble getting along with others
* Dramatic
* Unpredictable
* Impulsive
* Dramatic
* Unpredictable
* Impulsive
93
New cards
Antisocial Personality Disorder
* Pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others
* Failure to conform to social norms
* Reckless disregard for saftey
* Lack of remorse
* Failure to conform to social norms
* Reckless disregard for saftey
* Lack of remorse
94
New cards
Borderline Personality Disorder
* Pervasive pattern of instability of interpersonal relationships, self-image, and affects
* Frantic efforts to aviod real or imagined abandonment
* Chronic feelings of emptiness
* Identity disturbance
* Frantic efforts to aviod real or imagined abandonment
* Chronic feelings of emptiness
* Identity disturbance
95
New cards
Autism Spectrum Disorder
* Nature of impairment changes with age
* Higher in Males
\
Causes of Autism
* 5% of siblings of children with autism are also autistic
* Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis
* Higher in Males
\
Causes of Autism
* 5% of siblings of children with autism are also autistic
* Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis
96
New cards
ADHD
* Most common psychological disorder of childhood
* 3 to 10 percent of school age children
* Can persist from adolescence to adulthood
* Current causes unknown
* 3 to 10 percent of school age children
* Can persist from adolescence to adulthood
* Current causes unknown
97
New cards
Inattention Type
* Often fails to give close attention to details or make careless mistakes
* Often has difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play
* Is often easily distarcted by extraneous stimuli
* Is often forgetful in daily activities
* Often has difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play
* Is often easily distarcted by extraneous stimuli
* Is often forgetful in daily activities
98
New cards
Hyperactivity-Impulsive Type
* Often fidgets or taps hands or feet or squirms in seat
* Often leaves seat in situations where remaining seated is expected
* Often has difficulty waiting his or her turn
* Often interrupts or intrudes on other
* Often leaves seat in situations where remaining seated is expected
* Often has difficulty waiting his or her turn
* Often interrupts or intrudes on other
99
New cards
Combined Type
Combination of Inattentive Type and Hyperactivity-Impulsive Type
100
New cards
Pyschotherapy
Improve symptoms of disorder through conversation between patient and therapist