Ch.1: What is Labour Economics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Labour Economics
Deals with the supply and demand of labour, an important factor of prouction
Examines how to determine three outcomes
Wages: the price of labour
Employment: quantity of jobs in the market
Distribution of labor income: amoung individals and households
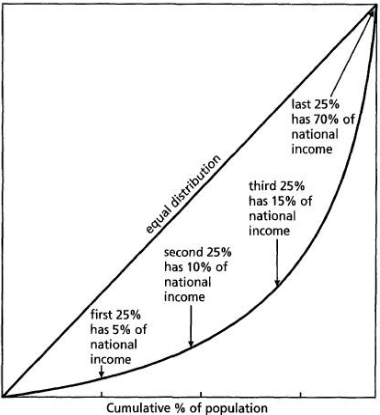
A Typical Lorenz Curve
Graphical rep. of the distribution of income or of wealth
Developed by Max O in 1905
Rep. wealth inequality
What is the Role of the Government in the Labour Market?
To reduce involuntary unemployment
To reduce waste of human resources
To Increase equity and fairness
To Prevent discriminatory practices
Oppurtunity Cost
The value of your next best alternative
Central concept
: Truck driver vs. chiropractor
Economic System
Market Economies: Free Enterprise Systems
Adam Smith, father of econ
Decentralized decisions and private ownership
Central planning=command economies
Mixed economies govt. and enterprises
Who makes the decision in a Market Economy?
Rational people and firms at the margin
Checking if marginal benefits exceeds the marginal costs
Individuals seek to max. their utility or level of satisfaction
Firms make decisions at the margin, adding shifts or hiring more employees
Four Main Outcomes
Supply: Who is supplying labour, how much?
Demand: Which employers are demandinf labour, what type and how much
Unemployment: The changing level and composition of labour
Earnings: The changing level and structure, who is getting paid what amounts
The Three Forces
Market Forces: Supply and demand
Instituional Forces
Govts.
Unions
Large companies
Sociological forces
Culture
Norms
Market Forces
Include the folowing sub forces of:
Supply
Demand
Shortages
Surpluses
Equilibrium
Institutional Forces
Internal labour markets
Personnel decisions within large firms
Government legislation, laws , rules
Large companies
: The decisions of Rogers or Amazon
Union bargaining
: Auto workers
Sociological Forces
Family structures
Demographics
Occupation and socioeconomic class
Labour force participation rates
Cultural values and biases
Customs
Positive Statements State
How the world is
Normative Economics
How the world ought to be
Ethics
Universal codes, the golden rule