Hematology and Hemostasis: Exam 2
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
PIVKA
Proteins induced by vitamin K deficiency or antagonists; the nonfunctional precursor forms of vitamin-K-dependent coagulation factors.
What is hemolysis?
Defined as the rupture or destruction of red blood cells. Hemolysis of a sample can be caused by improper collection or certain pathologic conditions (like in hemolytic anemia)
Which blood cell has the greatest specific gravity?
Erythrocytes (RBC's)
Buffy coat
a thin light colored layer of white blood cells and platelets than lie between a top layer of plasma and red blood cells
A Packed Cell Volume (PCV) test evaluates what percentage of whole blood contains ____________
Erythrocytes (RBC's)
What is a blood smear test used for?
Performing differential white blood cell counts, estimating platelet numbers, and looking at the morphologic features of WBCs, RBCs, and platelets
When performing a blood smear on a sample from a non-anemic patient the spreader slide should be held at a ______ degree angle
30 degree
A low neutrophil count indicates
autoimmune issues, nutritional deficiencies, cancer (leukemia, lymphoma, myelofibrosis), viral or bacterial infections, & medication side effects (usually from chemo)
Low lymphocyte levels usually suggest a patient is
stressed or using corticosteroid class drugs
A low Basophil count indicates
acute infection, severe allergies, hyperthyroidism, & medication side effects
Which leukocytes are involved in allergic reactions and parasitic infections?
Eosinophils and Basophils
absolute value is calculated by:
multiplying the total WBC count by the percentage of each cell type
Which type of WBC is the most abundant WBC in the peripheral blood of most mammals?
Neutrophil
Which type of WBC is the largest WBC in peripheral blood?
Monocyte
A CBC uses which color top collection tube?
Purple (EDTA)
A blood chemistry panel uses which color top collection tube?
Green (Heparin)
Which color top blood collection tube would be used for coagulation tests?
Blue (Citrate)
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) is an indicator of the _______ of the average RBC
Size
Plasma with a cloudy appearance is characterized as _________
lipemic (fatty)
Plasma with a red tinge is characterized as ____________
Hemolyzed
Which species normally has yellow colored plasma?
Horses
Which cell gives rise to all blood cells?
The pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)
Erythropoiesis
Production of RBC that occurs in red bone marrow (adult animals) and in the liver and spleen (fetuses). Erythropoietin is released from the kidney when oxygen levels are low. Stages of maturation are Rubriblast, Protubicyte, Basophilic reticulocyte, Polychromatophilic reticulocyte, Metarubicyte, and Reticulocyte
Rubriblast
The most immature stage of red blood cell development. Contains one or more nuclei and a basophilic cytoplasm.
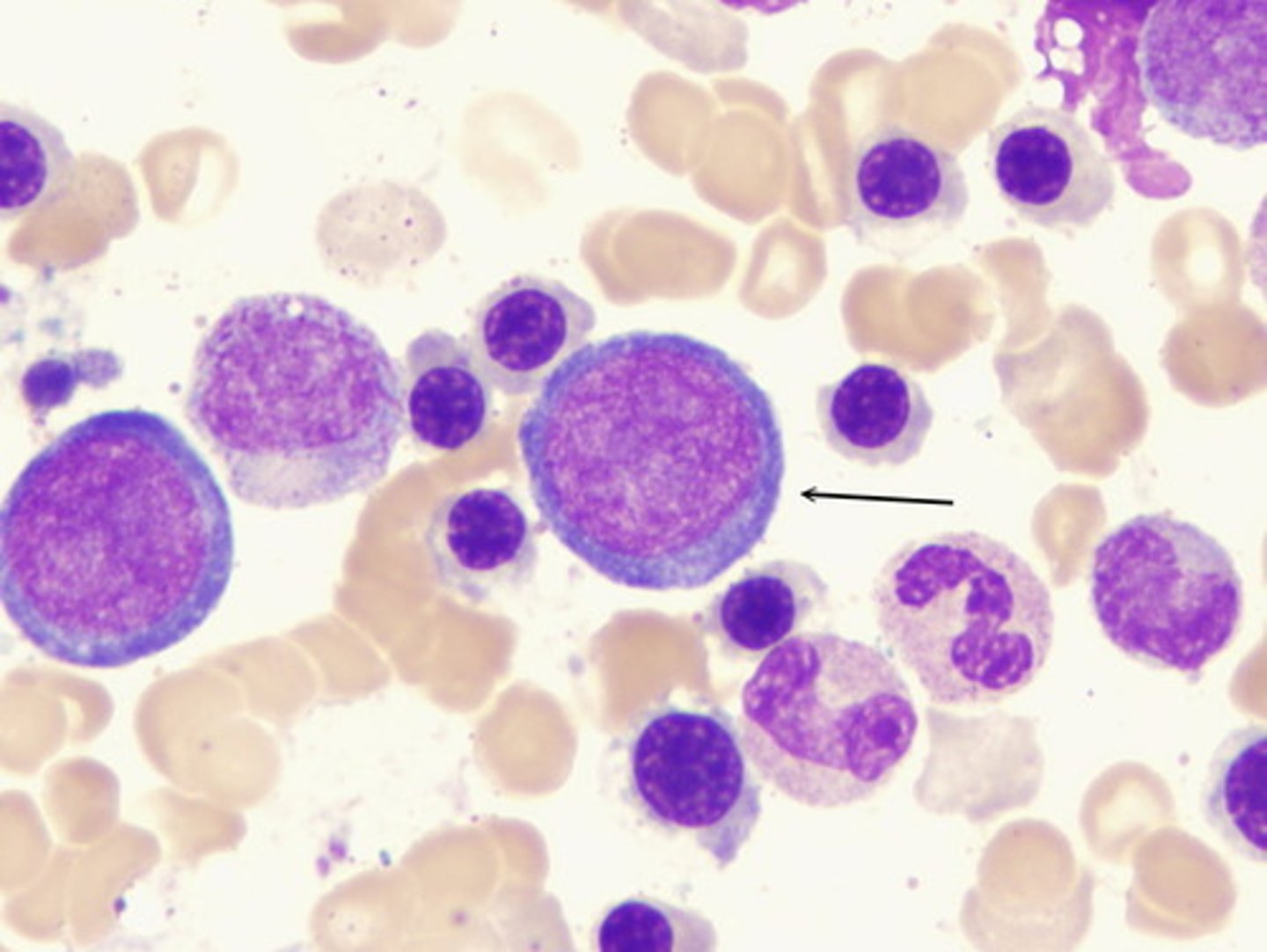
Prorubicyte
Second stage of RBC maturation. These cells are smaller than Rubriblasts and have a denser cytoplasm with no visible nucleus
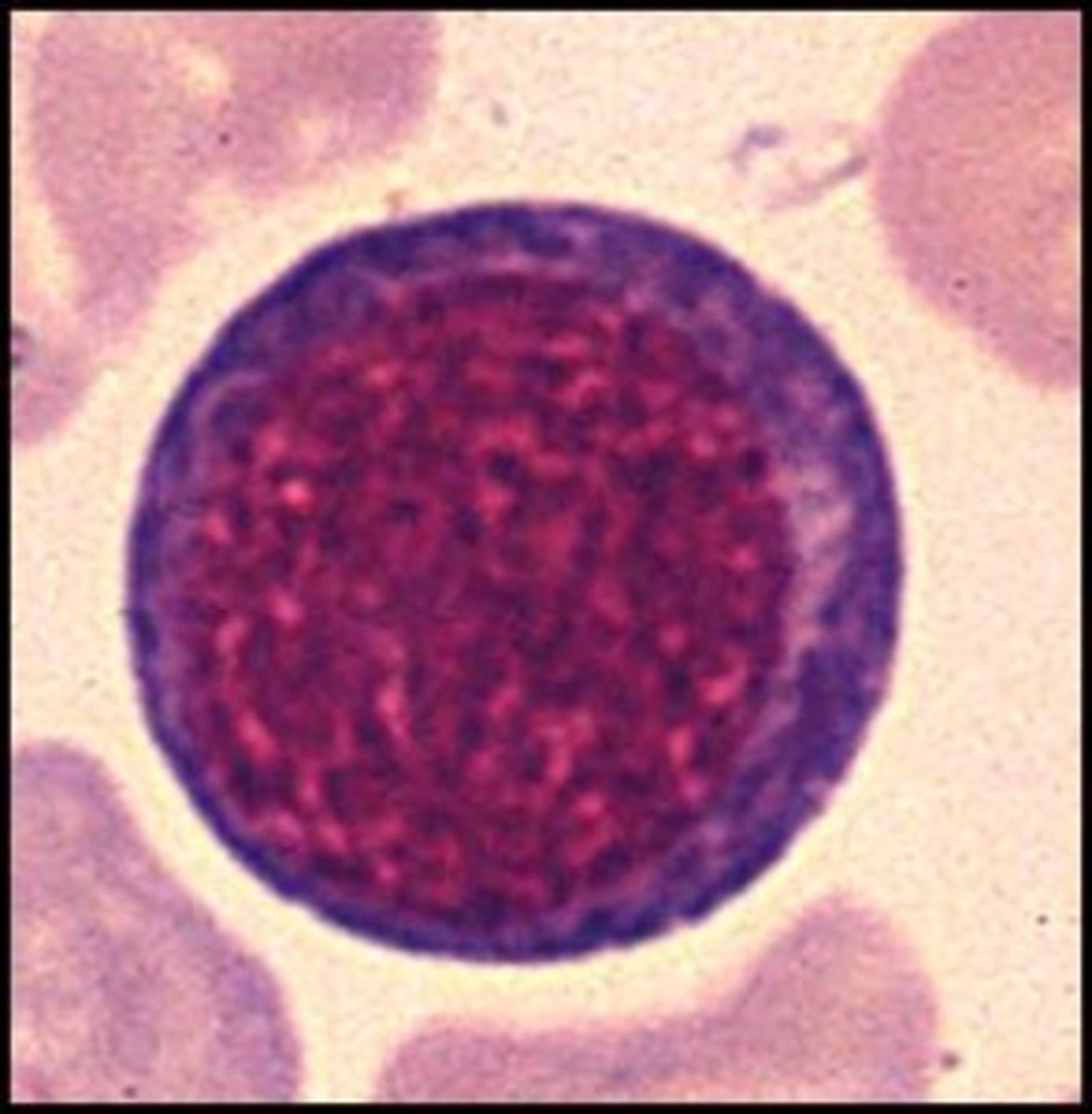
Metarubicyte
Smallest cell in the RBC maturation series. These cells have a condenses nucleus and a red cytoplasm. These cells cannot divide. Hemoglobin formation finishes in this stage.
Thrombopoesis
Platelet formation. Controlled by the release of thrombopoietin primarily from the liver, sometimes the kidney. Stages of maturation are Megakaryoblast, Promegakaryocyte, and Megakaryocyte. These cells become so large that the cytoplasm extends into sinuses and is sheared off to create proplatelets which fragment into platelets
Which organ is the primary producer of the cytokine controlling thrombopoiesis?
Liver
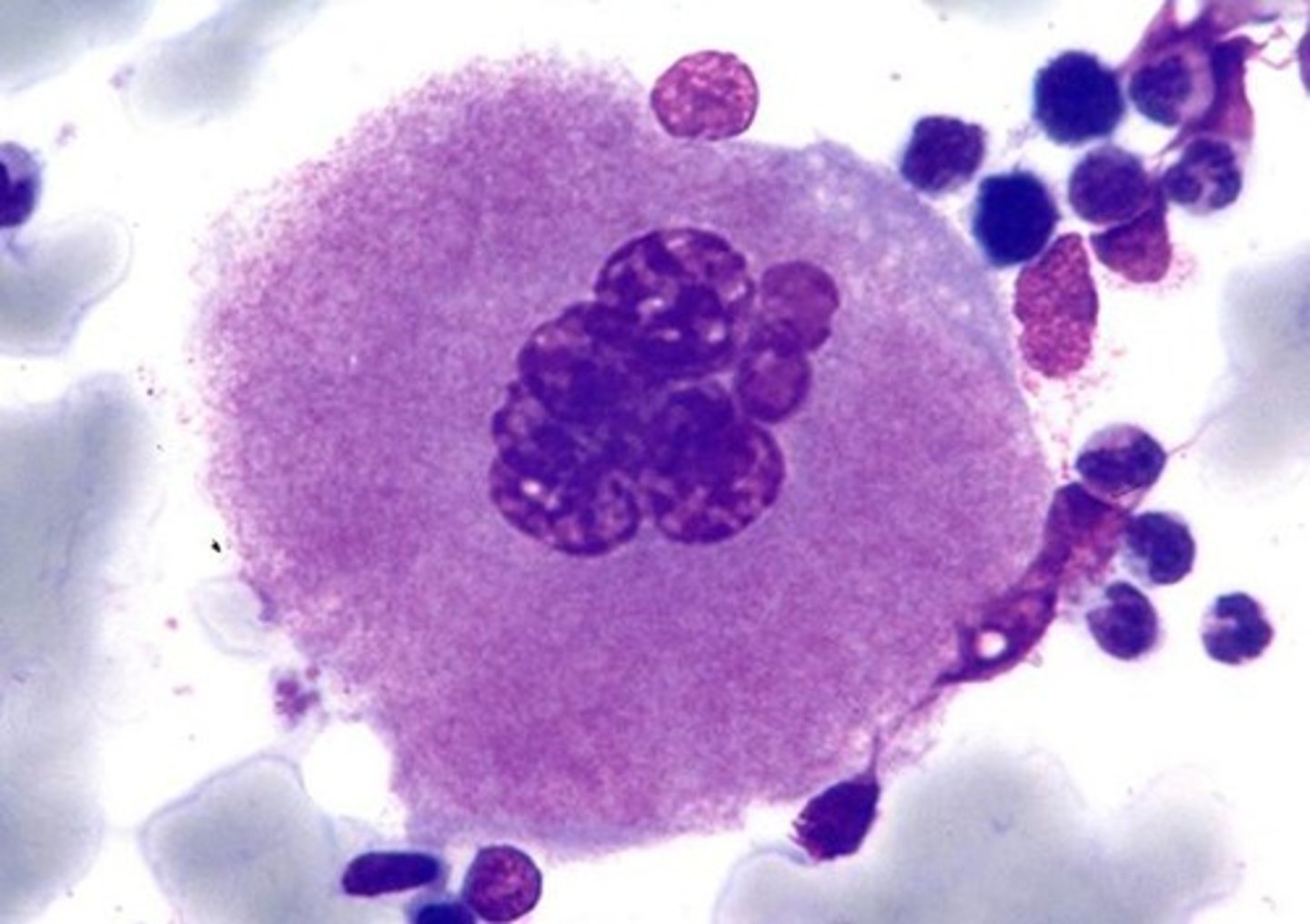
Megakaryocyte
Last stage of thrombopoiesis. These cells have several nuclear lobes and a cytoplasm with reddish granules. Cytoplasm is sheared off by bone marrow sinuses to become platelets
Granulopoesis happens in the:
Bone marrow
Which stages of granulocytes are in the proliferation pool?
Myeloblasts, Promyelocyte, and Myelocytes
Which stages of granulocytes are in the maturation pool?
Metamyelocytes and Band cells
Band/stab cells
Last stage of immaturity before becoming a mature granulocyte. These white blood cells have a horseshoe shaped nucleus
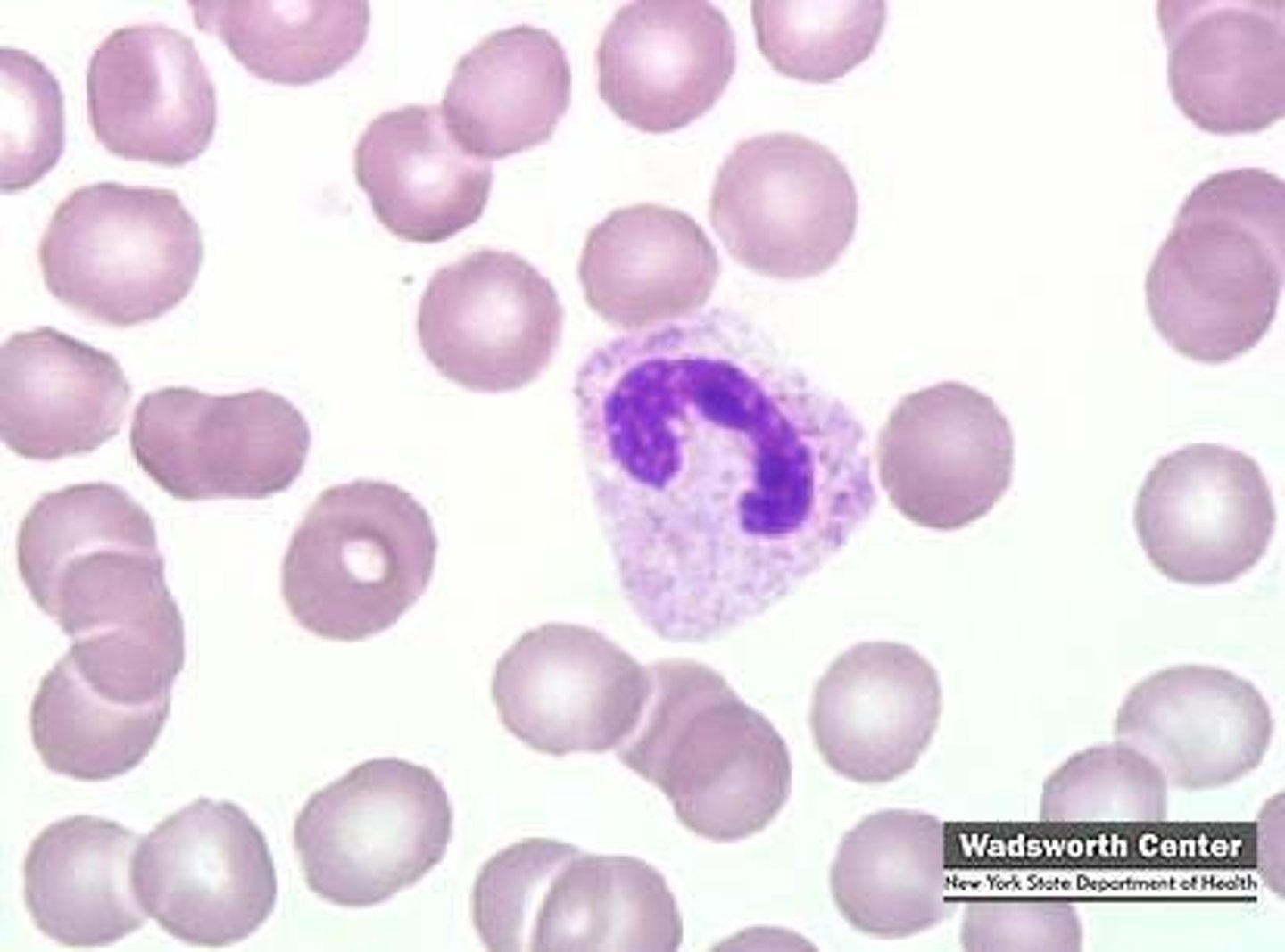
Myelocyte
Third stage of Granulopoesis. Myelocytes come from promyelocytes and develop into metamyelocytes. Cells in this stage are small in size and begin the production of granules
Monopoiesis
Production of monocyes. Stages of maturation are Monoblasts, Promonocytes, and Monocytes. Monocytes may become macrophage cells if they interact with certain cytokines
Lymphopoiesis
Production of lymphocytes. Maturation happens in the thymus (T-lymphocytes), bone marrow and other lymphoid tissues (NK lymphocytes), bone marrow, Peyer's patches, and the bursa of fabricius (B-lymphocytes)
-pneia
ending used when blood has a decreased number of cells
Neutropenia
a decreased number of neutrophils
-philia or -cytosis
increased number of cells in the blood
Left-shift
An increase in the number of immature neutrophils in response to disease
Leukemia
Neoplastic cells in the blood or bone marrow
Packed Cell Volume
(AKA hematocrit if done by an analyzer) volume percentage of erythrocytes present in a sample of centrifuged blood
A red ring on a microhematocrit tube indicates:
The tube is heparinized
A blue ring on a microhematocrit tube indicates:
The tube has been untreated
What should you do when reading a PCV result?
Line up the top of the clay plug with the 0 line and read below the buffy coat
A below normal PCV result indicates
anemia or an inadequate amount of blood to anticoagulant in the collection tube
Sodium fluoride
Additive in collection tubes used for preserving blood glucose. This anticoagulant should not be used with enzymatic tests
A well hydrated animal with a 50% PCV should yield a sample that is
50% cells and 50% fluid. A 10ml sample yields 5 ml of fluid
Order of draw for collection tubes
Blue, red, tiger top, green/tan, purple, and grey
Polycthemia/Erythrocytosis
An increase in the number of RBCs in blood
Impedance analyzers
Electronic cell counters that use the impedance method (pass a current of electricity between electrodes separated by a glass tube with a small opening) and count cells in size ranges
Impedance analyzers classify cells based on:
Size
Quantitative Buffy Coat System
A type of hematology analyzer that uses centrifugation and staining to provide a count. Provides a hematocrit value and estimates for WBC and platelet concentration. Main disadvantage in abnormalities in WBC may be undetected unless a blood smear is manually done
Quantitative buffy coat analyzers provide _____________ cell counts
estimated (NOT actual) cell counts
Laser-Based flow Cytometer Analyzer
A kind of analyzer that uses a focused laser to evaluate the size and density of cells. Results are based on the way light scatters when it hits cells. These analyzers can provide erythrocyte indices, EDW, and platelet parameters
Erythrocyte indices are used to diagnose
Different types of anemia
Nonregenerative anemia
Bone marrow is not responding to the need for more RBC production because of bone marrow issues, kidney dz, etc
How do you calculate the Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) of a blood sample?
Divide the PCV by 6 to get the RBC concentration ----> divide the PCV by the RBC concentration ----> multiply this number by 10 to get the final value (unit is Femtoliters or fL)
How do you calculate the Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) of a blood sample?
Divide the PCV by 6 to get the RBC concentration ---> divide the PCV by 3 to get the hemoglobin conc ---> divide the hemoglobin conc value by the RBC conc value ---> multiply this number by 10 to get the final value (unit is Pictograms or pg)
How do you calculate the Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) of a blood sample?
Divide the PCV value by 3 to get the hemoglobin concentration ---> multiply this number by 100 to get the final value (unit is in grams per deciliter or g/dl)
Erythrocyte indices
Used to classify anemias. This test provides an objective measure of the size and average hemoglobin concentration by comparing the sample to morphologic features
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) uses the unit
Femtoliters or fL
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) uses the unit
Pictograms or pg
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) uses the unit
grams per deciliter or g/dl
Hemocytometers
gridded slide under microscope. Cells can be counted in a known area, and that number can be estimated to find the full volume of a blood sample
An increased PCV result is commonly due to _________________
dehydration
Normal PCV range for dogs
37-55%
Normal PCV range for cats
30-45%
Normal PCV range for horses
32-57%
Normal PCV range for cattle
24-42%
Methemoglobin
Occurs naturally in RBC and in plasma but can be converted into hemoglobin for oxygen delivery
What is the drawing order for blood collection tubes?
Blue (citrate), red, tiger top, green/tan (Heparin), purple (EDTA), and grey/white (Oxalates/Sodium flouride)
Poikilocytes
abnormally shaped erythrocytes
Leukemoid response
Mistaken for leukemia because this condition causes higher than normal leukocyte levels. Usually caused by inflammatory disease
Granules are characteristic of a _________ granulocyte
mature
Schistocytes
fragmented red blood cells formed because of shearing
Blood samples can be frozen. (T/F)
False! Blood samples that cannot be viewed immediately should be refrigerated, not frozen. Freezing can cause lysis of blood cells
Disadvantages to heparin
It interferes with the staining of erythrocytes (meaning it cannot be used for blood smears) and can cause clumping of WBC, clumping of platelets, and interferes with WBC morphology (meaning it shouldn't be used for CBC's)
Disadvantages to EDTA
Causes blood cells to shrink if the tube is underfilled and the anticoagulant to blood ratio is off.
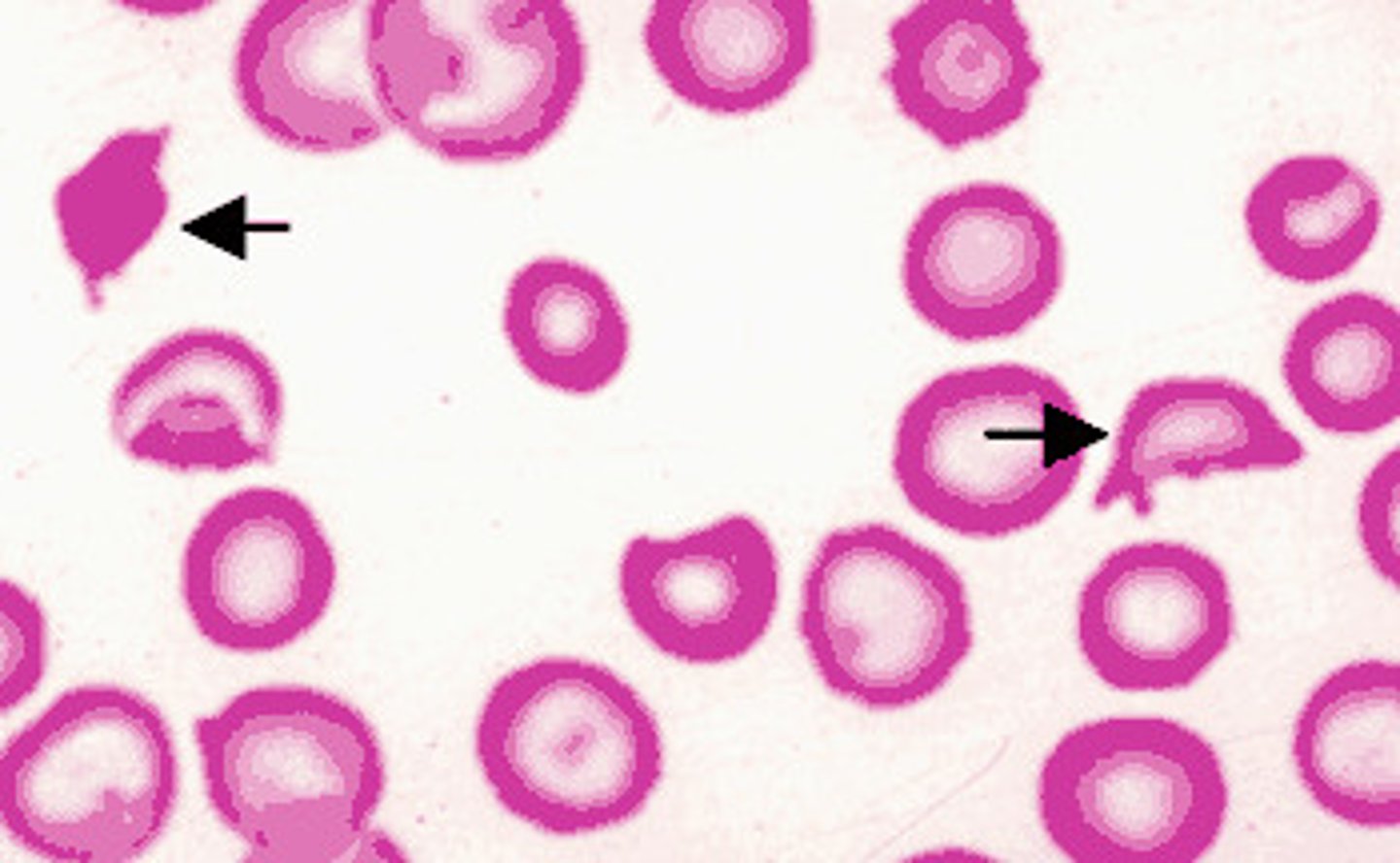
Acanthocytes (Spur cells)
Spiculated RBCs with a few unevenly distributed surface projections. These cells are seen in patients with altered lipid metabolism (dogs with hemangiosarcoma, cats with hepatic lipidosis, etc
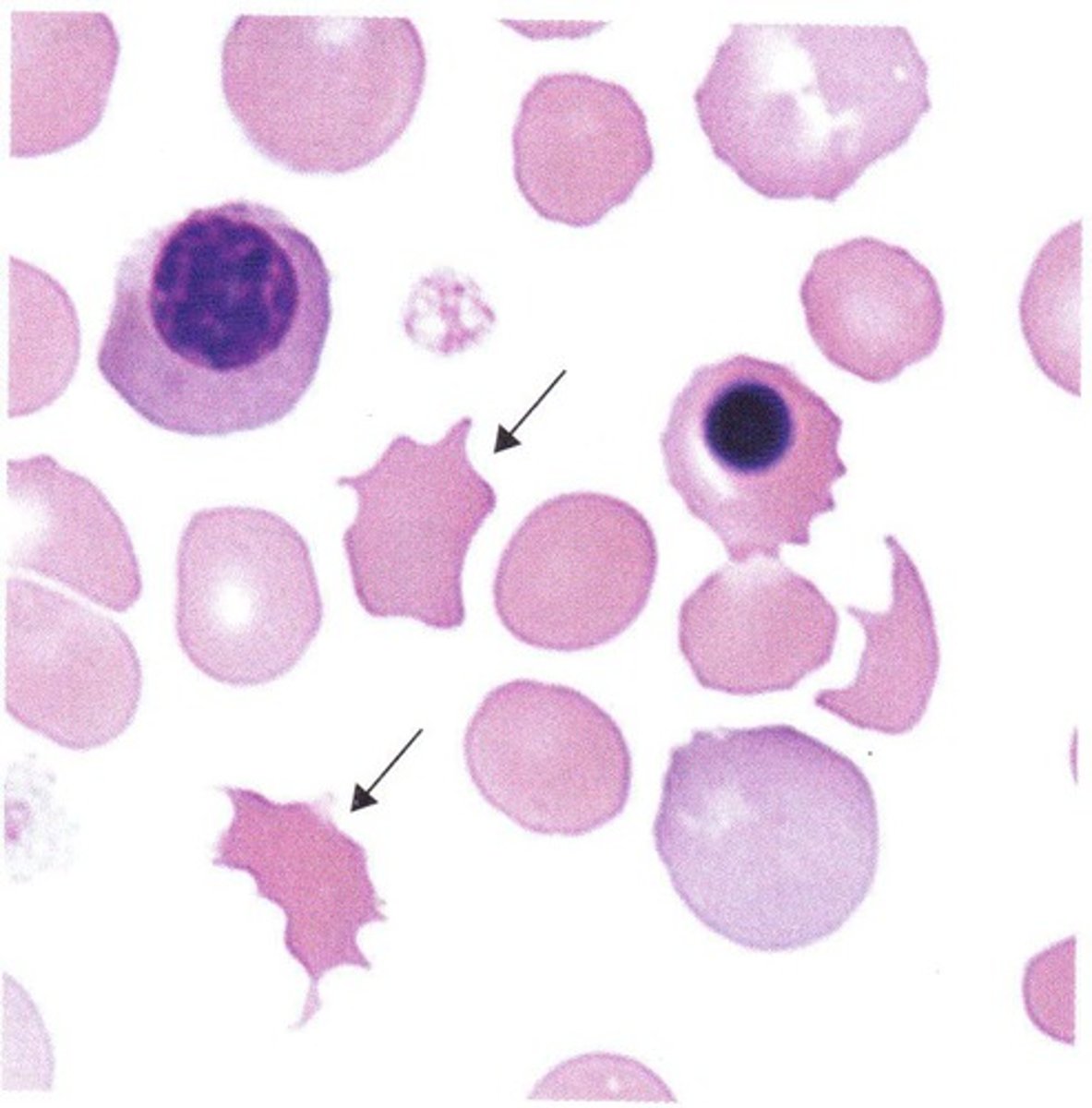
Echinocytes (Burr cells)
Spiculated RBC with numerous short, evenly spaced, blunt to sharp surface projections of uniform shape and size. Seen in dogs with lymphosarcoma, after exercise in horses, and in healthy pigs. Also occur after snake bites in dogs or because of prolonged sample storage
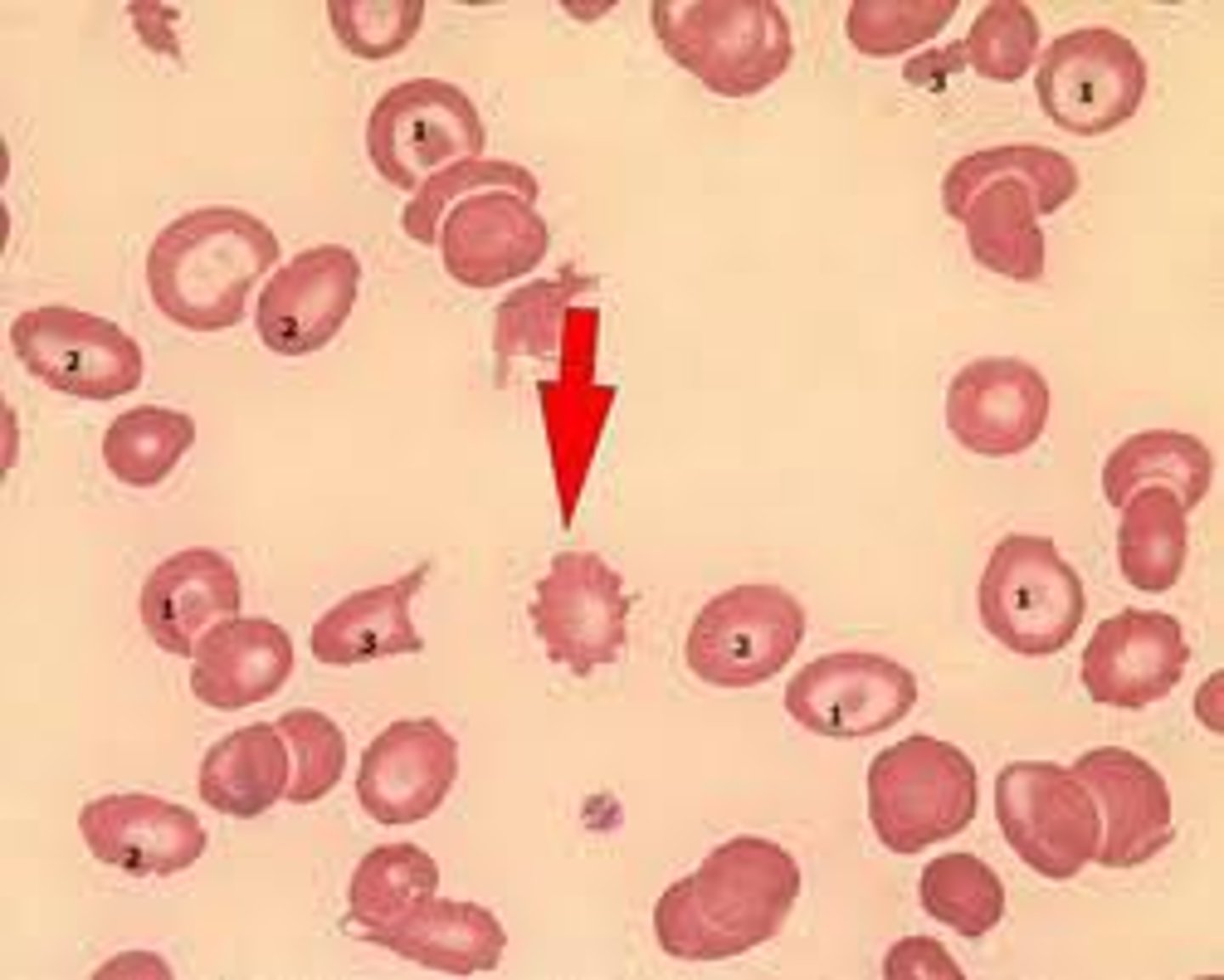
Drepanocytes
Sickle shaped cells of angora goats and sheep. Thought to be an in vitro phenomenon caused by high oxygen tension
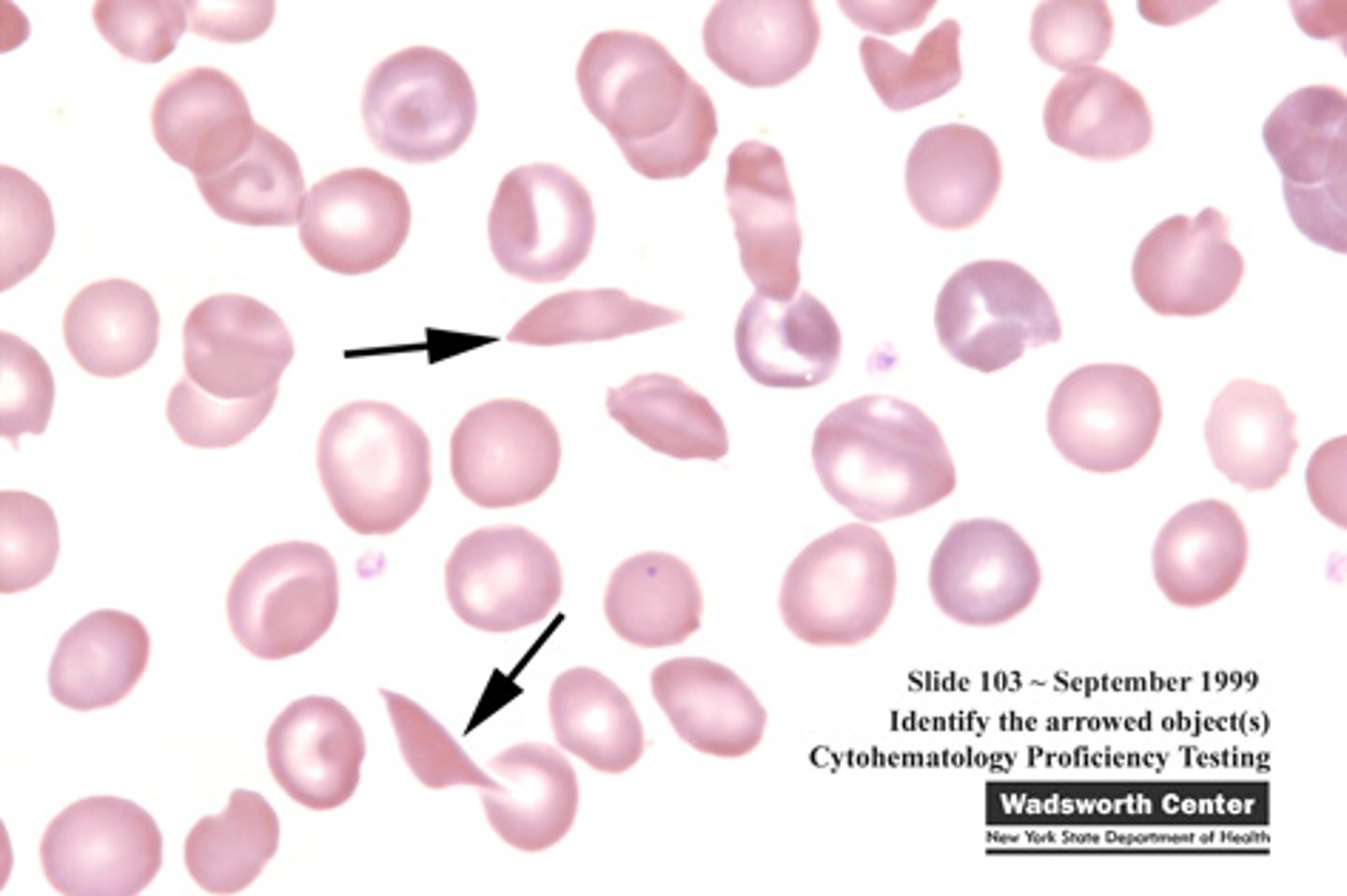
Keratocytes (Helmet cells)
Presence of these cells is associated with hemangiosarcoma, neoplasia, hepatic diseases, and anemia. May appear to have vacuoles. Caused by intravascular trauma
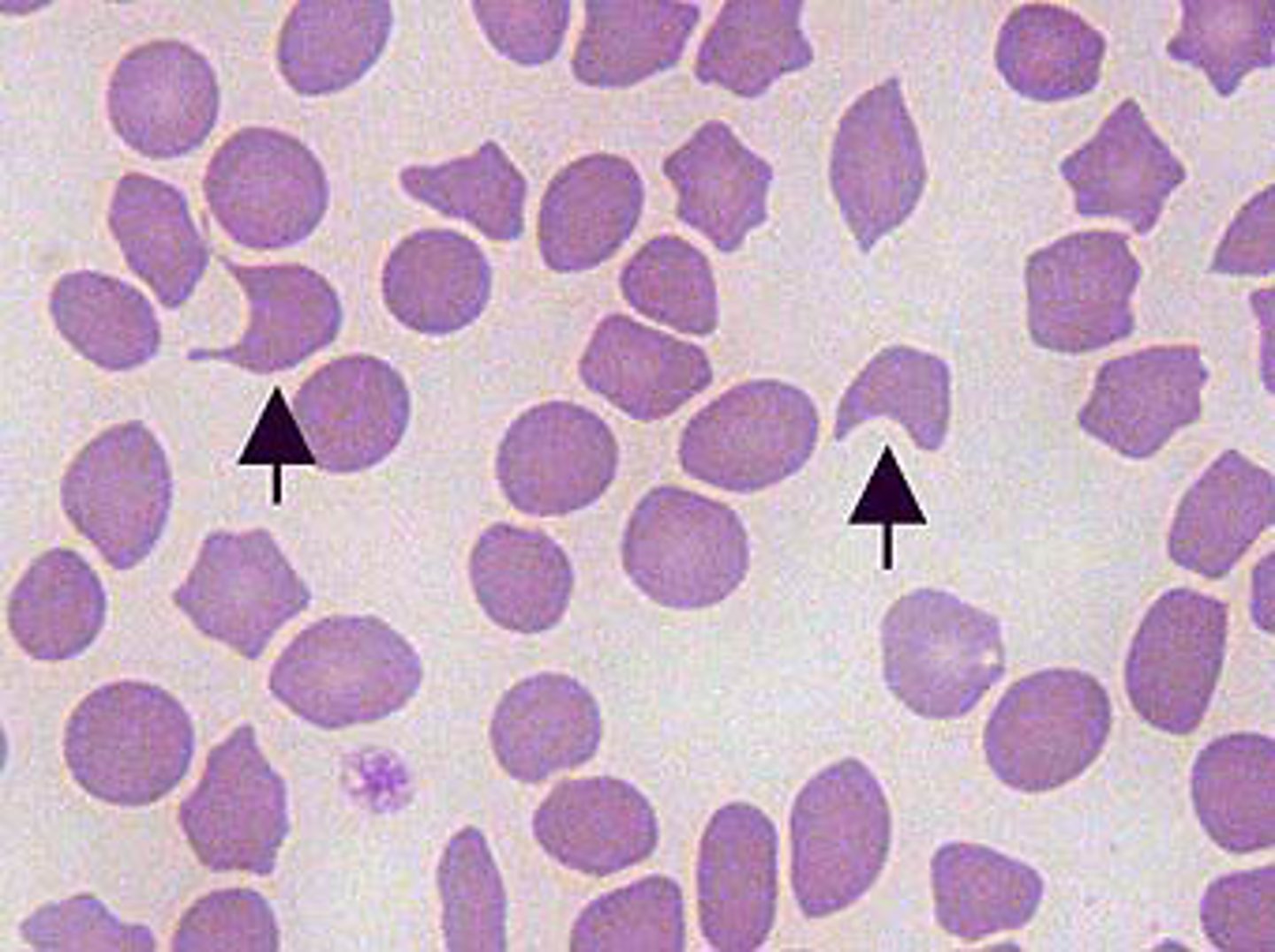
Spherocytes
Darkly staining RBC with reduced or no central pallor. Not easily identified in species other than dogs. These cells suggest the immune mediated destruction of RBC's which results in hemolytic anemia.
Leptocytes
Characterized by increased membrane surface area relative to cell volume- cells may take a variety of shapes.
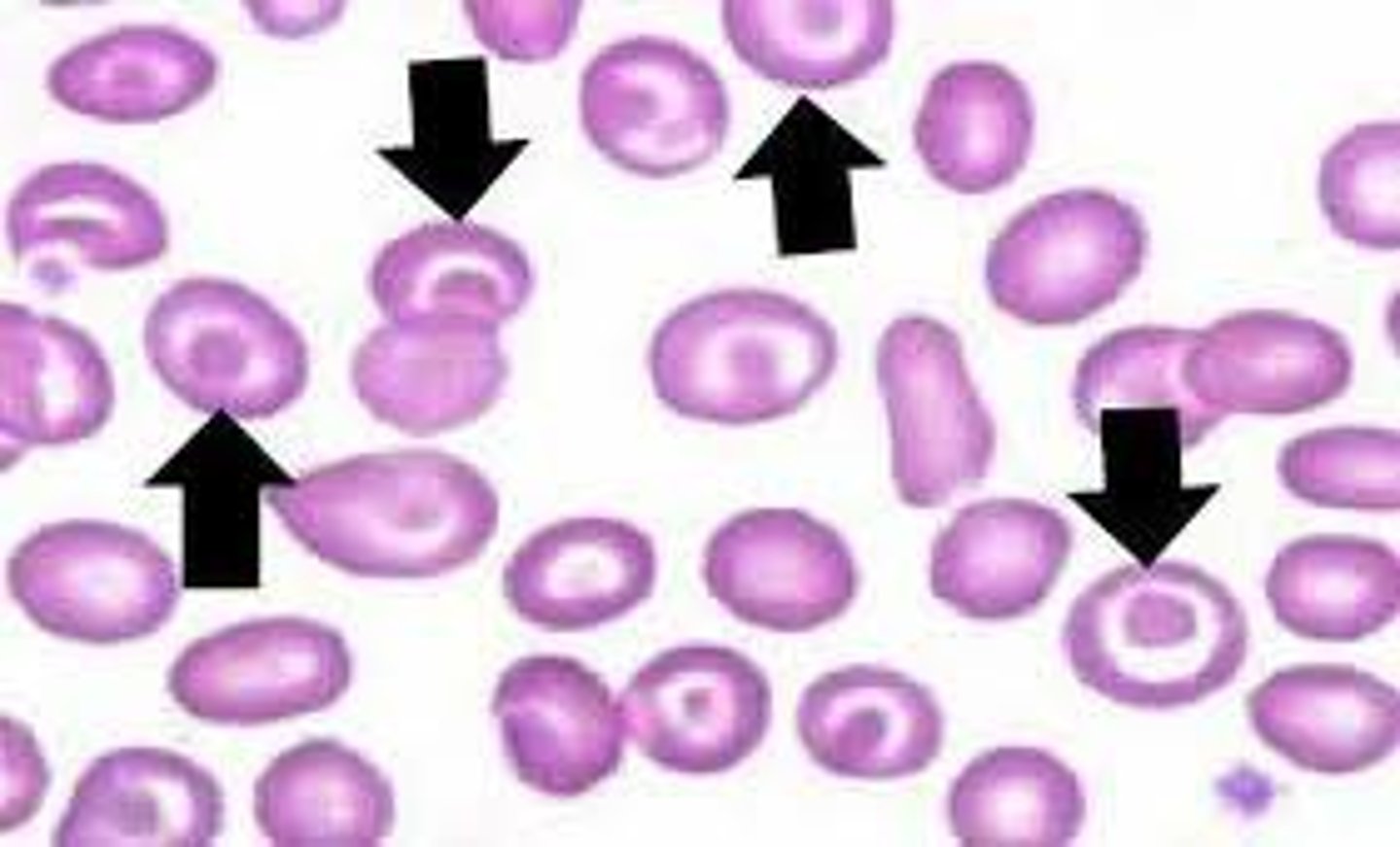
Codocytes (Target cells)
Leptocytes with a central area of pigment surrounded by a clear area and then a dense ring of peripheral cytoplasm. May be seen in normal smears but can be associated with anemia, liver dz, and some inherited disorders
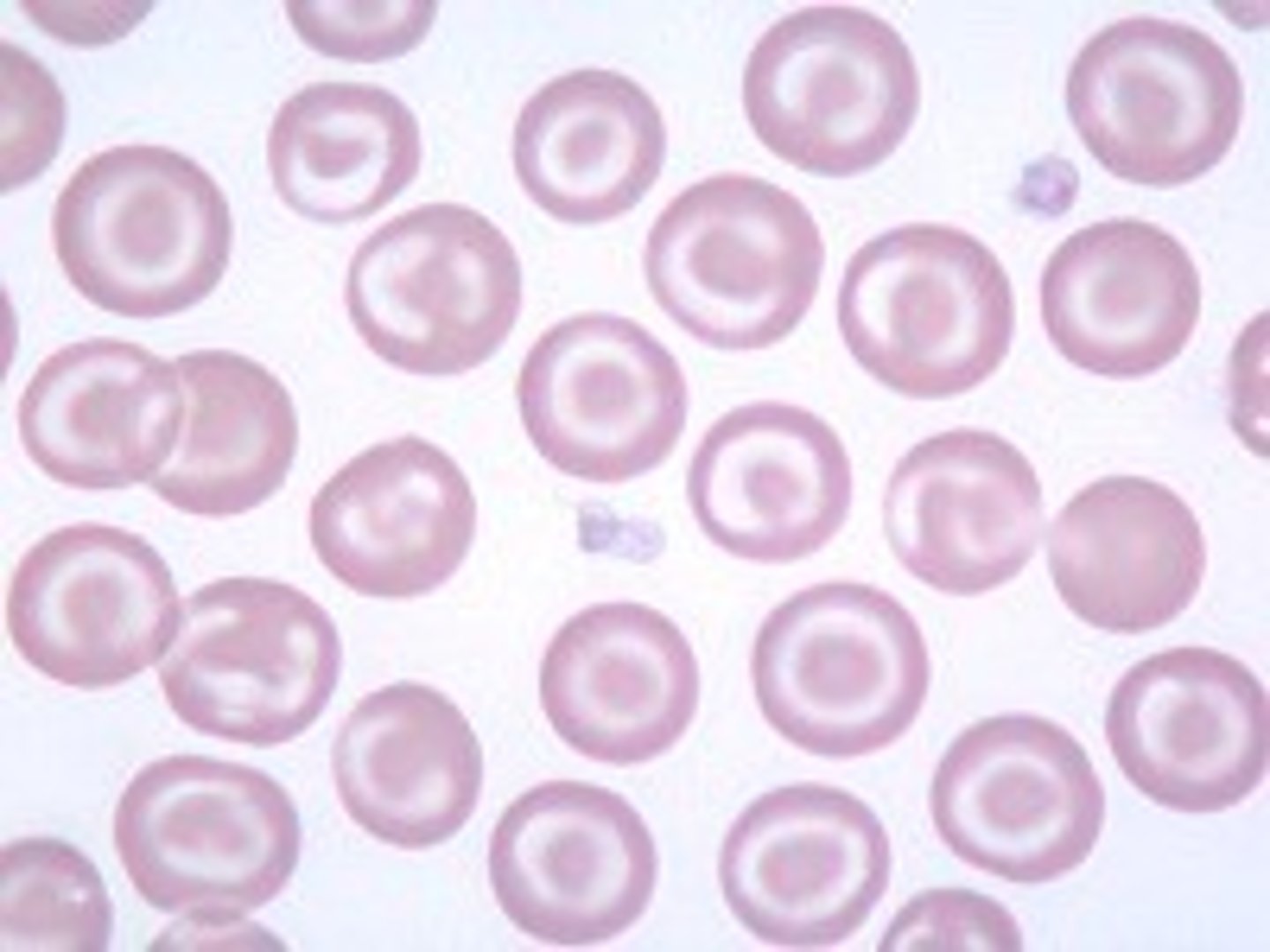
Stomatocytes
Folded lepatocyte cells that hae a transverse raised fold that extends across the center of the cell as well as a clear pale region in the center of the cell
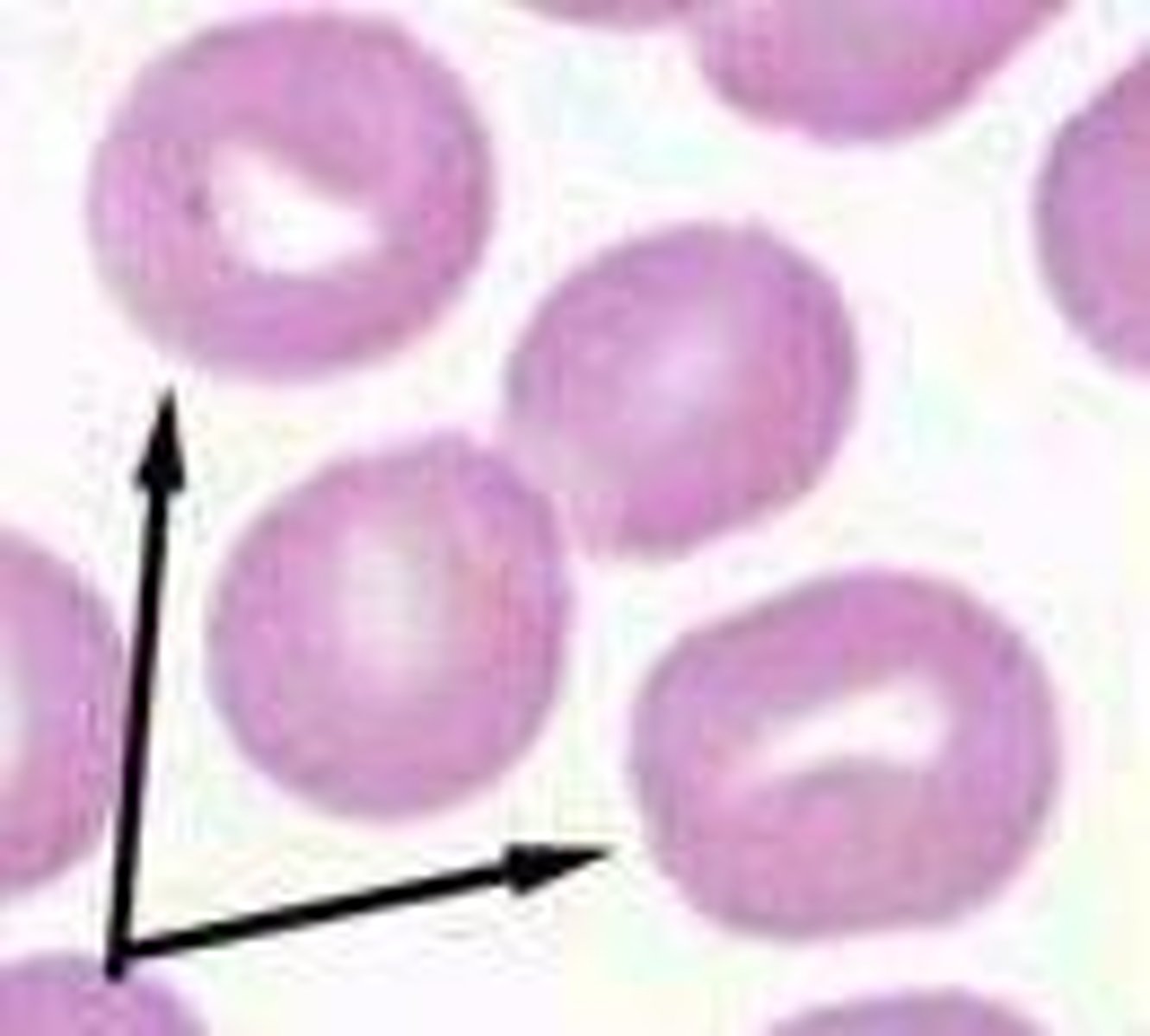
Basophilic stippling
Small dark blue inclusions within RBC's. Observed in Wright stained cells and represents residual RNA. Common in immature RBC's in ruminants, occasionally in cats in a response to anemia, and characteristic of lead poisoning
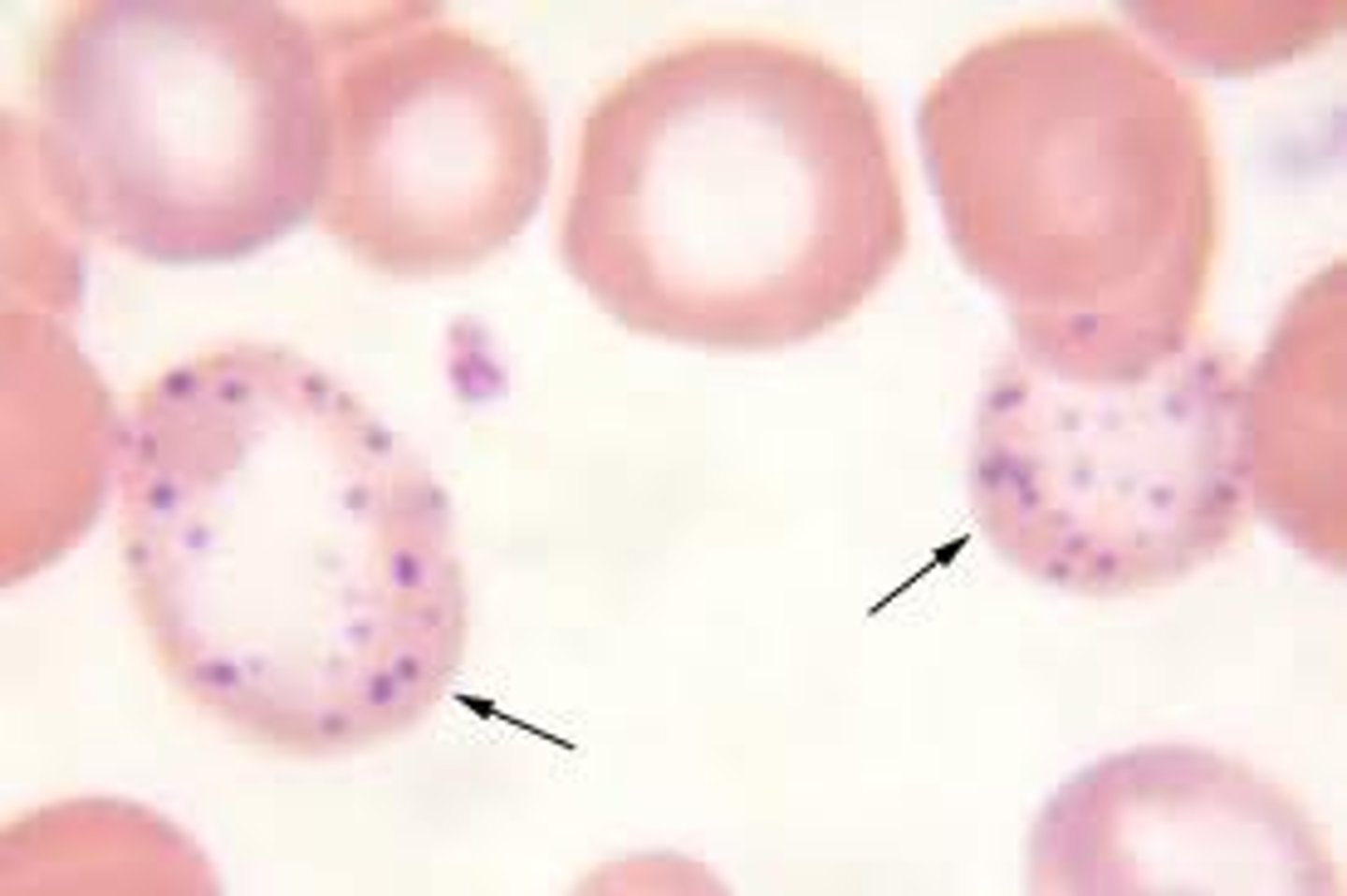
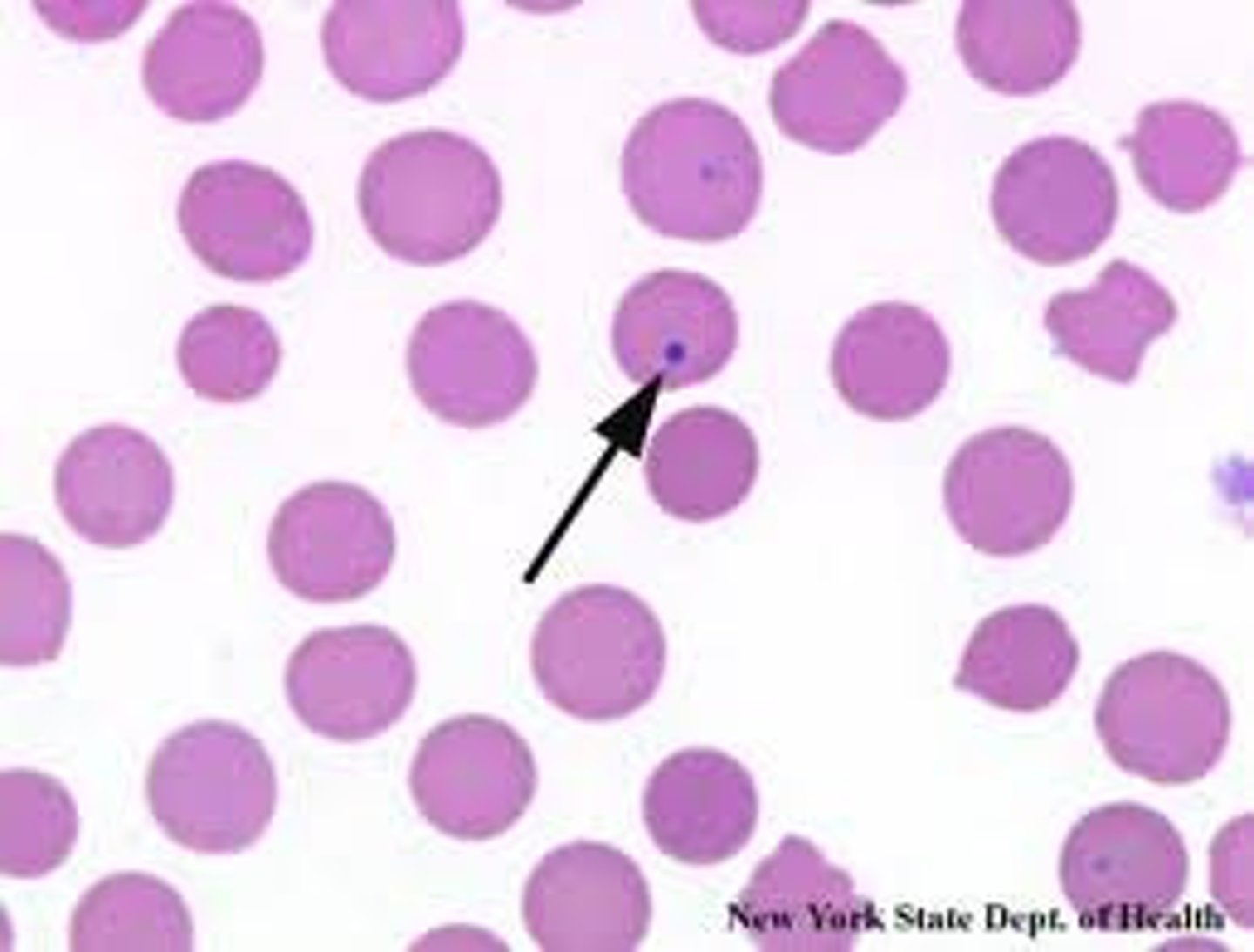
Howell-Jolly bodies
Basophilic nuclear remnants seen in young erythrocytes during the response to anemia. Increased numbers indicates spleen disorders
Bone marrow samples can be described as:
acellular (aplasia), hypercellular (hyperplasia), & hypocellular (hypoplasia)
Which species rarely releases reticulocytes into circulating blood?
Horses
Normocytic anemia is associated with
secondary to acute or chronic disorders
Macrocytic anemia (large red blood cells) is associated with
a temporary increase in response to regenerative anemia
Microcytic anemia (small red blood cells) is associated with
Iron deficiency
Hypochromatic anemia
Anemia where red blood cells have a smaller amount of hemoglobin so they stain a lighter color. Associated with iron deficiency or newly released reticulocytes
Normochromic anemia
Anemia where red blood cells have a normal level of hemoglobin. Cells stain red in color
Iron deficient anemia
Associated with nutritional issues or chronic blood loss. Characterized by microcytic RBC's and a low MCHC value
Production disorders
Disorder where erythropoiesis is reduced or defective. Erythrocytes are normocytic
hemolytic anemia
characterized by an inadequate number of circulating red blood cells due to the premature destruction of red blood cells by the spleen
Wright stains and Wright-Giemsa stains are ______________________ type stains
Romanowsky