Bone Anatomy and Physiology
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parts of a bone, cellular level of the skeletal system, feedback loop of PTH and calcitonin
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Where is fat stored within the bone?
Medullary cavity
Through the action of osteoclasts,
bony matrix is dissolved
________ bone reduces the weight of the skeleton and reduces the load on muscles.
Spongy
Red bone marrow functions to __________, whereas yellow bone marrow functions to ________.
Produce blood cells, store fat
What happens when blood levels of calcium drop below normal?
parathyroid hormone secretion increases and osteoclast activity increases
What is the function of the hormone calcitonin?
increase calcium absorption to bone and decrease calcium excretion to blood.
Elevated levels of calcium ions in the blood stimulate the secretion of which hormone?
Calcitonin
A lack of exercise could lead to which of the following to happen?
Results in porous and weak bones.
While on a school skiing trip in Colorado, 18 year old Heidi falls and breaks her tibia and fibula in a comminuted fracture. Blood tests reveal elevated levels of PTH and calcium. What disease would be suspected?
Osteoporosis
What does the presence of an epiphyseal plate indicate?
Bone length is increasing
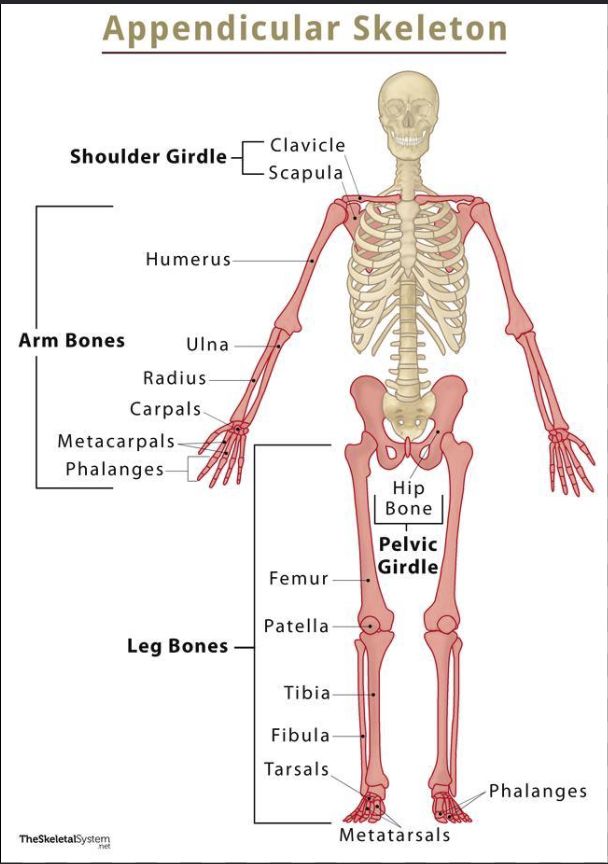
Identify the bones that belong to the appendicular skeletal system.
There are 4 stages in the healing of a bone fracture. Which of the following is the correct sequence?
Bone remodeling
Bony callus formation
Hematoma formation
Fibrocartilage callus formation
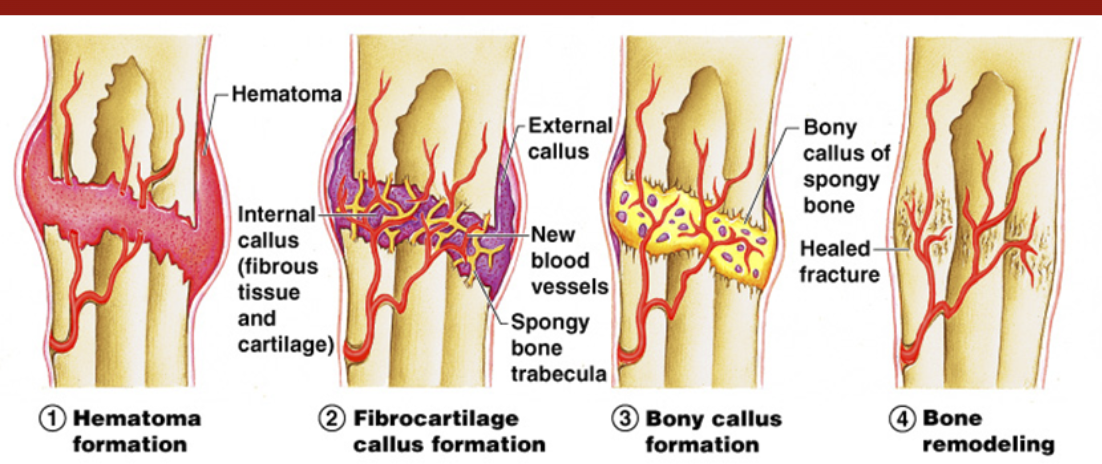
3,4,2,1: Hematoma formation, Fibrocartilage callus formation, bony callus formation, bone remodeling
________ fractures are completely internal; they do not break through the skin.
Closed
Which of the following types of fractures causes the bone to shattered into many pieces?
Comminuted
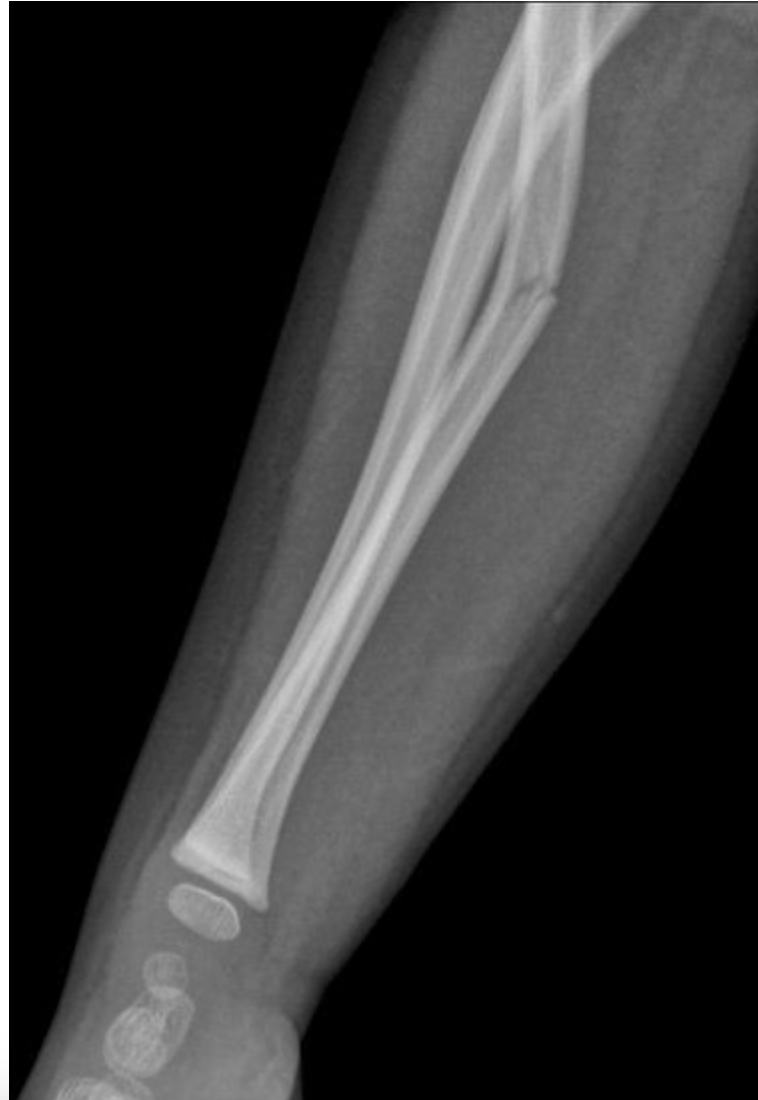
Below is an x-ray of a forearm. Identify the two bones present in the image.
radius, ulna
This is an x-ray from a 10 year old child. Identify the type of fracture present in the x-ray below.
greenstick
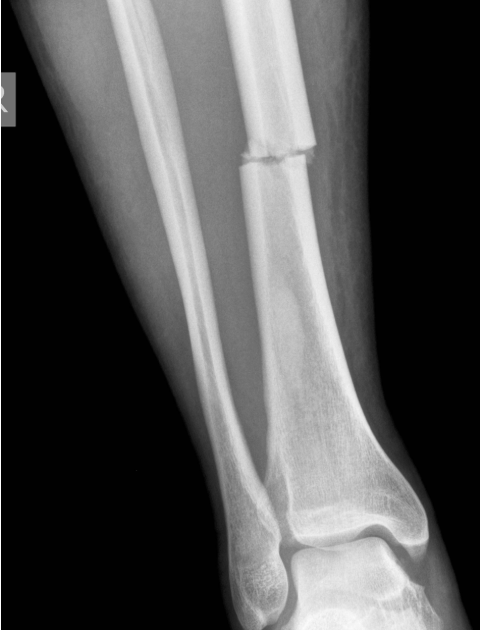
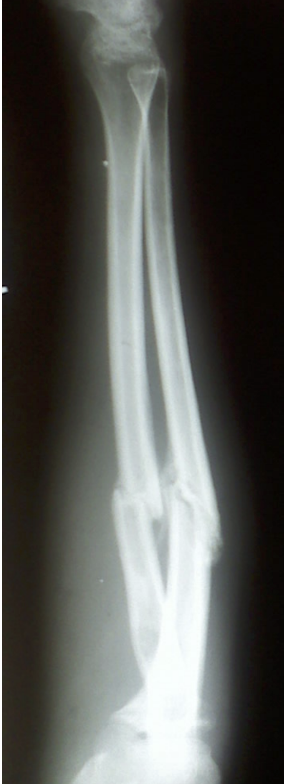
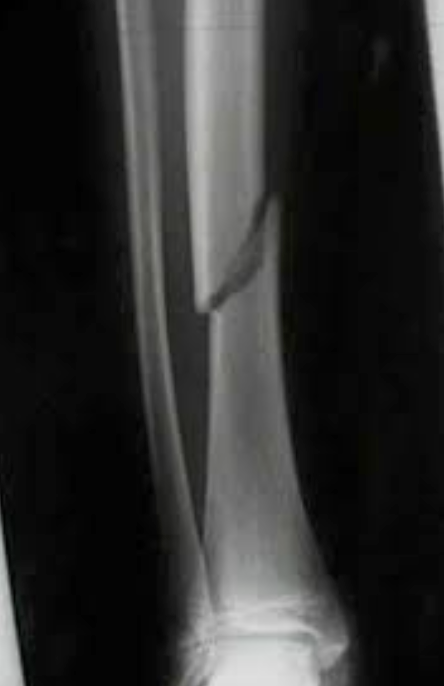
Identify the type of fracture present in the x-ray of this tibia.
transverse
Explain how hyperparathyroidism leads to osteoporosis in young adults. Your explanation should include the following terms: osteocytes, osteoclast, osteoblast, parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, and calcium.
Osteocytes can be broken into two different groups, osteoclasts which break down bone, and osteoblasts which build up bone. When there is high blood calcium levels, calcitonin is released which promotes osteoblasts to use the calcium to build up bone. When there is low blood calcium levels, parathyroid hormone is released and promotes osteoclasts to break down bone for it's calcium. Hyperparathyroidism is the overproduction of the parathyriod hormone even when blood calcium levels are high, and over time more and more bone is broken down for calcium. This leads the bones to become weak and porus as the osseos tissue is siphoned away due to the overproduction of PTH, leading the condition osteoporosis.
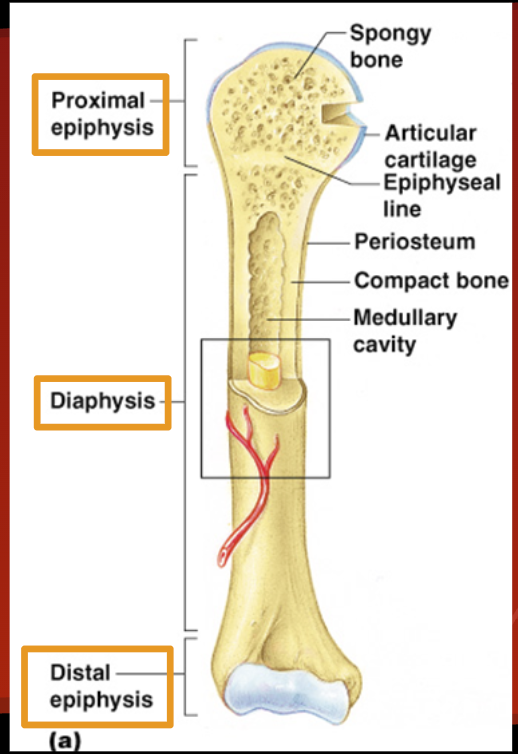
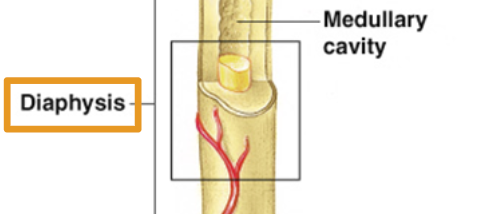
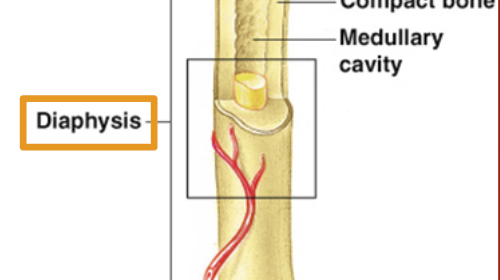
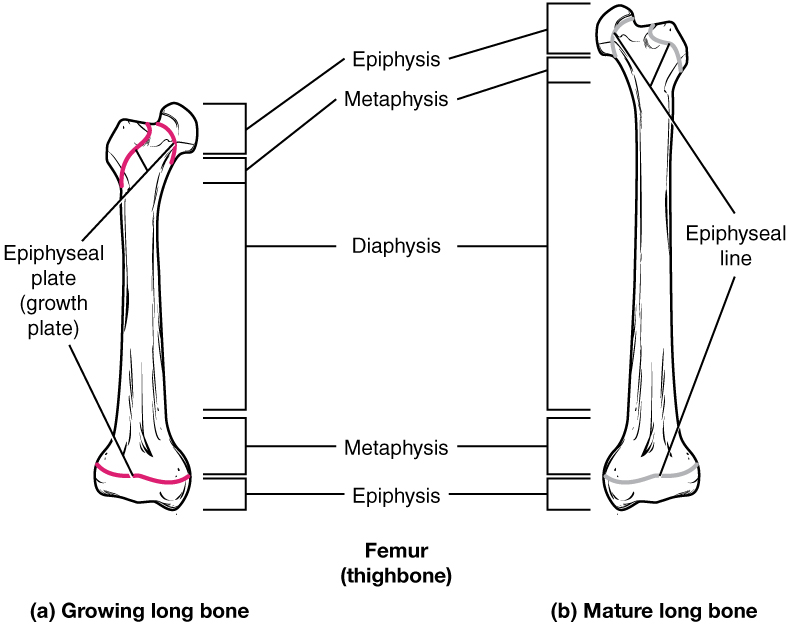
Diaphysis
Shaft of bone: Compact bone
Epiphysis (head)
Proximal and distal
Spongy bone
Red bone marrow = where blood cells form
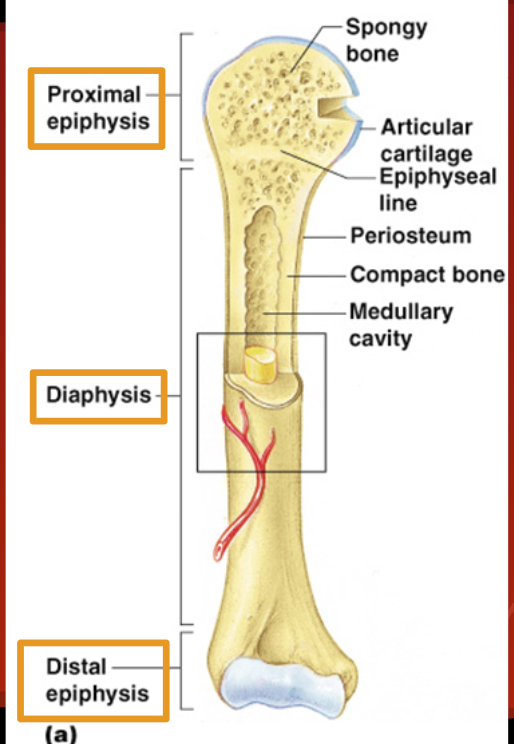
Articular Cartilage
Cushions ends of bones so joints can function.
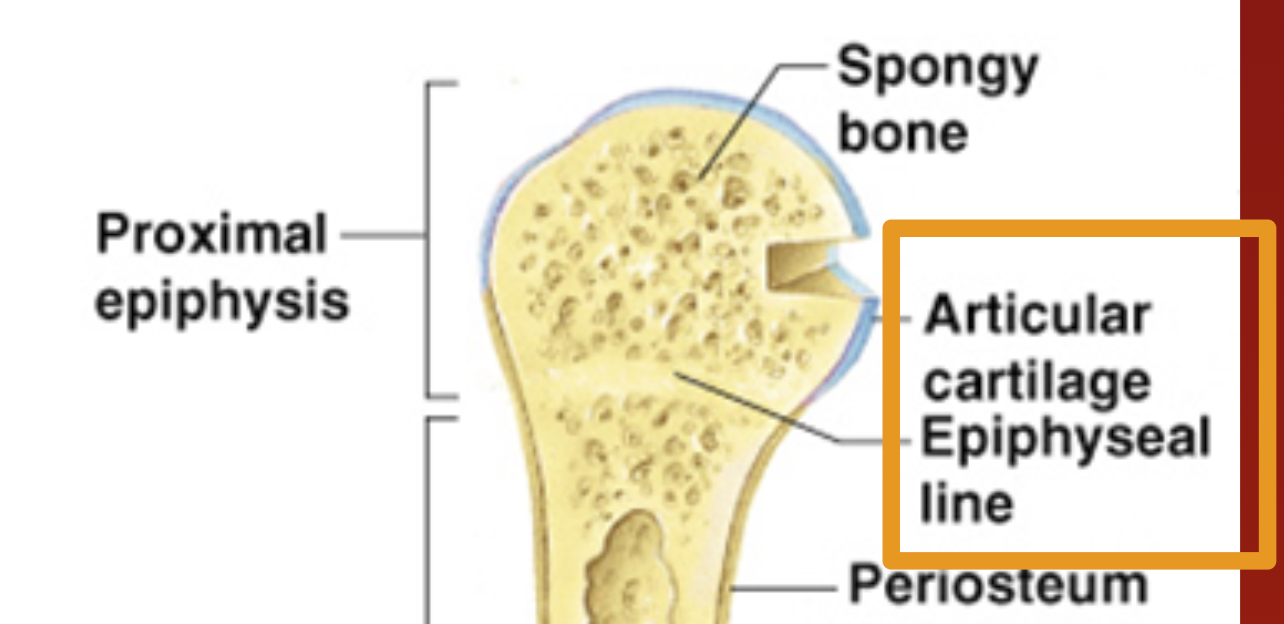
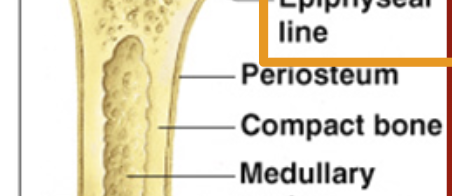
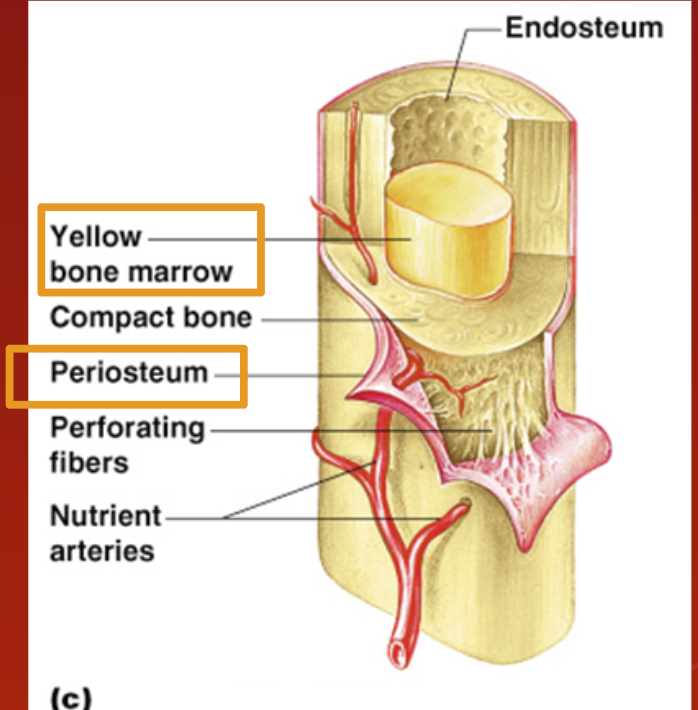
Periosteum
Membrane on outside of bone
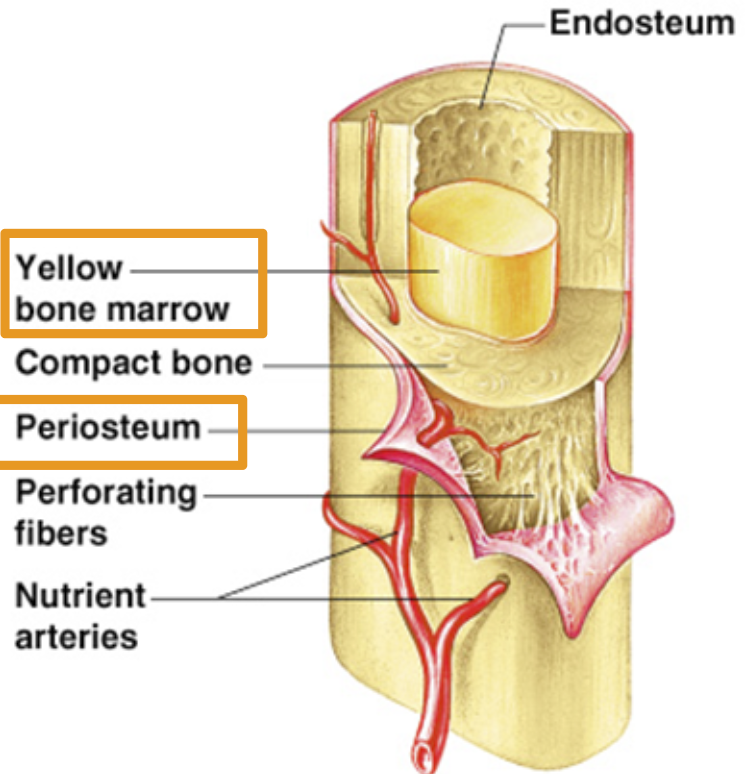
Medullary Cavity
Yellow bone marrow stored here.
adipose tissue (commonly known as body fat) stored.
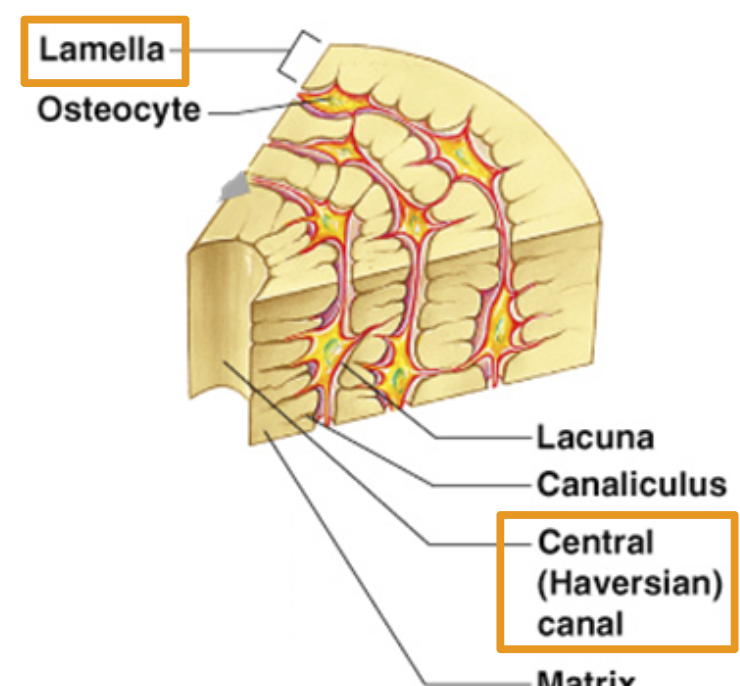
Osteocyte
Bone cell
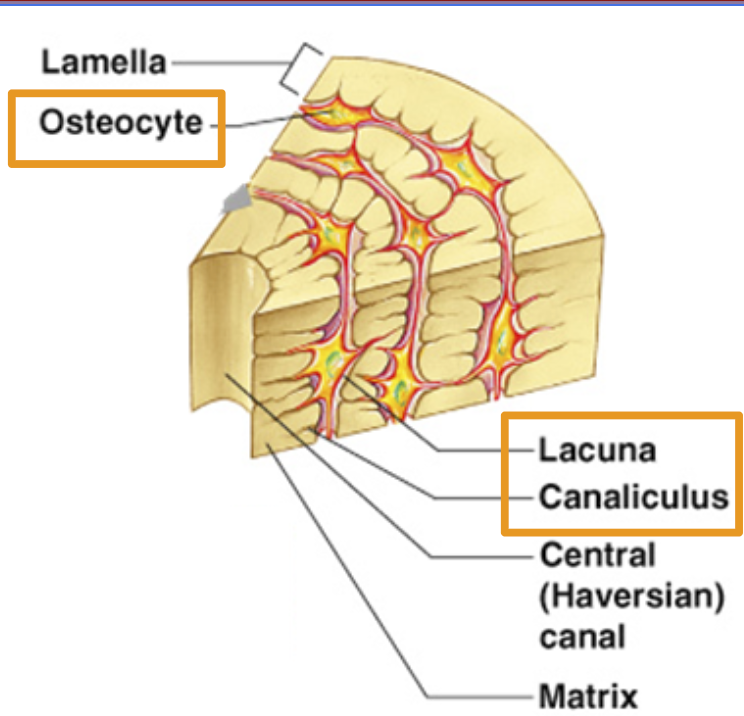
Lacuna
where bone cells sit.
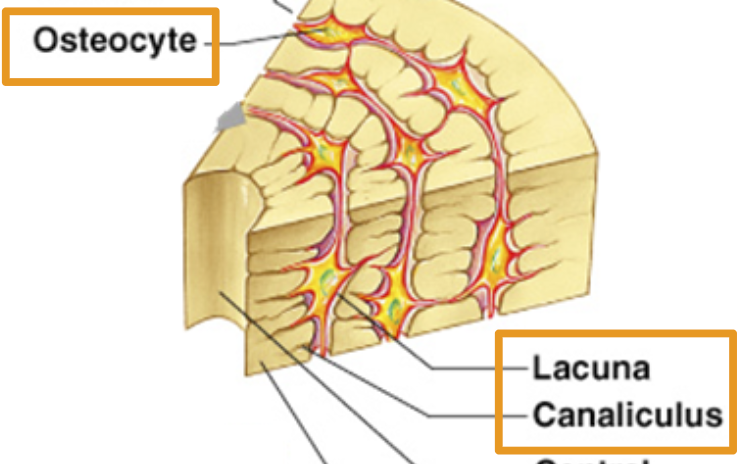
Canaliculus:
Canals that connect lacunae. Deliver nutrients to bone cells.
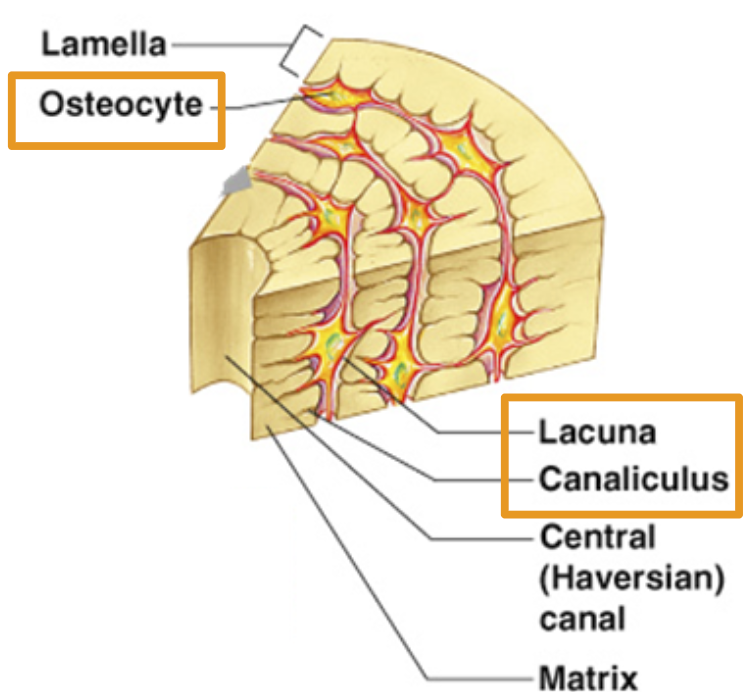
Lamella
Rings of bone tissue
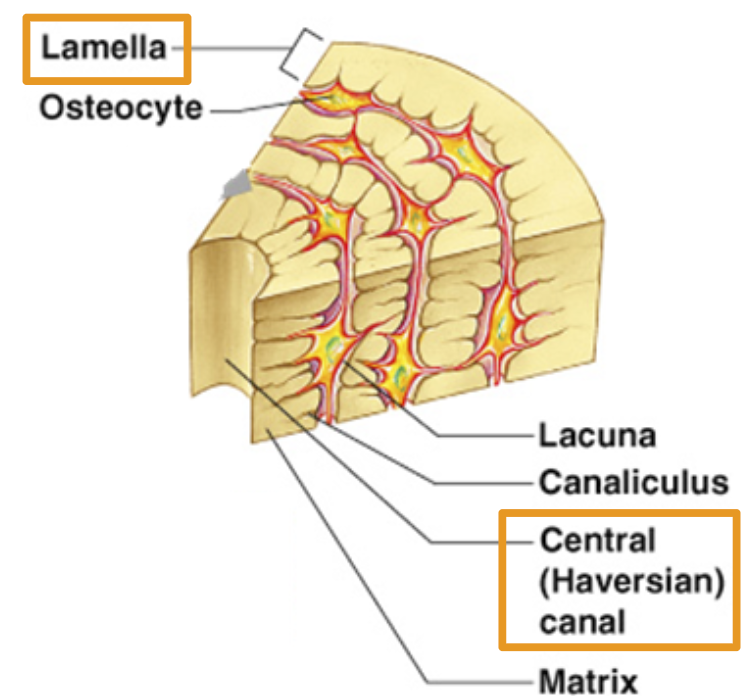
Central Haversian Canal
Openings for blood vessel to move through bone.
Bone growth Formation: Ossification
In an embryo: bone is cartilage
In a fetus: bone slowly converts from hyaline cartilage to bone
In a child: hyaline cartilage converts to bone tissue
Ossification:
process of turning cartilage into bone by depositing phosphorus and calcium.
Bone Growth
Grow in length and width
Length: under articular cartilage and under epiphyseal plate as cartilage forms.
Width: osteocytes grow under periosteum.
The epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate, which is the growth plate in long bones, gradually turns into bone throughout childhood and adolescence
The presence of an epiphyseal plate (also known as a growth plate) indicates that a bone is still in a period of growth and lengthening
Increases bone length
Epiphyseal line
Once the cartilage growth stops and is fully replaced by bone, marking the end of bone growth in length
What is bone growth determined by
Controlled by Ca2+ levels in the blood
High blood Ca2+ leads to bone formation by addition of osteoblasts
Low blood Ca2+ leads to bone breaking down by osteoclasts
Bone Remodeling
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): determines WHEN bone is broken down or formed in response to Ca levels.
Stress/gravity acting on bones determines WHERE bone matrix is broken down or formed.
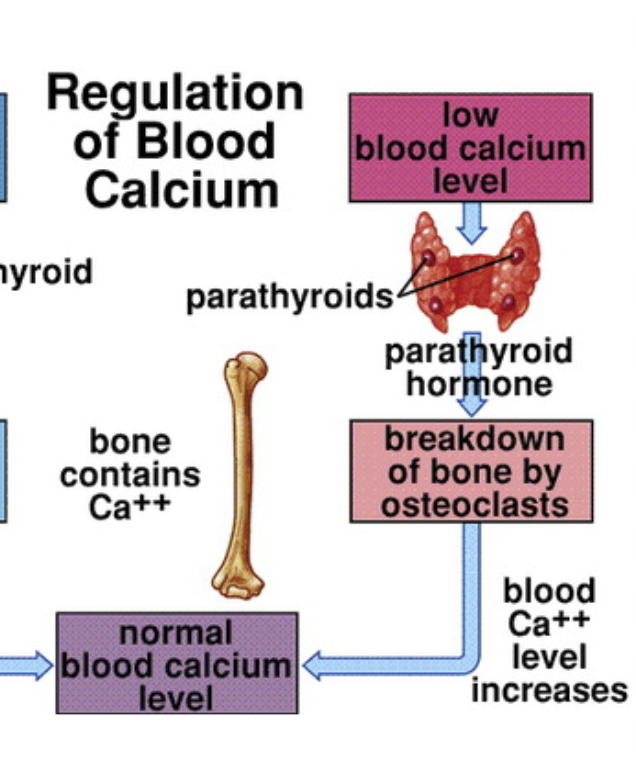
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH):
Secreted by the parathyroid glands (small glands behind the thyroid). when low calcium levels are detected
Stimulates breakdown of bone (osteoclasts) to release calcium
Increases blood calcium levels.
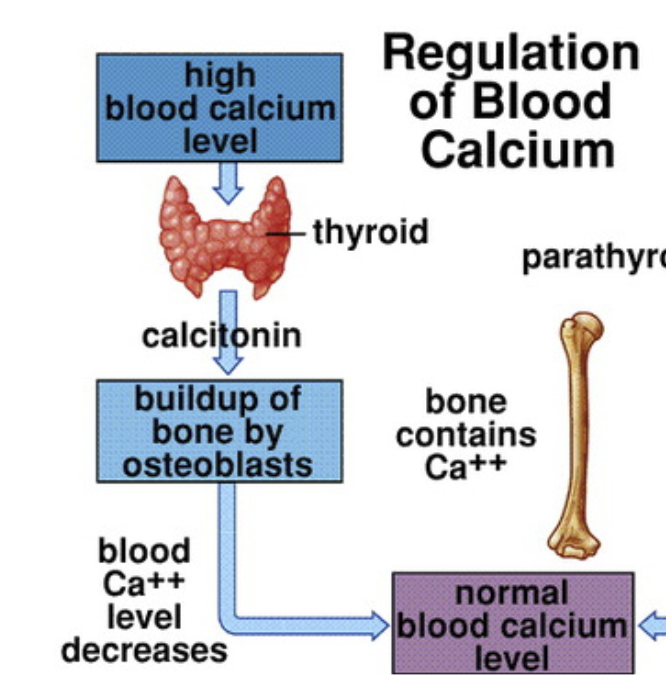
Calcitonin
When high calcium levels are detected
Secreted by the thyroid gland (specifically by C cells).
Inhibits bone breakdown; promotes calcium storage in bone (Osteoblasts)
Decreases blood calcium levels.
Osteoclasts
Break down bone, PTH (stimulates activity)
Osteoblasts
Build new bone, Calcitonin (stimulates activity)
Explain the relationship of PTH and levels of calcium in the blood.
When Blood Calcium is Low,
The parathyroid glands detect the drop.
They release PTH into the bloodstream.
PTH works to increase blood calcium levels by stimulating osteoclasts (bone-breaking cells) to break down bone and releases calcium into the blood.
How does a disruption of the above relationship lead to osteoporosis?
Chronic overproduction of PTH leads to Hyperparathyroidism where too much PTH is released over time (even when calcium levels are normal), bone is constantly broken down by increased osteoclast activity
Excessive loss of bone mass and minerals.
Bones become porous, fragile, and prone to fractures
Calcium levels in the blood stay high
Leading to osteoporosis
Explain the relationship of calcitonin and levels of calcium in the blood.
The thyroid gland detects the elevated calcium.
It releases calcitonin into the blood.
Inhibits osteoclasts (cells that break down bone).
Reduces the release of calcium from bones into the blood.
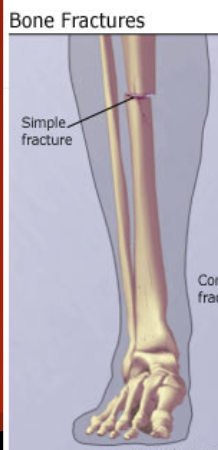
Fractures: Closed/Simple:
Bone breaks cleanly without penetrating the skin.
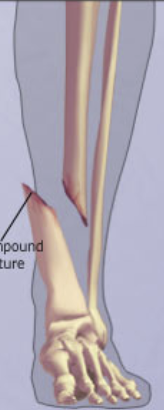
Fractures: Open/Compound
Bone breaks through skin.
Transverse
Fracture occurs at exactly 90o horizontal angle.
Oblique
Fracture occurs sloped up/down at an angle.
Fracture: Comminuted
Bone breaks into many fragments.
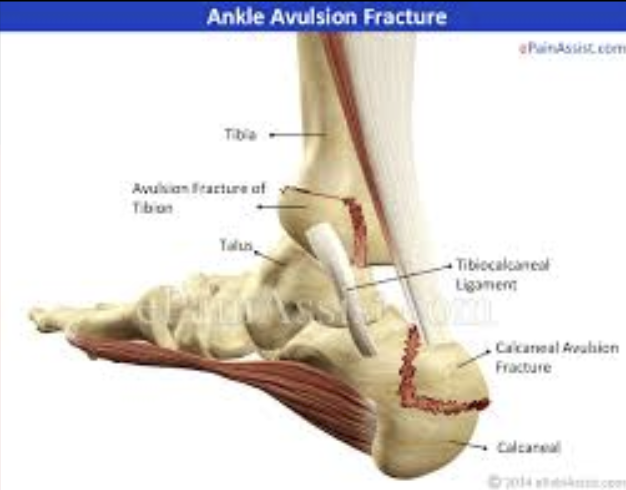
Avulsion
A ligament or tendon pulls away from its attachment on the bone and a fragment of the bone breaks with it.
Compression and Depression
Compression: Bone is crushed
Depression: Bone is pressed inward.
Impacted
Broken bone ends are forced into each other.
Spiral
Ragged break due to excessive twisting.
Fissure/Hairline
An incomplete bone fracture; multiple small lines are often visible, but do not pass through the entire body.
Greenstick
Bone breaks incompletely, like a green twig.
Most common in children with growing bones.
Treatment for Fractures
Reduction: realignment of broken bone ends.
Closed Reduction: physician’s hands put ends back together.
Open Reduction: surgery is performed and bone ends are tied together by pins/wires.
Healing Process for Fractures
Takes 6-8 weeks
Hematoma forms
Fibrocartilage callus forms
Bony callus forms
Bone remodeling occurs
External callus forms here (scar tissue)
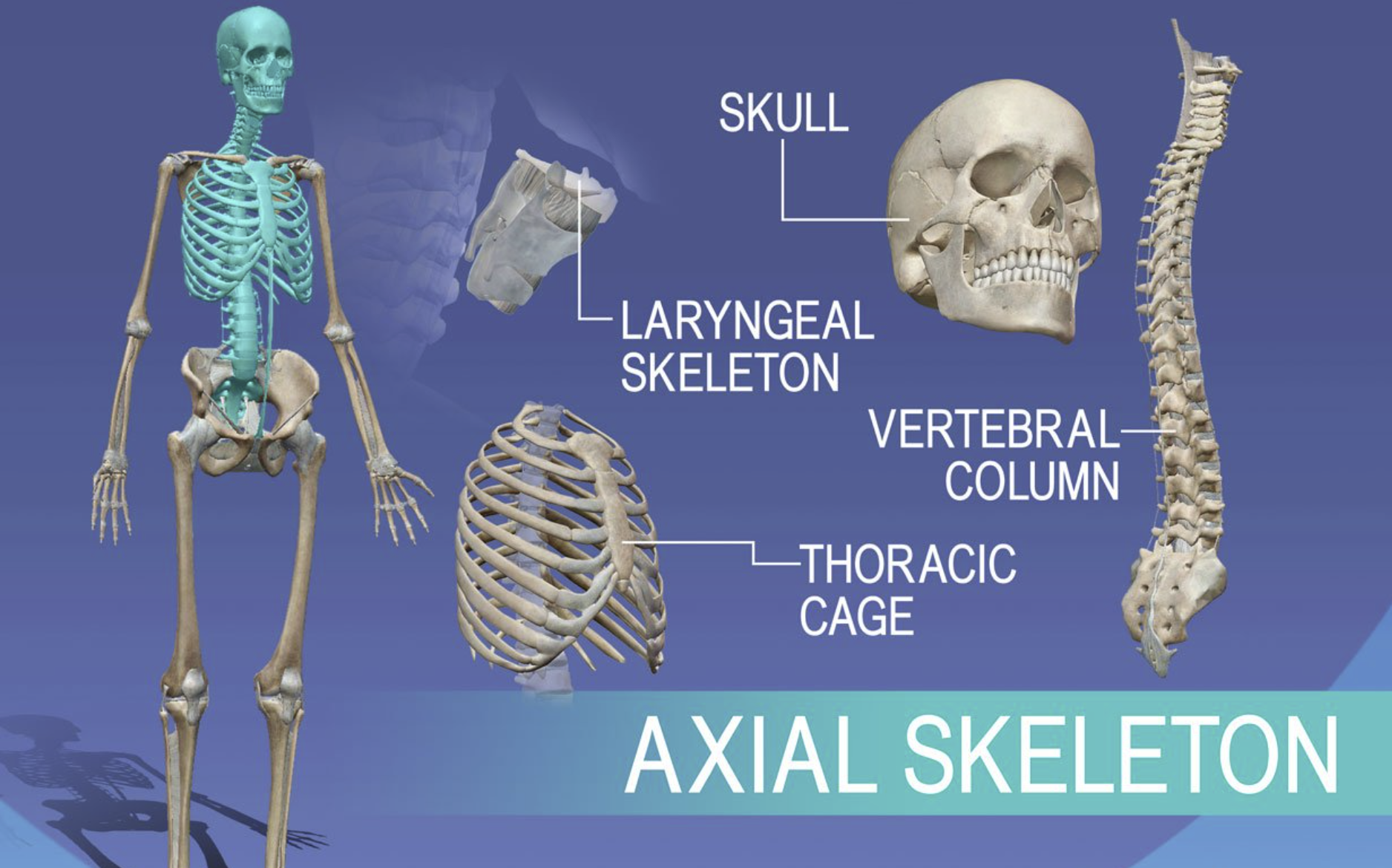
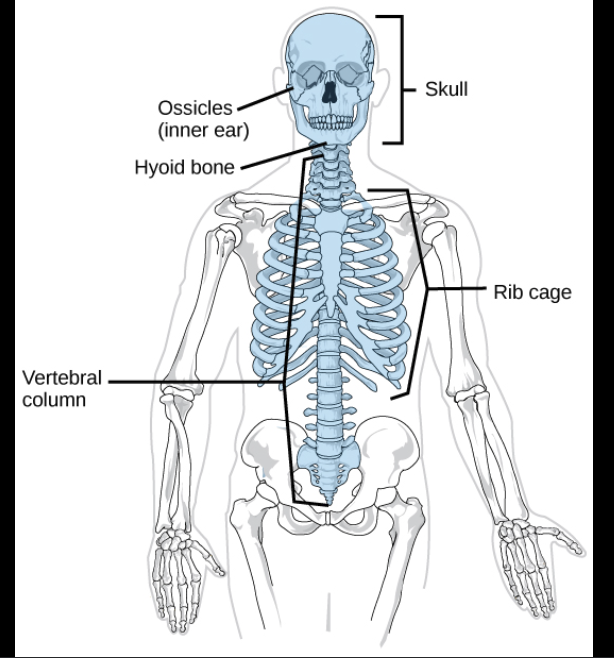
Axial skeletal system
Central core of body, that supports and protects brain and spinal cord
Skull
Spine
Rib Cage
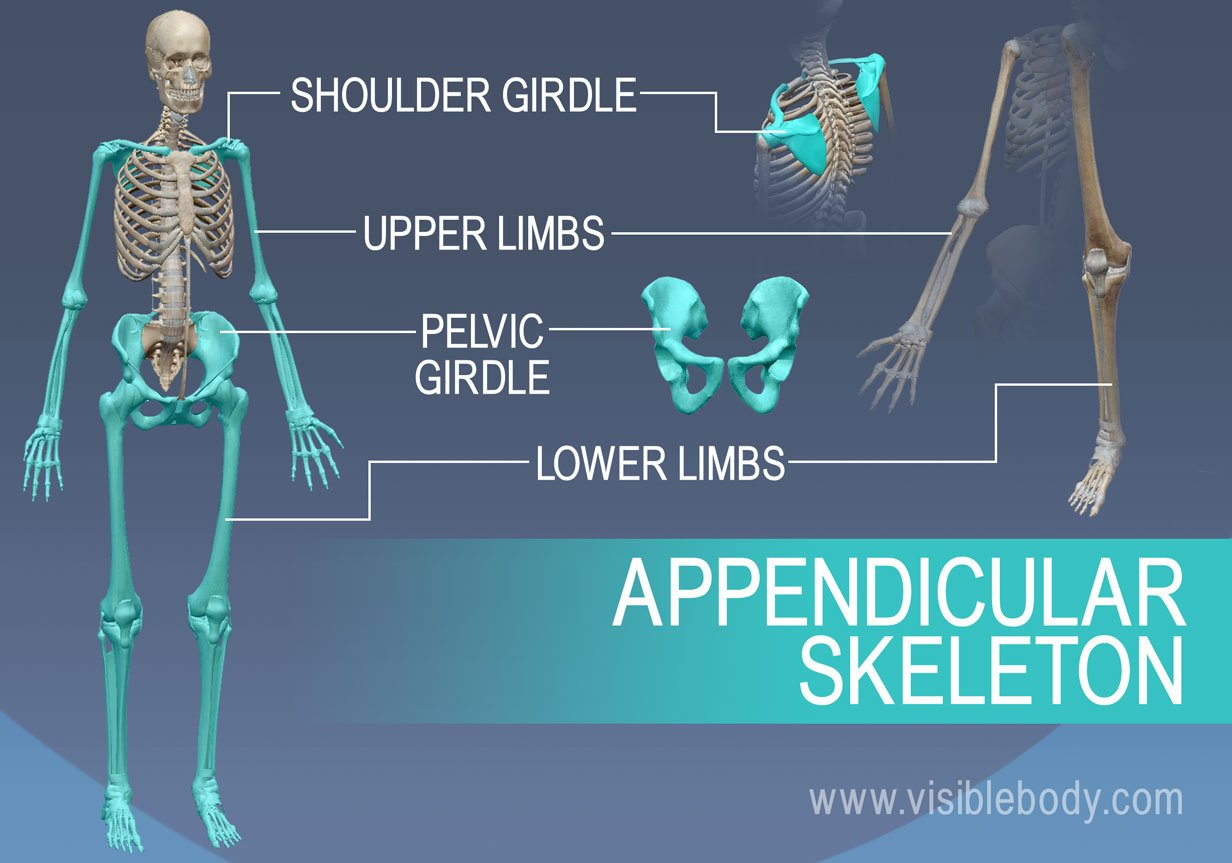
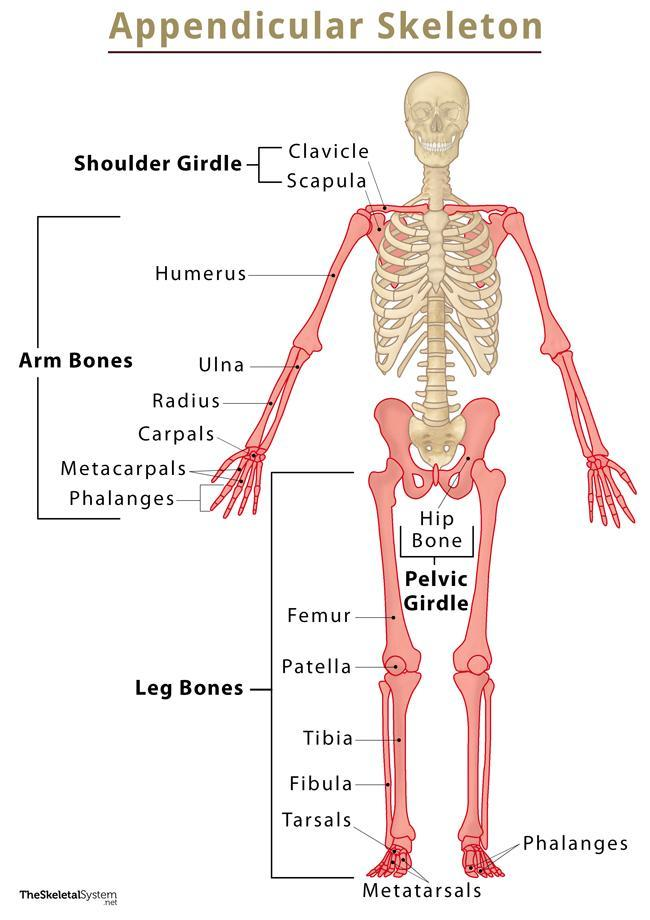
Appendicular skeletal system
Bones of limbs that connect them to the axial skeletal system, responsible for movement.
Upper limbs
Lower limbs
Shoulders
Hip Bones
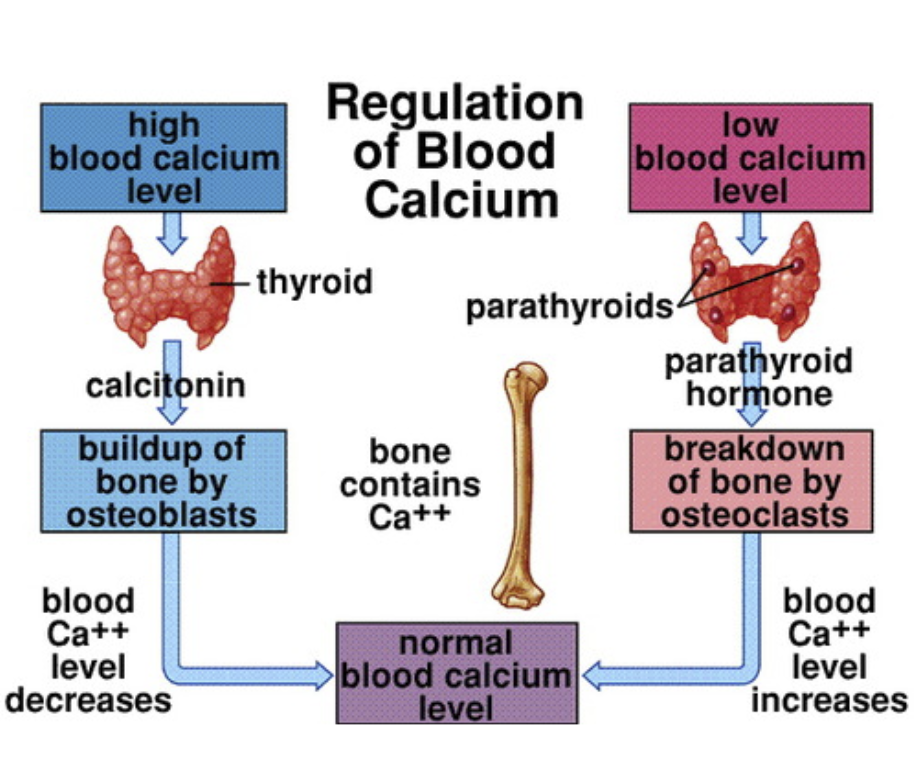
Regulation of low blood calcium
Stimulus: When low blood calcium is detected
Sensor/Integrator: Parathyroids
Effector: Parathyroid hormone is released to encourage breakdown of bone by osteoclasts
Blood level calcium increases to return it back to homeostasis
Regulation of high blood calcium
Stimulus: high blood calcium is detected
Sensor/Integrator: Thyroids
Effector: Calcitonin is released to encourage build up of bone by osteoblasts
Blood level calcium decreases to return it back to homeostasis
Osteoporosis
A condition where bones have decreased bone density because they have become more porous (larger pores) and weak due to lack of bone tissue
Can be controlled by diet, exercise, and smoking