S3.2.5 Naming
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
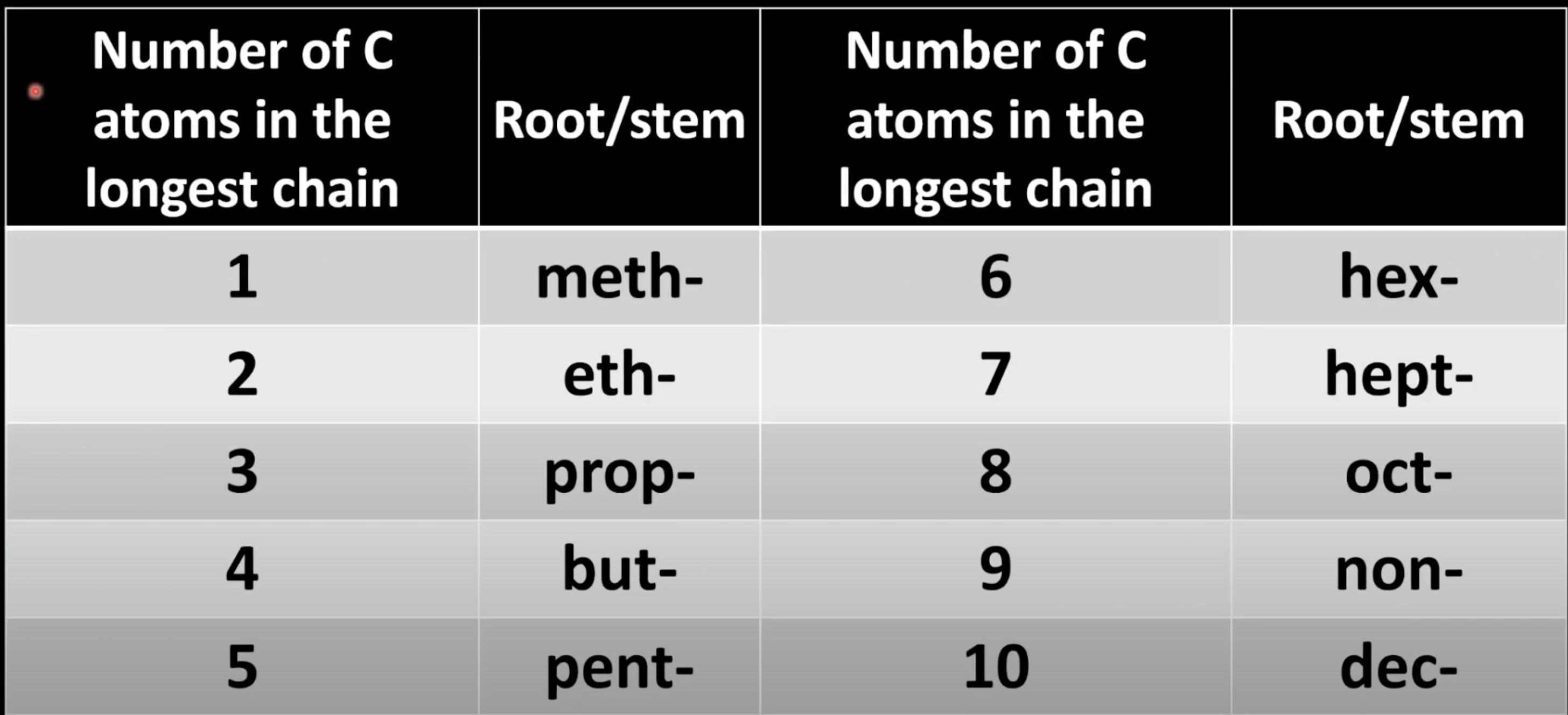
Alkane names use prefixes based on carbon chain length.
Suffix is -ane.
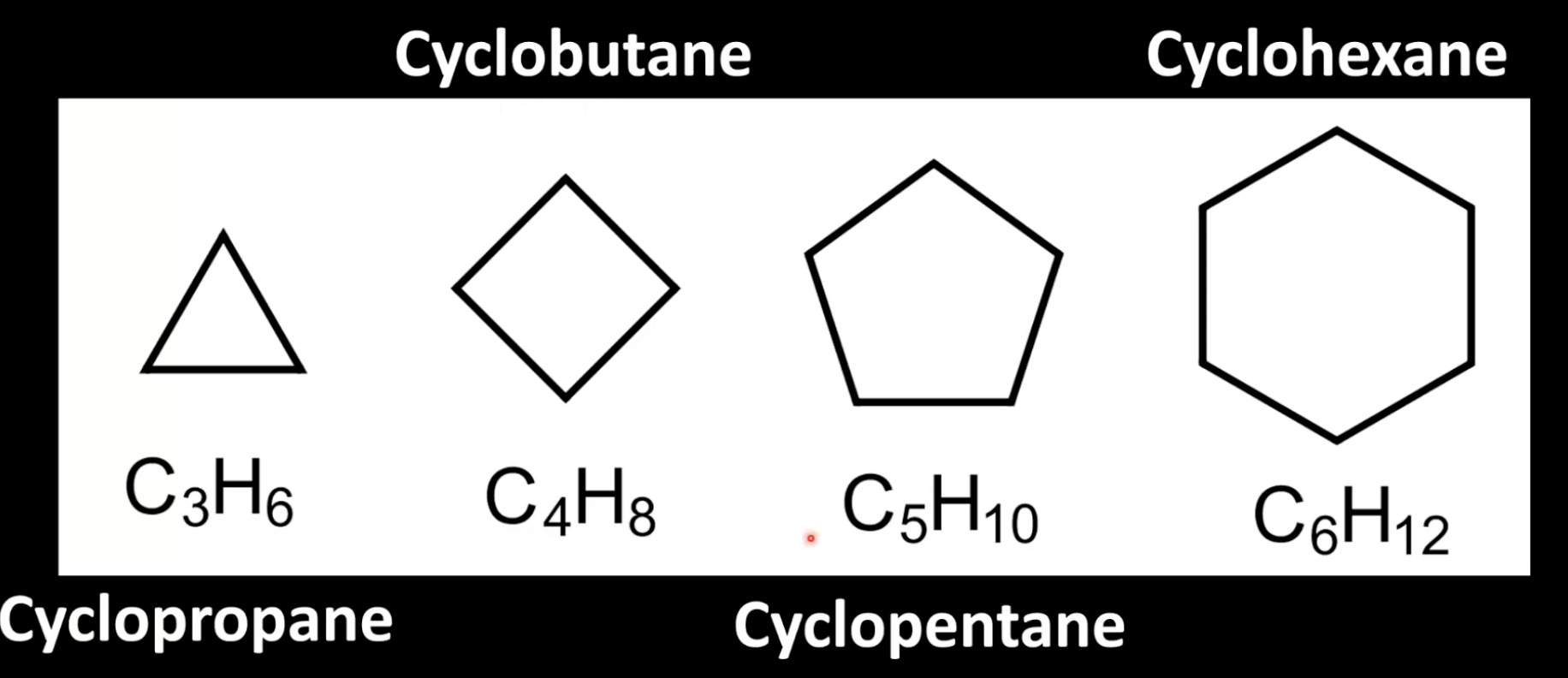
Naming Cyclic Alkanes
Cyclic alkanes have ring structures with formula CnH2n.
Prefix is Cyclo-
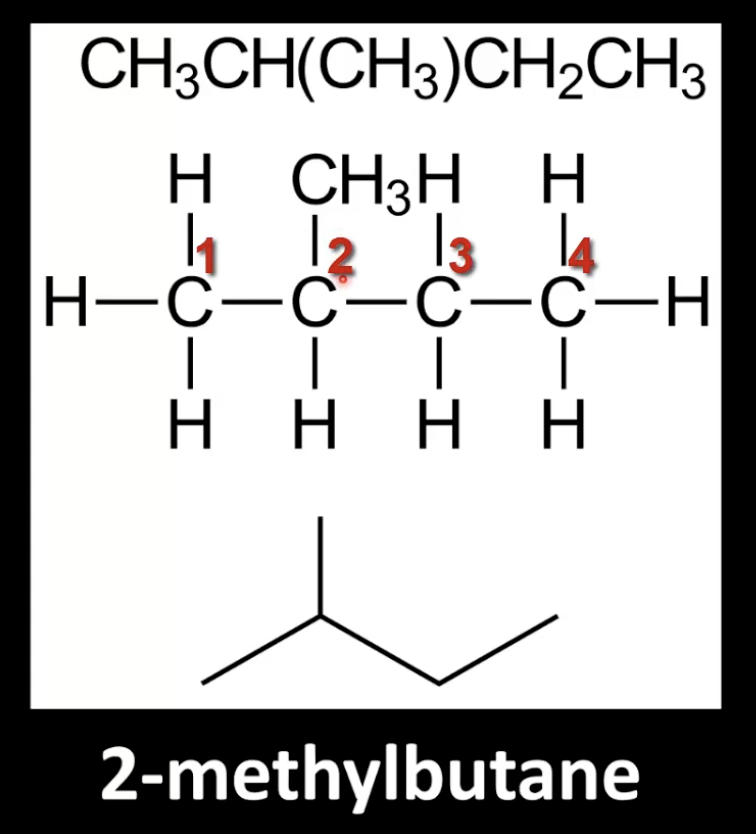
Have branches which are alkyl substituents like –CH₃ or –C₂H₅.
Naming Branched Alkanes
Identify the longest continuous carbon chain.
Number the carbon chain to give the branches the lowest numbers.
If multiple identical alkyl groups exist, use di-, tri-, etc.
C=C bond has high electron density attracting electrophiles.
π bond is weaker than σ bond, allowing electrophilic addition.
Identify the longest chain with the C=C bond and assign the lowest number to the bond.
Add the suffix -ene.
Use numbers to indicate the position of the double bond.
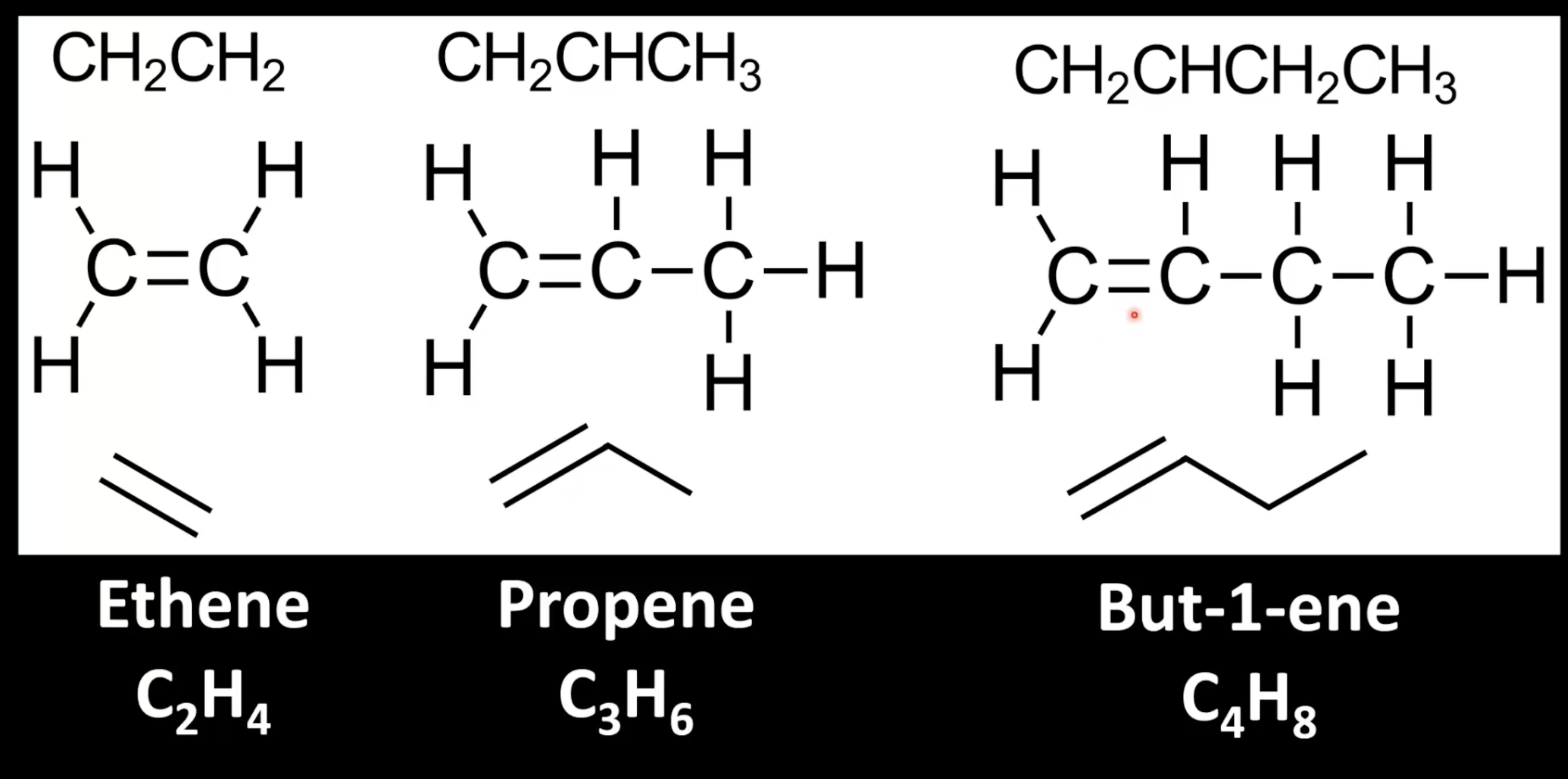
Alkenes with same molecular formula but different C=C positions are isomers.
Position numbering affects naming (e.g., -1-ene vs -2-ene).
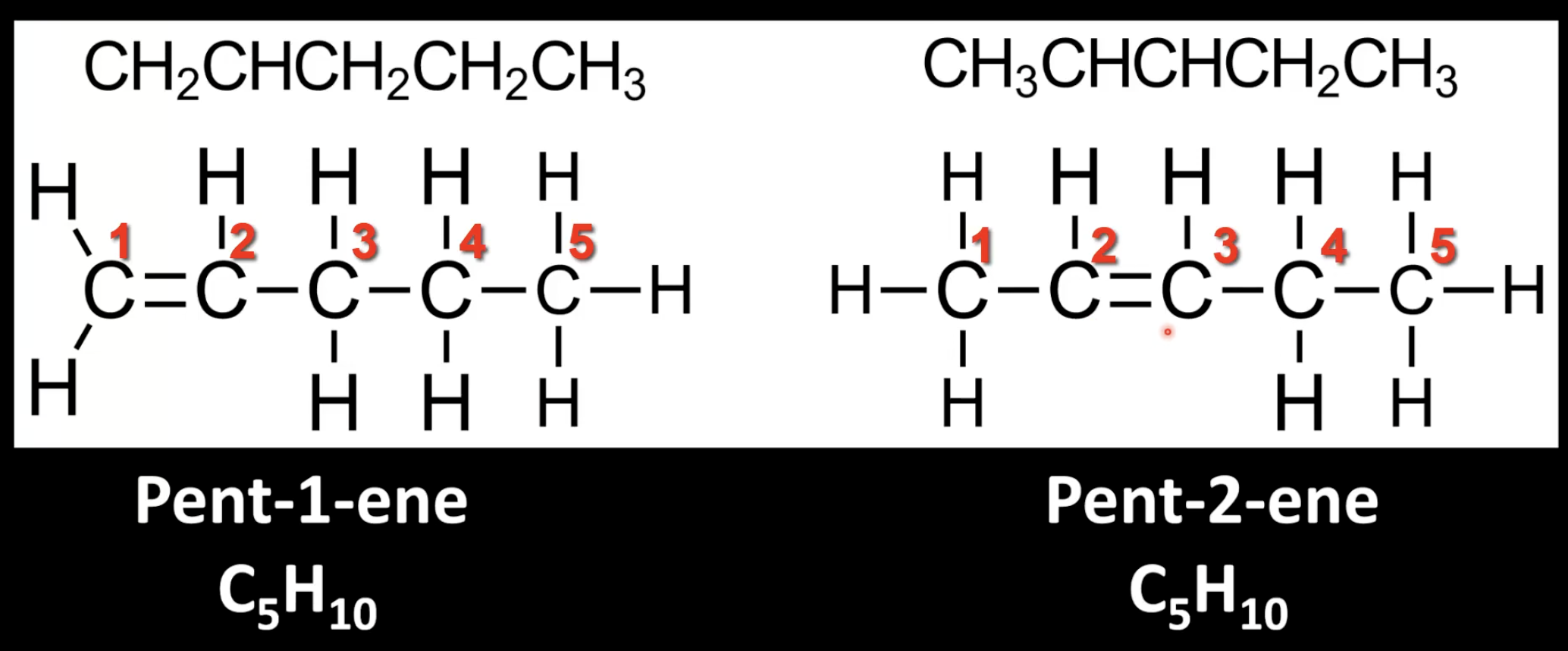
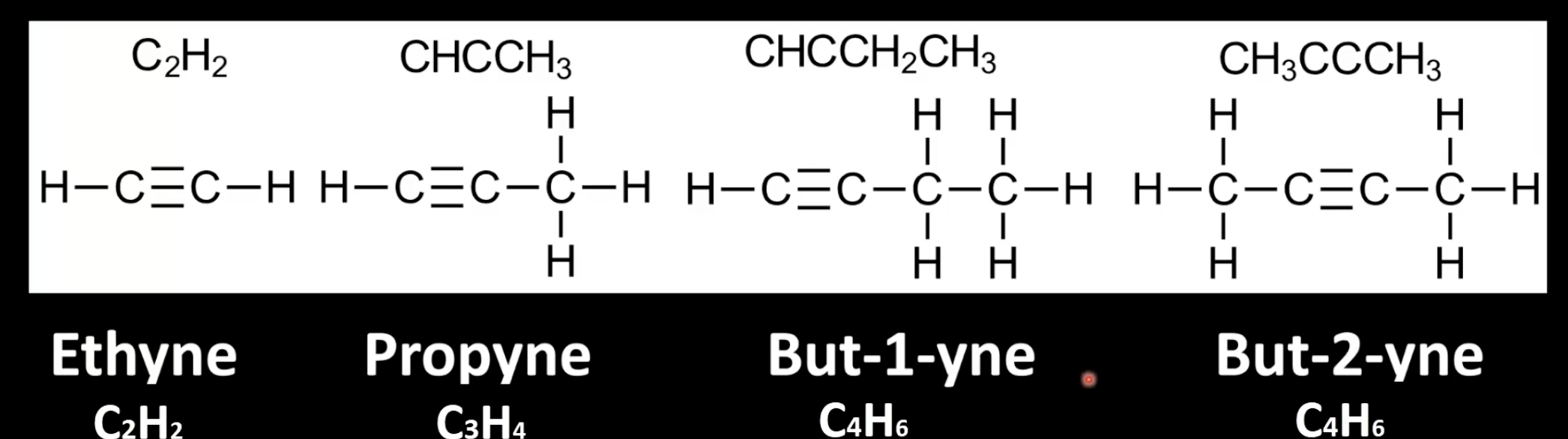
Find the longest carbon chain containing the triple bond and number it for lowest position.
Add the suffix -yne to the root name
Indicate triple bond position with a number.
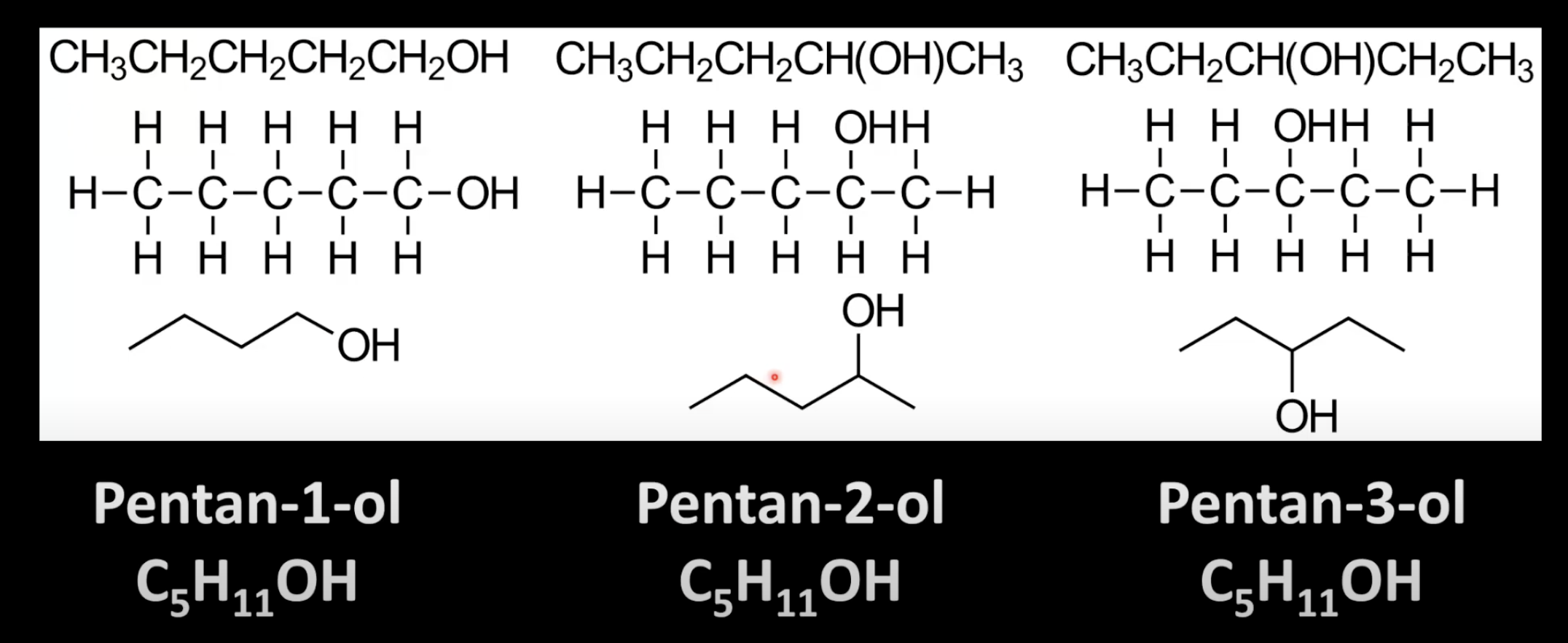
Identify the longest carbon chain with hydroxyl group and assign the lowest number to it.
Change the -e of the parent alkane to -ol.
Use a number to indicate OH position if needed.
Identify the longest carbon chain including the COOH group, which is always carbon-1.
Replace the -e of the parent alkane with -oic acid.
Number branches from the COOH carbon.
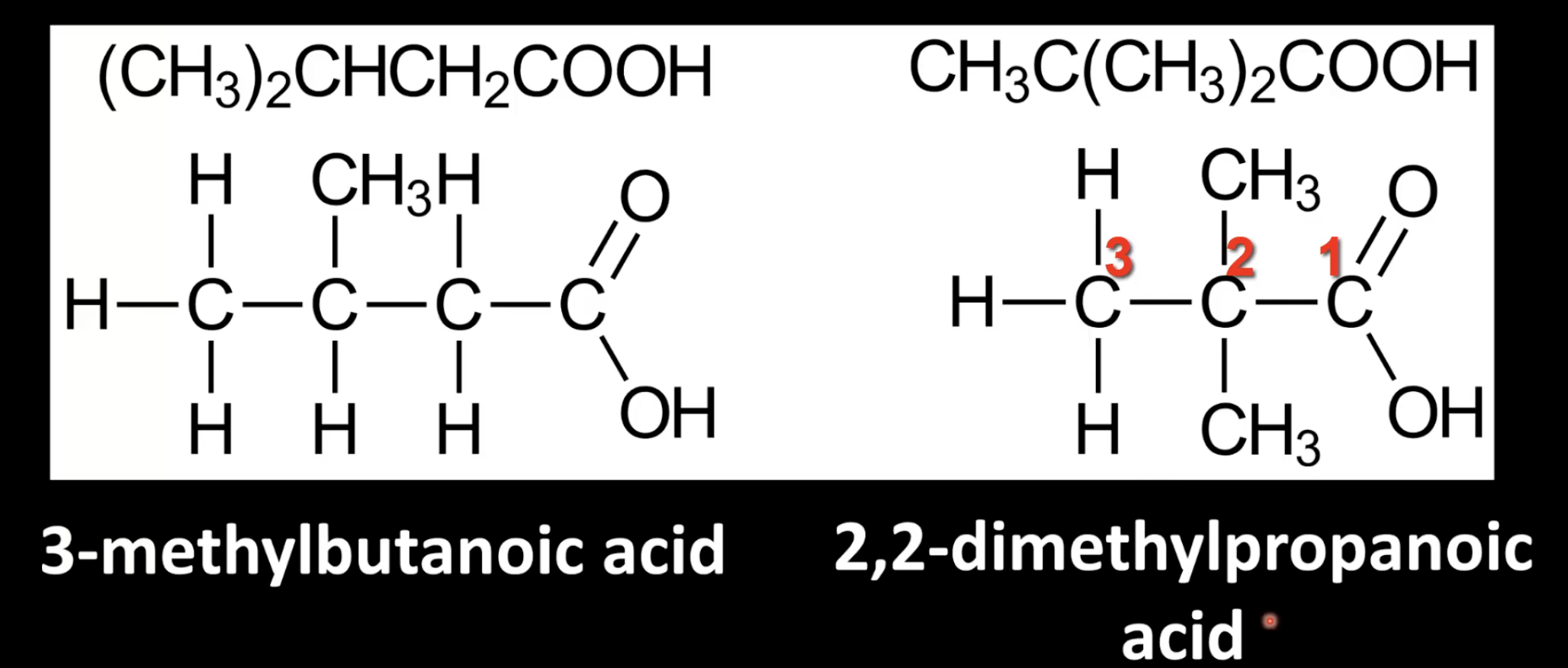
Aldehydes have the -CHO functional group.
Name them by replacing the -e of the parent alkane with -al.
The carbon in the -CHO group is always carbon 1.
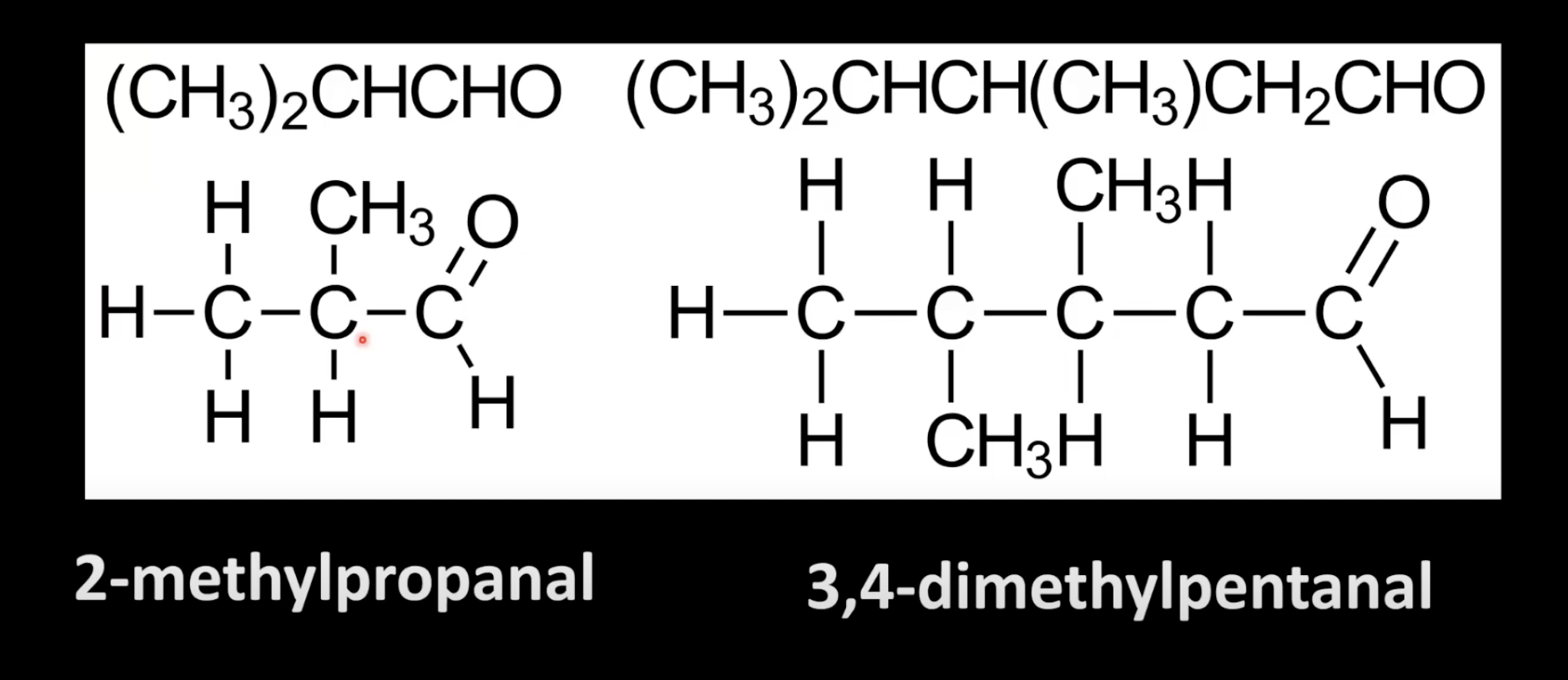
Ketones have the C=O group bonded to two carbon atoms.
Name them by replacing the -e of the parent alkane with -one.
Number the chain to give the C=O the lowest possible number.
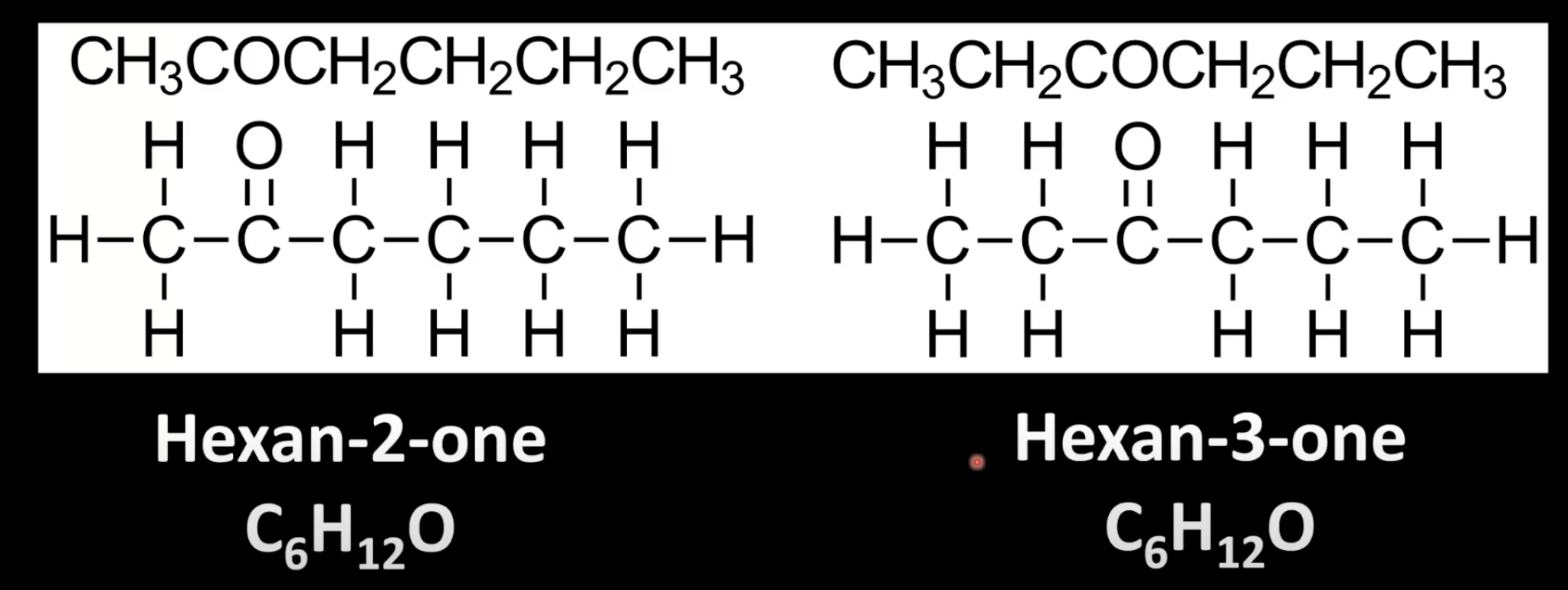
Identify longest carbon chain with -NH2 group
Number it to give lowest possible position to -NH2
Name as 'alkane number-amine' (e.g., propane-1-amine).
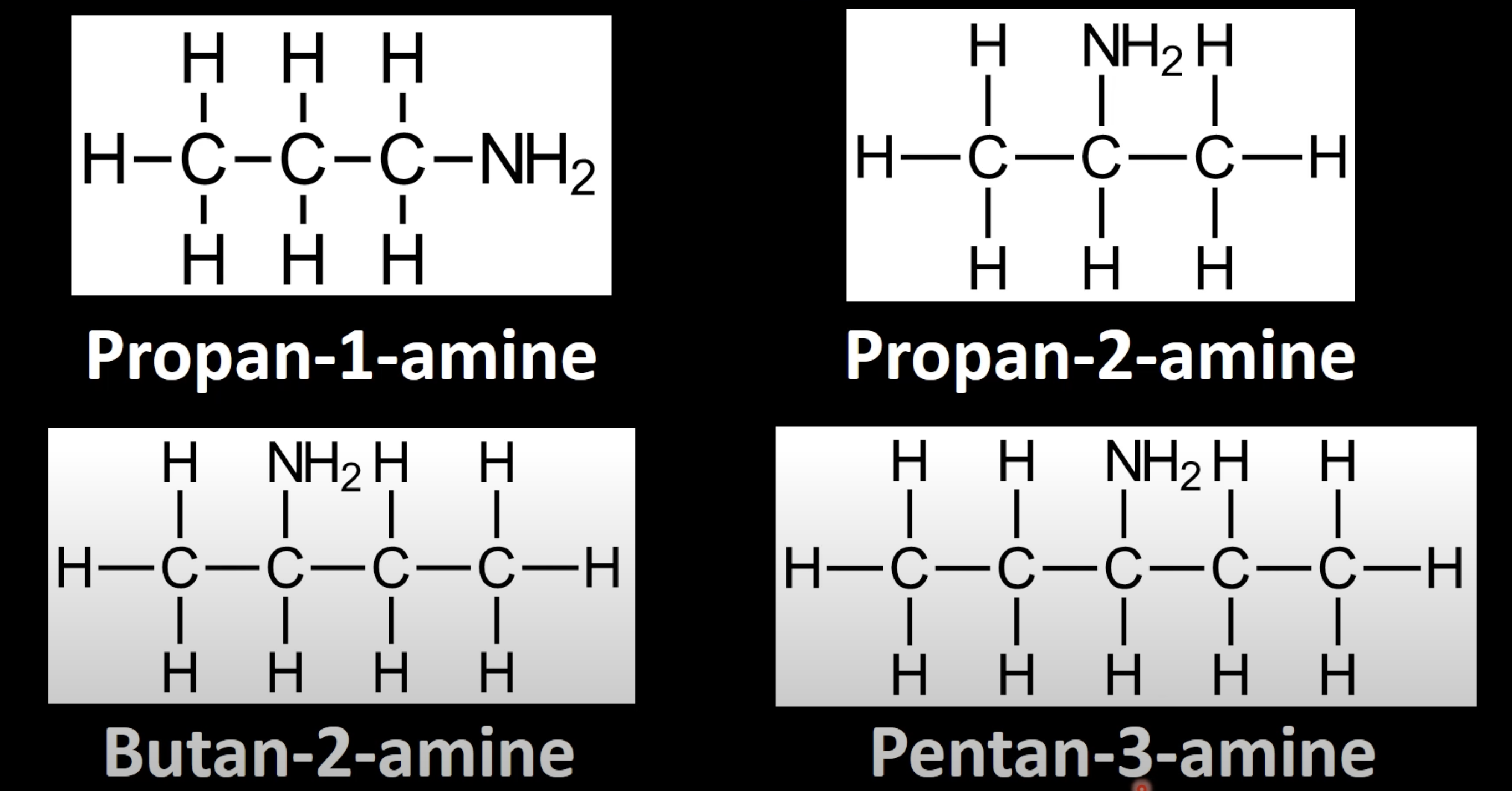
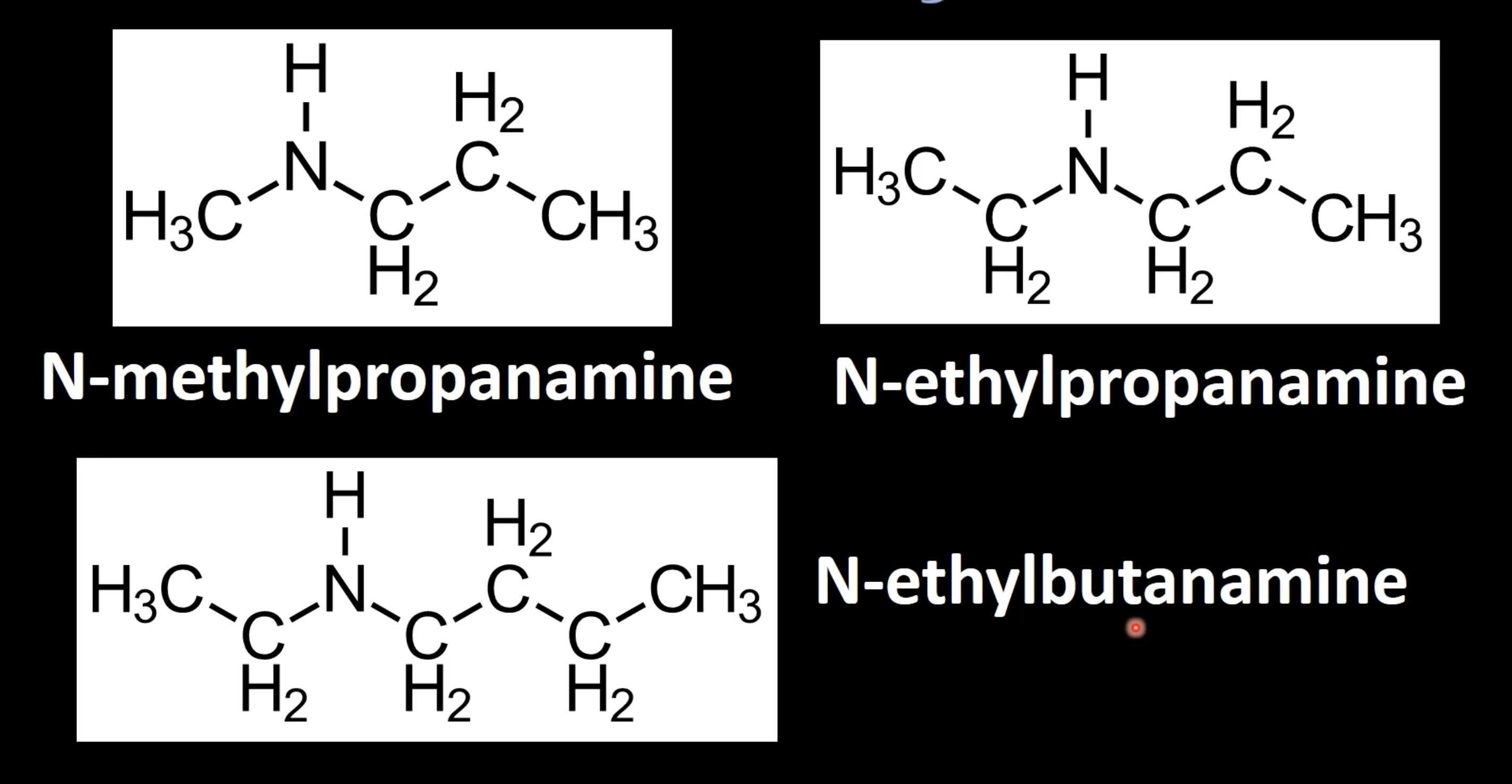
Use uppercase 'N' to indicate alkyl group(s) attached to nitrogen
Name as 'N-alkyl parentamine' (e.g., N-methylpropylamine).
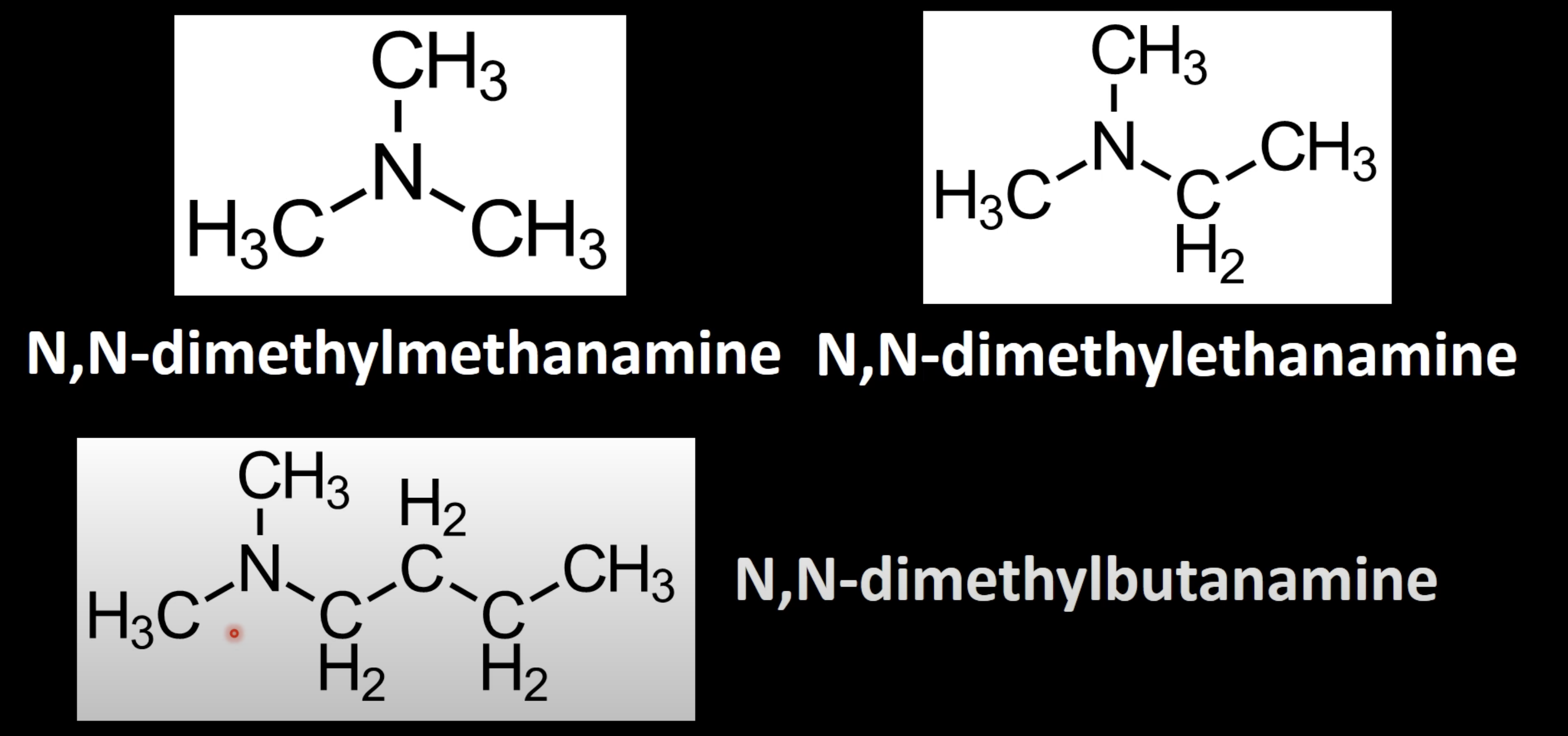
Use uppercase 'N,N' for two alkyl groups on nitrogen
Name as 'N,N-dialkyl parentamine' (e.g., N,N-dimethylbutanamine).
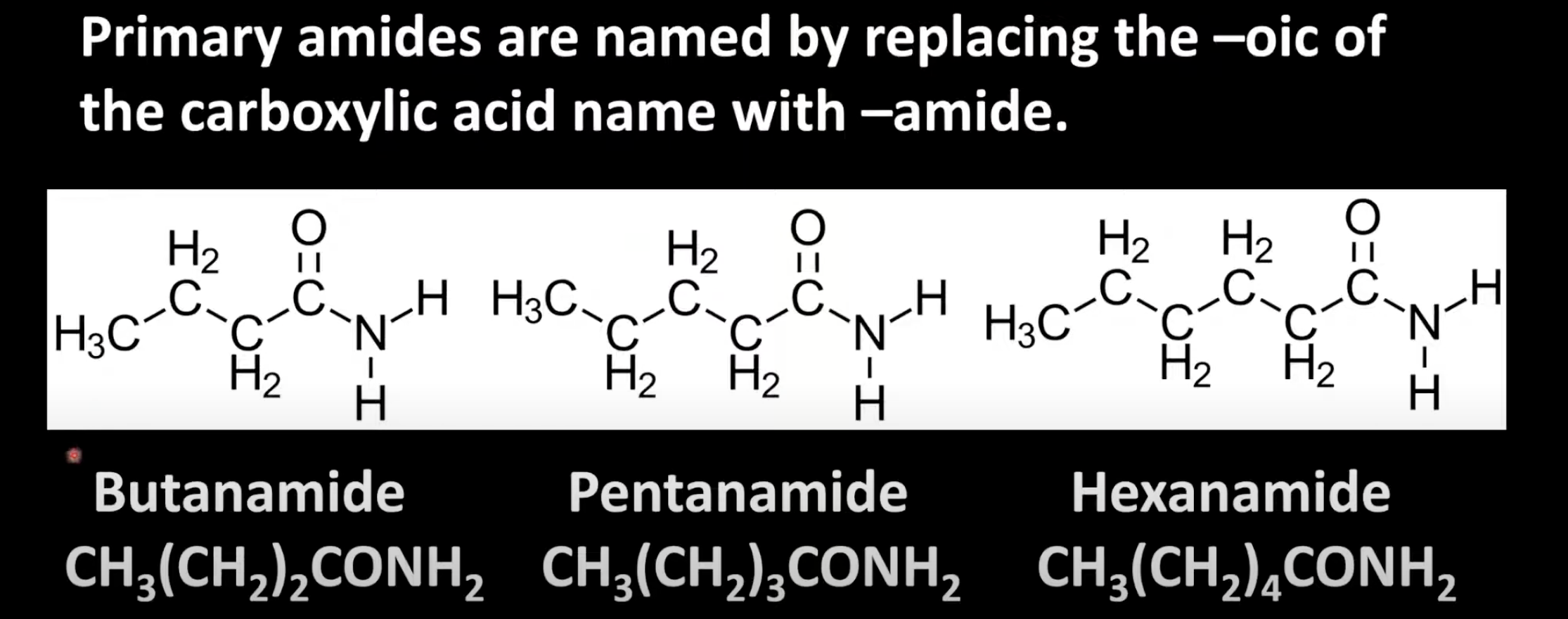
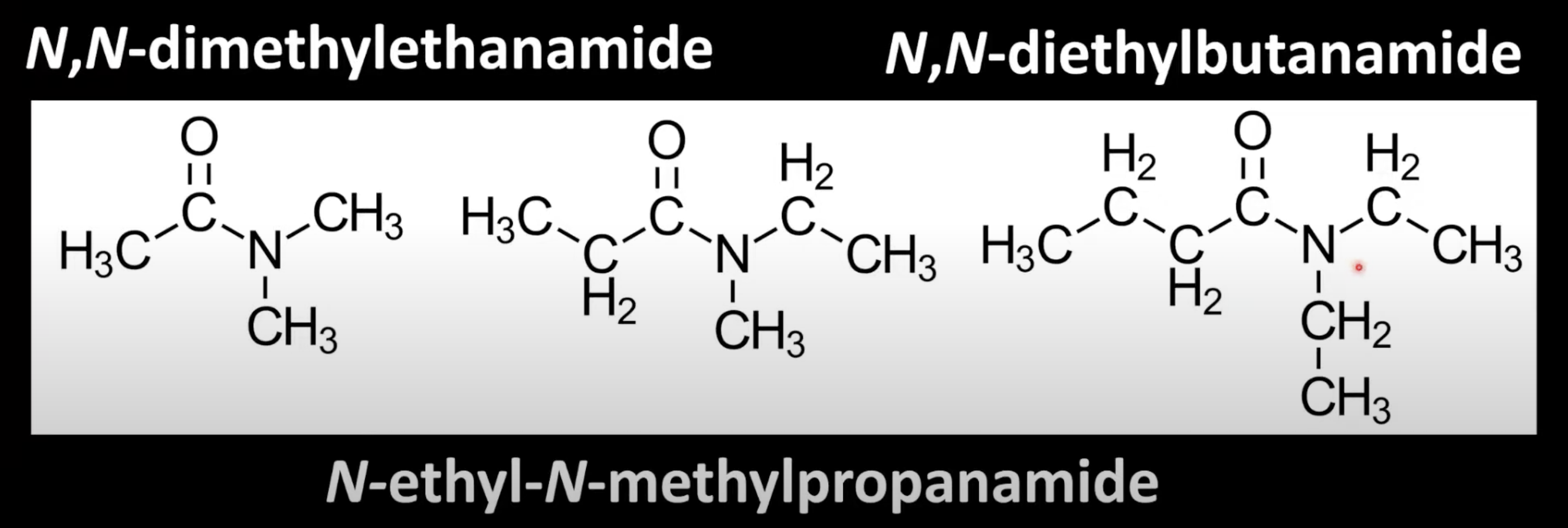
Replace '-oic acid' of carboxylic acid name with '-amide'.
Carbon chain length gives the prefix (e.g. ethane → ethanamide).
No alkyl group on nitrogen.
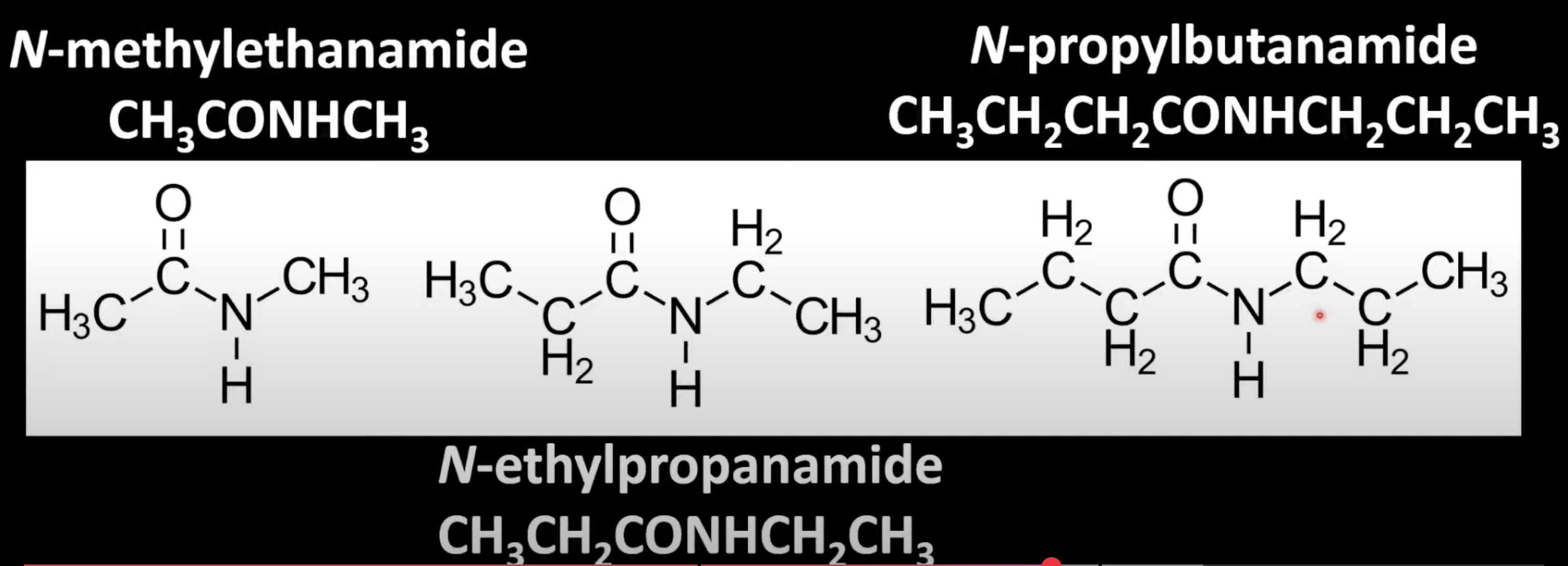
Use 'N-' to denote alkyl groups attached to nitrogen.
Base name is from the amide chain
Prefix the N-alkyl group (e.g. N-methylpropanamide).
Use 'N,N-' to denote two alkyl groups on nitrogen.
Alphabetize substituents and attach them to the amide name (e.g. N-ethyl-N-methylpropanamide).
Naming Ethers
Ethers have 2 alkyl groups bonded to O.
Shorter group (with O) becomes alkoxy substituent.
Longer group becomes alkane stem.

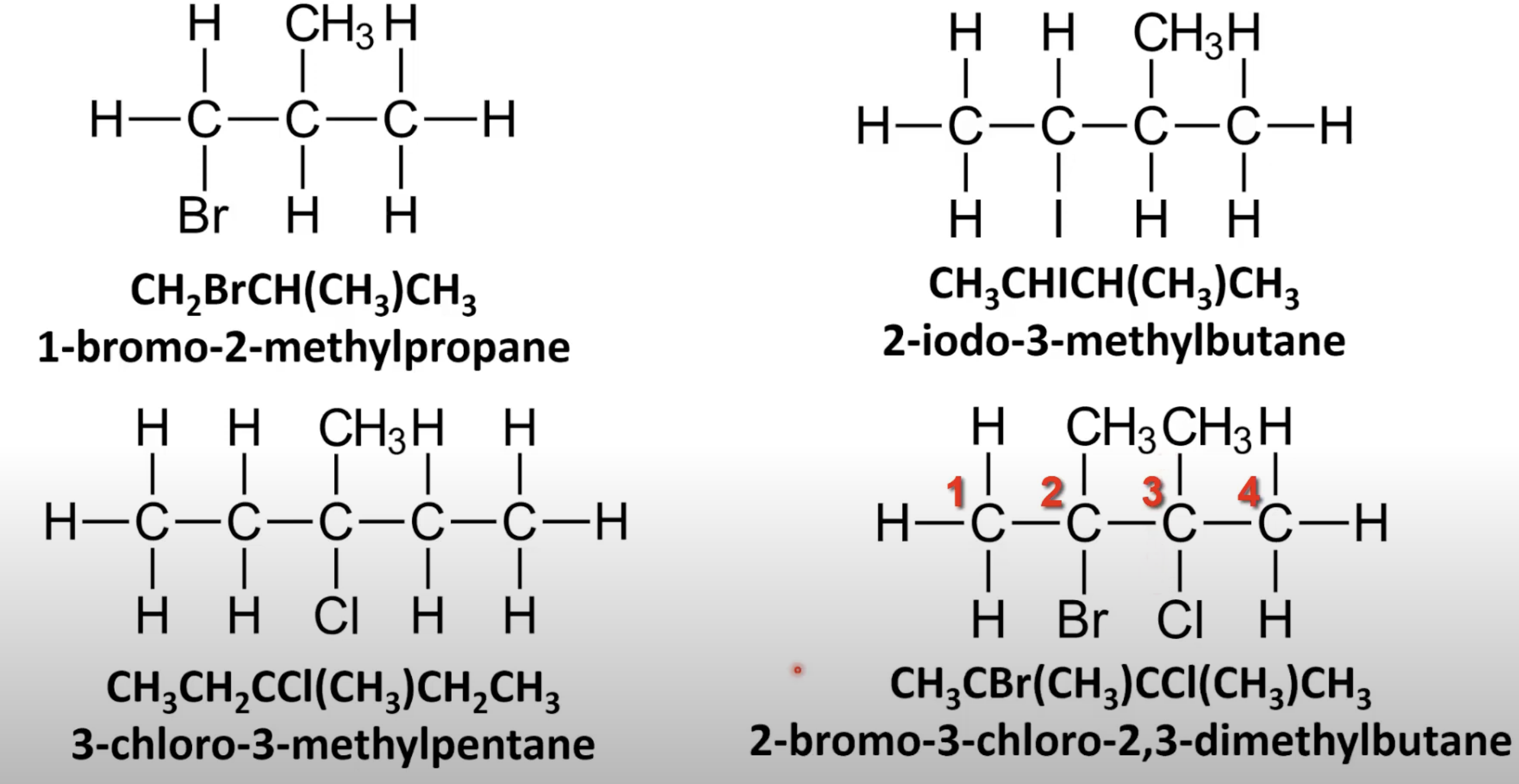
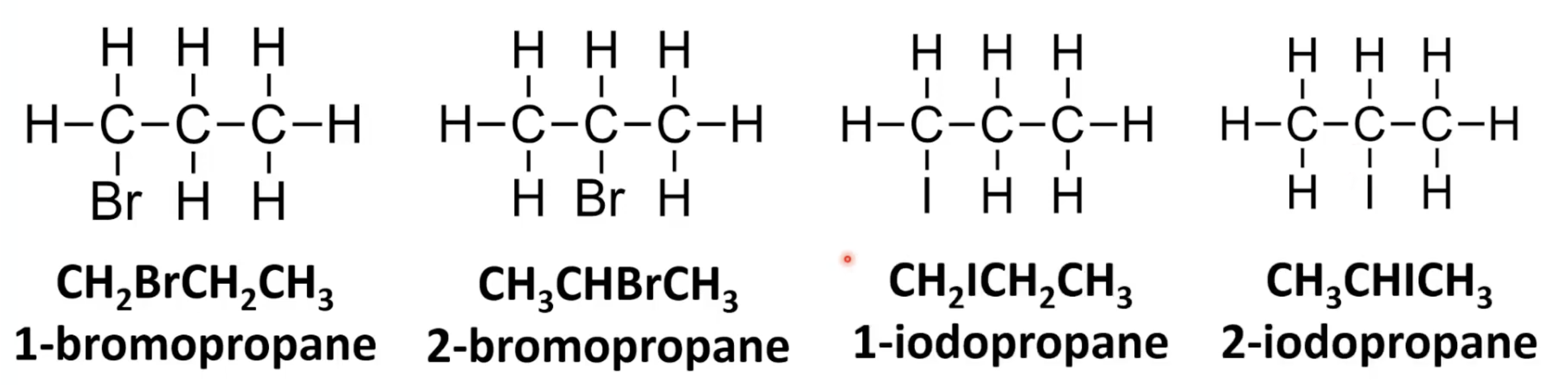
Identify longest carbon chain with halogen.
Use halogen prefix + alkane name.
Number chain to give halogen lowest possible number.
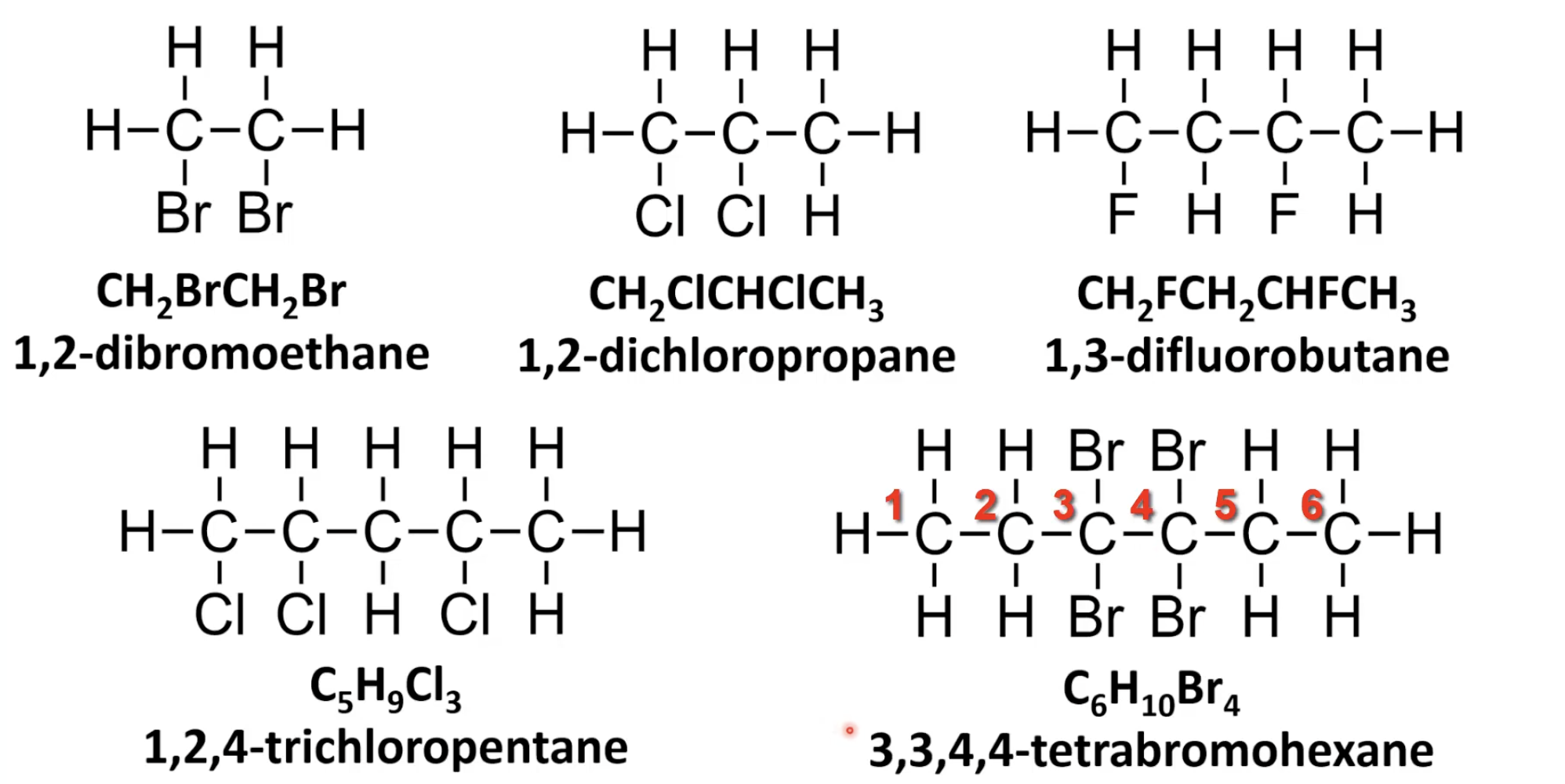
Use prefixes di-, tri-, tetra- with position numbers.
Number chain for lowest set of locants.
List halogens alphabetically with positions.
Number chain for lowest total position numbers.
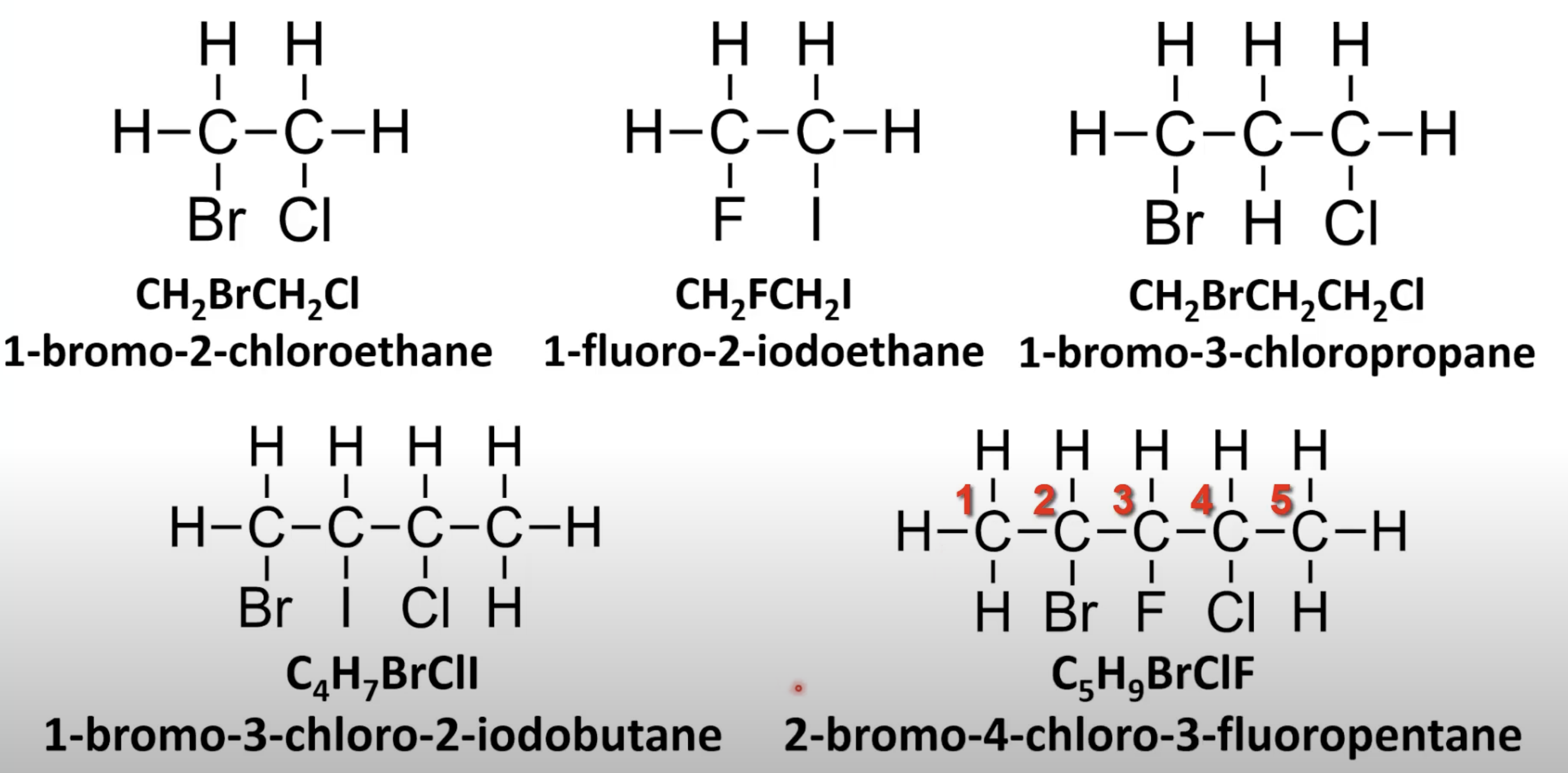
Name alkyl branches and halogens in alphabetical order.
Use position numbers and longest chain as base.
Lowest numbers take priority.