Sustainable Packaging Exam 1
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
US- more of recommendation for recycling, not as heavily regulated
EU- banning, more content regulation
What are the main differences between European and U.S. sustainable plastic policies?
Steady State Economy
•A theory that describes equilibrium of consumption and production, birth rate and death rate, resource utilization and regeneration
•Is only achieved after growth or recession of an economy
•Cannot account for growing populations, i.e. need for population control
circular economy
•Economic theory / practice where production, use, and waste are combined in a single
system of reuse
•Oppose to a linear economy of production, use, dispose
•Accounts for dynamic systems of use and reuse, extraction and regeneration
•Takes into account both technical and biological regeneration
circular economy
open loop recycling
closed loop recycling
zero waste strategies
ecological footprint
•Measures demand and supply of nature
•“This includes all biological and ecological assets that a functioning population would require to produce natural resources for sustenance. ”
•Measured in global hectares, or gha, an average value of the productivity of different land types / regions.
•Measures how much regenerative capacity a process requires from the earth
pollution prevention act 1990
energy star program 1992
two acts of legislation fostered by the EPA that led to greater monitoring of sustainability and eventually the rise of LCA
energy
atmospheric emissions and quality
2 most monitored results of an LCA
socioeconomic impact assessment
what does SEIA stand for?
direct: if taken away, it would have an immediate impact on a community
indirect: those arising from changes in the system but not caused directly by changes
What is the difference between direct and indirect impacts in SEIA data?
primary: assess using surveys and focus groups, qualitative and quantitative data, often costly
secondary: analysis of existing data sources, trends in data over time, not costly
What is the difference between direct and indirect impacts in primary and secondary data?
•Analysis of existing data sources, trends in data over time
•Limitation: May not be same type or scale of data
•Minimal cost / time to procure
What is the difference between direct and indirect impacts in secondary data?
modeling techniques used to understand direct and indirect impacts in SEIA
all kinds of what?
input-output analysis
integrated modeling
computational general equilibrium
input-output analysis
- Prepares tables linking and quantifying transactions, prepares multipliers for each sector
-has trouble with changes that occur
integrated modeling
Combines I/O analysis and econometrics econometrics uses non-linear economic relationships to predict effect of changes to economic structures
computational general equilibrium
-Models the entire economy of nation or region
-Broader range of variables, incorporates changes in prices to goods etc.
-Very data intensive, most used in academic modeling
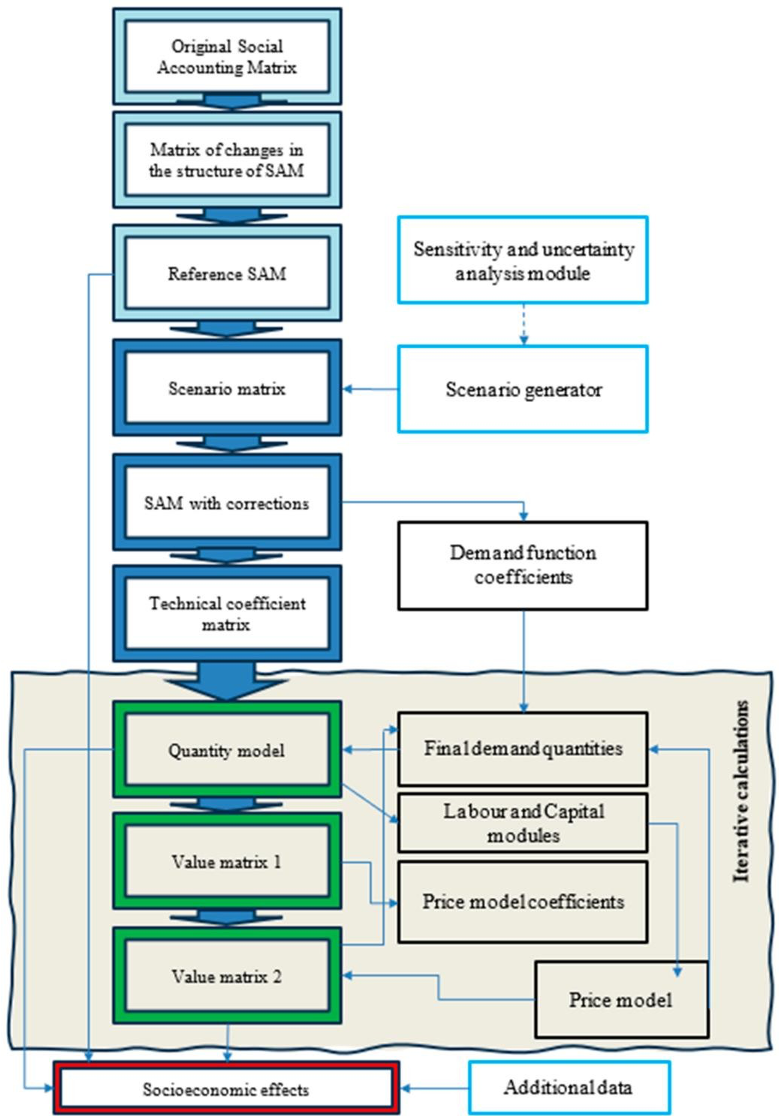
social accounting matrix
looks at all the interactions/relationships you want to study
Contingent Valuation Method
Method of discovering dollar amount people would be willing to pay for goods or services not typically paid for
willingness to pay
how much consumer is willing to pay for goods or services
Surveys used to gauge valuation of goods/services as cost or tax
utility difference model
states there is a threshold to the difference in utility (benefit) b/w two alternatives that a consumer can discern
identify
monetize
compare
main steps in a cost benefit analysis
cost benefit analysis
Used to evaluate price/expense and benefits of project
Used to secure max return on investment
Done before project is carried out
All costs evaluated based on time: direct, indirect, intangible
goal scope and definition
life cycle inventory
impact assessment
interpretation
4 phases of an LCA
functional unit
-As per ISO 14044, FU is “the quantified performance of a product system for use as a reference unit”.
-Quantifies the function of a system in terms of the service offered.
-Not a ratio; must be quantifiable and additive, such that the impact of two FUs is double that of one FU
system boundary
determines which unit processes to be included in the LCA study
Identification of key parameters and potential improvement options using sensitivity analysis and uncertainty analysis: IDENTIFY HOT SPOTS
What is the role of interpretation in LCA?
midpoint categories
weighs and aggregates the emissions into midpoint impact categories (I.e. GHG in CO2eq)
•you’re still at the level of individual impacts
endpoint categories
aggregates impact categories into damage categories (human health, ecosystem quality, resources)
•when you get a result which is one datapoint and is a daily (# of deaths/day your process causes)
•takes elementary input and multiplies by CF to get kgCO2eq (midpoint)
How do you use midpoint and endpoint characterization factors?
What the ISO standard says about allocation
“Where physical relationship (i.e. kg, m3, etc.) cannot be established or used as the basis for allocation, the inputs should be allocated between the products and the functions in a way which reflects other relationships between them. For example, environmental input and output data might be allocated between co-products in proportion to the economic value of the products.”
system expansion
preferred method of allocation?
???
other methods of allocation that can be used
through system expansion to account for the avoided production of other materials/energy that the coproduct provides
How is allocation used when there is a coproduct to the main product?
system expansion
seeks to capture change in environmental impact as a consequence of a certain activity and there by generate information on consequences of actions
attributional LCA
ALCA
defined by its focus on describing the total environmental
impacts of one system
uses average data
consequential LCA
CLCA
defined by its aim to compare between two products or processes, or a change in initial product or formulation
uses marginal data
reference flow
the products needed to fulfill the function of the FU
system
a group of dynamically interacting elements, organized to achieve one or more functions
unit process
Smallest element in LCA analysis, obtained as an expression after identification of processes and elements required to fulfill the function, for which both inputs and outputs are quantified
elementary flows
Flows that link unit processes to the environment
Can be categorized into two types: input and output
input elementary flows
Flows corresponding to the use of natural resources, such as extracted raw material, energy and land us
output elementary flows
Flows exiting a unit process in the form of emissions to water, air or soil
primary energy demand
the sum of all energy used across the lifecycle for the Functional Unit
nonrenewable energy demand
petroleum, coal,gas, uranium, etc.
midpoint
refers to the fact that this point is on the impact pathway between inventory results and damages
normalization
converts complicated units into fractions of building product's scores per impact category
grouping
§A qualitative/semi-quantitative process that helps prioritize results by sorting/ranking
weighting
§Combines multiple scores for different midpoint or damage categories into a single score for each scenario compared….“Single Score Method”
???
How can you interpret midpoint and endpoint impact graphs to understand process contributions?
biorefinery
A concept where biomass is used to produce multiple raw materials, products, and energy to replace the typical petroleum refinery concept
BTX
Benzene, Toluene, and Xylene
the raw material for most chemicals used in the world today.
sustainable forestry
forestry practices that mimic natural patterns of disturbance and regeneration
•Sustainable Harvest Practices – take into consideration long-term regeneration of forests
forest stewardship council
what is FSC?
•Wood extraction: removing bark, cutting into chips, screening oversized chips
•Separated bark is used to produce syngas (a mixture of hydrogen gas and carbon monoxide)
•Wood chips are cooked in a digestor; dissolve lignin and create cellulose pulp
•Pulp is screened off; black liquor is concentrated by evaporation
•Concentrated black liquor is burned to produce energy (steam)
•Green liquor dissolved in water and then forms white liquor
•The cellulose fiber is further screened, heated, and bleached to get a high whiteness level
•Bleached pulp is sent to a pulping machine where screening, dewatering, drying and sheet formation occur.
main processes at a pulping mill (detailed)
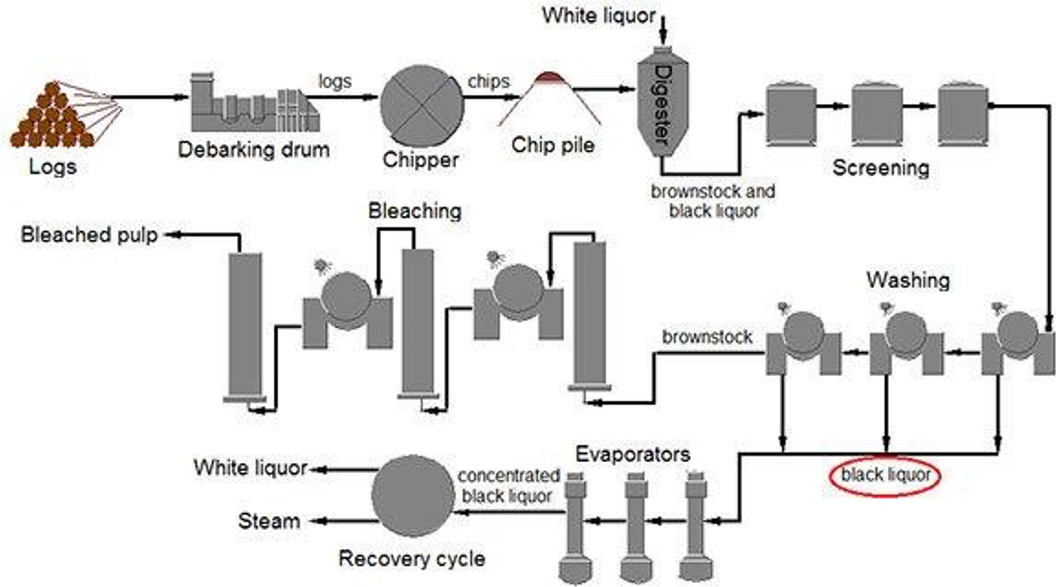
debarking
digester
screening
washing
either evaporating or bleaching
main processes at a pulping mill (simple)
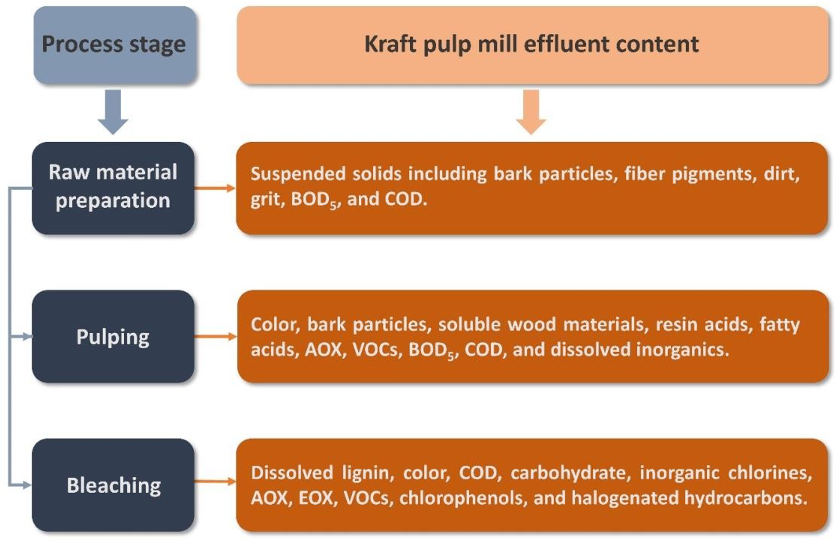
What are the main effluents at a pulping mill?
cellulose (30-50%)
lignin (15-35%)
hemicellulose (25-35%)
main components of wood?
fibers: pulp, biofibrils, and biocomposites
extractives: renewable diesel or biochemicals
lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose: biochemicals
logs: for sawn goods and plywood
bark and branches: for renewable diesel and energy
product streams that come from each component of wood
there is a natural recycling process that a pulping plant relies on:
Lignin supplies energy for recovery boilers and process steam
Sulfur and inorganic materials (green liquor) is not recovered to replenish the cooking medium (white liquor)
interrupting this to harvest lignin/tall oils could disrupt the natural cycle
What is the importance of recycling energy and chemicals at a pulping plant?
sustainable paper has a natural/raw look and feel, and is not as strong as high gloss or coated paper
What are the characteristics of more sustainable paper vs. high gloss / coated paper?
clay coated news backboard
solid bleached sulfate
folding box board
natural kraft, unbleached
duplex paper
different paper types? (5)
clay coated news backboard
Made from recycled newsprint, paper, and corrugated
Low cost folding cartons
High water adsorption
Low cost, used in cereal cartons and other similar materials
Contains clay coating – creating difficulties when recycling
solid bleached sulfate
High quality paperboard
Used in boxes for retail from bleached pulp fibers
Can be coated on both sides
Used in cosmetics, baked items – high end appearance
High bleaching amount, virgin fibers, high cost
folding box board
•Paperboard from multiply pulp
•Smooth surface, high printing ability
•Durable, high stiffness
•Can use recycled paper
•Requires more energy to recycle due to multiple layers
natural kraft, unbleached
•More natural look and feel
•From wood pulp or recycled sources
•Often uses clay coating for water barrier or with Polyethylene for strength
•Not as strong as other paperboard, can be recycled if uncoated
duplex paper
•2 pieces of paper fused together
•Exterior often coated to be glossy / water resistant
•Used to make cartons for higher value products / pharmaceuticals
• High-quality paper often includes highly bleached/glossed paper that reduces recyclability
•Coatings reduce recyclability and increase chemical usage
what makes certain paper types more/less sustainable than others?
high energy requirements and GHG emissions
high oxygen and water vapor permeability than plastic
many of the barriers used inhibit recyclability by typical processes
What are the challenges of paper packaging and barrier properties?
Perfluoroalkyl Substances
what does PFAS stand for?
PFAS
Used in non-stick coatings on cookware, and paper coatings to increase barrier protection to grease
danger of PFAS
Migration into food/water
Exposure to marine life has longer residence times due to contamination of food chain
jackets
upholstery
carpets
papers
building materials
food contact materials
impregnation agents
cleansers
polishes
paints
ski waxes
polar bears
where is PFAS found? (name 3-5)
Crushing/dissolving
Grinding / fiberizing
Filtration / Separation
Cleaning, Screening
Ink and toner released in flotation process, further cleaned to create white pulp
steps in the paper recycling process? (5)
chemicals used in recycled pulp production
hydrogen peroxide
sodium hydroxide
sodium metabisulfite
???
what makes recycled paper more sustainable?
aerobic
is composting aerobic or anaerobic?
mesophilic bacteria break down cellulose into glucose
thermophilic higher degree bacteria and fungi take over
hyperphilic this is where pathogens and seeds are destroyed. Complex carbs are fully broken down, and some proteins decompose.
slowly return to mesophilic.
Curing, compost is allowed to come back to ambient temperature and is sifted / ground to soil sized particles
process for composting (windrow)?
aerobic process that does not produce harmful gases like landfills (anaerobic process) do
why is compost desired for food waste?
static pile with passive aeration
static pile with aeration
windrow
in-vessel
vermicomposting
biosolid composting
different methods of composting (6)
static pile with passive aeration
warm air (from microbial activity) is directed upwards out of the pile, while cool air is sucked in through the sides
static pile with aeration
Air is forced through the compost pile with blowers (often “reverse aeration where air is brought down from the top of the pile to mitigate against moisture loss)
windrow
long piles of compost continually turned to increase aeration. Pile turning used to set different temperature profiles. (6 weeks)
in-vessel
use of enclosed space or drum for composting. Mechanical agitation is often used to increase aeration
vermicomposting
Use of earth-worms to create rich soil amendment material
biosolid composting
wastewater treatment plants collect solids after filtration.
The solids need to be treated to destroy harmful pathogens.
Composting has been found to be an effective tool for turning biosolids into nutrient rich soil amendment.
Industrial vs. home composting
Contamination of compost with microplastics and PFAS
Slower rate of composting of some “certified” biodegradable products.
Lack of access to industrial composting
challenges of composting a package?
biodegradation
disintegration testing
visual inspection
respirometry test
how is compostability measured?
BPI
Compost manufacturing alliance
TUV OK
how is compostability certified?
BPI
Currently only has commercial composting certification
Compost manufacturing alliance
Uses disintegration testing to certify compostability
TUV OK
European certification for home composting
labels used for composting
