Part One: Excretory System
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Does not include all learning objectives (loop of henle stuff not on here)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
osmolarity
total solute concentration of a solution expressed as a milliosmoles of solute per litre
osmoregulation
is based on controlled movements of solutes between the body's internal fluids and external environment. Helps keep ur body fluid from being too diluted r too concentrated
osmosis
occurs when two solutions separated by a permeable membrane differ in osmolarity
units of osmolarity
300 mOSm/L
know what the osmolarity of human blood is
300 mOSm/L
define iso-osmotic, hypo-osmotic, and hyper-osmotic
Iso-osmotic: if two solutions are iso-osmotic, the movement of water is equal in both directions (net movement of water is zero!)
Hyper-osmotic: higher solute concentration, lower free water concentration
Hypo-osmotic: Lower solute concentration, higher free water concentration.
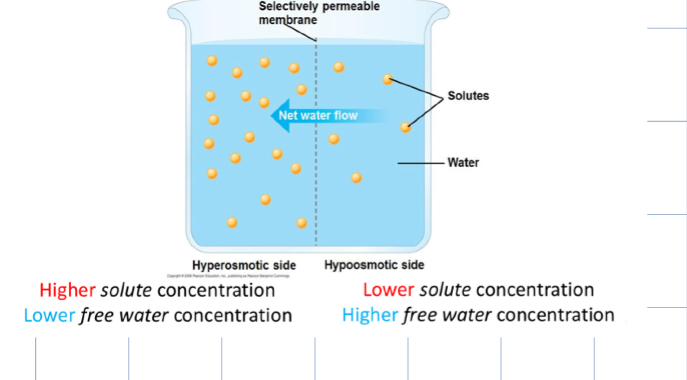
if two solutions differ in osmolarity then?
NET flow of water is from the hypoosmotic solution to the hyper osmotic solution
know the parts of the human kidney , as well as other structure attached to this organ
Renal Cortex + Renal Medulla: kidney is divided into these two regions.
Renal Calyx: minor calyx collects urine from one renal medulla while each major calyx collects urine from minor calyces.
Renal Pelvis: collects urine from all the major calyces
Renal artery: supplies kidney blood
Renal vein: drains blood
Ureter: where urine is expelled
List other organs (besides kidney) that are involved in excretion
Skin: water + electrolytes lost thru sweat glands
Lungs: removes co2
Large Intestine: removes solid waste and some water in form of feces
Liver: breaks down toxic substances in blood
. Know the flow of urine starting from collecting ducts all the way to the urethra.
Collecting Ducts
Minor Calyces
Major Calyces
Renal Pelvis
Ureter
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
filtration
involves transfer of soluble components like water and waste from blood (glomerulus) across bowman's capsule and into nephron.
reabsorption
involves absorption of molecules ion and water that are necessary for the body to main homeostasis from inside the nephron back into blood.
secretion
involves transfer of molecules (like hydrogen ions, drugs, urea) from blood into nephrons.
Bowman’s capsule
surrounds and receives filtrate from the glomerular capillaries
nephron
functional unit of kidney: about 1 million of these in each adult kidney!
-Consists of a long single tubules and a ball of capillaries called the glomerulus
Explain how the structure of the glomerulus allows for efficient filtration
Glomerulus has capillaries which have fenestrated endothelium (pores), + podocytes (membranes can fold into slits and ridges) which are permeable to small molecules which can then be filtered out.
It’s a tangled ball of capillaries (instead of one straight vessel)
→ This creates a large surface area
→ More space = more filtering can happen at once
Identify parts of the human nephron
Explain difference between afferent and efferent arteriole
Afferent Arteriole: supplies nephron with blood (a branch of the renal artery that divides into the capillaries of the glomerulus)
Efferent Arteriole: Blood leaves the glomerulus (subdivides forms peritubular capillaries)
peritubular capillaries
Peritubular capillaries surround the proximal and distal convoluted tubules
vasa recta
capillaries that extend downward which serve the loop of henle.
Understand when humans release antidiuretic hormone (ADH) + what the target site of this hormone is in the nephron, and the end result following binding of this hormone at the target site
when blood osmolarity rises above 300 more adh is released
adh is produced in the brain, and released into blood circulation b4 arriving at collecting ducts of the kidney
ADH: increases water RA in collecting ducts of kidney
-retains water and helps body keep hydrated