Topic A : Fundamentals of Forces
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
2.1what is a scalar quantitiy
it has magnitude (size) but no specific direction
2.2what is a vector quantity
has both magnitude and specific direction
2.3what is the difference between vector and scalar quantities
vector has both magnitude and direction whereas scalar only has magnitude
Describe, with examples, how objects can interact:
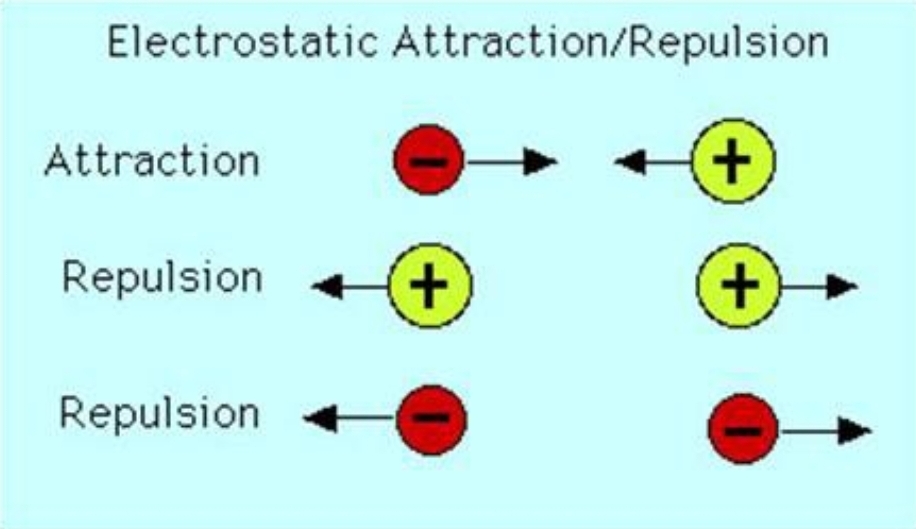
a) at a distance without contact, linking these to the gravitational, electrostatic and magnetic fields involved
-a force is something that affects the motion or shape of an object
-some forces can act at a distance, without any contact between bodies, due to the action of a field
Describe, with examples, how objects can interact:
b. by contact, including normal contact force and friction
forces can also act when objects touch:
-friction, a force that opposes motion, occurs when objects rub against each other
-air resistance occurs when an object moves through air
-contact forces push touching objects apart, and are responsible for supporting objects when they're lying stationary on the ground
Describe, with examples, how objects can interact:
c. producing pairs of forces which can be represented as vectors
newton's third law of motion sates that:
-when one object exerts a force on another object, that second object will exert an equal force on the first object in the opposite direction
Explain examples of the forces acting on an isolated solid object or a system where several forces lead to a resultant force on an object and the special case of balanced forces when the resultant force is zero
-if the forces acting in opposite directions are equal in size, then there will be no resultant force: the forces are BALANCED
What is newtons first law
An object will remain at rest or move at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant external force
2.14 Recall Newton’s first law and use it in the following situations:
a. where the resultant force on a body is
zero, i.e. the body is moving at a
constant velocity or is at rest
if the resultant of all the forces on an object is zero, we say that the forces are balanced. balanced forces will not change the velocity of an object
2.14 Recall Newton’s first law and use it in
the following situations:b. where the resultant force is not zero, i.e.
the speed and/or direction of the body
change(s)
if there is a non-zero resultant force on an object, the forces are unbalanced. unbalanced forces will change the speed/direction of an object
What does an object mocing in a circular orbit at A CONSTANT SPEED have ?
a changing velocity
What is needed for a motion in a circle
a resultant force known as a centripetal force that acts towards the centre of the circle
define weight and recall and use the equation
W = m x g
Weight is the force on a mass due to gravity pulling the object down
what is weight measured in
Newtons
2.18 Describe the relationship between the weight of a body and the gravitational field strength
The weight of a body is directly proportional to the gravitational field strength acting on it
15.1 Explain, using springs and other elastic
objects, that stretching, bending or
compressing an object requires more than one
force
stretching, bending or compressing an object requires more than one force if you just pushed a spring, then it would move in a certain direction. But if you pushed both ends of the spring, the spring would compress
15.2 Describe the difference between elastic and inelastic distortion (elastic distortion)
Elastic distortion is a temporary change and allows the object to return to its original shape when the forces are removed.
15.2 Describe the difference between elastic and inelastic distortion (inelastic distortion)
inelastic distortion causes permanent change to the objects shape when the forces are removed.it is irreversible
15.3 Recall and use the equation for linear elastic distortion including calculating the spring constant:
force exerted on a spring (newtons,N)= spring constant(newton per metre,N/m)× extension(metres,m)
F = k X x
15.4 Use the equation to calculate the work
done in stretching a spring:
𝐸 = 1/2 × 𝑘 × 𝑥 ²
energy transferred in stretching (joules,J)= 0.5 × spring constant (newton per metre,N/m)× extension(metre,m)2
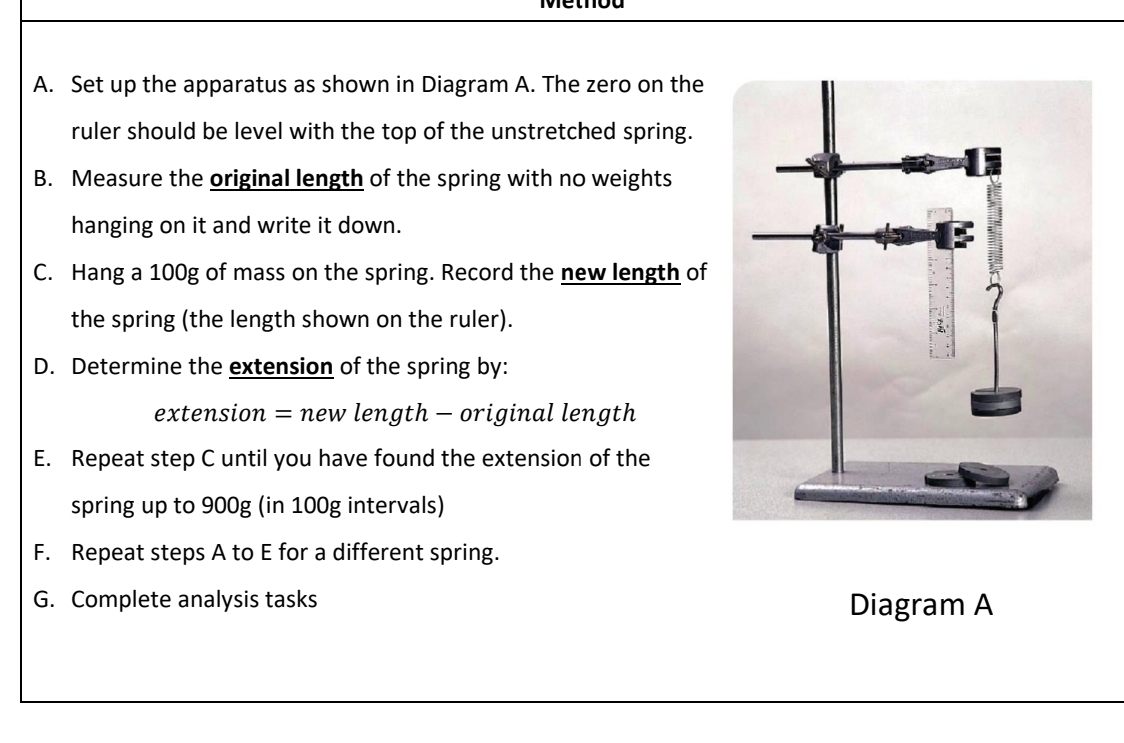
15.6 Core Practical: Investigate the extension
and work done when applying forces to a
spring