Yoga
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
posture
body built with a curve in the spine to provide support and balance to the muscle skeletal system; critical for protecting the central nervous system
ligaments
connects bone to bone; poorly vascularized; made of collagen; works with joint capsules; transfer force
tendons
connects bone to muscle; nutrient fluid diffusion & some blood vessels; made of white waves of collagen; limited extensibility, around 6%
fascia
covers muscles and joint capsules & tissues; more of this than just muscles; intertwined with the muscle
muscles
red; have very good blood supply
What happens when you lean the head forward?
an increase of 10 pounds in the spine
anterior pelvis tilt
glutes back; back muscles dominating; more compression in soft tissue, back pain, and alter discs
posterior pelvis tilt
glutes forward; abdominal dominant; loss of natural low spine cuvature
neutral spine
balance in abdominal and back muscles; help offset muscle imbalance
imbalance of the posture (poor curvatures)
unproper way to set your neck and pelvis
inflammation and pain occurs
tension varies
interferes with nerve impulses
physical symptoms of poor curvatures
digestive issues
weakened immune system
heart issues
dizziness
trouble sleeping
headaches
loss of balance
carpal tunnel
sciatica
changes in sleep hormones
bodily stress examples
slouching
airplane chairs
toilet seating
birth trauma
looking at a cell phone
poor nutrition
Why does posture matter?
all of the body is connected (1 unit); helps your organs work efficiently and supports healthy brain chemistry by improving breathing, circulation, and neurotransmitter balance
pelvis
sacrum & ilium (main bones); weight bearing; little mobility; supports organ functions such as the reproductive system and abdominal contents
shoulder girdle
clavicles & scapulas; non-weight bearing; tremendous range of motion (RoM); important for hand movement
clavicles
acts as a strut to keep humerus (upper arm bone) away from the torso
scapulas
supporting and moving platforms that connects arms to torso and ribcage; butterfly piece in back
biomechanical process DOES NOT
prevent the compression of the humeral head against the acromial arch
What is the goal that is achieved by maintaining a good posture?
healthy movement habits (neutral posture)
modifications
available to build/strengthen a weakness
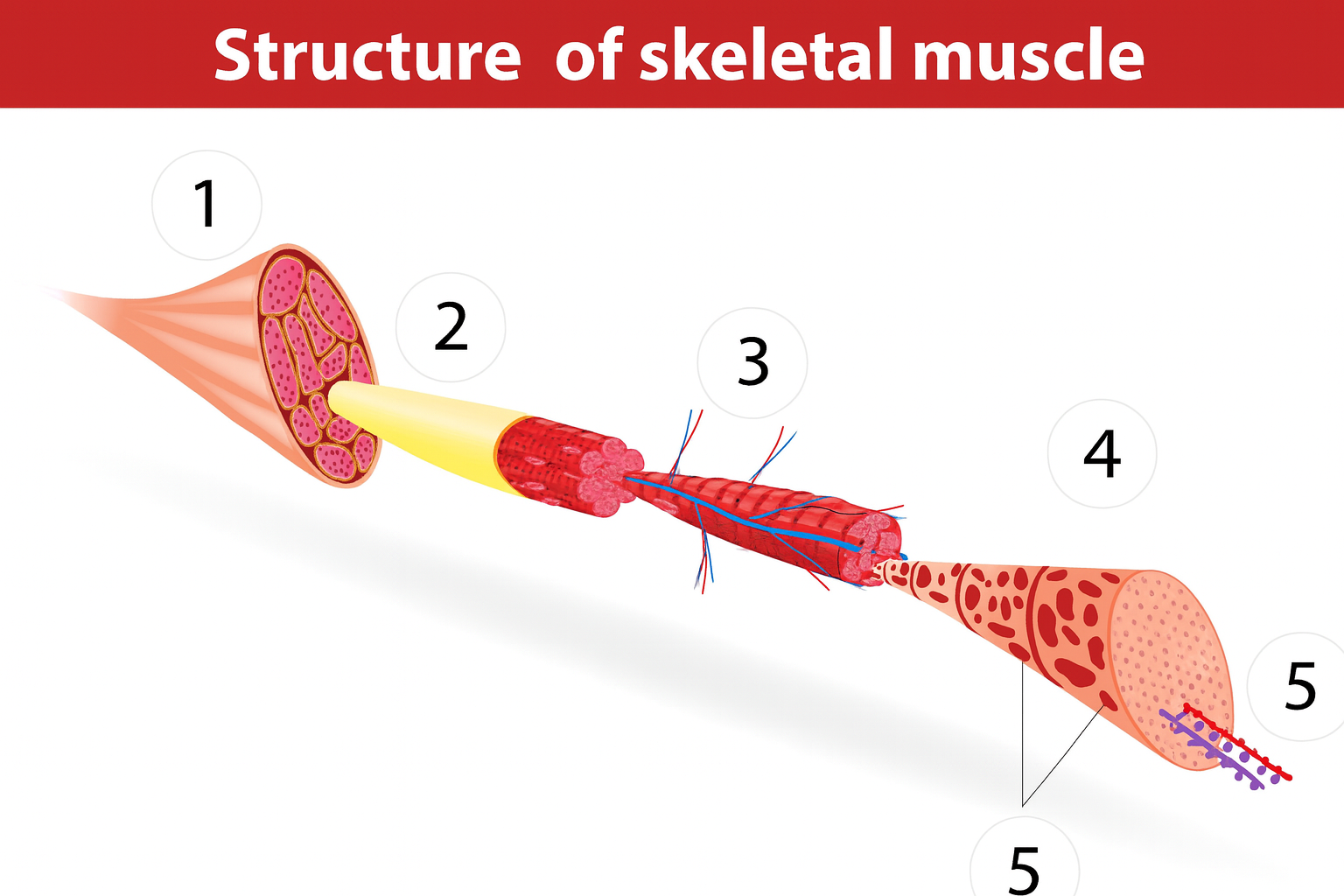
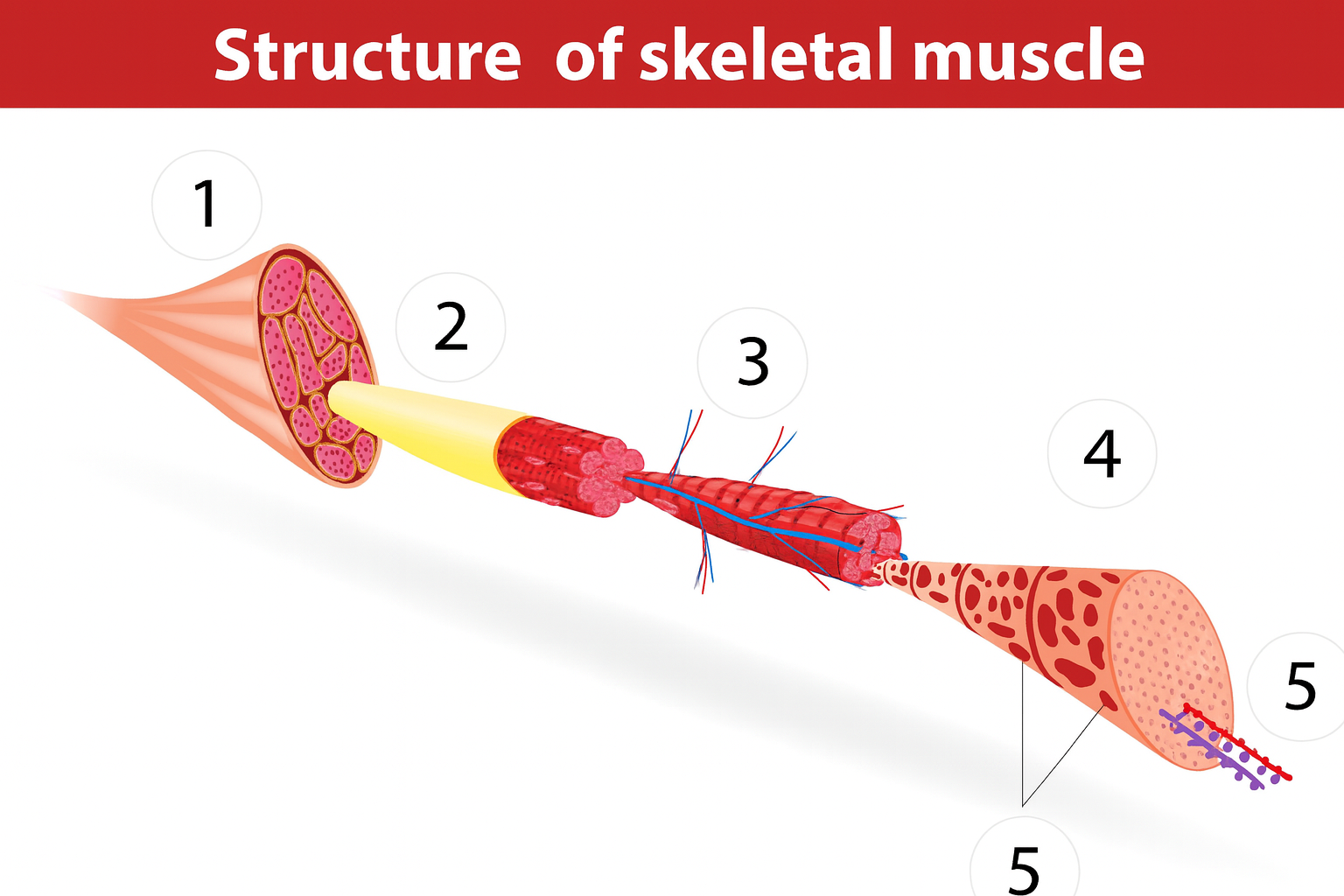
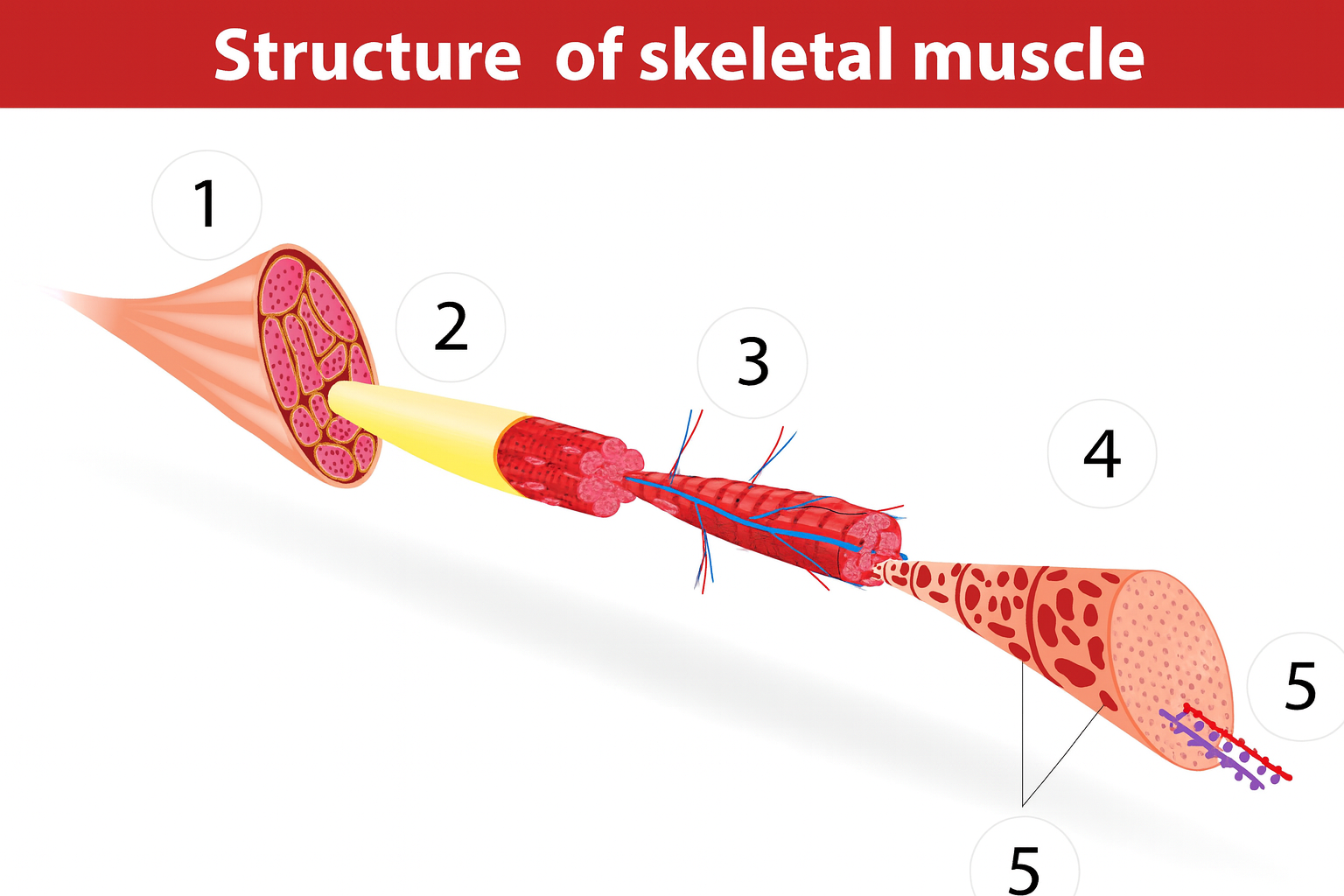
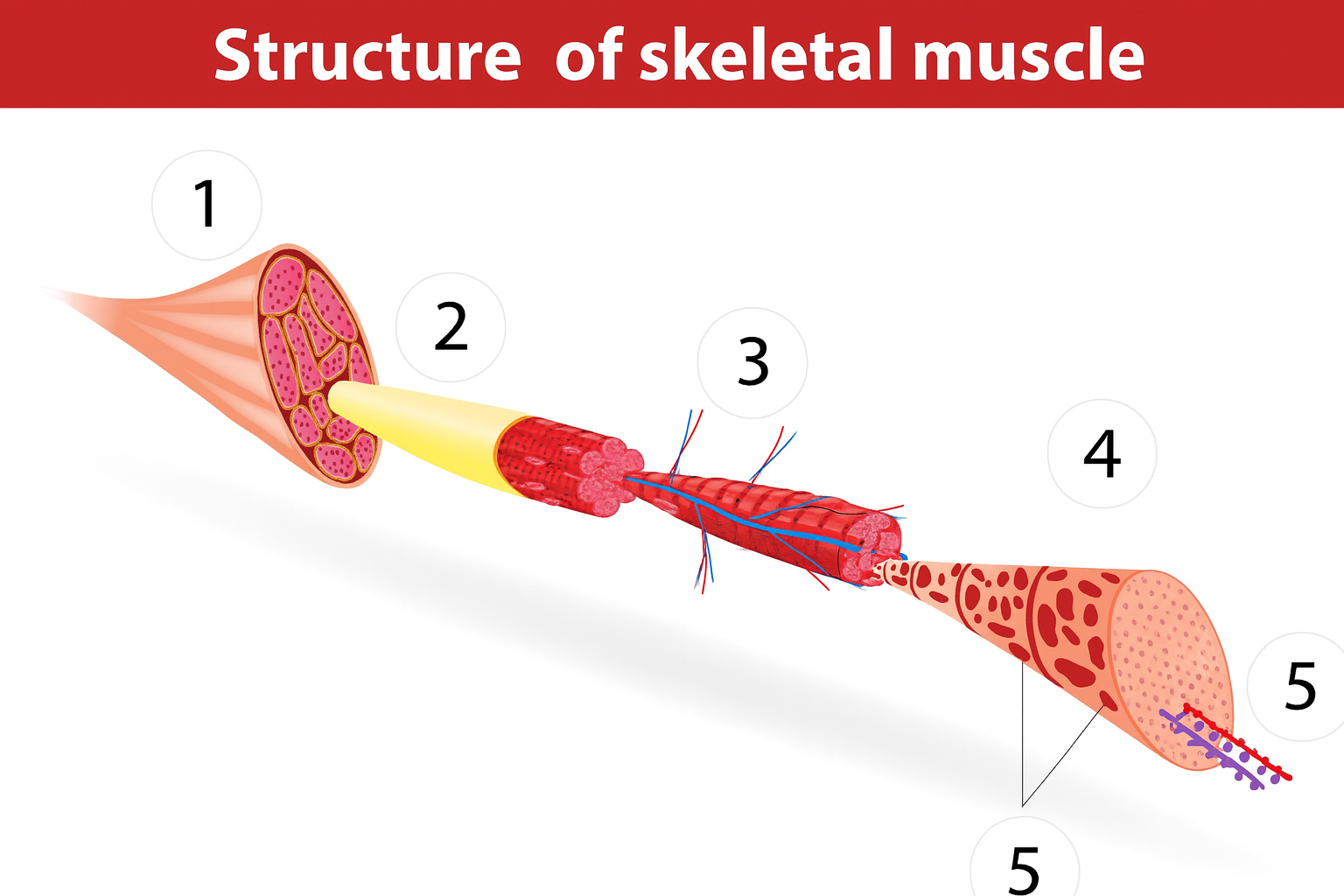
1
muscle
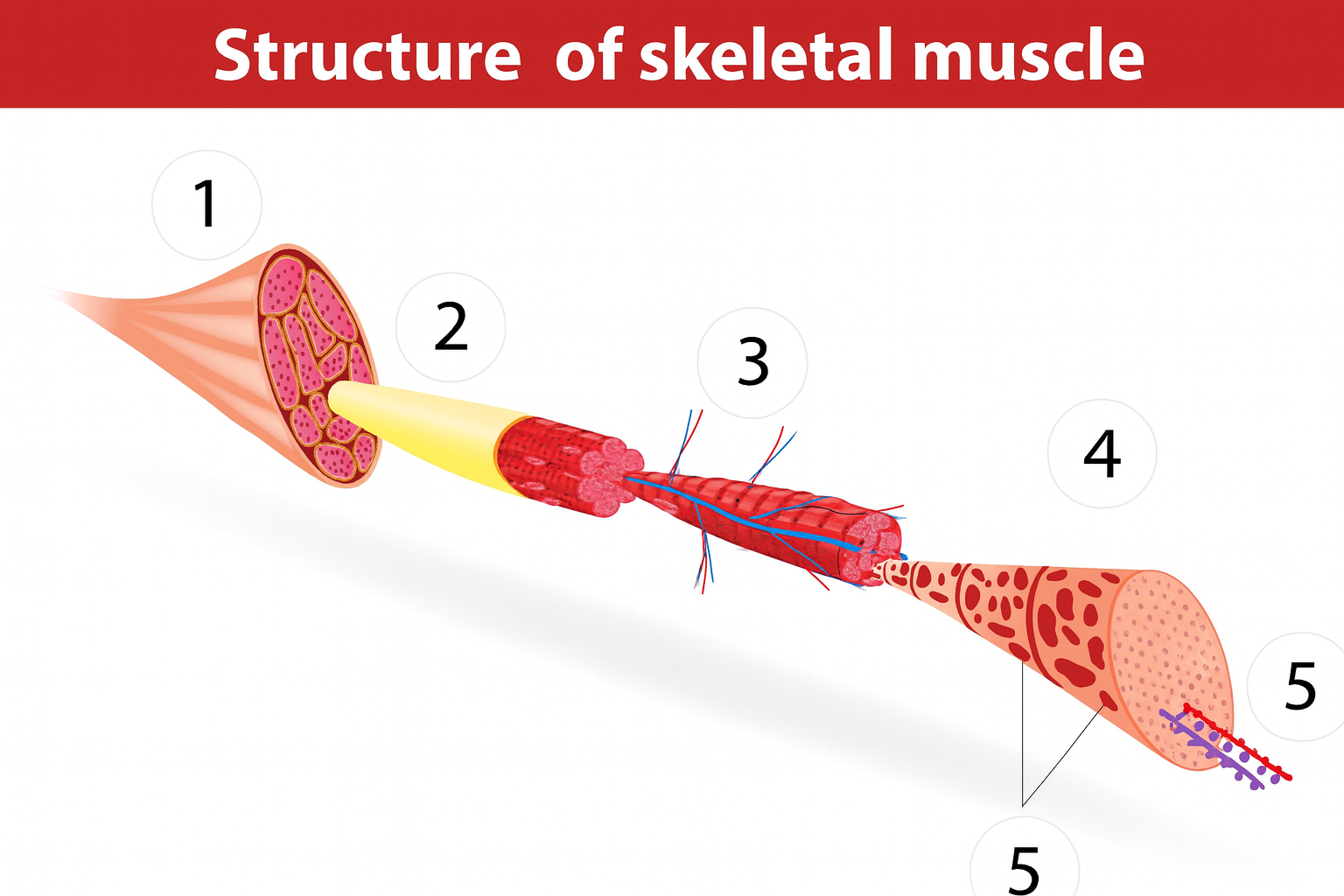
2a
fascia
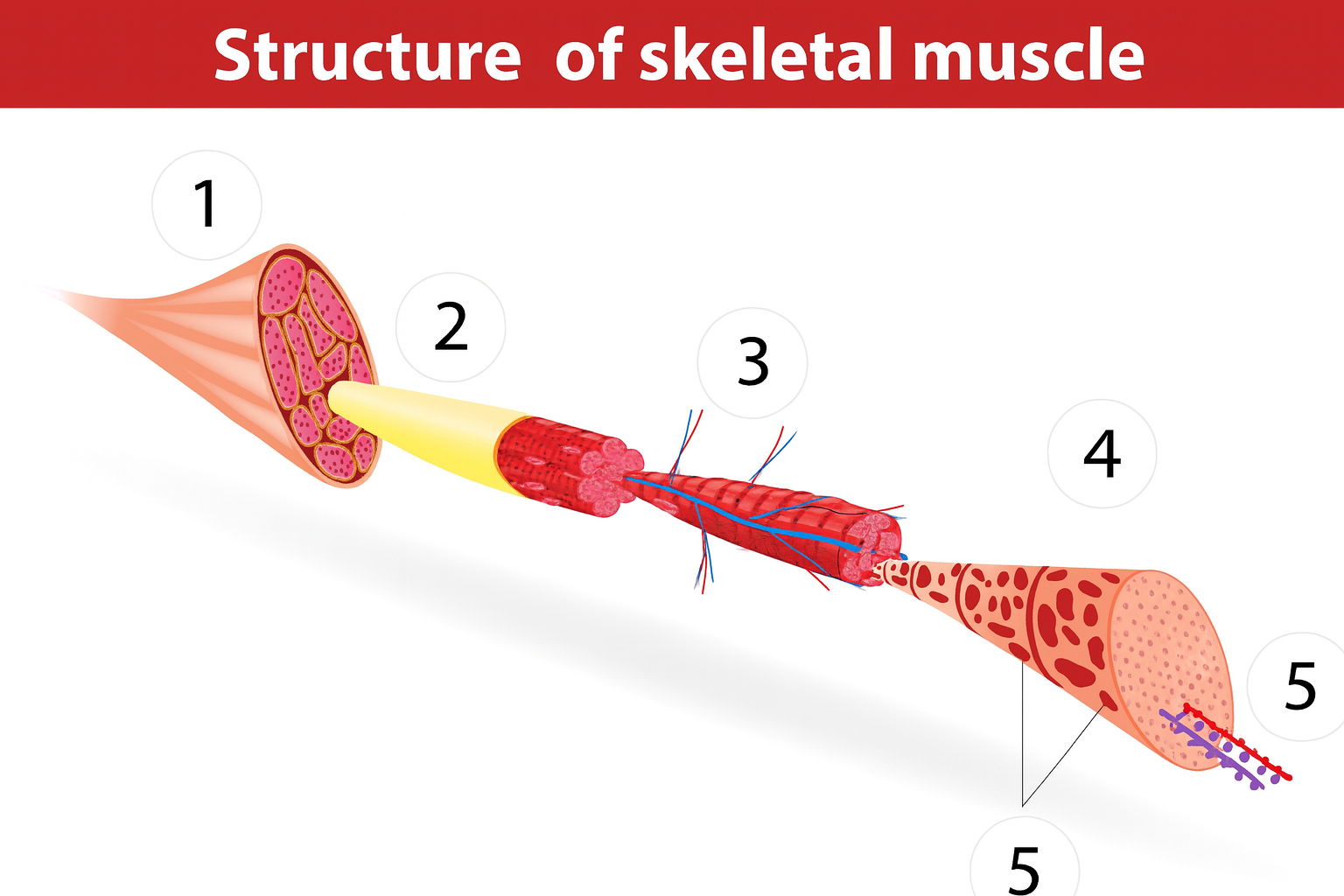
2b
muscle fibers
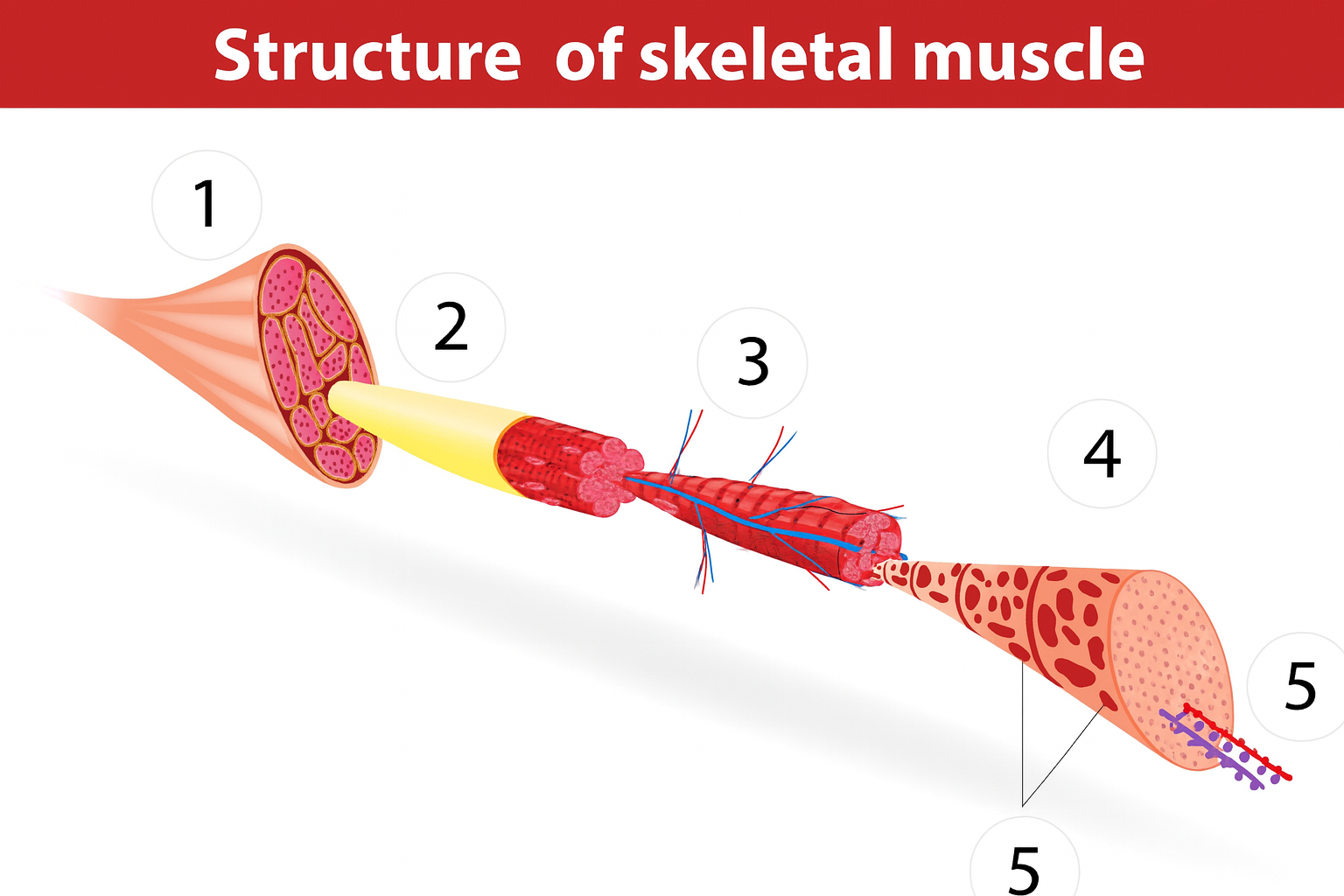
3
blood vessels
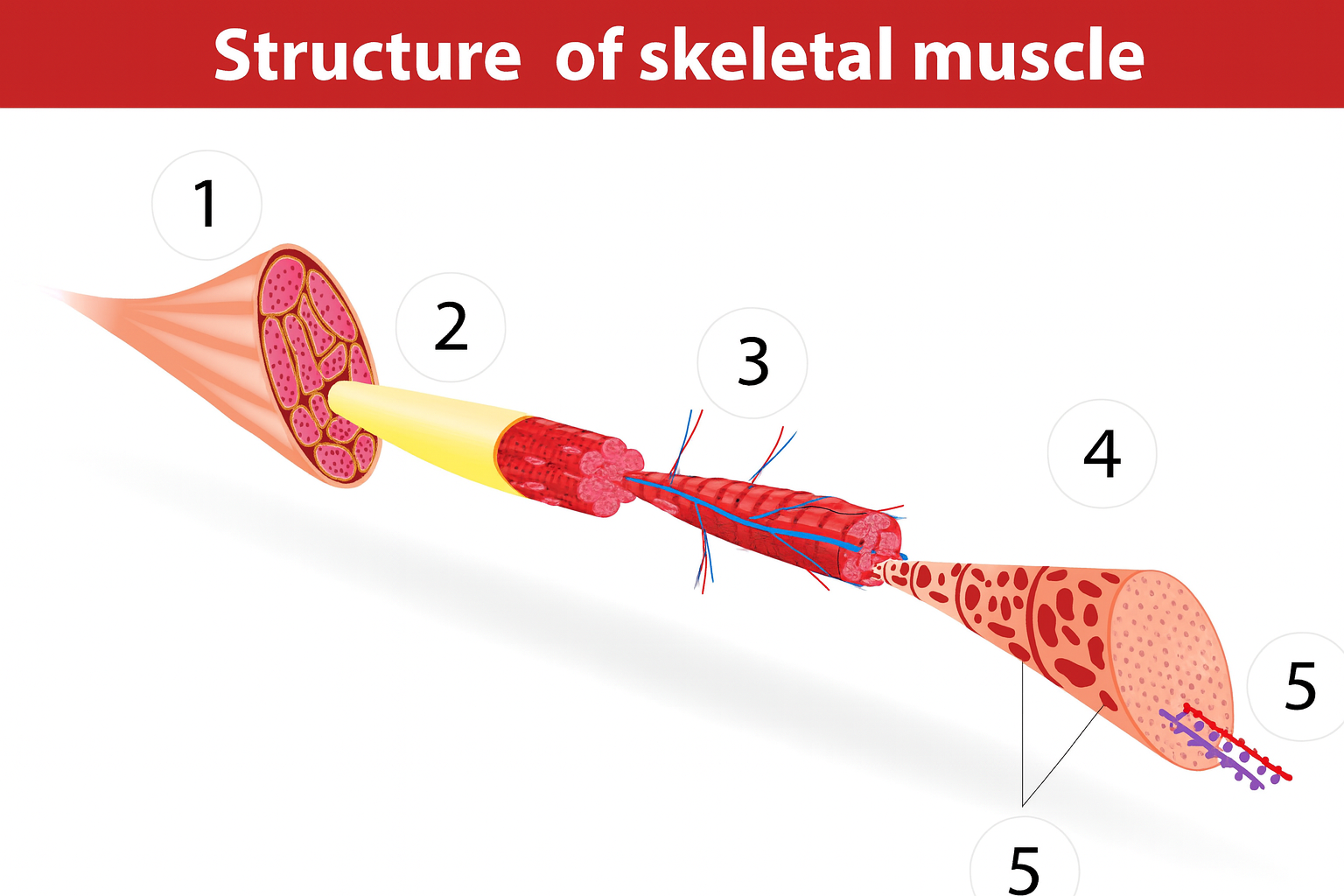
4
sarcomere
5a
myofibril
5b
actin
5c
myosins
Cardiac and smooth muscle is (voluntary or involuntary).
involuntary
Skeletal muscle is (voluntary or involuntary)
voluntary
muscle fibers
long cylindrical cells containing several nuclei; when contracted in unison, a muscle can produce enough force to move the body
What will muscles do when they receive signals from the nervous system?
move or relax
sarcomere
run adjacent to one another down the length of the myofibril; contain thick and thin protein filaments; slide; millions of bands composed with myofibrils (thread line strands)
What are muscle contractions controlled by?
actions of calcium
calcium ions
stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and are released in response to signals from the nervous system to contract
Muscle function generates (relaxation or tension).
tension
How does the muscle function lengthen?
at a point of 2 attachments
joints
bone to bone connections; limited extensibility; limits friction which leads to protection of the joints and cartilage; needs lubrication
nerves
transmits signals and nutrition (neuron-transmitters); very flexible
concentric movement
muscles shorten
isometric movement
muscles are neutral
eccentric movement
muscles lengthen
stabilizers
allow different muscles to function as needed for an exercise movement
actin
a thin protein; gets pulled towards myosin; an electric charge to depolarize cell; troponin and tropomyosin
myosin
a thick fibrous protein; pulls actin
Why do actin and myosin need to be close together for a contraction to occur?
in order for them to connect, they need to be close to one another; “grabbing the monkey bar”
muscle anatomy
composed of many tissues
strands/bundles/fibers fascicles
fascia intertwined
muscle fibers/myofibers/myocytes
blood vessels
sarcomeres
cardiac contraction
helps blood circulate
smooth contraction
surrounds organs
skeletal contraction
cylindrical; striata; moves bones
blood vessels
can grow around muscles to help endure intense workload
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
depolarizes cell and as a result, calcium is released; mitochondria produces this; crucial for contractions, tightness, and releasing the binding of the actin; phosphate molecule ADP
Muscles are always moving by …
relaxing and contracting
muscle functions
generates tension
limited extensibility
do not grow longer, attach from 2 attachments
give movement to the bones (stability/mobility)
receptors
receptors
let you know if you are doing putting to much pressure on your body (neuro-communicators and nutrient transmitters)
What two parts of the muscle are essential in order to stretch and balance tension in the human body?
fascia and sarcomere
Why do we stretch?
increase range of motion (RoM)
release tension
avoid injury/soreness
relaxation
What needs to be focused on in order for stretching to be effective?
particular purpose of stretching
3 Stretch Roles
reduces stiffness
increases athletic performance
increase joint nourishment
range of motion (RoM)
movement within a joint (joint provide this motion)
locked joint
impingement (something inside joint is being pinched or squeezed); limits mobility
hypermobility
large RoM due to a soft or looser tissues; tissue disorder
flunction stretching
more towards anterior
extension stretching
more towards posterior
rotation stretching
moving torso
lateral stretching
moving sideways; ex: bending to the left or right
The human body wants tendons and ligaments to be … (do not overstretch these components.
stiff
What do joints need to function properly?
stimulation, hydration, and nutrient movement
What is never the cause of tightness in a single muscle or movement limitation/painful condition?
stretching
What does every move me we make involve?
many muscles, fascia, and other structural integrations that all work together
What does every pattern of tension we feel involve?
chronic tightness in a number of muscles
Is stretching always the answer to curing tightness?
no
overstretched
greater tension because something has to support the strained joint
What action causes tightness?
movement that challenges elongation of any muscle; need to consider the limit of elongation so it does not harm the body
passive/static
“hold” at least 30 seconds
“relax” → stretch without strength
“deepen” → can override proprio-receptors (bands, hand towels, etc.)
can stretch connective tissues (tendons and ligaments)
for therapeutic purposes only
can apply additional force or pressure
ex: 4’s (pulling leg actively in), hold heel to glutes with hand (stretches the quad)
What does passive stretching do to the body?
loosens up ligaments and can lead to tightness
dynamic/active
activated muscles (strongly engaged, an active flow, and build connections)
movement in the full range of motion
joints moving
builds strength with flexibility and balance
for everyday fitness
eccentric contraction
ex: pendulum swings (neutral pelvis)
eccentric contraction
builds strength and stretches at the same time; proper elongation of the body
What three ways is extensibility limited in different people?
1) collagen density (little wavy line)
2) where the joint location is (able to do splits easier)
3) muscle strength (development of strength overtime)
What is an example of passive stretching?
staying in splits (may cause more harm than benefit)
What two characteristics are used to build muscle?
strength & endurance
What are some reasons as to why we are tight?
loosened ligaments
muscles are overworking to protect
imbalance in the muscles (weak muscles)
What are some goals for movement?
move through a full range of motion (nurtures mobility)
build connections (nurture proprio-receptors and core/back connection)
What does stretch tolerance vary in?
depends on the person and their ability
Why may we still be tight?
fascia is intertwined with muscles and could have adhesions
Ways to improve adhesions:
foam rolling (before workout), fascia massage, red light therapy, etc.
pranayama
regulating and controlling breathing; increase body’s resilience to tolerate stress and increase energy levels
Brain cell functions with low energy and high stress:
blood pressure disorders
toxins
sugar overload
toxic fats
BPA…
past trauma
brain fog, anxiety, depression, fatigue, etc.
What could be some causes of brain fog, anxiety, and fatigue?
drugs
leaky gut
poor circadian rhythm
lack of motivation
neurotransmitter imbalances
Neurotransmitter imbalances impacts:
mood, energy, passion, hormones, etc.
Examples of toxins:
indoor pollutants, heavy meals, pesticides, glyphosates (chemicals to kill weeds), EMFs, mold, etc.
2 key drivers at cellular level
1) mitochondria functions
2) redox → oxidation and antioxidation
neurotransmitters
2 systems that activate brain-body messages (vagus nerve and limbic)
vagus nerve
longest nerve; connects all organs; responsible for taking our entire body out of stress mode and puts it into rest/rejuvenation/relax mode
vagal nerve
controls pulmonary; regulates respiratory; provides sensory feedback from lungs to brain; links emotional and cognitive with digestive
Most influential system =
vagal nerve + intercoastal muscles
cells (neurotransmitters)
toxins hinder functions; normally they grow, divide, and engage in normal functions of the organelle; all have a lifespan; to tolerate stress load (internal/external), the root is the mitochondria
younger cells
high efficiency versus old cells
autophagy
“self recycling” or “cleansing house”
hemoglobin protein
oxygen is generated where it needs to go