Anatomy Lab practical 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/315
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
316 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Human Anatomy
the understanding of the structure of the human body
3
New cards
Human Physiology
study of the function of the human body
4
New cards
Scientific Method steps
Question
Research
Hypothesis
Experiment
Data Analysis
Conclusion
Communication
\
Research
Hypothesis
Experiment
Data Analysis
Conclusion
Communication
\
5
New cards
Hypothesis
a testable proposal that seeks to explain a scientific question
6
New cards
Experiment
Testing done to prove or disprove the hypothesis
7
New cards
Data
pieces of information or facts obtained and later examined to support or reject the proposed hypothesis
8
New cards
What is the ratio between a millimeter (mm) and a cubic centimeter
1 to 1
9
New cards
What is the metric unit for length
meter
10
New cards
What is the metric unit for volume
liters
11
New cards
What is the metric unit for mass
grams
12
New cards
What is the metric unit for time
seconds
13
New cards
Kilo
1,000 times greater
14
New cards
Deca
10 times greater
15
New cards
Deci
1/10 as much
16
New cards
Centi
1/100 as much
17
New cards
Milli
1/1000 as much
18
New cards
Micro
1/1000000 (one millionth as much)
19
New cards
Nano
1/1000000000 (one billionth as much)
20
New cards
Independent variable
the single variable that is changed to see how it effects the subject
21
New cards
Dependent variable
the results caused by the change in the independent variable
22
New cards
What is the scale for pH
Acidic (0-7)
Neutral (7)
Basic or Alkaline (7-14)
Neutral (7)
Basic or Alkaline (7-14)
23
New cards
What makes something acidic or basic.
When the substance is placed into a liquid and the substance dissociates or breaks apart, an Acidic solution means more H+ broke over from the overall substance then OH-, this is then opposite for a basic solution. If the solution is neutral, that means the substance dissoicated evernly into H+ and OH- ions.
24
New cards
Hydroxide ion
OH-
25
New cards
What does pH refer to
the concentration of H+ ions
26
New cards
What is the difference between the pH of 5 and the pH of 6 on the scale.
the concentration of the H+ ion would be in difference of 10. There are 10 times more H+ ion in a solution with the pH of 5 then there are in the pH of 6
27
New cards
Buffers
materials that resist change in pH
28
New cards
Covalent bonds
molecules where bonded atoms share electrons
29
New cards
Ionic bonds
electrons from one atom are transferred to another atom and the result is an atom with a positive change and an atom with a negative charge (this is done because atom what to have a full electron shell of 8 electrons)
30
New cards
Which type of bonds are dissociated in water
Ionic bonds
31
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
when the electrons of the hydrogen atom are attracted to another atom
32
New cards
Regional anatomy
the study of particulate areas of the body
33
New cards
Systemic anatomy
the study of organ systems
34
New cards
What are the 11 organ systems
Reproductive
Urinary
Nervous
Muscular
Respiratory
Skeletal
Lympathic
Integumentary
Digestive
Endocrine
Circulatory
Urinary
Nervous
Muscular
Respiratory
Skeletal
Lympathic
Integumentary
Digestive
Endocrine
Circulatory
35
New cards
Reproductive organ system
the gonads (testes and ovaries)
contain the sex producing cells of the body and the organs (uterus, vagina, penis, seminal vesicles)
contain the sex producing cells of the body and the organs (uterus, vagina, penis, seminal vesicles)
36
New cards
Reproductive organ system function
transport of sec cells and the development of the fetus
37
New cards
Urinary organ system
kidneys, urinary bladder, urethra
\
the kidneys are the filters of the body, the urinary bladder the storage organ and the urethra exit tube
\
the kidneys are the filters of the body, the urinary bladder the storage organ and the urethra exit tube
38
New cards
Urinary organ system function
ridding the body of nitrogenous wastes, adjusting chemical balance of body fluids, and maintaining blood volume
39
New cards
Nervous organ system
brain, spinal cord, nerves
40
New cards
Nervous organ system function
coordinates body movements, interprets environmental cues, and integrates information
41
New cards
Muscular organ system
individual muscles
42
New cards
Muscular organ system function
muscles move and strengthen joints, generate heat
43
New cards
Respiratory organ system
nose, larynx, trachea, lungs
44
New cards
Respiratory organ system function
the lings exchange gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between blood and air
45
New cards
Skeletal organ system
each bone with the blood and nerves found in each bone
46
New cards
Skeletal organ system function
supports the body, protects delicate organs, and produces blood
47
New cards
Lymphatic organ system
the lymph noes, spleen, thymus, tonsils
48
New cards
Lymphatic organ system function
to protect the body from foreign particles (bacteria, viruses, fungi)
the immune system
the immune system
49
New cards
Integumentary organ system
skin ,hair follicles, nails
50
New cards
Integumentary organ system function
protects the body against microorganisms, keeps the body from drying out, and produces vitamin D
51
New cards
Digestive organ system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, intestines
52
New cards
Digestive organ system function
provides nutrients and water to the body and removes waste
53
New cards
Endocrine organ system
organs that produce hormones
thyriod glands,adrenal glands
thyriod glands,adrenal glands
54
New cards
Circulatory organ system
the heart, blood, and blood vessels make up this system, the heat is the pump of the system and the blood vessels are the delivery and return portion of the system
55
New cards
Circulatory organ system function
transporting oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other material through the body
56
New cards
Anatomic position
body is upright, facing forward, arms and legs straights, palms facing forward, feet flat on the ground, eyes open
57
New cards
Quadruped
four legged animals
58
New cards
Dorsal
the back side of the animal
59
New cards
Ventral
the belly side of the animal
60
New cards
Anterior or cephalic
front or head end of the animal
61
New cards
Posterior or caudal
rear or tail end of the animal
62
New cards
proximal
refers to region close to the mouth
63
New cards
Distal
refers to region close to the anus
64
New cards
Parietal
in reference to the body walls
65
New cards
Visceral
in reference to area closer to the internal organs
66
New cards
Ipsilateral
same side of the body
67
New cards
Contralateral
refers to being on the other side left or right
68
New cards
Superior
above
69
New cards
Inferior
below
70
New cards
Medial
towards the midline
71
New cards
Lateral
towards the side
72
New cards
Superficial
towards the surface
73
New cards
Deep
towards the core
74
New cards
Anterior
to the front
75
New cards
Posterior
to the back
76
New cards
Cranial cavity
houses the brain
77
New cards
vertebral canal
encloses the spinal cord
78
New cards
thoracic cavity
superior to the diaphragm housing the lings and the mediastinum
79
New cards
Mediastinum
which contains the heart the pericardial membranes and the large vessels associated with the heart
80
New cards
Abdominopelvic cavity
is inferior to the diagram and is subdivided into the abdominal and pelvic cavities
81
New cards
What are the three sectioning planes
transverse plan
frontal plane
sagittal plane
frontal plane
sagittal plane
82
New cards
Transverse plan
a cut that divides the body or organ into superior and inferior parts
horizontal cut
horizontal cut
83
New cards
Frontal plane
a cut that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
84
New cards
Sagittal plane
a cut that divides the body into left and right portions
85
New cards
Median (Midsagittal) plane
a cut that divides the body or organs equally into left and right portions
86
New cards
Parasagittal plane
a cut that divides the body into unequal left and right portions
87
New cards
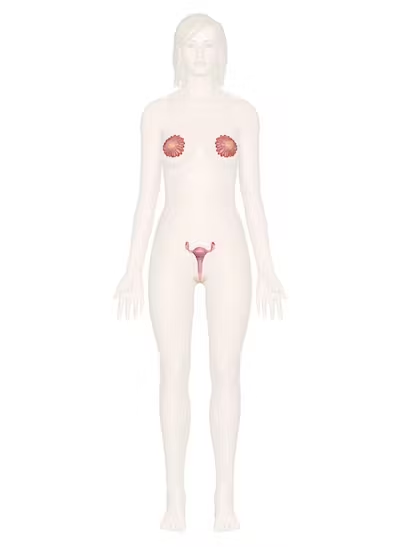
What organ system is this
Reproductive
88
New cards
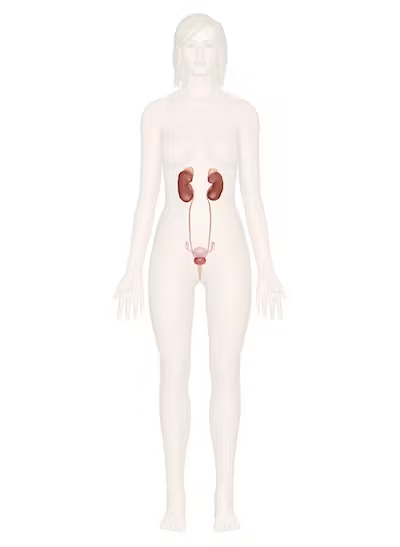
What organ system is this
Urinary
89
New cards
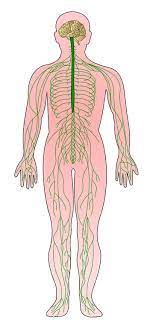
What organ system is this
Nervous
90
New cards
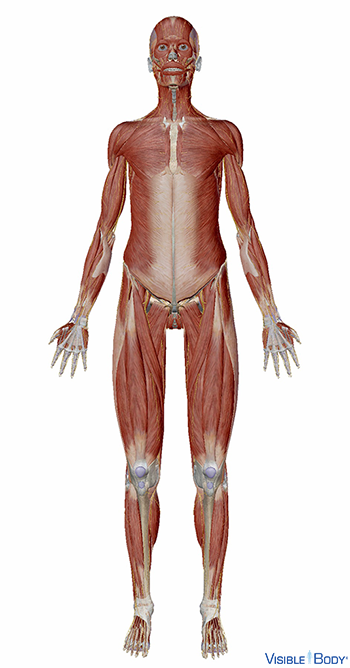
What organ system is this
Muscular
91
New cards
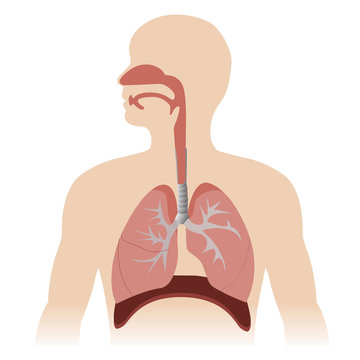
What organ system is this
Respiratory
92
New cards
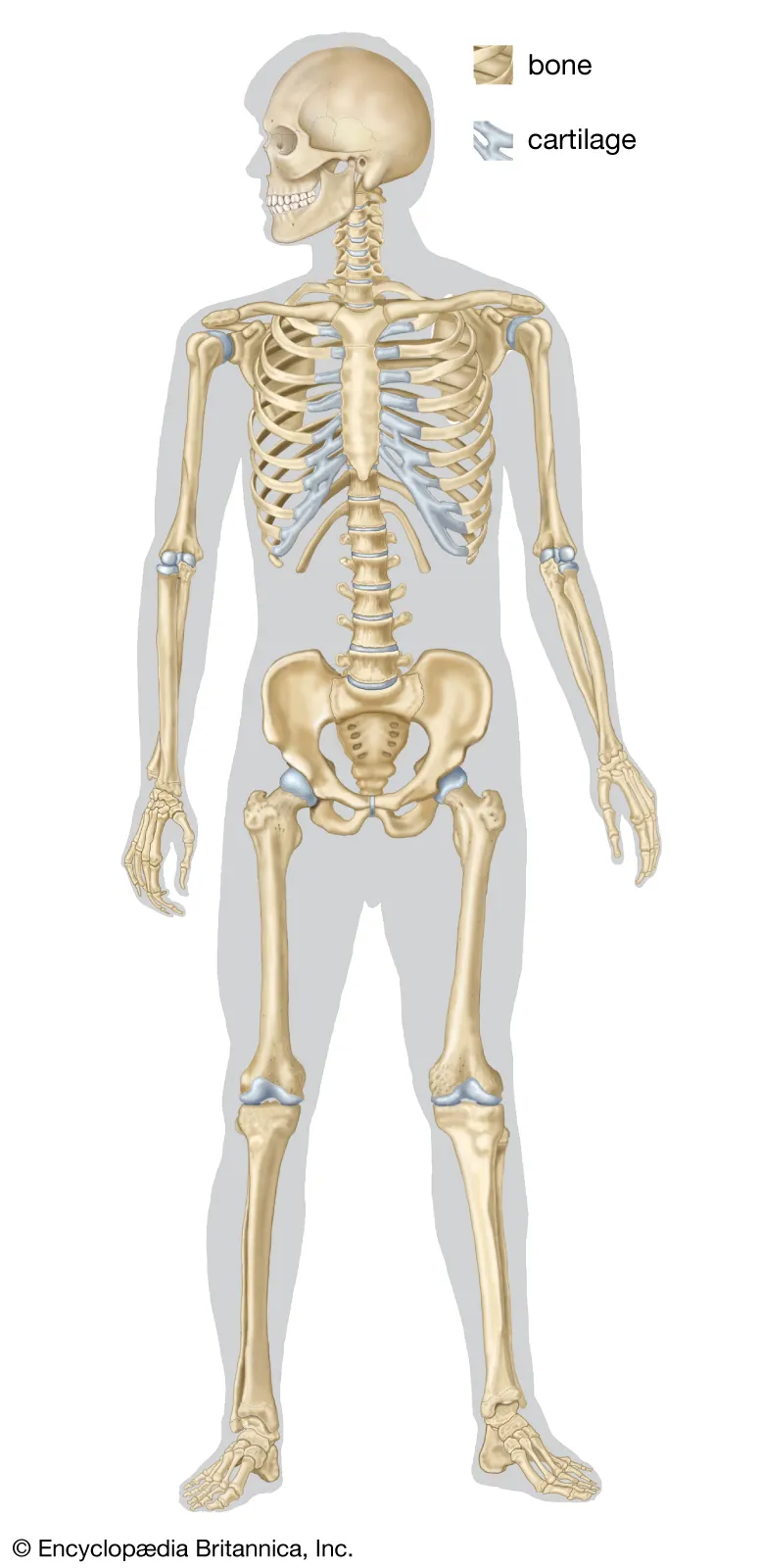
What organ system is this
skeletal
93
New cards
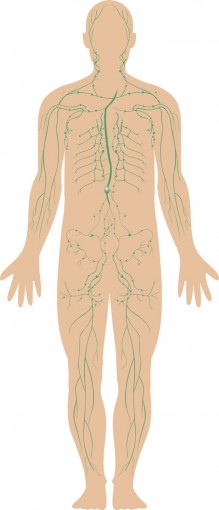
What organ system is this
Lymphatic
94
New cards
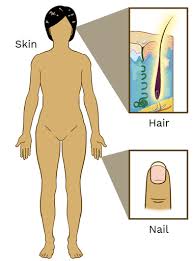
What organ system is this
Integumentary
95
New cards
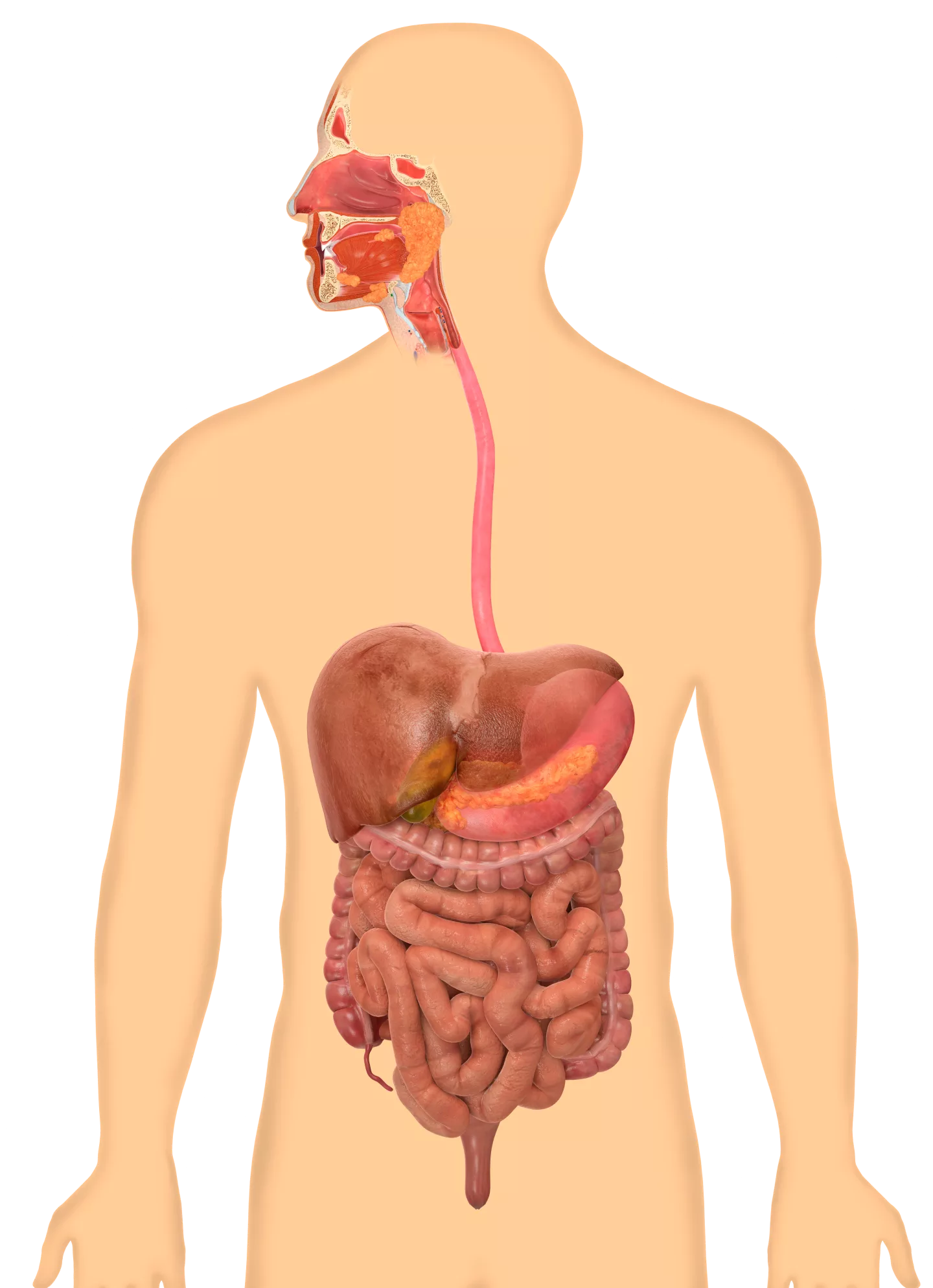
What organ system is this
Digestive
96
New cards
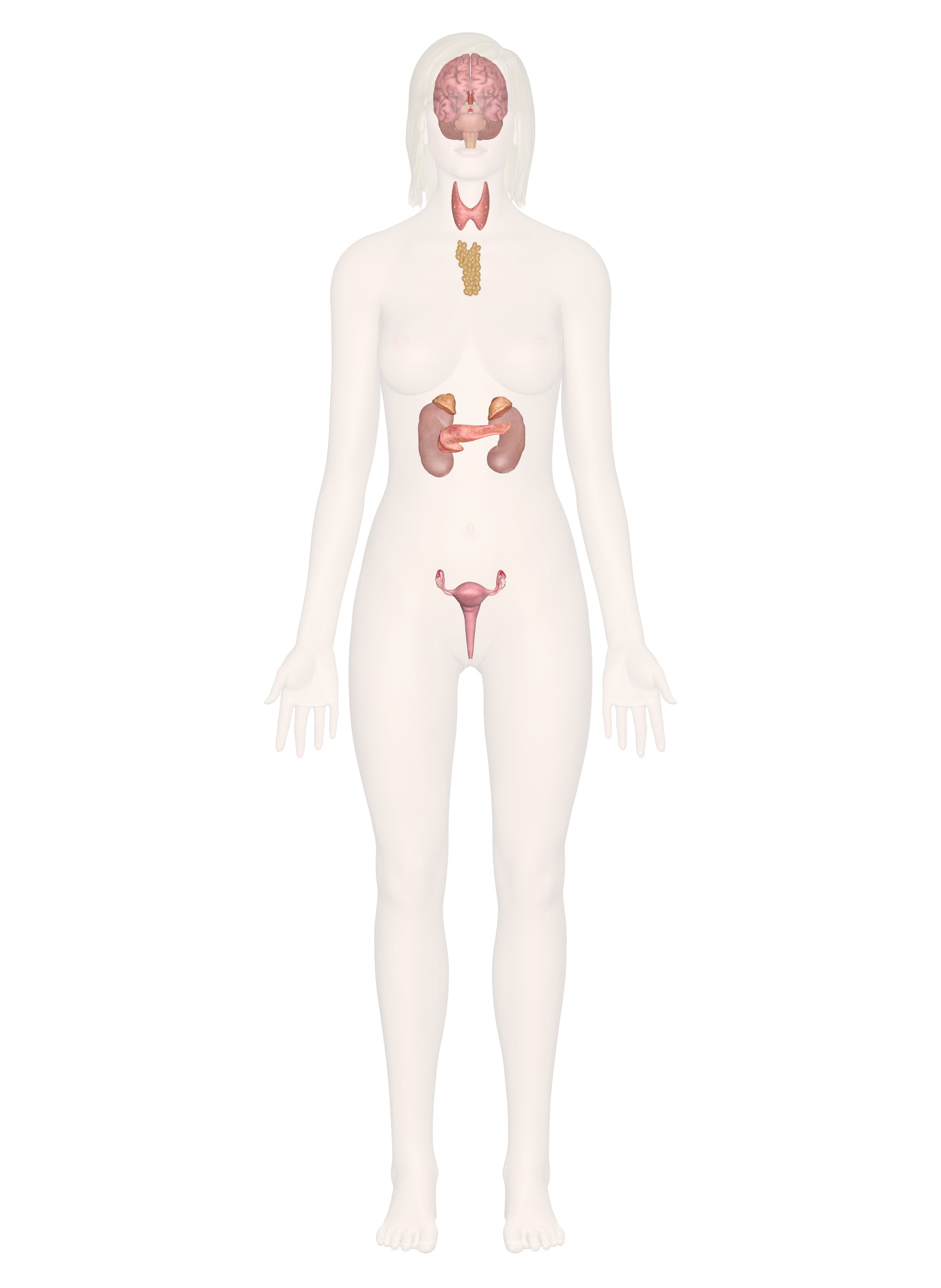
What organ system is this
Endocrine
97
New cards
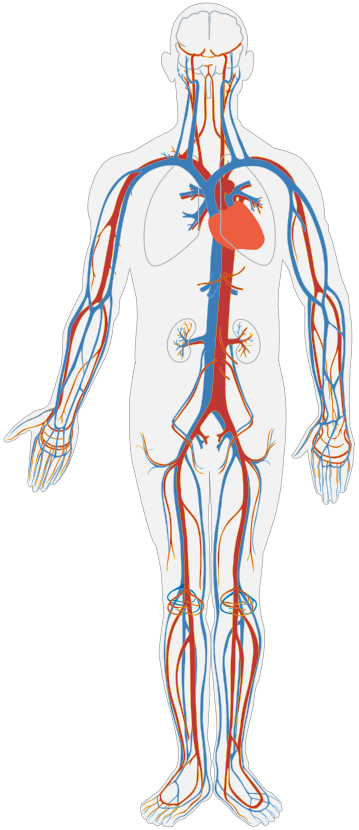
What organ system is this
Circulatory
98
New cards
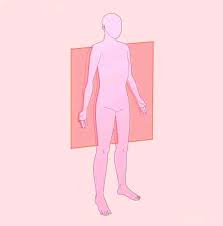
What sectioning plane is this
Frontal plane
99
New cards
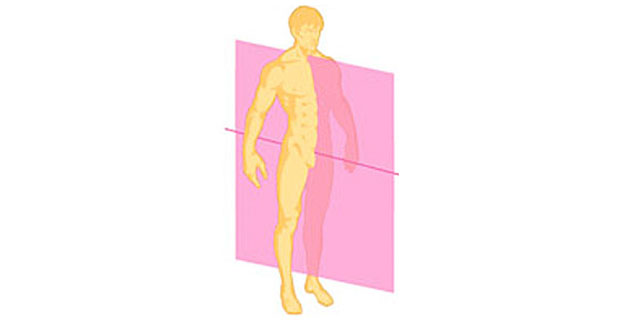
What sectioning plane is this
Sagittal plane
100
New cards
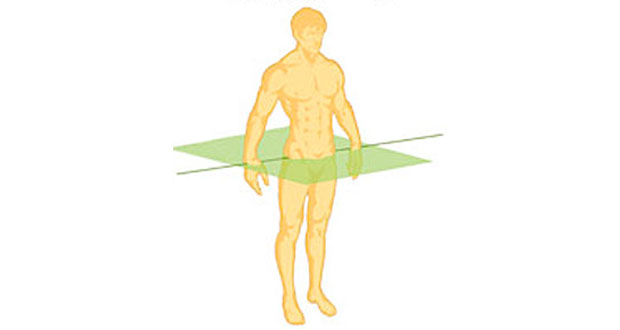
What sectioning plane is this
Transverse plane