LBYZOOL Activity 07-09 (Lab Exam 3)
Anura
Order frogs and toads belong in
Frog
- "Rana pipiens"
- smooth or slimy skin that is moist
- long, strong, hind legs that aid them in leaping
- big bulging eyes
1/282
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Toad External Anatomy, The Skeletal System, & The Muscular System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
283 Terms
Anura
Order frogs and toads belong in
Frog
- "Rana pipiens"
- smooth or slimy skin that is moist
- long, strong, hind legs that aid them in leaping
- big bulging eyes
Toad
- "Rhinella marina"
- thicker, bumpy, skin that is usually dry
- shorter hind legs, more suitable for walking
- more subtle eyes
2 Major Layers of Frog Skin
Epidermis & Dermis
Epidermis
layer of frog skin:
- stratified epithelium
- has 2 sublayers: stratum corneum & germinativum
stratum corneum
sublayer of frog epidermis:
- outermost stratified layer
- thin dead squamous keratinized cells
- constantly removed when shed
Ecdysis
- aka molting
- process when frogs shed its skin
stratum germinativum
sublayer of frog epidermis:
- living cuboidal to columnar stratified epithelial tissue
- continuously divide to replace the shed-off layer
chromatophores
- connective tissue which contains pigments
- at the junction of epidermis and dermis
melanophores
black pigment containing cells found at the junction of the dermis and epidermis
Dermis
layer of frog skin:
- inner layer of skin
- has 2 sublayers: stratum laxum/spongiosum & compactum
stratum laxum/spongiosum
layer of frog dermis:
- outer sublayer of dermis
- loosely arranged connective tissue & blood vessels
- cutaneous glands gives spongy appearance
cutaneous glands
posion glands & mucous glands
poison gland
gland in stratum laxum/spongiosum:
- larger glands
- less numerous
- posses thin epithelial wall
- blue arrow

mucous glands
gland in stratum laxum/spongiosum:
- small
- more numerous
- thicker wall
- red arrow

stratum compactum
layer of frog dermis:
layers of white fibrous connective tissue
dorsal
back or upper surface of an organism
ventral
stomach or lower surface of an organism
anterior
head end of an organism
posterior
tail end of an organism
bilateral symmetry
left & right halves of an organism are mirrored portions
main axis of toads
horizontal axis
3 planes of the toad body
frontal, sagittal (longitudinal), & transverse (cross)
frontal
plane dividing the body into dorsal & ventral sections
sagittal
plane dividing the body into left & right sections
transverse
plane dividing the body into anterior & posterior sections
locations relative to the center of the body
medial, lateral, proximal, proximal, & distal
medial
location near the middle
lateral
location to the sides
proximal
part of a structure that is nearer the origin
distal
part farther from the origin
regions of the body
axial & appendicular regions
axial region
region:
- head & trunk
- joined together by a very short neck, thereby restricting movement of the head
- structural functions
head
portion in axial region:
contains snout, mouth, external nares, eyes, browspot, tympanic membrane, & paratoid gland
snout
external part of head:
- blunt apex found on the tip of the head
- most anterior portion of the head
mouth
external part of head:
- for feeding
- extending tongue
external nares
external part of head:
- paired openings at the tip of the snout connected to internal nares (breathing)
- arrow 1

eyes
external part of head:
- dorsolateral portion of the head
- used to push down food; closes when they swallow
- contains: upper & lower eyelids, nictitating membrane
upper eyelid
part of eye:
thicker eyelid; does NOT move
lower eyelid
part of eye:
thinner eyelid; moves
nictitating membrane
part of eye:
- thin, transparent
- protects eyeballs
- keeps eyes moist when underwater
- arrow 2

browspot
external part of head:
- circular spot between the eyes
- displays where part of the skull development took place
tympanic membrane
external part of head:
- Posterolateral to the eye
- ovoid region of tightly drawn skin
- frog’s ear / ear drum
- covers auditory canal
- protects inner ear from outer environment
- arrow 3

paratoid gland
external part of head:
- behind tympanic membrane at each side of head
- large swelling
- large aggregate of poison glands
- secrete poisonous mucus
- only found in toad
- arrow 4

Croak
- only male frogs can do this
- to find a mate & defend their territory
Trunk
portion in axial region:
contains sacral hump & cloacal aperture
sacral hump
external part of trunk:
pelvis is elongated and higher at the spine
cloacal aperture
external part of trunk:
- aka anus
- most posterior part of the trunk on the dorsal side
- exit cavity for excretory, urinary, reproductive system
appendicular region
region:
- forelimbs & hindlimbs
- function for movement
Forelimbs
portion in appendicular region:
- anterior pair
- short
- used to raise or support the body when the frog is at rest
- contains: upper & lower arm, wrist, & hand
brachium
external part of forelimbs:
- upper arm
- arrow 6

antebrachium
external part of forelimbs:
- lower arm / forearm
- arrow 5

carpus
external part of forelimbs:
wrist
manus
external part of forelimbs:
- hand
- 4 digits + prepollux
prepollux
5th rudimentary thumb
hindlimbs
portion in appendicular region:
- posterior pair
- long
- well adapted for jumping and swimming
- contains: thigh, shank, & pes
thigh
external part of hindlimbs:
- upper leg
- arrow 7

crus
external part of hindlimbs:
- shank / lower leg
- arrow 8

pes
external part of hindlimbs:
- foot
- contains tarsus, metatarsus, 5 fully-webbed toes + prehallux
- arrow 10

tarsus
external part of hindlimbs:
- long ankle
- arrow 9

metatarsus
external part of hindlimbs:
instep
prehallux
6th rudimentary toe
skin on the dorsal side
skin with warty appearance
sex-distinguishing external characteristics
skin pigmentation in jaw, thumb pads, & relative size
male frogs
sex of frog:
- distinct dark pigmentation on skin on the ventral side of the jaw
- generally smaller
- thumb pads are enlarged or swollen
Nuptial pad
- patch of textured skin on male's enlarged thumb
- helps cling to female during amplexus
amplexus
- mating position of frogs
- false copulation
- release sperm to water and not inside the female
female frogs
sex of frog:
- pigments are diffused (NO distinct dark pigmentation)
- relatively bigger
- thumb pads of the inner fingers are NOT swollen
chloroform
- liquid used as an anesthesia for the frog/toad specimen
- rinsed off the dead/preserved specimen before dissection
skeletal system
organ system:
- serves as support or framework for the softer parts of the body
- provide a firm surface for the attachment of muscles used in movement and locomotion
- supplies calcium to the blood
- important site in the formation of blood cells
2 Types of Skeleton
Exoskeleton & Endoskeleton
Exoskeleton
type of skeleton:
- hardened bony or horny structures that develop in the skin and provide external protection to the animal
- poorly developed in frogs
- 2 kinds: chitinous & calcium-carbonate
chitinous exoskeleton
type of exoskeleton:
- made up of chitin
- arthropods, insects, arachnids, crustaceans
calcium-carbonate exoskeleton
type of exoskeleton:
- hard shell
- phylum mollusca: snail, bivalves (scallops)
Endoskeleton
type of skeleton:
- almost entirely of bone and cartilage
- skeleton of frog
Tendon
connective tissue that serves as attachment of (skeletal) muscles and bones
Aponeurosis
broad, flat, and sheet-like tendon
2 Types of Bone Structure
Compact Bone & Spongy Bone
Compact Bone
type of bone structure:
- dense layer from the outside of the bone
- presence of concentric osteons

osteon
- functional unit of compact bone
- made up of lacunae, osteocytes, haversian canal, lamellae, & canaliculi
lacunae
part of osteon:
tiny spaces in the matrix
osteocytes
part of osteon:
bone cells trapped in lacunae
haversian canal
part of osteon:
series of microscopic tubes with blood vessels and nerves
lamellae
part of osteon:
concentric rings of bone
canaliculi
part of osteon:
- passageways for materials to move between cells
- tiny channels between the lacunae
spongy bone
type of bone structure:
- aka Cancellous Bone
- Sponge-like meshwork consisting of trabeculae
- spaces are continuous & occupied by yellow bone marrow & blood vessels
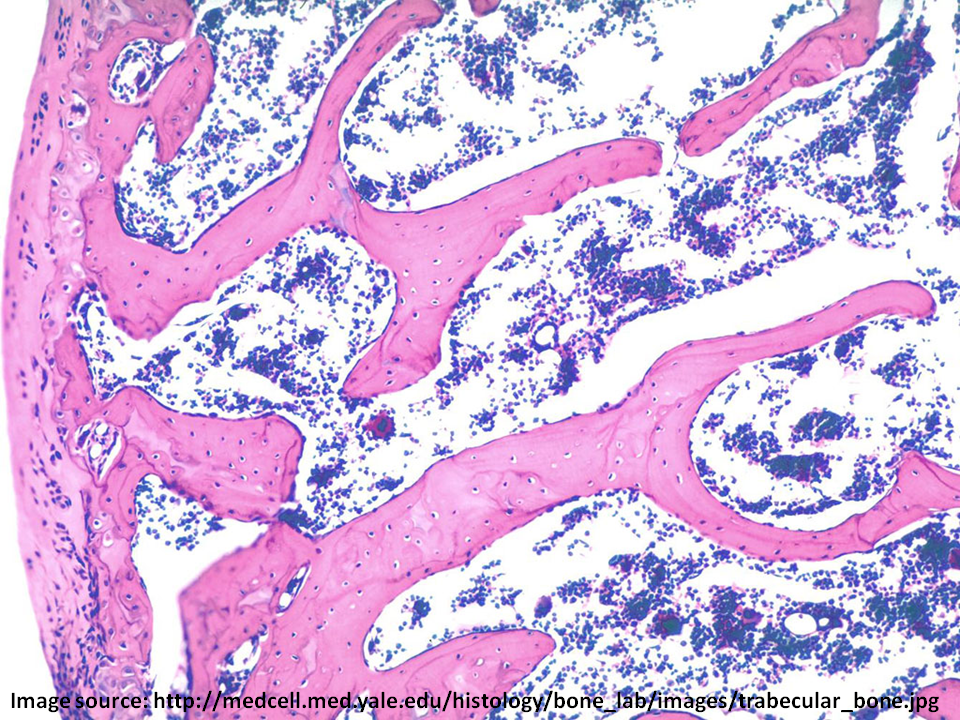
trabeculae
series of branching, overlapping plates of matrix in the spongy bone
spaces in spongy bone
- storage/pockets to hold blood-forming cells (hemopoietic tissue) of bone marrow
- function in weight reduction
yellow bone marrow
adipose tissue around the trabeculae
axial endoskeleton
endoskeleton according to position:
- located at the center or axis of the body
- skull, visceral skeleton, vertebral column, ribs, & sternum
appendicular endoskeleton
endoskeleton according to position:
- located laterally or in the region of the extremities or appendages
- pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, forelimbs, & hindlimbs
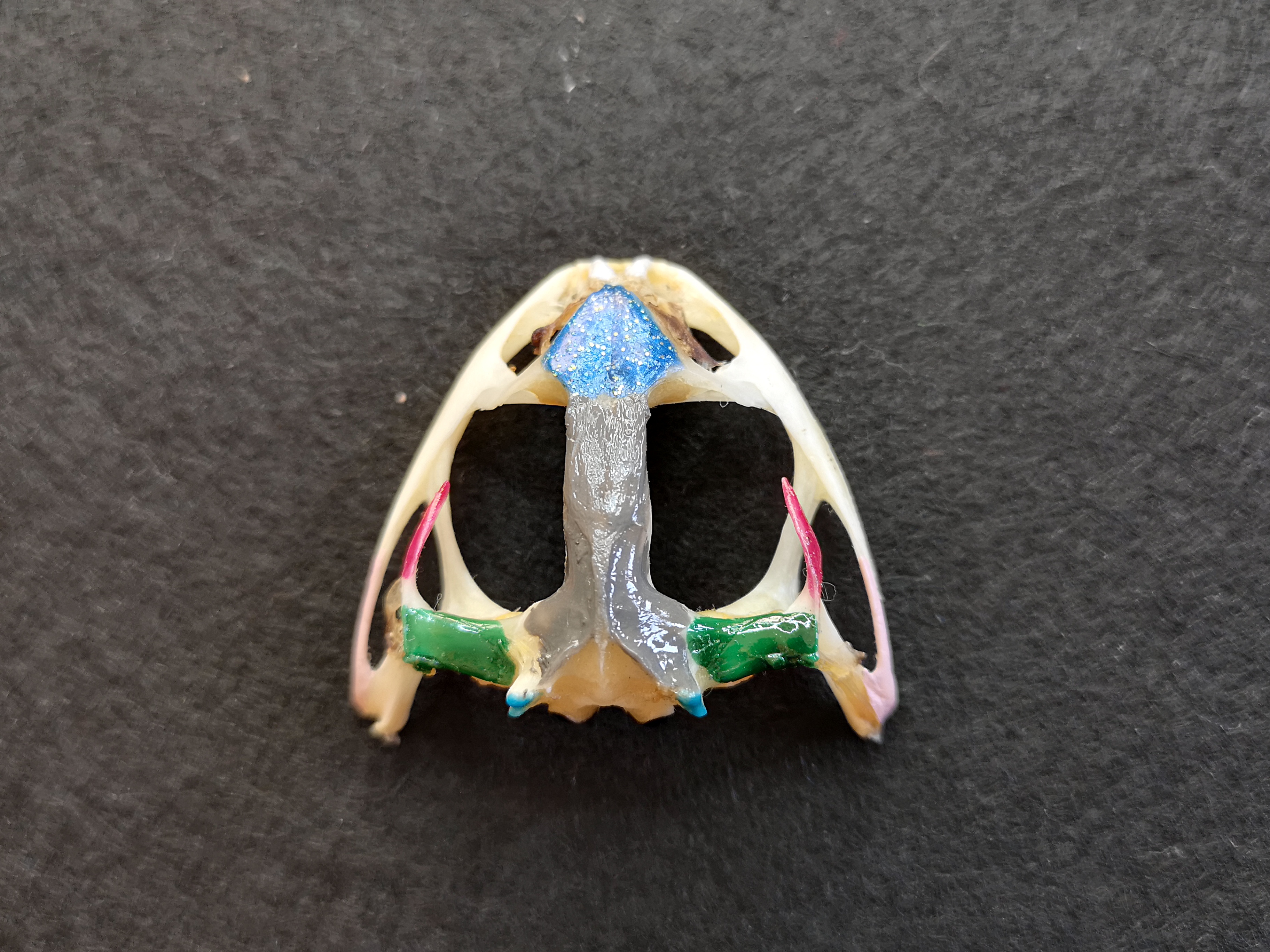
skull
- flattened dorsoventrally
- wider posteriorly and narrow anteriorly
- encloses the brain and sense organs
- includes cranium & the visceral skeleton
cranium
aka braincase
nasal bones
bone in skull:
- flat, triangular-shaped bones on the dorsal surface of the skull behind the nares
- dark blue portion
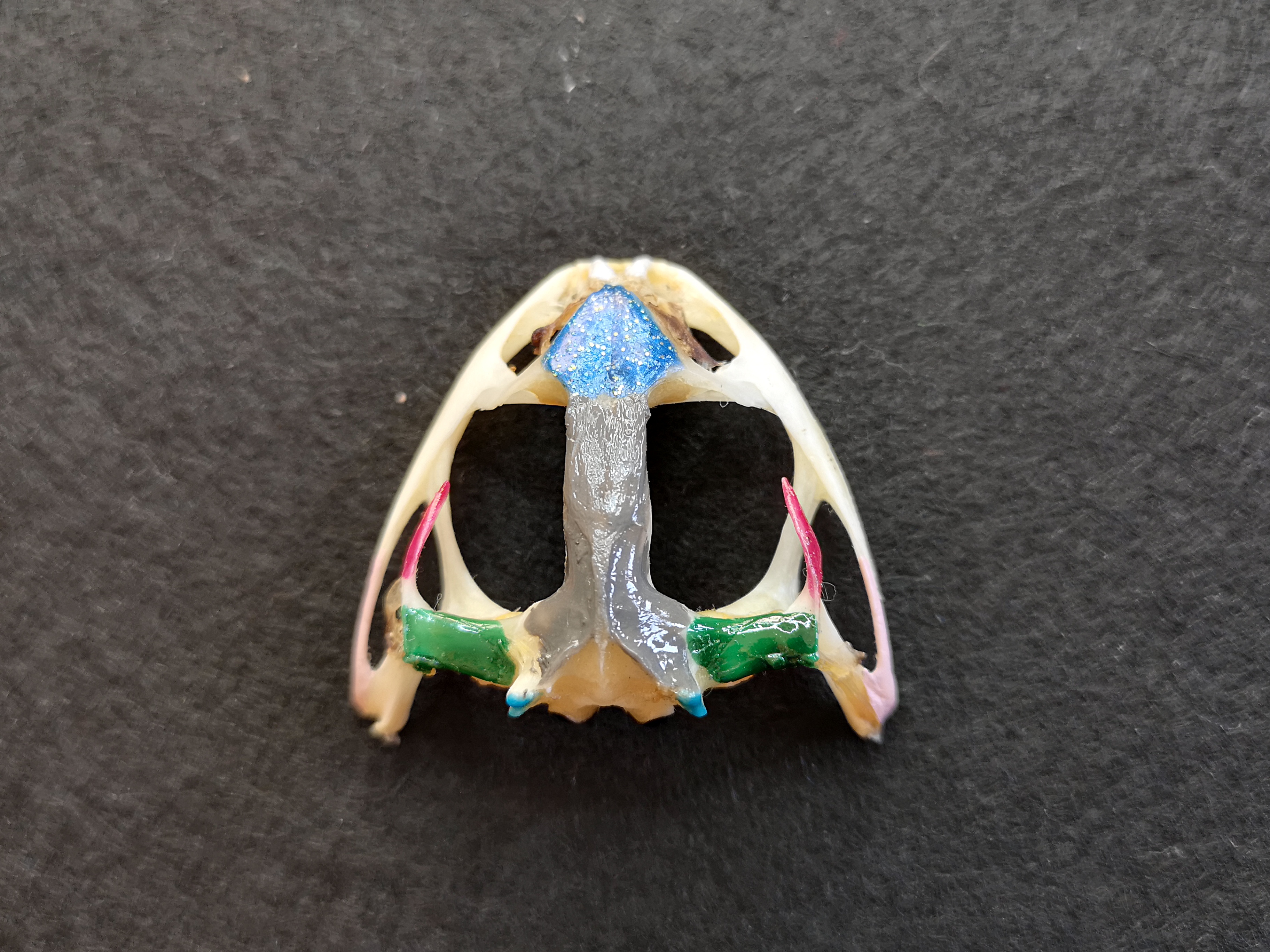

sphenethmoid
bone in skull:
median, single irregularly shaped bone posterior to nasal bones
frontoparietal
bone in skull:
- 2 long slender flat bones, posterior to the nasal bones
- may be fused so they appear as a single bone
- cover most of the brain
- wide at posterior end, where they join the prootics
- gray portion
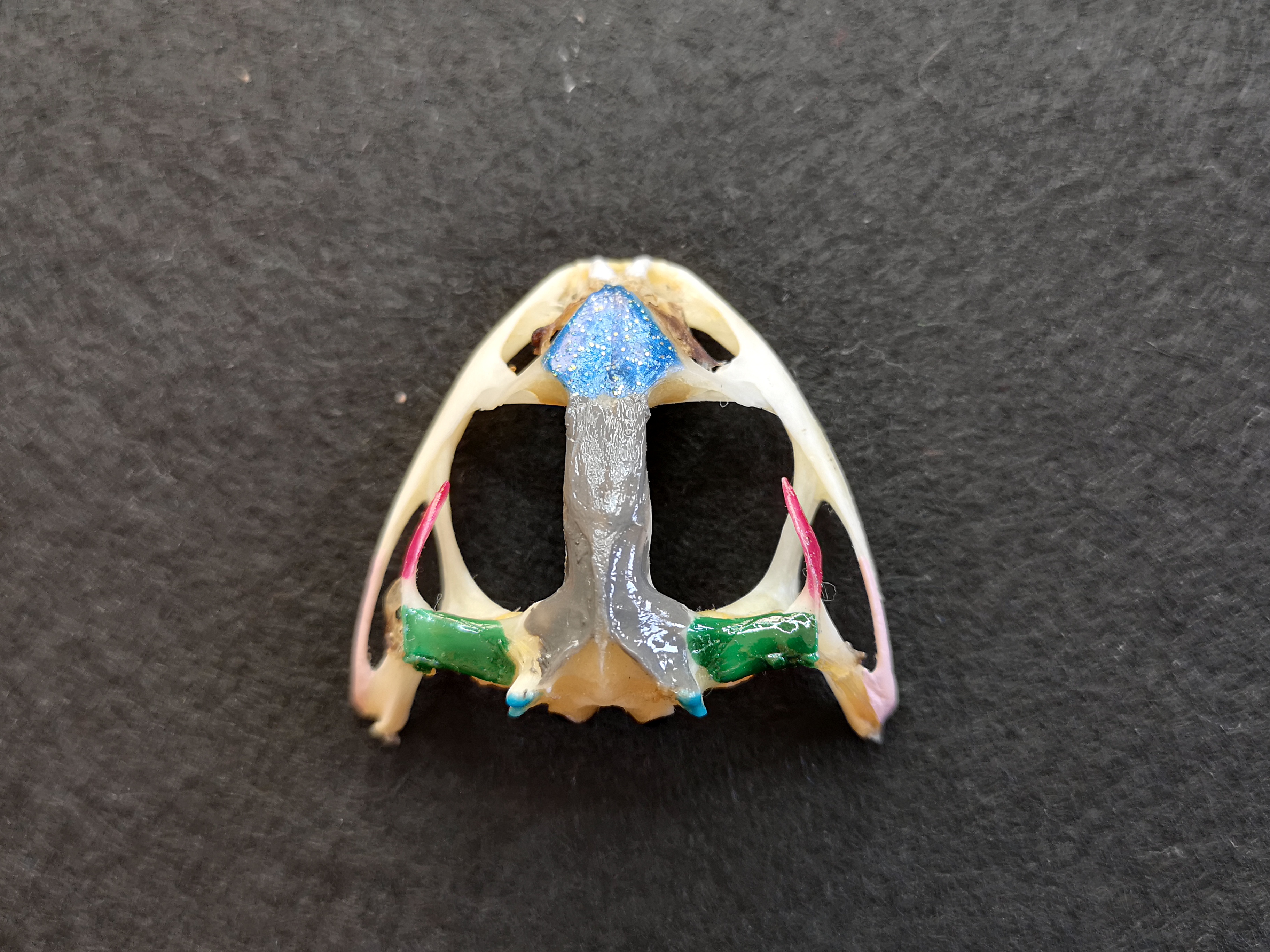

prootics
bone in skull:
- joined by frontoparietals
- enclose inner ears
- dark green portion
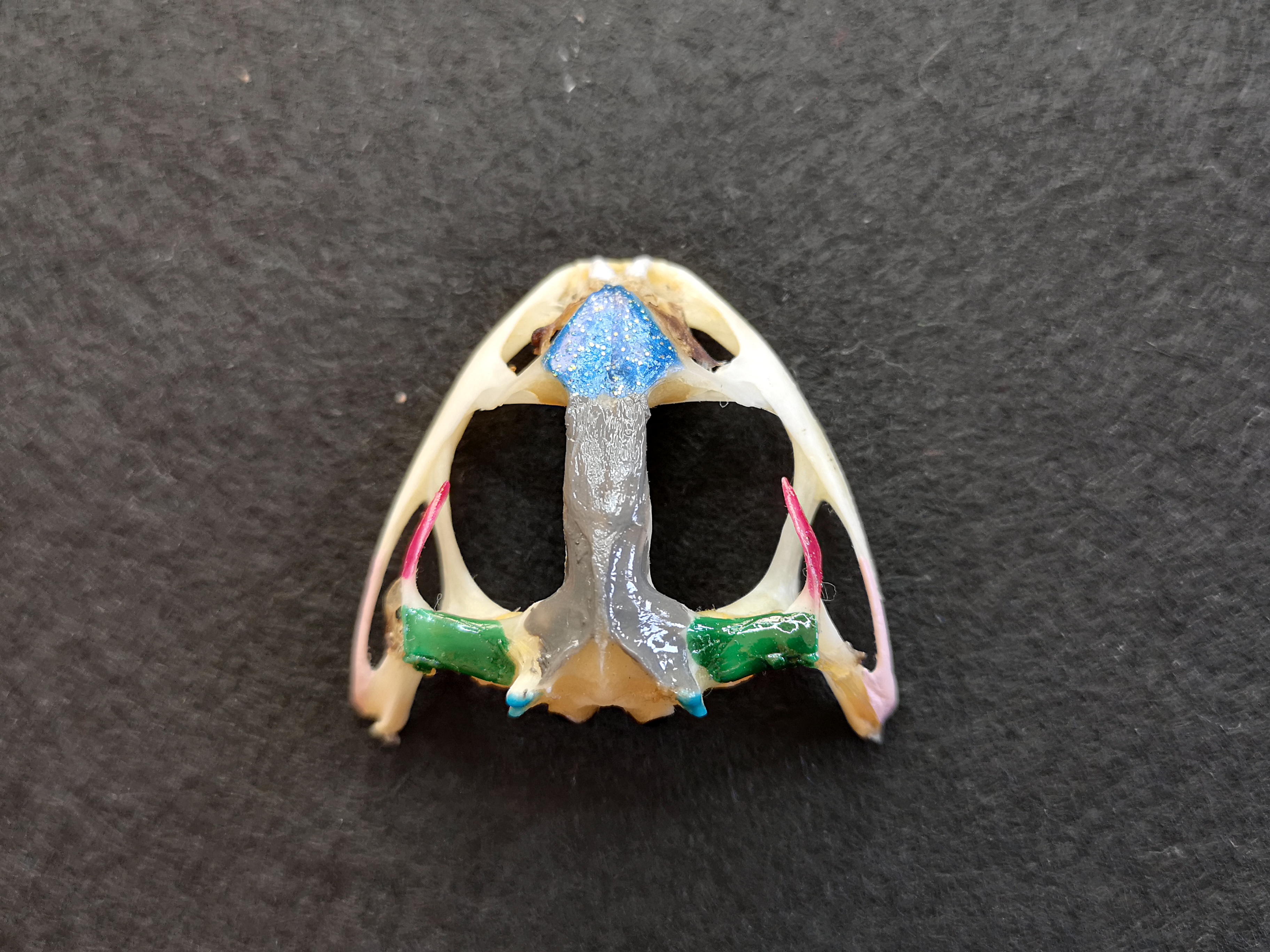

foramen magnum
bone in skull:
- large opening at the posterior end of the skull where spinal cord passes
- uncolored area under the gray portion

exoccipital
bone in skull:
- surrounding the posterior part of the brain
- bottom gray portion
occipital condyles
bone in skull:
- pair of prominent bones projecting from exoccipital
- light blue portion
