kinetics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what is the rate of reaction?
the gradient of [A] vs time i.e. -d[A] / dt
[A] and [P] plotted against time
gradients?
[P] is its mirror image
at the same time points -d[A]/dt = d[P]/dt
gradients have same magnitude but opposite sign
![<p>[P] is its mirror image </p><p>at the same time points -d[A]/dt = d[P]/dt </p><p>gradients have same magnitude but opposite sign </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6efb29e0-bcee-47fd-9e7e-e8acb586fed0.png)
enzymes
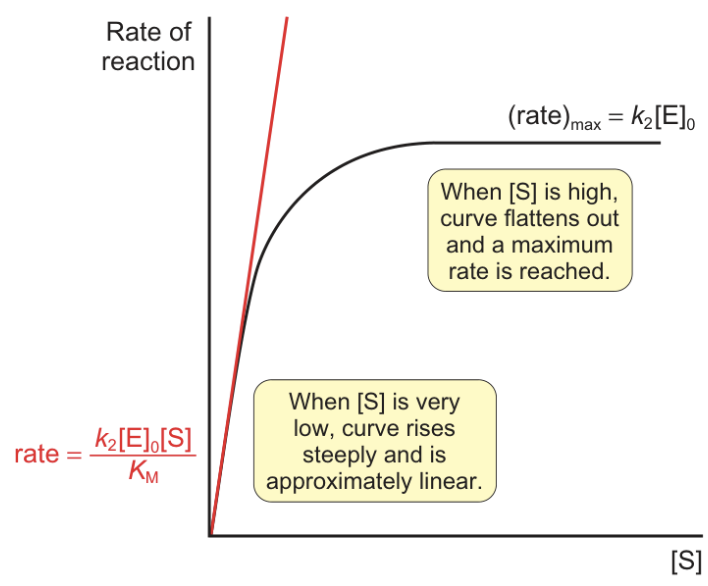
what is rate like when [S] is low?
what is rate like when [S] is high?
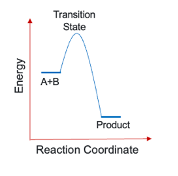
what is an elementary reaction?
up to 2 reagents come together, form a transition state and then products
what are the 2 types of elemental reactions?
unimolecular
bimolecular
unimolecular - if number of reagent molecules doubled, how does rate change?
what is the rate equation?
rate is doubled
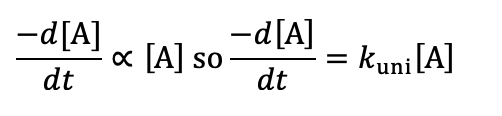
biomolecular - if number of reagent molecules is doubled, how does rate change?
rate is quadrupled
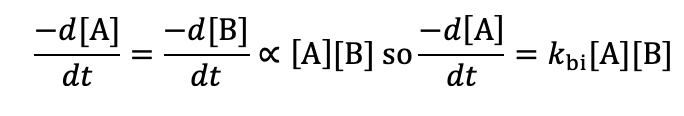
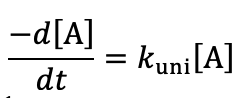
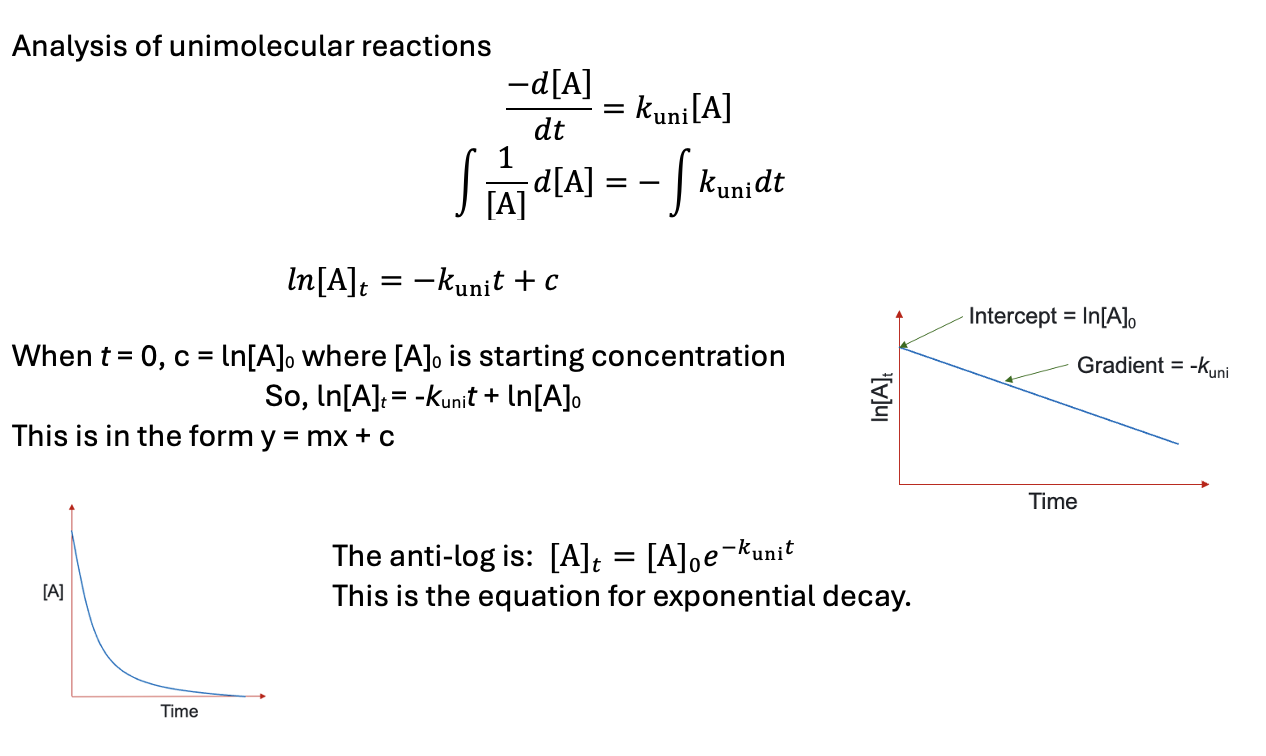
how to solve uni molecular differential equation?
what is the antilog?
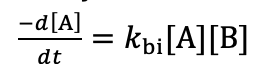
why is solving the bimolecular differential equation problematic?
how to get around this?
two variables (A and B)
get around this by having one in great excess. concentration essentially constant
bimolecular - how do you find [B]t?
[B]t = [B]0 – [A]reacted
=[B]0-([A]0-[A]t)
what is the differential equation when it is A + A → P?
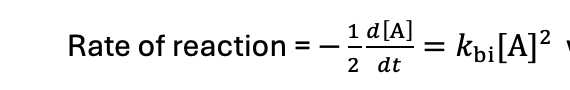
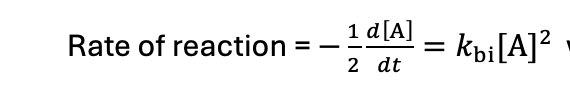
how to solve the bimolecular differential equation when both reactants are the same?
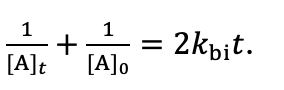
2 ways of determining orders of reaction?
integral method
differential method
what is the integral method?
determine the shape of [A] vs time
manipulate to give straight line
what is plotted to show linear first order?
ln[A] vs time
what is plotted to show second order linear?
1/A vs time
what is the differential method?
either
take gradient along a decay and plot gradient vs [A]
take initial gradient and repeat experiment at different values of [A]0
![<p>either</p><ul><li><p>take gradient along a decay and plot gradient vs [A]</p></li><li><p>take initial gradient and repeat experiment at different values of [A]<sub>0</sub></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/29dff642-de32-427f-8694-e5fed98f5df8.png)
why is it sometimes beneficial to use initial rates to calculate order?
100% reactants so no chance of secondary chemistry
effects of impurities limited
what is a relaxation reaction?
removal of excess energy
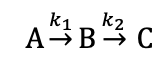
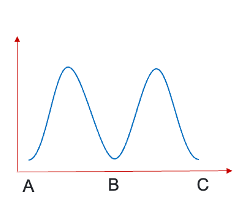
for this sequence of reactions, what is the reaction profile?
what does the shape depend on?
shape depends on ratio k1:k2
what does the magnitude of rate coefficient depend on?
activation barrier
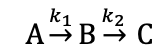
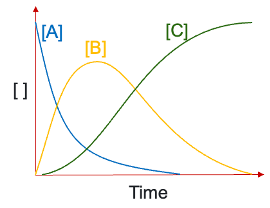
conc vs time graph (includes all A, B and C)
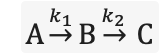
what are the rate equations for each compound?
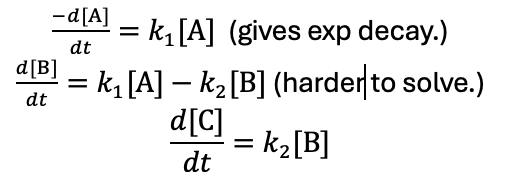
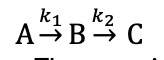
explain growth and decay of each compound if k1>>k2?
what is conc vs time graph now
what is rds?
A decays exponentially but faster
growth in B matches decay of A - virtually all A converted to B as k2 is small
growth in C matches decay of B
B to C is rds
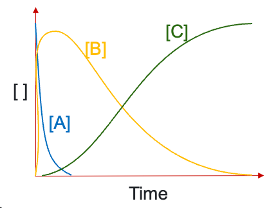
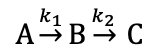
explain growth and decay of each compound if k2>>k1?
what is conc vs time graph now
what is rds?
B is very reactive intermediate, [B] never builds up as it reacts as soon as it forms
growth in C matches decay of A
A to B is rds
![<p>B is very reactive intermediate, [B] never builds up as it reacts as soon as it forms</p><p>growth in C matches decay of A </p><ul><li><p>A to B is rds</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2c68c469-3a5c-4aa6-813b-76172b2b6179.png)
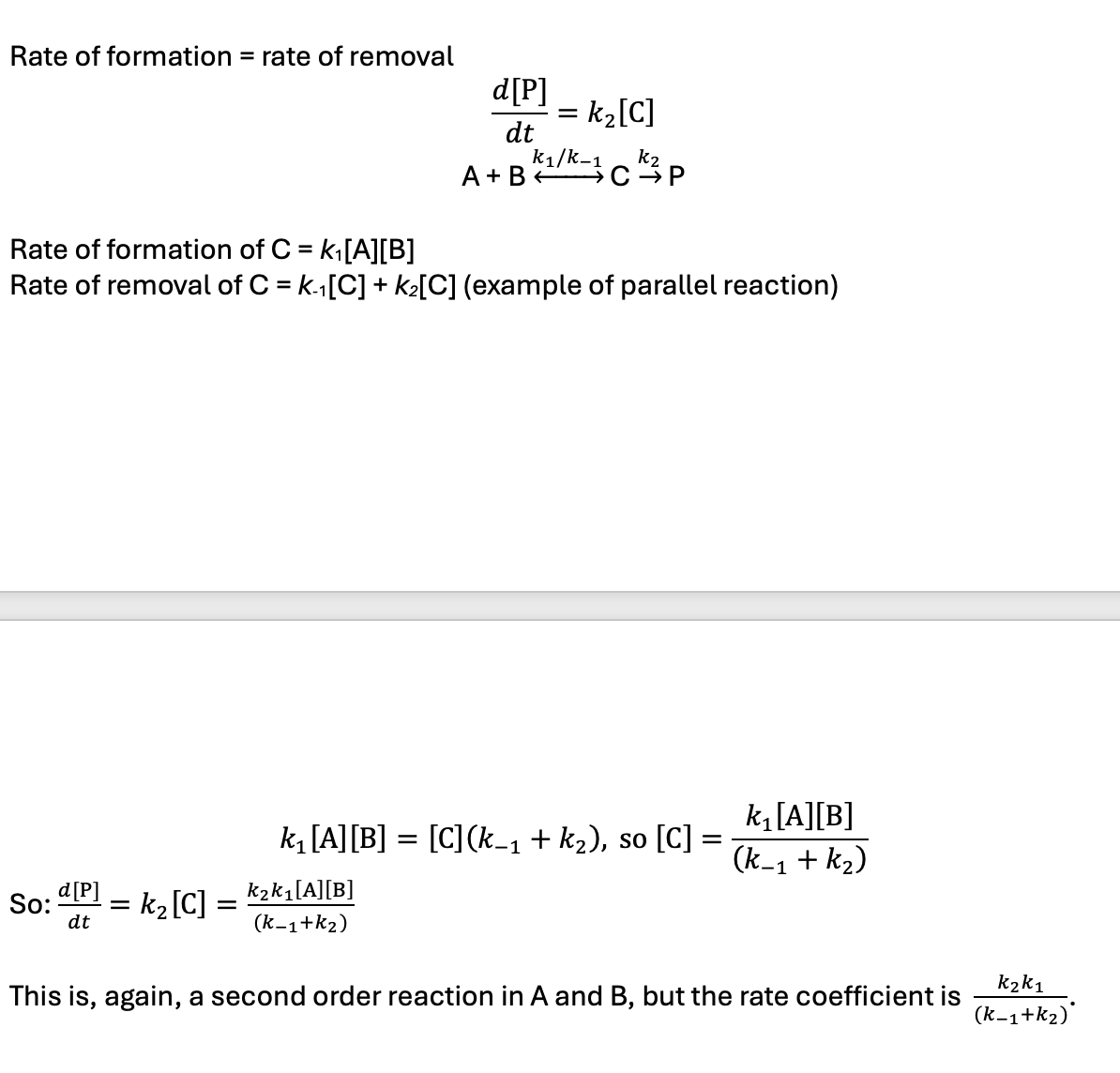
what is steady state hypothesis?
rate of formation = rate of removal of intermediate
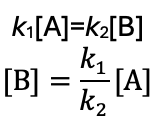
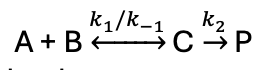
if k-1 >> k2 what happens?
what is the rate equation?
what order of reaction?
an equilibrium is established between A, B, and C
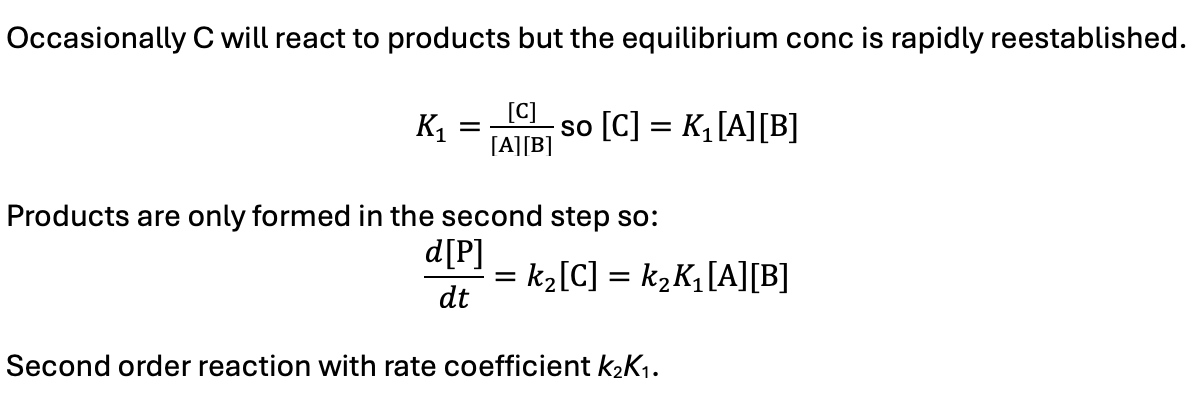
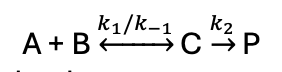
if k2 >> k-1 what happens?
what is the rate equation?
C is reactive intermediate (steady state hypothesis)
equilibrium not established as it reacts rapidly after it forms