physiology of women exam one
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Period poverty
Lack of money or access to menstrual hygiene products, 1 in 4 US students experience period poverty
puberty
transition from childhood to adulthood, puberty is not mensuration, it begins a year before mensuration occurs
when does puberty occur in females
8-13 but is happening earlier every year
what is menarche?
onset of menstrual periods influenced by genetic, social and economic factors, also influenced by 1. body fat(high and low body fat can delay menarche), 2. nutrition (must be healthy enough to support a regular cycle), 3. sleep
basal body temperature
-BBT
-temperature first thing in the morning Hormonal influence
-must be taken before any activity (basal=at rest)
-can be used as a way to track your cycle
Menstrual migraines
-occurs just before the onset of menstruation due to estrogen dropping
-more severe, last longer and often do not respond to medication
-attempts to prevent: avoid triggers, increasing phytoestrogens, and maintaining blood sugar levels
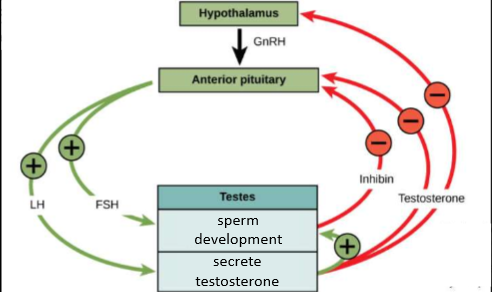
male reproductive cycle
-Equivalent to what is occurring in women just shorter
-LH—secrete testosterone—leading to sperm development and testosterone release
FSH- sperm development and the release of inhibin
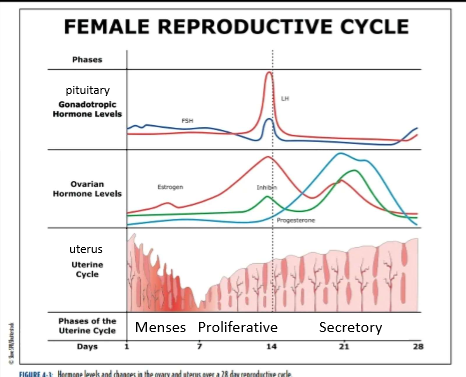
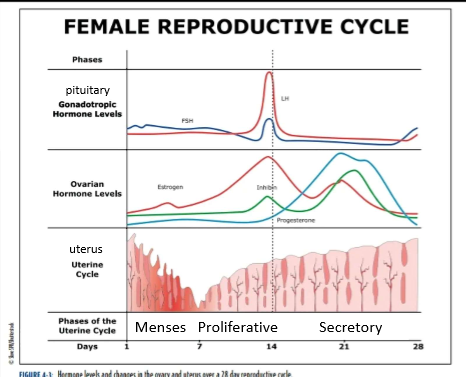
uterine cycle phase names
menses
proliferative
secretory
menses phase
days 1-7
low levels of estrogen and progesterone
lost of stratum functionalis layer (part of the endometrium that sheds) and blood
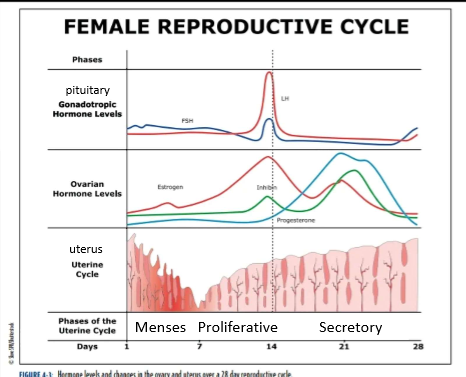
proliferative phase
days 8-14
estrogen stimulates the stratum functionalis to thicken
lining is being told to rebuild via estrogen
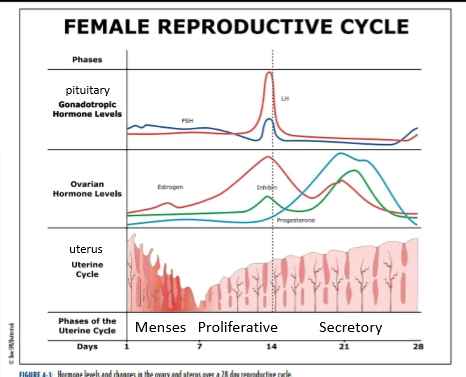
secretory phase
days 15-28
high levels of progesterone tells the stratum functionalis to thicken/dilation of glands
drop in estrogen and progesterone around day 21 induces stratum functionalis breakdown.
what is happening during the uterine (endometrial cycle)
the endometrium/stratum functionalis is thickening
the stratum functionalis layer is shedding (if the egg is not fertilized)
ovarian cycle phases
follicular
ovulation
luteal
Follicular phase
FSH induces follicular growth and secretion of estrogen
follicle secretes estrogen to promotes follicle development
days 1-13
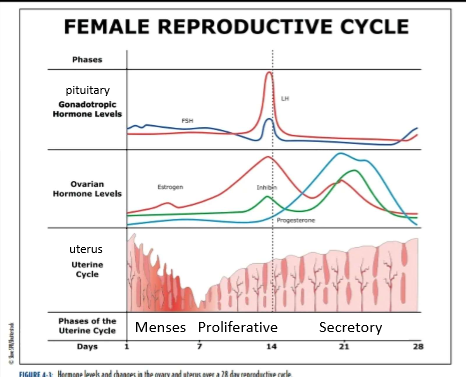
ovulation
day 14, only occurs on a single day
estrogen surge
LH surge
Secretion of progesterone begins
egg is released from ovary
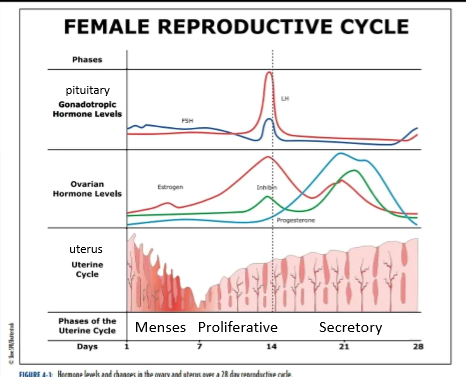
Luteral Phase
days 15-28
follicle, now the corpus ludium secretes both estrogen and progesterone
Progesterone secretion is higher
Hormone secretion drops around day 21 or 7 days after ovulation
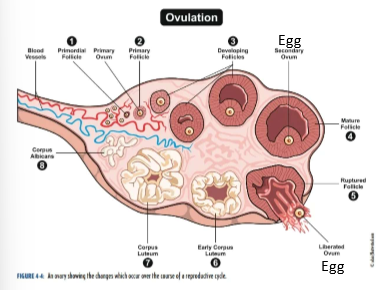
What is occurring in the ovary during the ovarian cycle? look at pic for steps
Steps 1-3
Primary follicle surrounds the egg and supports development
follicle releases estrogen
the follicle gets bigger as the egg develops
Step 4
continued development
follicle at its largest
Step 5
Egg is released from ovary and will enter to fallopian tube
Steps 6-7
follicle becomes the corpus luteum
releases both estrogen and progesterone but main hormone is progesterone
Step 8
becomes the corpus albicans and dies
Extras:
egg/ovum development and release-1 egg per month
Hormones are released-estrogen and progesterone
BPA
endocrine disruptor
can bind to both estrogen and testosterone receptors
linked to menstrual cycle irregularities, miscarriages, and breast, ovary, and prostate cancer
Endocrine Disruptors
Chemicals with similar structures to hormones
can bind to hormone receptors
activate or block hormone receptor activity
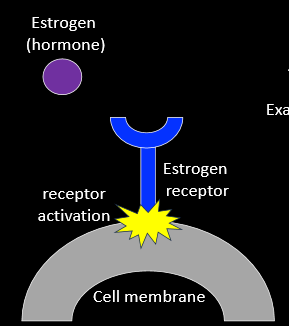
Hormones Activity
hormone binds to a receptor
activation of the receptor causes a response
i.e. uterus-thickening of lining
Androgen (Testosterone)
male characteristics
increase facial and body hair
reduce scalp hair
increase muscle mass
increase size/strength of skeleton
increase metabolic rate
increase red blood cells
Progesterone (Progestin)
uterus
prepares for implantation of embryo
cervical
thickens mucus
contractions during labor
breast tissue
tenderness
proliferation of milk glands during pregnancy
Estrogen (estradiol, estriol, estrone)
female characteristics
breast tissue
fat deposits
hips and back of arms
fat deposits
bones
increase growth
close epiphyseal plate
uterus
Thicken lining
cervical
thins mucus
bruising
increase strength of capillary walls
lower LDL “bad cholesterol levels
reduces livers metabolism of alcohol and drugs
Inhibits immune function
Reproductive sex hormones
female
estrogen(estradiol, estrdiol, estrone)
progesterone(progestin)
male
testosterone(androgen)
hormones of the menstrual cycle
Gonadotropic Hormones
Gonadotropic releasing hormone
GnRH
Luteinizing Hormone
LH
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
FSH
Reproductive Sex Hormones
estrogen
Progesterone
testosterone
Gonadotropic Hormones
controls secretion of reproductive hormones
Hypothalamus
GnRH
Pituitary Gland
FSH
LH
Endocrine System
hormones
Regulate body functions using hormones
organs/structures of the endocrine system
Brain:
hypothalamus and pituitary gland
make hormones
reproductive system:
ovary gland
an endocrine organ
when these three systems work together, they regulate the menstrual cycle
cycle
Series of events that are regularly repeated in the same order
the reproductive system
produces sex cells(sperm and eggs)
also known as gametes
fertilization through sexual intercourse
main job is fertilization and procreation
support growth and development of fetus(women only)
sex differentiation of reproductive organs
differentiation of sex organs does not occur until week 6 or 7 weeks of development
syr gene indicates male reproductive organs
lack of this will produce female reproductive organs
homologous structures in reproductive system
these structures are of the same origin
differ depending on if the person is male or female
ie- ovary and testes or clitoris and penis
gonads male versus female
homologous structures
male
testis
reproductive organ
produces sperm
produces testosterone
female
reproductive organ
produces egg/ovum
produces estrogen and progesterone
female gonad-ovary
produces egg
all a females eggs are present in the fetus and are depleted over time
actual number is debated
this is where the egg/ovum develops and is released during ovulation
fallopian tube and fimbria
fallopian tube
site of fertilization
fimbria
pull egg into fallopian tube
fallopian tube and fimbria are connected
egg will travel through fallopian tube to get to the uterus
uterus
location of menstruation and fetal development/growth
uterus gets bigger as development occurs
uterine layers
has three layers
endometrium
most inner layer
tissue that changes during mensuration, the part that sheds
myometrium
muscle
like this for labor/delivery
will shrink after birth because its very pliable
perimetrium
thin
covers muscle
just a membrane
cervix
connects uterus to vagina
opens only during ovulation and childbirth
a gateway between vagina and uterus
cervical mucus is normally thick but will thin during ovulation
body wants to prepare itself for fertilization
closed cervix + thick mucus= not ready for sperm
open cervix + thin mucus = ready for fertilization
vagina
internal muscular tube leading to the uterus
protective lining
low pH
normal flora/bacteria
low pH to protect from infections
anti-biotics can disrupt this
vaginal lubrication
secretions that coat the vagina
high distensibility
very stretchy—when not stretched, it will collapse on itself
entry for sperm
most vulnerable spot in the female reproductive tract because it is the entry from the outside
vulva
external genitalia
mons pubis
fatty tissue
clitoris
erectile tissue
labia
folds of skin
vestibule
area inside labia, has openings for vagina and urethra
pelvic floor muscles
muscles that support the bladder, uterus, vagina, and rectum
labor and delivery put a lot of stress on these muscles
they may not go back to 100%
pelvic floor exercises may help this-kegels
strengthen and ton these muscles
help improve urinary control, reduce incontinences and support pelvic health
gynecological exams
physical exams to look for infection, abnormal changes in reproductive systems
Palpitation of abdomen
Enlargement or tenderness
inspection of external genitalia
Inflammation or sores
inspection of vagina and cervix
infections or cancers
inspection of uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes
size, position, shape, position, sensitivity
inspection of breast tissue
palpation for abnormal growth
pap smear
samples of cervical cells
precancerous cells
cancer cells
human papillomavirus (HPV)
Recommended annually
prep for pap smear
do not have vaginal sex for two days before the exam
do not use tampons, vaginal creams, foams, jellies, lubricants, douches or medicines for two days before
schedule the apt. for after your period ends
testes/testicles
sperm develops in the testes
millions per day
Descend just before birth
located outside the body cavity
to lower temperature for sperm development
male reproductive system
accessory ducts
transport sperm outside the body
epididymus
vas deferens
urethra
Accessory glands
make fluid for semen
seminal vesicle
prostate gland
penis
organ for reproduction and urine elimination
intersex conditions
reproductive anatomy or physiology that do not match what is typically defined as female or male
gender affirming care
puberty blockers
hormone therapy
Surgeries
female v. male body stuctures
similar
same at the base level
differ in reproductive and organ systems
number of chromosomes
46
same number in men and women
differ between xx and xy(men)
half of chromosomes come from sperm and half come from egg
sperm determines sex
egg is always x
what is a chromosome
dna is packages into structures called chromosomes, which are kept in the nucleus of our cells
what is a gene
a segment of dna
set of instructions to build a protein
proteins have a job
Insulin
INS gene
instruction to make insulin protein
made by cells in the pancreas or the digestive system
releases when food is eaten and insulin tells the cells to take in sugar from the blood
keratin
KRT gene
instructions to make keratin proteins
these are found in hair, nails and skin
structural components
makes nails hard
skin is a barrier
hair growth
SYR gene
Instruction to make the protein called testis determining factor
gene only found on the y gene
when is sex defined
around 6-8 weeks of fetal development
reproductive organs are bipotential until this point
sex v. gender
sex
2 sexes
chromosomes
reproductive anatomy
hormones
gender
genetic sex
social influences
external expression and social perception
gender identity
internal sense and may not align with genetic sex assigned at birth
very specific to the individual
examples of homeostasis
sweating when running on a hot day triggers a thirst response
heart beating faster, breathing increase in order to pump blood to muscles to replenish
nervous system
components
brain
spinal cord
nerves
functions
communication in the body
senses
movement
cognition
reflexes
Nerves that extend out from spinal cord and brain
-work together for essentially everything in the body
-communication within the body that regulates the senses
-allows skeletal muscle movement
-cognition=learning, memory, language-->higher order functioning
-reflexes=tough something hot, your body reacts
endocrine system
components
endocrine glands
functions
regulate body functions through hormones
homeostasis
regulates body functions
hormones=proteins
each gland regulates the body through making hormones
pth and calcitonin
regulate bone density
growth hormone
regulates growth
adrenal gland
fight or flight response
regulate adrenaline
integumentary system
components
skin
hair
nails
functions
barrier to outside environment
touch
Absorption of sunlight to produce vitamin D
Skeletal system
components
bones
parts
collagen for flexibility
minerals for rigidity
exercise for bone health
weight-bearing and strength training to build and maintain density
loss of density = osteoporosis
constantly built and broke down through life
bone cells do both—oppose each other
functions
structural support
protection of organs
movement
with muscles
storage of minerals
storage of fat
makes blood
red blood cells carry oxygen through the body
important for energy
these cells die and must be replaced
bone marrow will make more
white blood cells
made in bone marrow
part of immune system
male v. female skeletal system
bone density is greater in males
females bone grow faster and stop growing earlier than males
earlier mensuration begins the earlier bones stop growing
female pelvis is wilder for childbirth
female femur angles inward
male brow bone ridges and jaw = more prominent
male bones are taller on average
muscular system
components and functions
cardiac muscles
heart contractions
smooth muscles
stretching and contracting
digestion
Skeletal muscles
movement
Muscle mass is greater in males
Cardiovascular system
components
heart
blood vessels
Coronary blood vessels
bring oxygen and nutrients to and remove waste from the heart
blood
functions
delivers oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells
removes waste from cells
cholesterol or blood clot can cause death of heart tissue that can cause a heart attack
women are protected from this due to estrogen
menopause stops results in loss of estrogen
heart attacks present different in women
whole body
heart pumps the blood
blood vessels distribute blood to body
all cells need energy to do their jobs, sugar will be circulated through blood
hormones are released in the endocrine glands and will travel through blood vessels to the designated area
blood picks up co2 that is made and brings it to the lungs to allow you to breath is out
your body cannot tolerate excess waste for an extended period of time
lymphatic/immune system
components
lymphatic vessels
lymph nodes
swell when fighting an infection
lymph fluid
immune cells
functions
fluid balance
fight infections
two systems work together
lymphatic system is a vessel that carries lymph, this is where white blood cells travel
immune system fight the infection but travel through the lymphatic system
respiratory system
components
nasal cavity
pharynx
larynx
trachea
lungs
function
move oxygen in
move carbon dioxide out
smell
digestive system
components
mouth
esophagus
stomach
intestines
liver
gall bladder
pancreas
functions
digestion and absorption of nutrients
one tube that goes from mouth, all the way down
take in nutrients your body needs to survive and fuel cells
urinary system
components
kidneys
bilateral
responsible for removal of waste
ureters
connect kidney to bladder
bladder
stores waste
urethra
exit
short in women= more prone to UTI
functions
removes waste through urine
balance fluids and electrolyes
contraception
prevention of pregnancy
prevent the sperm from reaching the egg
can be done by targeting hormones or anatomy
changes in vaginal canal
extends when women is aroused
normal
2-5 inches
aroused
5 - 8 inches
considerations when choosing a contraceptive method
safety
smokers have higher risk of blood clots when using hormonal method
effectiveness
amount of risk
lifestyle
partner cooperation
consistency
cost
reversibility
protection from STI
condoms and complete abstinence only
medical condition or medication interactions
theoretical v. use effectiveness
Percentages can be misleading because theoretical effectiveness versus use effectiveness
Theoretical is how effective it should be when used perfectly
Use effectiveness is effectiveness with average use, more real
continuous and periodic abstinence
cont.
avoiding intercourse
prevents STI
periodic
fertility awareness
abstain from sex during fertile times
ovulation timing
egg is viable for 72 hours
sperm is viable for 72-96 hours
24% pregnancies/yr
withdrawal
penis is withdrawn before ejaculation
avoid sperm entering vagina
first few drops of ejaculate contain most concentrated sperm
pre-ejaculatory fluid may contain sperm
22% pregnancies/ yr
spermicides
chemical inserted into the vagina near cervix
often not inserted high enough up
block movement/kill sperm
28% pregnancy per year
when the only contraception
often used as a secondary method
need to sit for 20-30 minutes before intercourse
only last a few hours
condoms
18-21 % failure rate
because
slipping
breaking
not being on right
rolling
leaking
all equal loss of physical barrier
Physical barrier
prevent STI
Diaphragms/ cervical cap
12 % failure rate
unique to each person
fitted by medical professional
use with spermicide
removed 6 hours after intercourse
sponges
12-24 % failure rate per year
similar to cervical cap
has spermicide in it
does not need to be fitted
oral contraceptive
the pill
1. combined
estrogen and progesterone
estrogen inhibits release of GnRH/LH/FSH
prevents egg development and ovulation
progestin thicken cervical mucus
progestin decreases thickness of endometrium
2. mini-pill
progesterone only
thicken cervical mucus
Decrease thickness of endometrium
can inhibit ovulation but not as consistent as combo pill
mothers must take this one bc combo pill will prohibit milk production
Menstruation occurs when taking placebo week
all are synthetic hormones
works because when there are too much of a hormone the body will stop making them
Constant hormones when taken at certain time
most effective when take at the same time everyday
9% failure rate every year
user error and fluctuation
side effects
blood clots
stroke
heart attack
high blood pressure
weight gain
migraines
gall stones
inflammation of gall bladder
implant
synthetic progesterone implanted in arm
slowly releases
Thicken cervical mucus
decrease thickness of endometrium
effective 1-7 year
1% failure rate
does not inhibit ovulation
injectable
synthetic progesterone
injected in arm or hip
thicken cervical mucus
decrease thickness of endometrium
effective for 3 months
6% failure rate
user
not staying on top of three month time span
injection
may not be distributed equally over the three months
patch
synthetic estrogen and progesterone
patch on skin
acts like combo pill
replaced every week
9% failure rate
vaginal ring
synthetic estrogen and progesterone
ring encircles the cervix
acts like combo pill
in place for 3 weeks, taken out for one
9% failure rate
IUD
hormonal
releases progesterone
thickens cervical mucus
inhibits thickening of endometrium
block sperm movement
may inhibit ovulation
2-3 effective
copper
non hormonal
releases copper
kills sperm
block sperm movement
effective for 12 years
less than 1% failure rate
acts as a partial barrier because of shape
male-gel application
hormonal
nesterone
testosterone and progestin
gel applied daily on shoulder and upper arms
inhibits production of sperm
still not at 0
in clinical trial
male—pill
non—hormonal
Blocks sperm production
in clinical trial
surgical sterilization
tubal ligation
cuts fallopian tube
less than 1% failure rate per year
non—reverable
makes it so the egg can’t get into the fallopian tube
menstruation can still occur because ovaries are still intact
surgical sterilization—male
vasectomy
less that 1% failure rate per year
much less invasive than women
blocks sperm from coming out
cuts vas deferens
reversible vasectomy
in clinical trail
gel is injected to the vas deferns
blocks sperm passage
last two years
emergency contraception
plan b
progesterone pill
inhibits ovulation when near that point in the cycle
changes thickness of lining
if taken within 72 hours = 89% effective
w/in 24 hours= percentage in the 90s
will not impact pregnancy if egg is already fertilized
is not an abortion pill but is still controversial
abortion
Pregnancy termination
overturn of Roe v. Wade gave rights to the states regarding abortion
Indiana
banned with few exceptions
rape
incest
mothers health
fetus not expected to survive pregnancy
Challenging to get bc proof and may not occur in timely manner
medical abortion
two pills
mifepristone
progesterone receptor blocker
even if fertizled egg is there, it can’t bind to anything and the lining will begin to break down
fetus is expelled with lining
prostaglandin
causes uterine contractions
expel contents of uterus
97% effective when taken within first 9 weeks
very early in pregnancy
contraceptive vaccines
vaccine stimulated the immune system to target sperm or reproductive hormones
anti-hCG vaccine
required for embryo implantation and growth
targets embryo—post fertilization===controversial
in-development, not yet in clinical trial
Comstock act
federal law the prohibits mailing obscene/dangerous items
contraceptives and abortion pills are deemed obscene
iffy because it is not always enforced
surgical abortion
surgical
cervix is dilated and the fetus is removed from the uterus
scraped out along with uterine linig
very controversial
what is female genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation is the partial or total removal of the external female genitalia. It can also be any injury to the female genital organs without medical reason.
List 2 reasons why FGM is a violation of the human rights of girls and women?
1. It is an act that further discriminates the sexes and promotes inequality between men and women.
2. It violates a person right to medical autonomy
What part(s) of the female genitalia are targeted in FGM?
Clitoral glans and clitoral hood
Labia minor
Vaginal opening(making it more narrow)
Are there any reported health benefits to FGM?
No