Session #2: Alginate Impression Material & Dental Stone
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is the purpose of impression materials
Used to make accurate replica of hard + soft oral tissues
Impression= negative reproduction of tissue
Dental stone/other material=positive cast
Impression vs. cast
Impression= carried to mouth in unset condition in tray & applied to area under tx
When set, it is then removed from mouth with tray
Cast= made by filling impression with dental stone/other model material
What is important for impressions
Accuracy, detail, quality of final replica= vv imp
Clinical impression technique & production of cast vary with each impression material
Desirable Qualities of impressions
Pleasant odor, taste, colour
Absence of toxic + irritant constituents
Adequate shelf life
Economically feasible with results obtained
Easy to use
Setting characteristics that meet clinical requirements
Satisfactory consistency + texture
Readily wets oral tissues
Elastic properties= easy removal + recovery
Adequate strength to prevent breaking/tearing upon removal
Dimensional stability over temp + humidity ranges
Compatibility with cast + die materials
Accuracy in clinical use
Readily disinfected w/out loss of accuracy
Impressions- Setting Mechanism
Irreversible
Most of the case
Reversible
Hydrocolloid
No longer acceptable bcs in past, reused material on clients
Impressions- Mechanical Properties
Elastic
Needs to be resilient, want it to be able to deform + take it out and retain its original dimensions after it is removed
Inelastic
What are some impression materials
Elastomeric materials: ***For high accuracy impressions, copies vv thin pits & fissures and gingival sulcus
Polysulfide
Polyether
Condensation silicone
Addition silicone
Hydrocolloids
Reversible
were available
Irreversible
typical alginate
Impression plaster
Impression compound
Zinc Oxide-Eugenol (ZOE) impression paste

Hydrocolloids
Reversible (Agar)
Gel/jelly type material
Physical change induced by temp
Irreversible (Alginate)
What are hydrocolloids
Substance that is microscopically dispersed uniformly throughout another substance
Tiny particles
Consist of 2 separate phases
Dispersed phase (powder)
Dispersion phase (water-hydrocolloid)
Size of colloid particles range from 1-20nm
Vv small particle = more reactive
Smaller also tend to form clusters-harder to mix
***Alginate= only one u use water for other pastes just hand mix
When taking impressions
What is the composition of alginate
Potassium alginate= dissolve in water + react with calcium ions
Calcium sulfate= react with potassium alginate to form insoluble calcium alginate gel
Sodium phosphate= react with calcium ions, provide WORKING TIME bfr gelation
Potassium titanium fluoride= counteract inhibiting effect of hydrocolloid on fluoride, silicates, borates setting on gypsum
Prevents fluoride, silicates, borates from preventing setting of hydrocolloid
Diatomaceous earth: control consistency of mixed alginate + flexibility of set impression
Zinc oxide: filler particles
Controlling setting time
Best regulated by amnt of retarder added during manufacturing process
Manufacturers make both fast setting (1.5-3 min) & normal setting alginate (3-4.5min)
Higher water temp-= shorter setting time
HEAT IS CATALYST FOR CHEMICAL RXNS
Mixing alginate
Pre-measure powder + water
Add + incorporate powder slowly to water
Avoid incoporating excessive air bubbles
Mix= vigorously + wipe against bowl
All powder must be incorporated
Critical Q: Why is it esp imp to add water to rubber mixing bowl bfr adding powder when mixing alginate impression material
Prevents Clumping:
If the powder is added first, water cannot evenly coat the particles, leading to dry clumps that are difficult to mix.
Ensures Even Hydration:
Pouring water first allows the alginate powder to gradually absorb moisture, leading to a smoother, more uniform mix without air pockets.
Minimizes Air Incorporation:
Adding powder on top of water reduces the chance of trapping air bubbles, which can cause inaccuracies in the impression.
Better Control Over Consistency:
It helps maintain the correct water-to-powder ratio, ensuring optimal working time, setting time, and strength of the final impression.
If done incorrectly (powder first), you may end up with grainy, uneven, or weak impressions that compromise accuracy.
Hand mixing vs. menchanical
Hand= fast set or regular set
Follow instructions precisely for mixing time
Smooth + creamy mixture that does not drip off
Clean handling devices (spatulas + rubber bowls)
Consistent
Mechanical mixing devices
Rotating mixture bowl
Mechanical mixer with time-control unit
Vacuum mixed for powder/water mixing
Dynamic mechanical mixer (for 2 paste alginate)
Convenience, speed, reduction of human error
Taking alginate impression
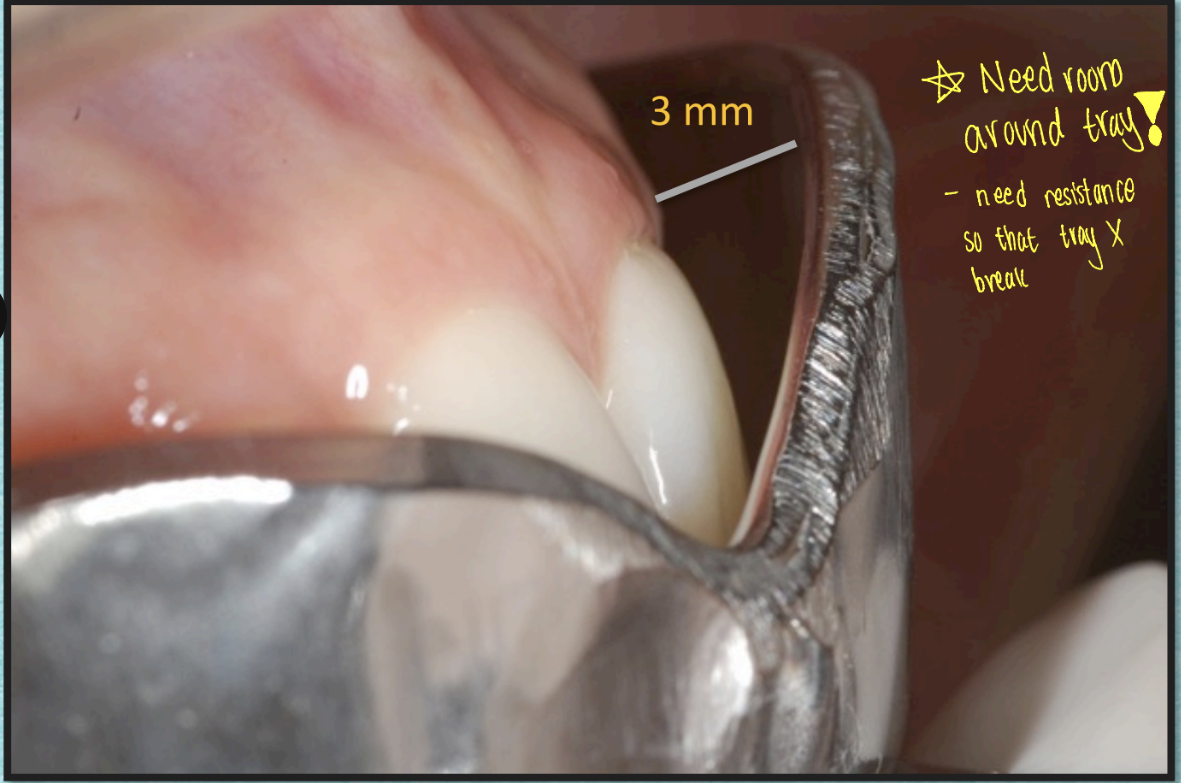
Alginate must be retained on tray
Perforated metal trays= preferred
Alginate tray adhesive (don’t rlly need)
Alginate= weak material
Thickness of alginate b/w tray + tissue ~3MM
Need to store alginate where there isn’t much moisture
Removing alginate impression
Wait 3 min after gelation
Remove along vertical path with snap
Avoid torquing or twisting impression
Break air seal with minimal handle
Alginate strength
Follow manufacturer direction
Deviation can have adverse effect on gel strength
Water/powder ratio
Insufficient spatulation
Overmixing
Alginate shelf life
Storage temperature
Moisture contamination
Individually sealed bags
Less chance of contamination
Correct water/powder ratio ensured
Alginate properties-Dimensional stability
Syneresis-shrinking of alginate in air
Imbibition-expansion of alginate immersed in water
Ideal: 100% relative humidity=best storage environment to preserve normal water content of impression
Cover in wet paper towel & seal in bag
If pouring impression must be delayed
Should be rinsed in tap water, disinfected, wrapped in wet paper towel, placed in sealed plastic bag
Critical Q: How can distortion of hydrocolloid impression be minimized during storage
1. Immediate Pouring (Best Practice)
Pour the impression as soon as possible (within 10–15 minutes) to prevent dimensional changes due to water loss (shrinkage) or absorption (swelling).
2. Proper Moist Storage (If Delayed Pouring is Needed)
Store the impression in a 100% humidity environment by:
Wrapping it in a damp (not soaking) paper towel
Placing it in a sealed plastic bag or a covered container
This prevents dehydration (shrinkage) and excessive water absorption (swelling).
3. Avoid Immersing in Water
Never store the impression submerged in water, as it will absorb water and expand (imbibition), leading to distortion.
Alginate properties-Compatibility with Gypsum
Alginate impressions produce
Insoluble calcium alginate - gypsum retarder
Sodium sulphate - gypsum retarder
Polysaccharide - gypsum retarder
***Gympsum retarder= chemical added to material to slow down rxn
Surface of gypsum models prepared from alginate
***gypsum models made from alginate impressions may have surfaces that are too weak or easily damaged, making them unsuitable for use as dies or working casts in dental procedures.
Excess water on alginate surface= rough stone
Dried alginate surface= adherence of surface to cast
Surface of alginate should be shiny but should have no visible water when pouring
Alginate properties-Disinfection
Rinse impression thoroughly
Disinfect on exposed surface
Wrap impression in disinfectant-soaked paper towel & place in sealed plastic bag for 10 minutes
Rinse & remove excess water
Disinfect quickly to prevent dimensional change
Current protocol
Household bleach (1-10 dilution)
Iodophors
Synthetic phenols
Alginate properties-Accuracy
Most alginate impressions not capable of reproducing finer details observed in impressions with other elastomeric impression materials
But alginate materials= sufficiently accurate to make impressions for removable partial dentures
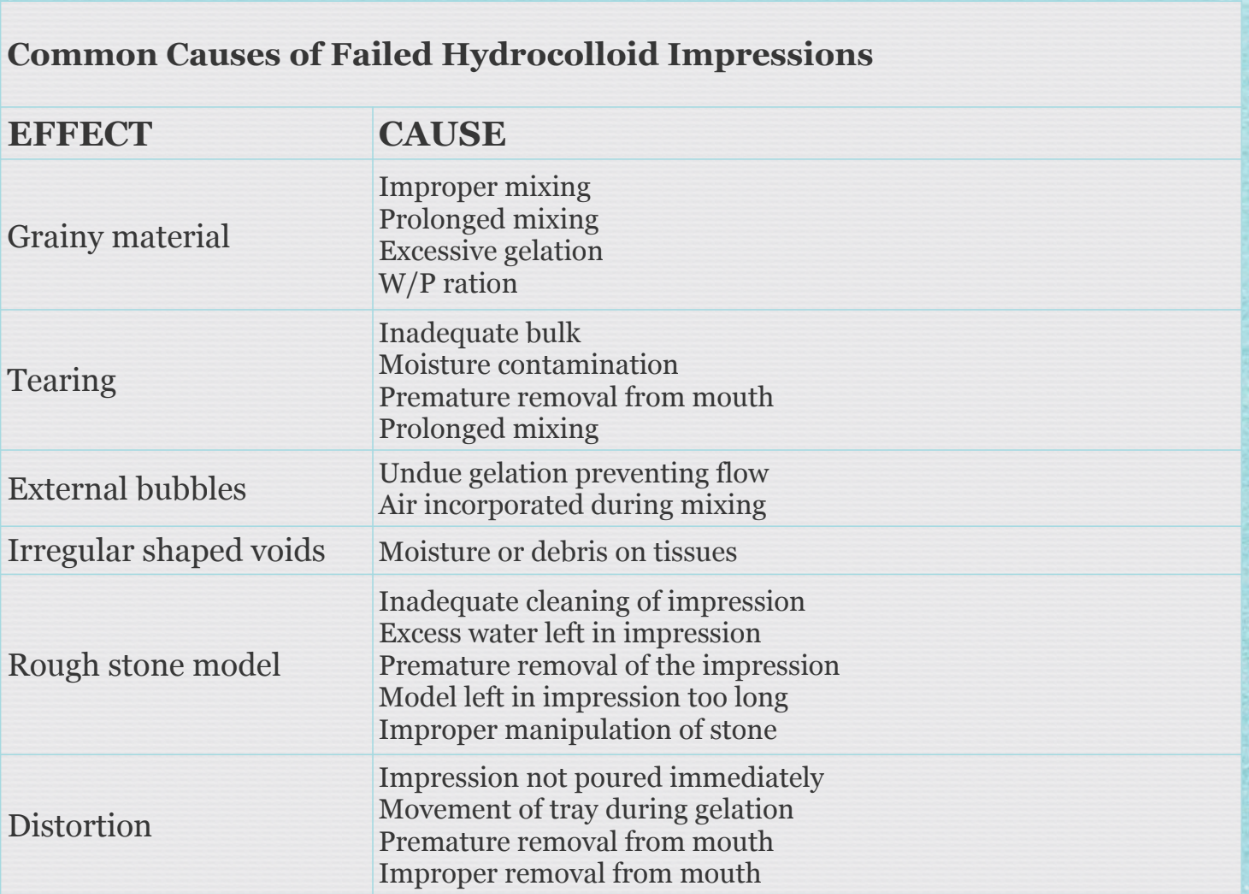
Alginate properties-Common cause of failed hydrocolloid impressions
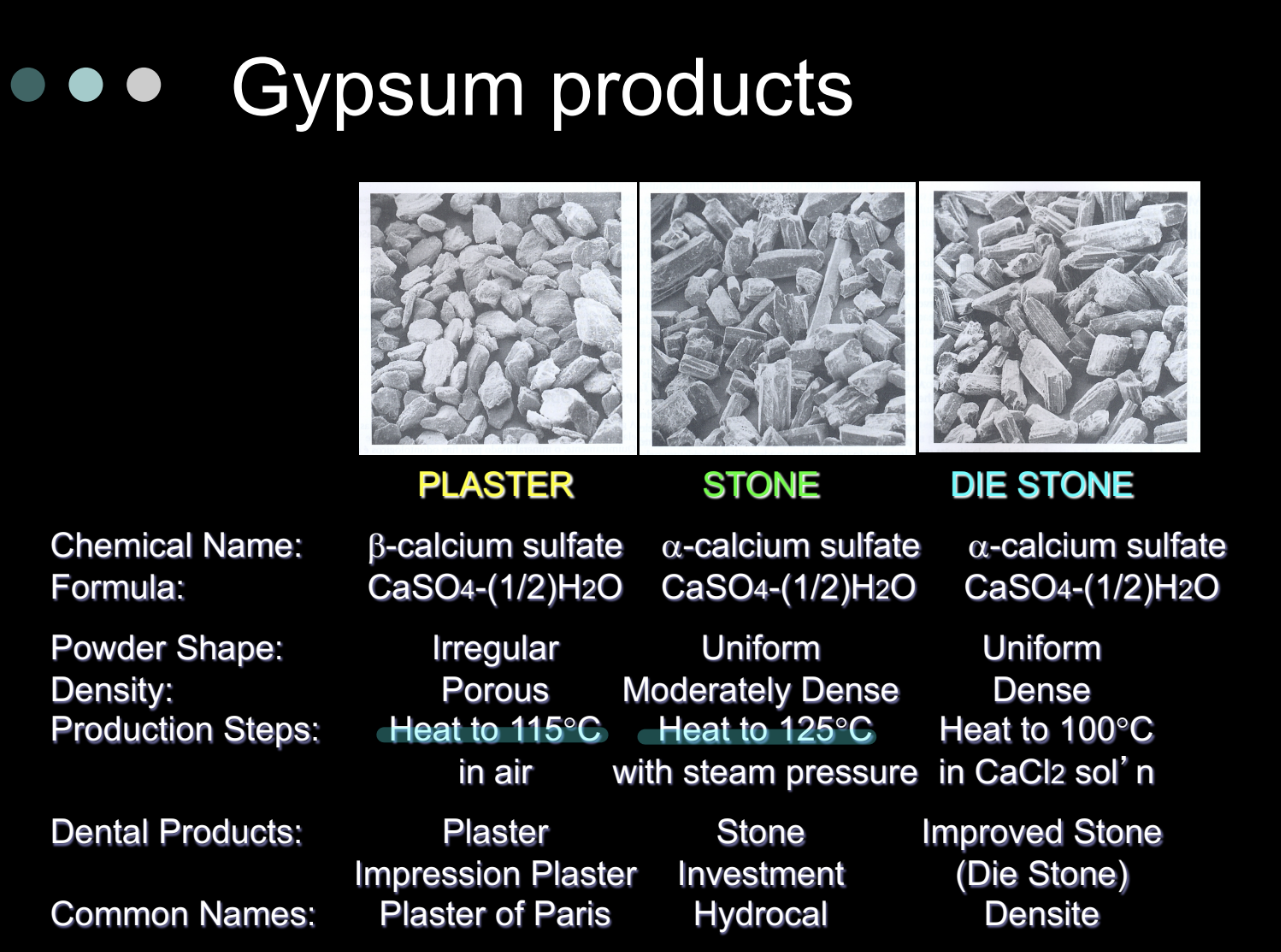
Gypsum products in dentistry
Plaster, stone (cast stone), improved stone (die stone), specialty stones, investment materials
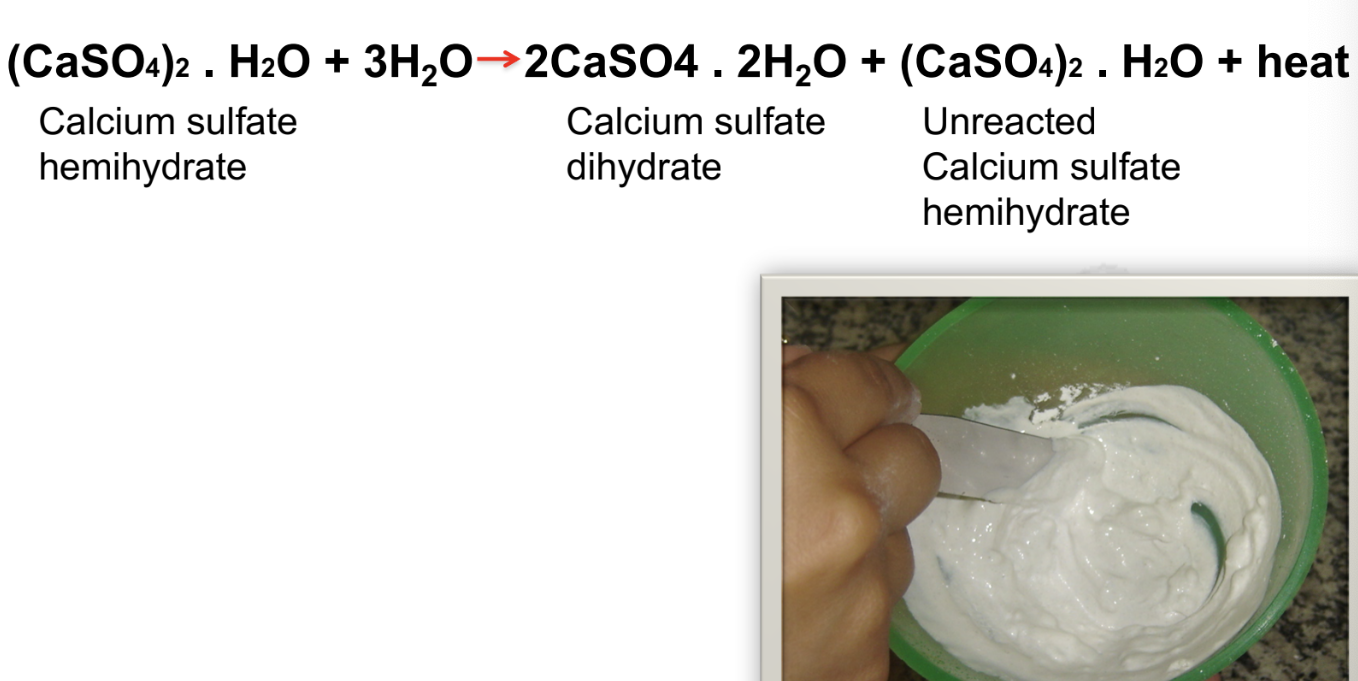
Gypsum = calcium sulphate, naturally occurs as dihydrate (CaSO4 & 2H2O)
What is calcination
Calcination=process of removing water of crystallization from calcium sulphate dihydrate
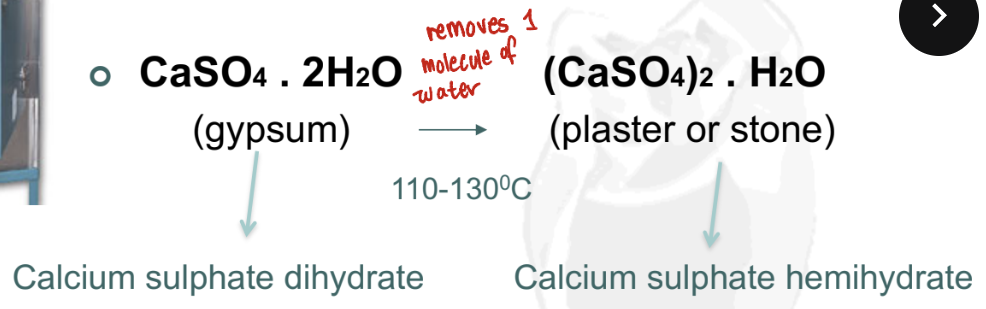
What is the setting mechanism of stone
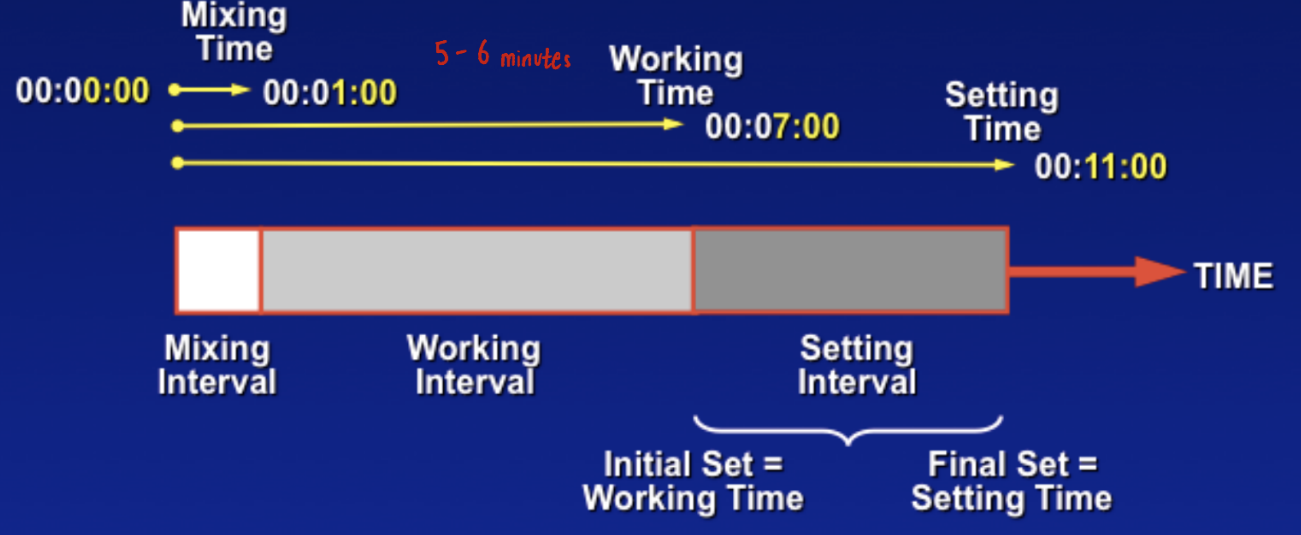
Mixing time, working time, setting time
What affects setting time
Water to plaster ratio vv imp
Higher ratio= longer setting time
Mixing time, longer mixing time= more speed + NRG applied, shorter setting time
Particle size
Smaller particles in powder = shorter setting time will be
Modifiers for controlling setting time
Accelerators
Potassium Sulfate (K2SO4)-max 3.4%
Slurry water (like if u use murky water with a lot of minerals, the particles will act as nuclei of crystallization-harden plaster)
Sodium chloride- [2%']
Retarders
Sodium borate (Na3BO4)
Sodium chloride (high [ ])
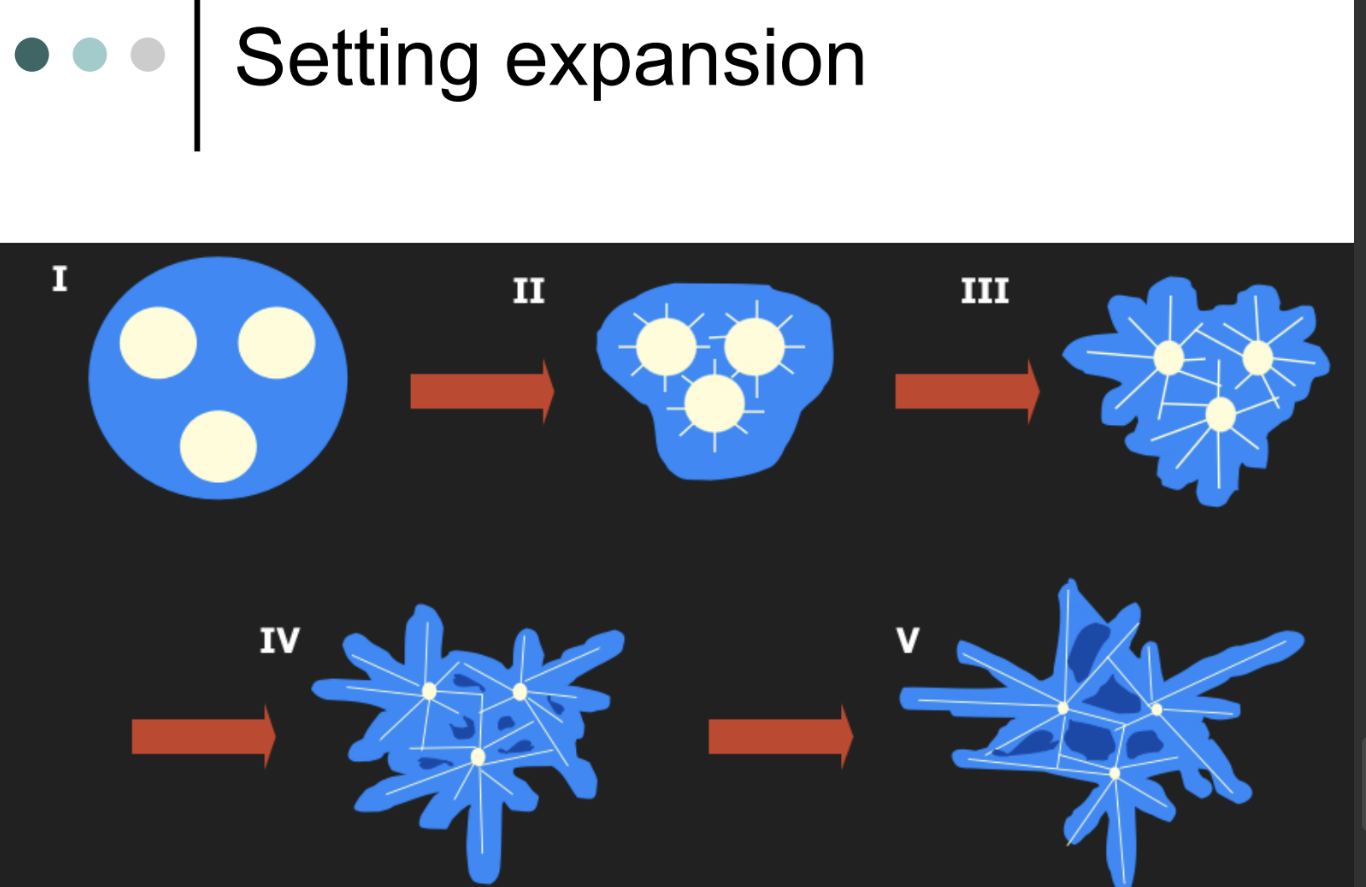
What does setting expansion look like
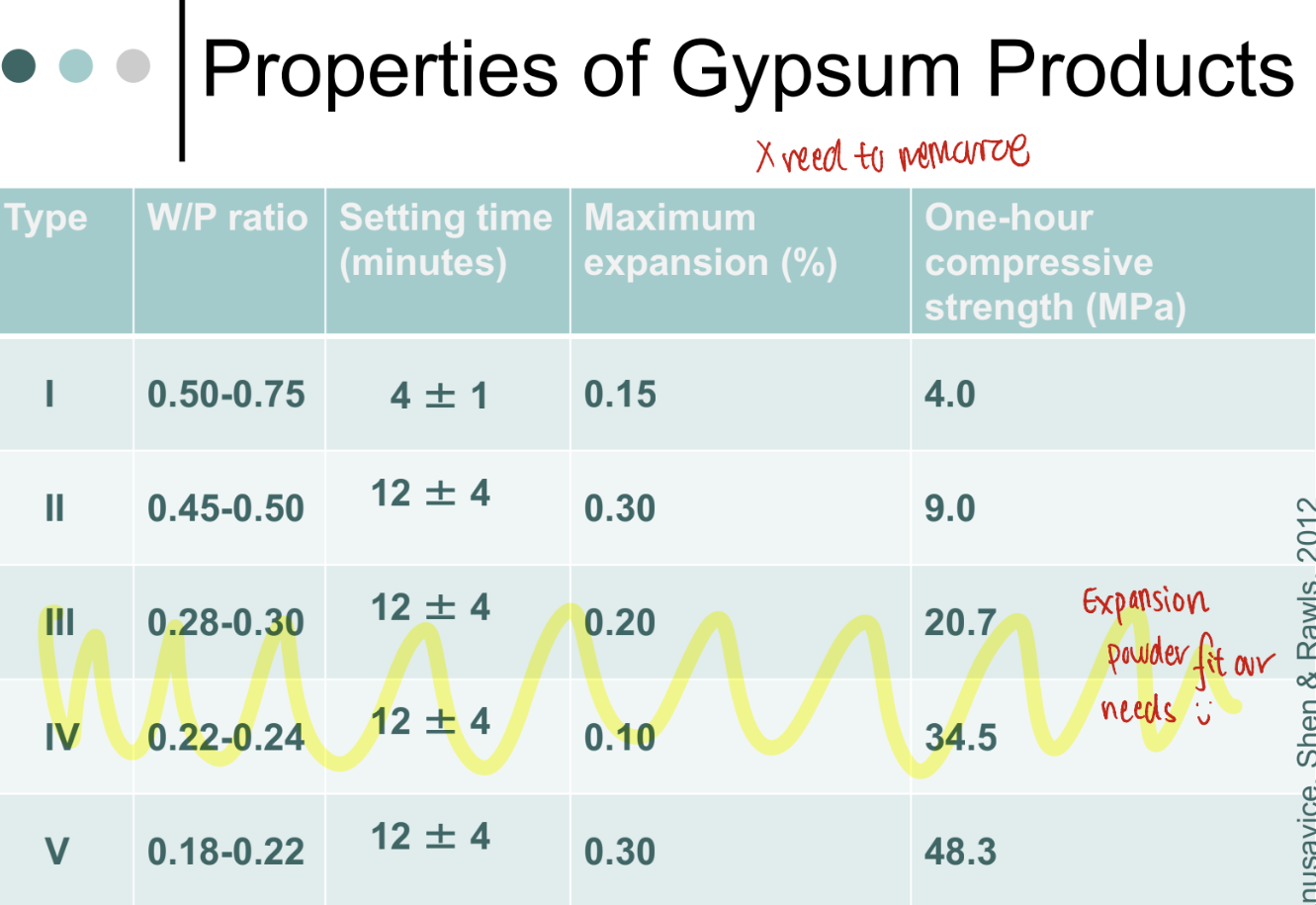
What are some factors that alter the strength of gypsum
W/P ratio
Mixing time
Accelerators + retarders
Types of gypsum products
Type I-Impression plaster
Type II-Model plaster
p weak
Type III-Dental stone
The ones we do
Type IV-Dental stone, high strength
Smaller particles
Type V-Dental stone, high strength, high expansion

How to mix gypusm products

Preparing the cast

How to care of gypsum products
Imp that all gypsum products be stored in DRY atmosphere
If relative humidity 70%+ —> plaster starts setting reaction
Few crystals produced act as nuclei of crystallization & accelerates the setting rxn
How to care of cast
Wait at least 40 min for removal
Avoid contact with water
Do not expose cast to temperature higher than 55 degre