Urine Microscopy Pics
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from Urinalysis and Body fluids Strasinger (2021) 7th edition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
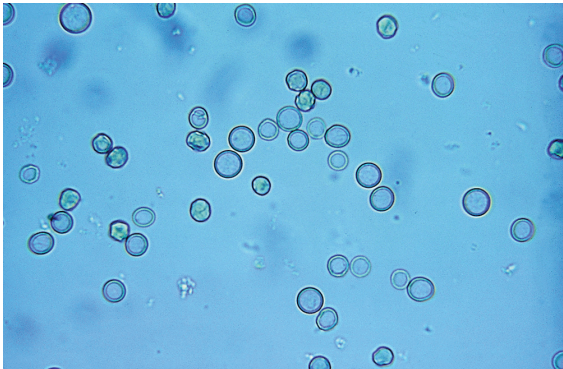
RBC in urine
Nonnucleated biconcave disks
Crenated in hypertonic urine
Ghost cells in hypotonic urine
Dysmorphic with glomerular membrane damage
Dysmorphic RBC in urine
Altered shape of red blood cells, often seen due to glomerular injury and indicative of renal pathology.
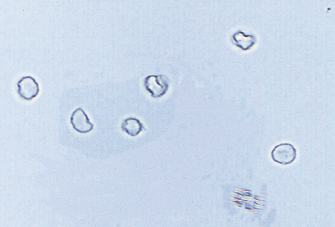
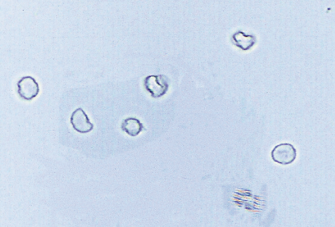
WBC in urine
Presence of white blood cells in urine, often indicating infection or inflammation in the urinary tract.
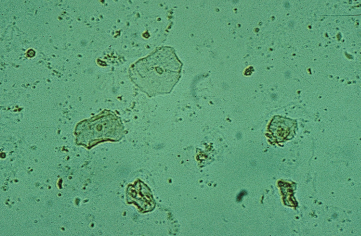
Squamous Epithelial cells in urine
Flat cells originating from the lining of the urinary tract, typically indicating contamination of the urine sample.
Transitional Epithelial Cells in urine
Cells that line the bladder and ureters, resembling cuboidal or columnar cells, often indicating bladder or urinary tract conditions.
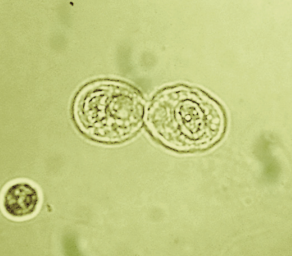
Renal Tubular Epithelial (RTE) Cells in urine
Cells derived from the renal tubules, often indicating kidney injury or disease.
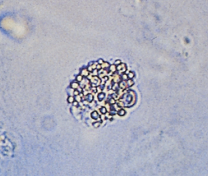
Oval Fat Bodies in urine
Lipid-laden renal tubular cells or free fat droplets, often associated with nephrotic syndrome.
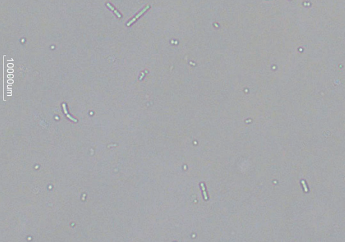
Bacteria in urine
Presence of bacteria in the urine, often indicating a urinary tract infection (UTI) or other infection in the urinary system.
Rod - Bacilli
Spherical - Cocci
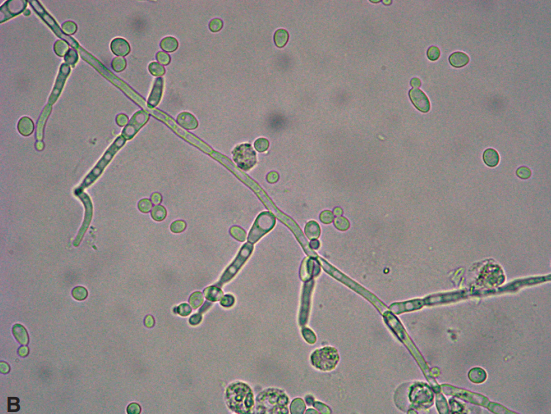
Yeast in Urine
Presence of yeast organisms in urine, commonly indicating a yeast infection or contamination.
Mycelial form - branching
Budding form - round
(often associated with Candida infections)
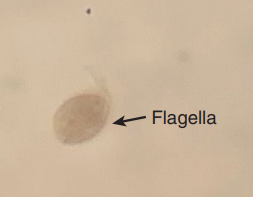
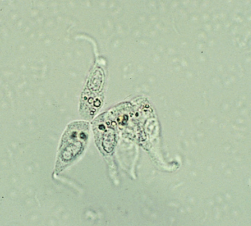
Trichomonas Vaginalis (T. vaginalis) in urine [parasite]
A protozoan parasite that can cause urinary tract infections and vaginitis, often identified through urine microscopy.
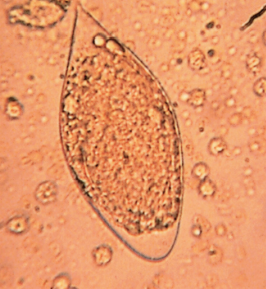
Schistosoma Haematobium (S. haematobium) in urine [parasite]
A parasitic worm that can cause hematuria and urinary tract infection, often found in urine samples. It is transmitted through contaminated water and can lead to serious complications if untreated.
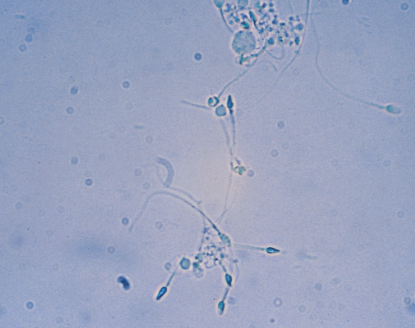
Spermatozoa in urine
The presence of sperm cells in urine, which can occur after ejaculation or due to retrograde ejaculation. Spermatozoa can indicate recent sexual activity or other reproductive health issues.
No clinical significance - reporting depends on lab protocols.
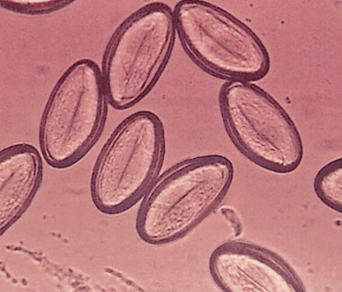
Enterobius Vermicularis (E. vermicularis) in urine [parasite]
A pinworm that primarily infects the intestines but may appear in urine samples, especially in cases of severe infection. It is transmitted through the fecal-oral route and is known for causing anal itching.
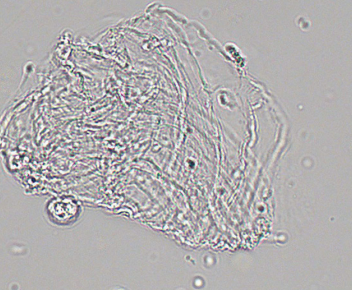
Mucus (clump) in urine
A gel-like substance that can appear in urine, often resulting from inflammation or irritation of the urinary tract. Mucus may indicate underlying conditions but can also be a normal finding.
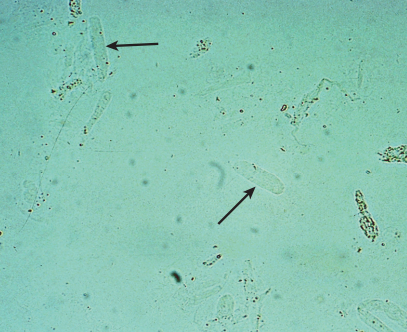
Hyaline Cast in urine
A type of urinary cast formed from the protein matrix, typically indicating concentrated urine or dehydration. Hyaline casts are often benign but can be associated with kidney conditions.
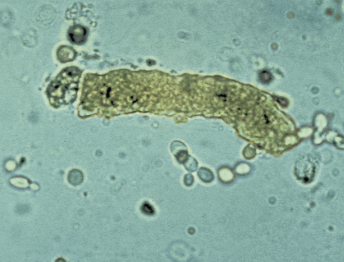
RBC cast in urine
A type of urinary cast that contains red blood cells, indicating possible kidney injury or glomerular damage. The presence of RBC casts often suggests conditions like glomerulonephritis.
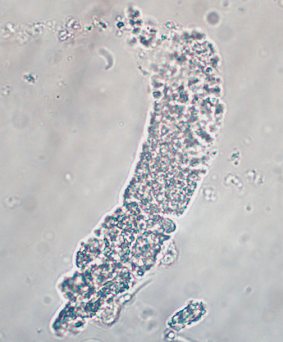
WBC cast in urine
A type of urinary cast that contains white blood cells, indicating inflammation or infection in the kidney, such as pyelonephritis or interstitial nephritis.
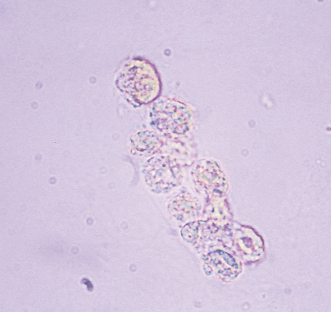
RTE cast in urine
A type of urinary cast made up of renal tubular epithelial cells, indicating tubular damage or injury. The presence of RTE casts often suggests conditions like acute tubular necrosis.
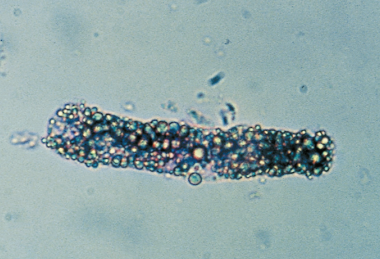
Fatty cast in urine
A type of urinary cast that contains lipids, typically seen in conditions such as nephrotic syndrome. Fatty casts are indicative of significant renal damage and proteinuria.
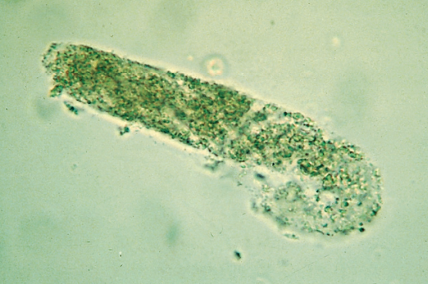
Granular cast in urine
A type of urinary cast composed of degenerated renal tubular cells or protein, often associated with various kidney diseases and conditions such as acute kidney injury.
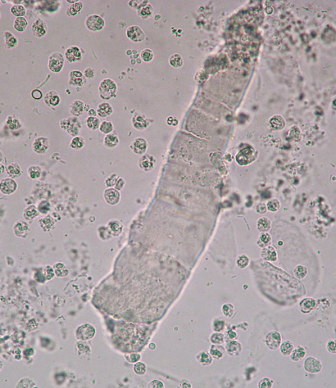
Waxy cast in urine
A type of urinary cast characterized by a smooth, waxy appearance, indicating advanced renal disease or chronic kidney dysfunction. Waxy casts are often seen in conditions such as chronic renal failure.
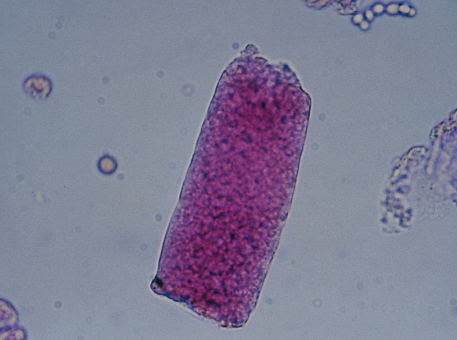
Broad cast in urine
A type of urinary cast that is wider than normal casts, often associated with severe kidney disease or renal failure. Broad casts indicate significant tubular damage and are commonly found in conditions such as chronic nephropathy.
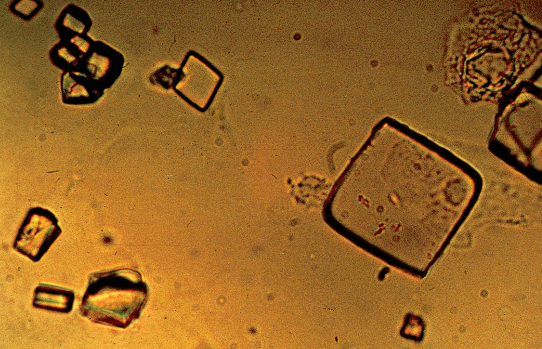
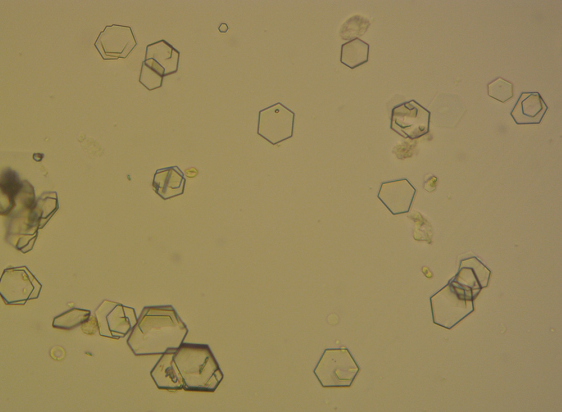
Uric Acid Crystal in urine
A type of crystal that forms in urine due to high uric acid levels, often associated with conditions like gout or dehydration. These crystals can vary in shape, commonly appearing as hexagonal or rhomboid shapes.
Acidic - Yellow-Brown Rosettes/Wedges
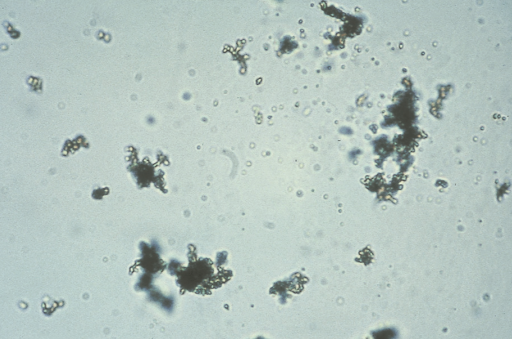
Amorphous Urate Crystals in urine
A type of urinary crystal formed from uric acid and its salts, often indicating excess uric acid in the urine. These crystals are usually found in acidic urine and can be associated with gout or metabolic disorders.
Acidic - Brick dust/Yellow Brown

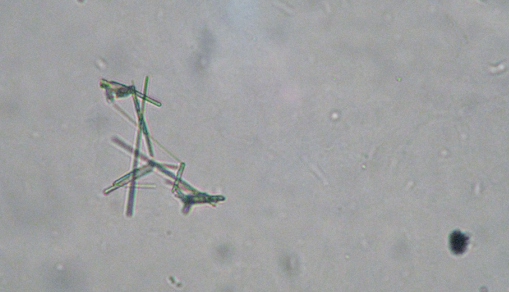
Sodium Urate Crystal in Urine
A type of crystal formed from sodium urate, commonly associated with hyperuricemia and conditions like gout. These crystals typically appear needle-shaped and are found in acidic urine.
Acidic - Colorless
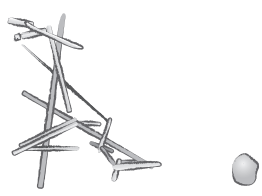
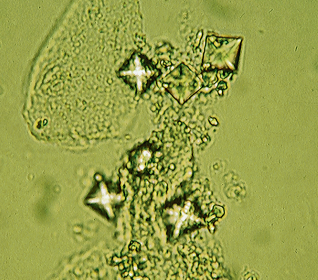
Calcium Oxalate Crystals in urine
A type of urinary crystal formed from calcium and oxalic acid, often indicating hypercalciuria or metabolic disorders. These crystals can appear as dumbbell-shaped or envelope-like structures and are typically found in acidic or neutral urine.
Acidic/Neutral - Colorless Envelopes/Ovals/Dumbbells
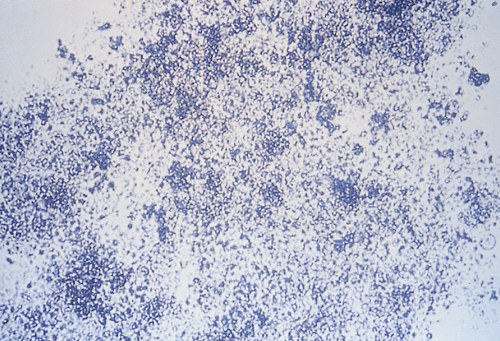
Amorphous Phosphate Crystals in Urine
A type of urinary crystal formed from phosphate compounds, often indicating alkaline urine. These crystals can appear as irregular shapes or granular deposits and are usually associated with urinary tract infections or other metabolic disorders.
Alkaline/Neutral - White-Colorless

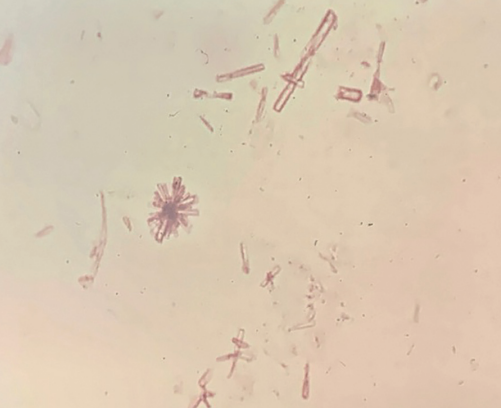
Calcium Phosphate Crystals in urine
Generally considered non-pathological and often present in the urine of healthy individuals, especially in alkaline urine.
Alkaline/Neutral - Colorless


Triple Phosphate Crystal in urine
Can be seen in healthy individuals with no clinical significance. Can be associated with urinary stones and UTI
Alkaline - Colorless “Coffin Lid”
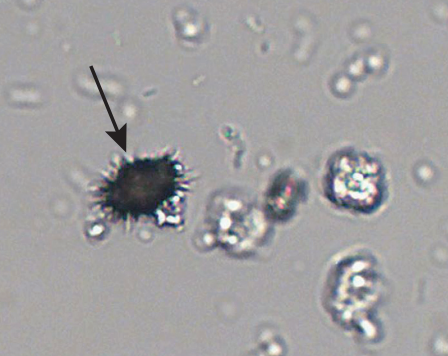
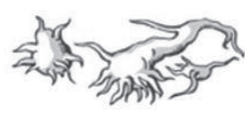
Ammonium Biurate Crystal in urine
Can be found in normal urine and are associated with renal stones
Alkaline - Yellow-brown “Thorny Apples”
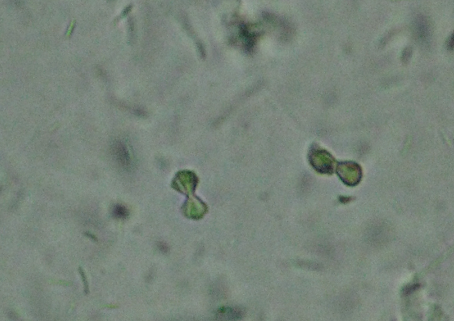
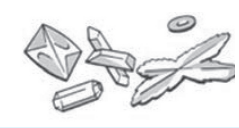
Calcium Carbonate Crystals in urine
No clinical significance
Alkaline - Colorless Dumbbells
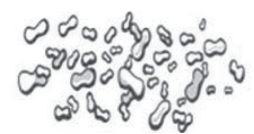

Cystine Crystals in urine
Clinically significant and indicate a metabolic hereditary disorder called cystinosis or cystinuria.
Acidic - Abnormal - Colorless Hexagonal Plates
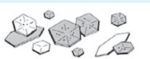

Cholesterol Crystals in urine
Can be seen in patients with nephrotic syndrome, chyluria, and disorders producing lipiduria.
Acidic - Abnormal - Colorless (notched Plates)
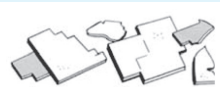
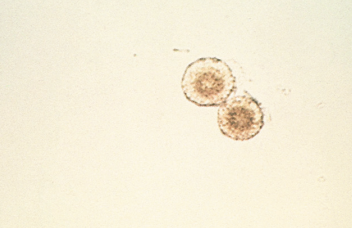
Leucine Crystals in urine
Can appear in patients with severe liver disease, terminal cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, and maple syrup disease
Acidic/Neutral - Abnormal - Yellow Concentric Circles
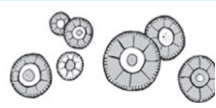

Tyrosine Crystal in urine
Associated with liver disease and with inherited disorders of amino acid metabolism
Acidic/Neutral - Abnormal - Colorless/Yellow needles


Bilirubin Crystal in urine
Associated with hepatic disease, producing large amounts of bilirubin
Acidic - Abnormal - Yellow (virus looking)

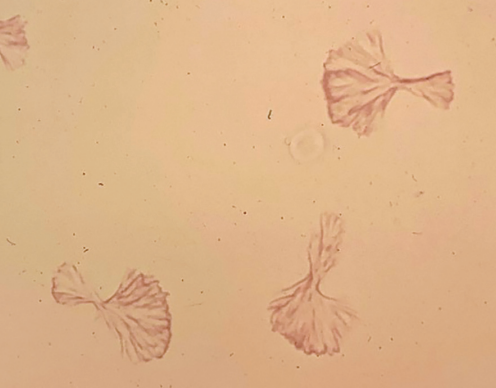
Sulfonimide Crystals in urine
Patients with UTIs are treated with sulfonamides
Acidic/Neutral - Abnormal - Varied (fan shaped)

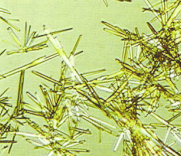
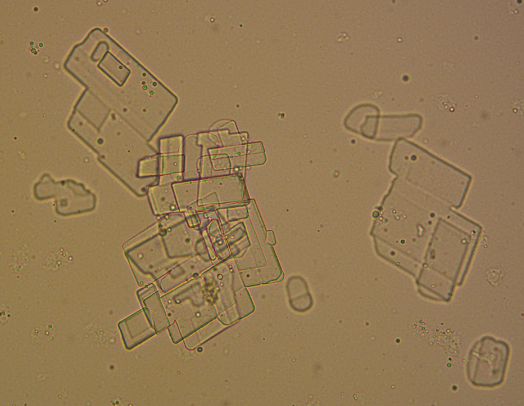
Radiographic Dye Crystals
Radiographic procedure.
Acidic - Abnormal - Colorless Flat Plates

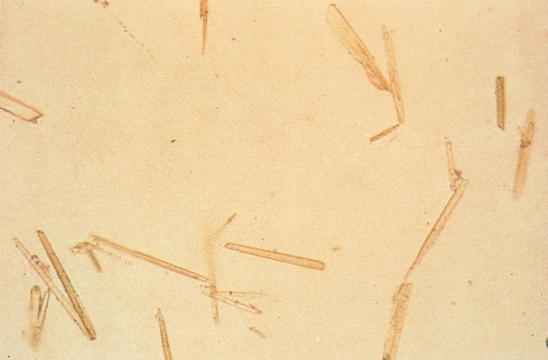
Ampicillin Crystals in urine
Indicative of large doses of ampicillin without adequate hydration (medication)
Acidic/Neutral - Abnormal - Colorless Needles

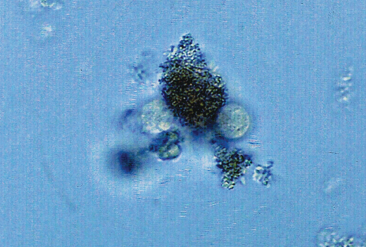
Feces w/ Oil droplets in urine
Contaminant/Artifact
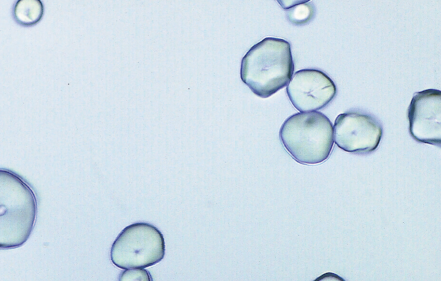
Starch Granules in urine
Contaminant/Artifact
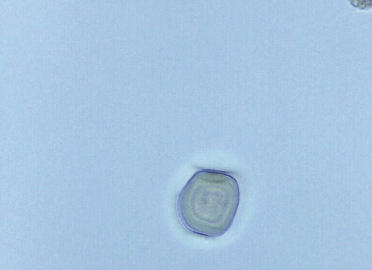
Pollen Granule in urine
Contaminant/Artifact
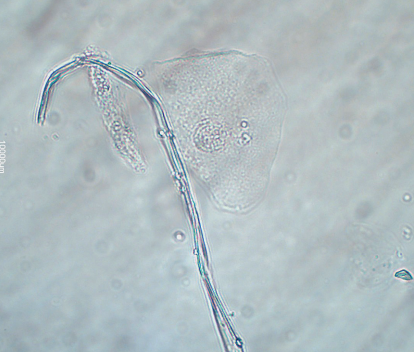
Fiber/Hair in urine
Contaminant/Artifact
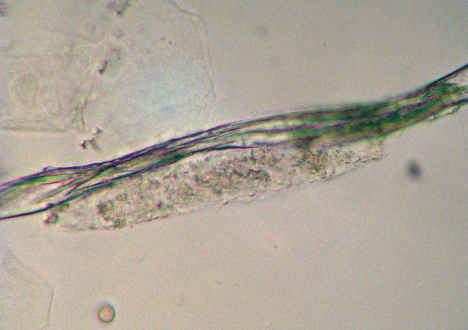
Vegetable Fiber in urine
Contaminant/Artifact
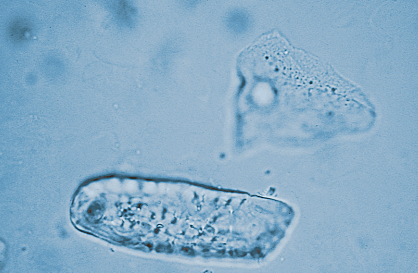
Diaper artifact in urine
Contaminant/Artifact