Microbiology Lab 4
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
it’s hard to focus on bacteria suspended in water AND it is hard to focus on extremely dense samples and they block the light
why are bacterial smears useful?
the bacteria deplete nutrients, toxic byproducts of metabolism build up, and there is a higher chance of contamination every time the plate is opened
why can’t we use the same nutrient broth culture or TSA plate all semester?
if the slide is still wet it can lead to lysis which destroys cell morphology
why does the slide have to be dried before heat fixing?
uses 2 stains - primary stain and a contrasting counter-stain
what is a differential stain?
1) Stain with crystal violet which is basic and has an affinity for peptidoglycan (stains all purple)
2) Cover with iodine which combines with the crystal violet to form a water-insoluble complex
3) wash with ethyl alcohol (decolorizer) which washes away the complex not bound in peptidoglycan
4) counter stain with safranin to re-stain the cells not stained after the decolorizer
explain the 4 steps of the gram stain
coarse adjustment
which part of the microscope quickly moves stage to focus?
fine adjustment
which part of the microscope moves the stage more slowly so you can get the exact focus?
10x magnification
how much magnification do the ocular lens add?
simple - use of single stain and useful for visualizing cell shape and arrangement
differential - use of 2 contrasting stains and useful for separation into groups and visualization of structures
simple vs differential staining
coccus

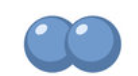
diplococci
tetrad

sarcina

staphylococci

streptococci
bacillus

diplobacilli

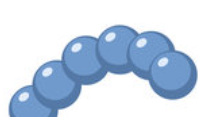
streptobacilli

palisades

coccobacilli

spirochetes

spirilla

vibrio

cell morphology - shape and arrangement
colony morphology - margin, color, size, elevation, and form
cell morphology vs colony morphology