Diagnosis and Management - OSCE 2024
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
What are the treatment options for eczema and give the order of when to use
1st line - emollients
2nd line - hydrocortisone (mild steroid)
3rd line - clobetasone (moderate steroid)
4th line - sedating antihistamine (if can't sleep)
describe emollient dosing
use regularly and liberally
describe hydrocortisone cream dosing
apply twice daily for a maximum of 7 days
describe clobetasone dosing
apply twice daily for a maximum of 7 days
what are the 1st and second line treatments for acne
1st line - benzoyl peroxide gel
2nd line - free derm gel
describe the dosing of benzoyl peroxide gel
apply once or twice daily to affected areas, avoid eyes
what is the extra information needed to be given with steroids
max 15g sold at a time, do NOT apply to face, genital area, broke or infected skin. Apply sparingly for a max of 7 days. Only use a pea sized amount for skin area the size of your hand.
what ages can you give hydrocortisone to
over 10s only
what ages can you give clobetasone to
over 12s only
what extra information needs to be given when giving benzoyl peroxide
can bleach hair, clothes etc
avoid the eye area
start very sparingly once a day, if irritation occurs be even more sparing, if skin can tolerate increase to twice a day
only pea sized amount needed
describe the dosing of free derm
use twice daily to affected areas
what are the first and second line treatment options for fungal infections
clotrimazole
terbinafine cream (laminal)
what ages can you use either clotrimazole or terbinafine cream on?
over 16s only
describe the dosing of clotrimazole
apply two to three times daily, normally for 2 weeks and then another 1-2 weeks after the lesion heals
describe the dosing or terbinafine
apply once daily fir 7 days only
what are the first and second line treatment options for athletes foot infections and groin (which can be used for what?)
1st line - tolnafate (foot and groin)
2nd line - undecenoates (foot only)
describe the dosing for both tolfanate and undecenoates
apply twice daily and continued for atleast 7 days after the lesion heals
describe the history taking needed for eczema
onset, where is it / how severe
recent travel?
occupational factors?
family/ household contract factors
When to refer eczema?
widespread/severe
secondary infection
pomphyolyx (fluid filed vesicles on hands)
facial lesions unresponsive to emollients
under 10s needing steroids
when to refer fungal infections?
on scalp
athletes foot in diabetics
what advice should you give to people with fungal infections?
wash affected area daily and carefully pat dry
what are the first, second and third line treatments for constipation
1st line - lifestyle advice
2nd line - bulk forming laxatives (Fybogel)
3rd line - Osmotic laxative (lactulose, macrogol sachets)
what additional information should be given for fybogel?
increase fluid intake
Up to 72 hours for effect
Contra in analgesics
continue until stools soften without straining 3x a week
what additional info should be given for lactulose/macrogol?
up to 48hrs for effect, lots of water!! continue treatment until stools soften without straining 3 times per week
if a child under 12 presents with constipation, what is the barrier to giving treatment
they need a prescription
what are the 1st and 2nd line options for treating diarrhoea
1st - oral rehydration (dioralyte)
2nd - Anti-motility drugs (loperamide or pesto bismol)
what age is pepto biysmol liscened for
over 16s only
what are the flavour options for dioralyte?
blackcurrant, citrus, plain
describe the dosing for dioralyte
1 or 2 sachets dissolved in 200-400ml water
describe the dosing for loperamide
2 capsules straight away followed by 1 after every loose bowel movement for a maximum of 8 in 24hrs
describe the dosing for peptobismol
30ml in dosing cup, take every 30mins to 1hr if needed - max of 8 in 24hrs
what are the treatment options for haemorrhoids
Germoloids (lidocaine) or Anusol plus HC (hydrocortisone)
who can hydrocortisone be used for
only over18s- can't be used in pregnancy
describe the dosing of germoloids
apply twice a day and after a bowel movement
describe the dosing of anusol plus HC
apply twice a day and after bowel movement, maximum of 4 times a day for 1 week
describe the 1st and 2nd line treatment options for IBS
1st line - hyoscine (buscopan IBS relief)
2nd line - meberverine (colofac IBS relief)
describe the side effects of buscopan (hyoscine)
dry mouth, constipation
what are the treatment options of mild dyspepsia
rennies (calcium and magnesium carbonates - antacids)
what are the side effects of magnesium salts and aluminium salts
magnesium can cause diarrhoea but aluminium can cause consipation
how do alginates work?
by forming a gel-like raft on top of stomach contents, preventing acid reflux
what are the 1st and 2nd line treatment options for heartburn
1.gaviscon (alginates)
2. PPI- omeprazole , esomeprazole etc
what can be taken alongside gaviscon for heartburn
Antacids
how long should treatment with PPI last?
no longer than 2 weeks if symptoms don't improve, max 4 weeks OTC treatment, see GP if symptoms reoccur after treatment
vomiting associated with gastroenteritis (stomach bug)
oral rehydration therapy (dioralyte)
what should be considered when giving dioralyte for vomiting
can the fluids even be tolerated?
what are the treatment options for migraine related nausea and vomiting? and what is the route of administration? and what age?
Prochloperazine buccal tablets (high in the top lip) over 18s only
what are the 1st and 2nd line treatment options for travel sickness
1st line -antihistamines (cinnarzine, promethazine)
2nd line - anticholinergics (hyoscine)
what ages are the antihistamines liscenced for?
adults only
what are the treatment options for mouth ulcers?
Not in any order
1. chlorhexidine mouth wash
2. Choline salicylate (bonjela)
3. lidocaine gel
3. hydrocortisone oromucosal tablet
what needs to be noted about the hydrocortisone tablet
should not be sucked, allow to dissolve close to ulcer
what needs to be noted about the bonjela get
dont use more than once every 3 hours
what is the pneumonic for red flags in constiption?
ALARM
Anaemia
Loss of weight
Anorexia
Recent onset of symptoms
Malaenia (blood in poo)
what are the red flag symptoms for diarrhoea
blood in stool
unable to drink fluids, dehydration associated vomiting
tiredness, weakness, dry mouth, sunken eyes, decreased utine output, thirst
weight loss
recent hospital stay or antibiotics use (CDIFF)
diarrhoea referral symptoms
recent foreign travel + presence of foul smelling, watery discharge
recent or sudden change in bowel habit
failed treatment
symptoms longer than 2-3 days in children or elderly
medicine induced
lifestyle advice for diarrhoea
plenty of clear fluids
avoid very sugary drinks
avoid milk and milky drinks
eat depending on appetite
careful hygiene
haemorrhoids referral symptoms
blood in stools
3rd or 4th degree harmorrhoids
persistent and/or sudden change in bowel habit
severe pain/stabbing / sharp pain with defecation
symptoms taht dont resolve within 7 days
haemorrhoids advice
avoid constipation (lots of fibre and water)
anal hygiene
dont ignore the call
avoid straining
positioning
haemorrhoids red flag referrals
unexplained weight loss
rectal bleeding
recent change in bowel habit
persistent bloating in females over 50
symptoms with family history of bowel cancer
patients with NO HISTORY IBD
haemorrhoids lifestyle advice
-any trigger foods to avoid?
-any stress or physiological changes that could have caused?
- avoid missing meals , have regular meals
-atleast 8 cups of fluid per day
-avoid fizzy drinks
-high fibre foods + greens
-daily oats, limit fruit to 3 x day
what are the risk factors for dyspepsia
pregnancy, medicines such asCCBS, steroids, smoking, overweight, family history
dyspepsia red flags
anaemia, coffee ground vomiting
loss of weight unexplained
anorexia
recent set of progressive and recurrent symptoms - including change in bowel habit
melena
abdominal or bacl pain with weight loss
what timeline should you refer dyspsia when treating
when treatment failed in 7-14 days
referral symptoms nausea and vomiting
-severe abdominal pain
-dehydration
-blood in vomit
-recurrent symptoms - can't keep fluids down -refer the same day if sick one or twice a days for 2 days , refer kids in 24 hrs , in neonates, refer any vomiting
-pregnancy
what are the possible causes of mouth ulcers?
stress
trauma
nutritional deficiencies
food sensitivities
questions to ask about ulcers
-how many do you have, one larger or smaller individual
-where are the ulcers? side, tongue, side of lips or near back of mouth?
-shape - small or big
-painful?
-any recently prescribed drugs or recent dose increases, cytotoxic drugs (imunosuprresors), NSAIDs, beta blockers
-can you think of a cause, trauma?, born from food? biting lip?
referral symptoms mouth ulcers
a single lesion lasting longer than 3 weeks (potential oral cancer)
larger than 1cm
crops of 5-10 or more, duration, painless ulcers
multiple size involvement
advice for mouth ulcers
-avoid cause (if known)
-decrease levels of house dust mites
-avoid drying soaps
-avoid perfumed toiletries
-avoid abrasive clothing
-sunshine
describe the questions to ask when history taking for acne
-duration, type and distribution of lesions
-previous treatment and response
-factors that may contribute to exacerbations
-physiological impact of acne- anxiety, low mood
-family history
when to refer for acne
moderate or severe with risk of scarring
occupational/ drug induced acne
OTC treatment failure after 2 months
Rosacea
advice for acne
-can take 8-12 weeks for improvement
-wash area carefully before application of treatment
-stress can make acne worse
-sunlight helps
-avoid greasy heavy moisturisers/ makeup
-avoid squeezing spots
what are 1st and 2nd line treatment options for bacterial conjunctivitis
1st line - self help (keeping it clean + hot compress)
2nd line - chloramphenicol
what are the dosing instructions for chloramphenicol eye drops and ointment
eye drops - STORE IN FRIDGE
-1 drop every 2 hours for 48 hours then 1 drop every 4 hours (max of 5 days treatment0
-chloramphenicol ointment (can make vision a bit blurry as oil) apply 3-4 times daily or once at night (at night recommended)
DONT USE CONTACT LENSES
when should you avoid chloramphenicol
under 2 years
avoid in pregnancy or breastfeeding
avoid If history of breast-feeding or bone marrow problems
what are the 1st and 2nd line treatment options for allergic conjunctivitis
1.self help (cold compress - cold wet towel) + sodium cromoglycate eye drops (opticrom allergy)
2.Otrivine antistin (combo)
DONT USE CONTACT LENSES
when should you use sodium cromoglycate
use continuously when exposed to allergen
when shouldn't u use otrivine antistine
avoid in patients with glaucoma and only use short term as rebound effects
what is the 1st line treatment option for dry eyes
hypromellose
what are eye red flags?
-pupils, irregular shape, non responsive to light (A&E) cloudy pupil
-iris (coloured part of eye) if red
-pain
-foreign body
-clouded cornea
-distortion of vision
-photophobia
-vomiting
describe the symptoms of conjunctivitis
-junk in corner of eye
-eye is crusted when you wake up
-both eyes infected but one eye before the other
-no other symptoms
self help for bacterial conjunctivitis
-bathe eyelids with lukewarm water / saline to remove any discharge
-use tissues to wipe eye and then discard
-avoid contact lenses
-wash hands, avoid sharing towels, good hygiene
symptoms of viral conjunctivitis
more likely just one affected eye
generalised redness
maybe associated symptoms of cough or cold
self help for allergic conjunctivitis
cold compress
avoid allergen
avoid rubbing eye
consider artificial tears
describe a sub conjunctival haemorrhage
red eye, from falling over or damage to eye, heals by itself
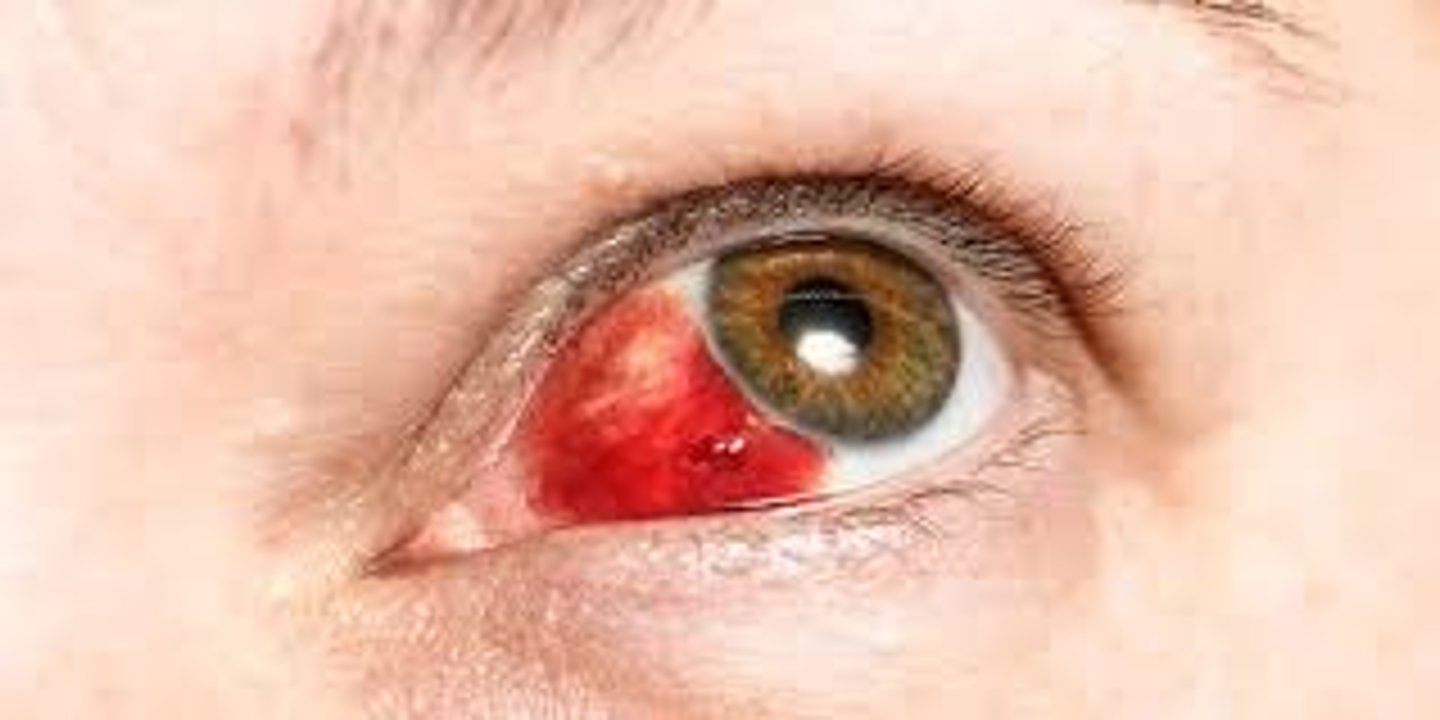
describe management of a subconjunctival haemorrhage
refer if there is any pain or photophobia or any vision problems, otherwise it is fine to leave, reassure patient
describe what episcleritis looks like
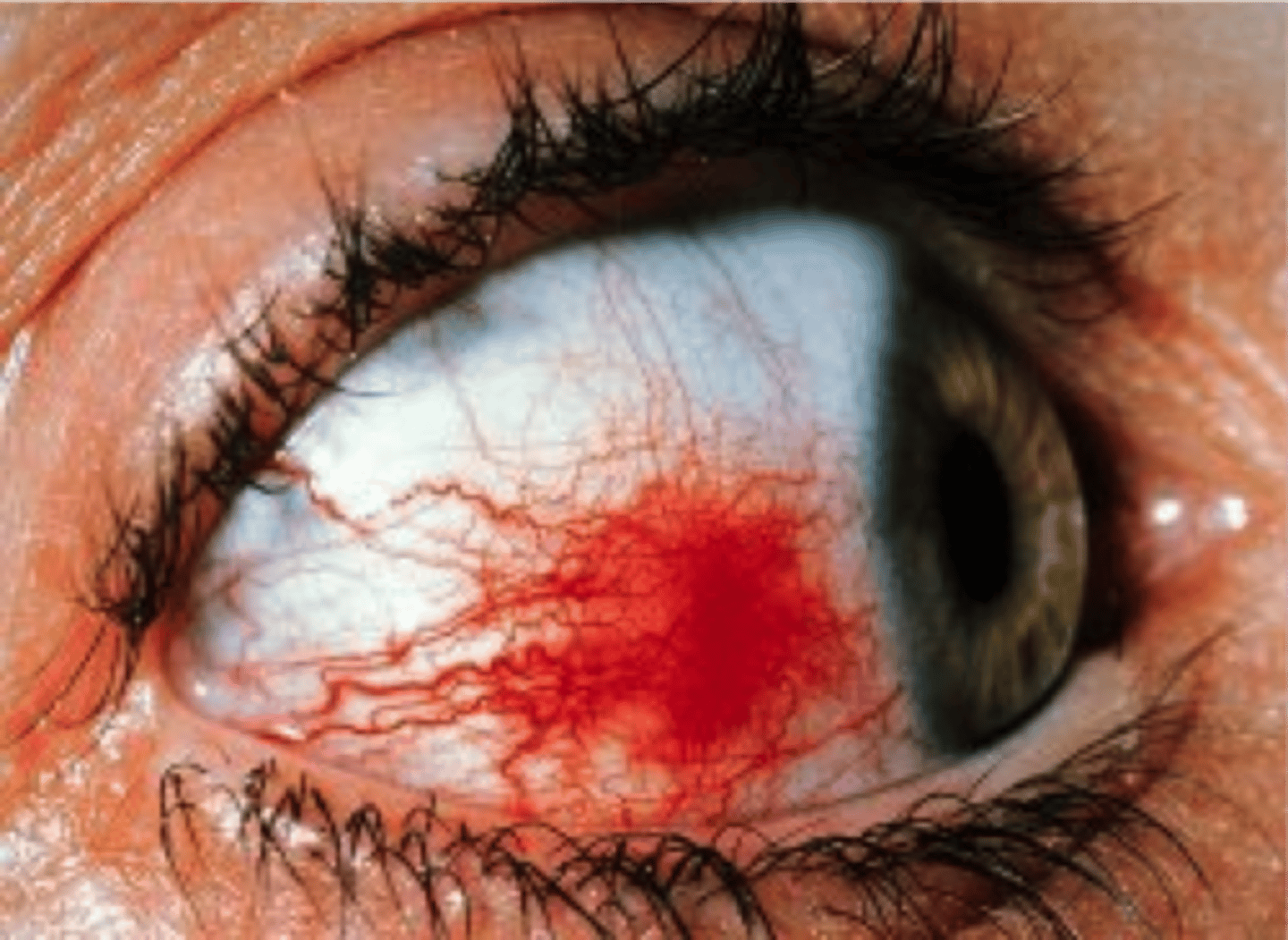
describe the management of episclerirtis
in general is it self limitng
refer to optician if experimenting any pain or discomfort, photophobia etc
suggest paracetamol / ibuprofen for discomfort
often linked to autoimmune disorder
describe keratitis
redness around the eye, can be very painful
watery discharge
photophobia
open leison to eye
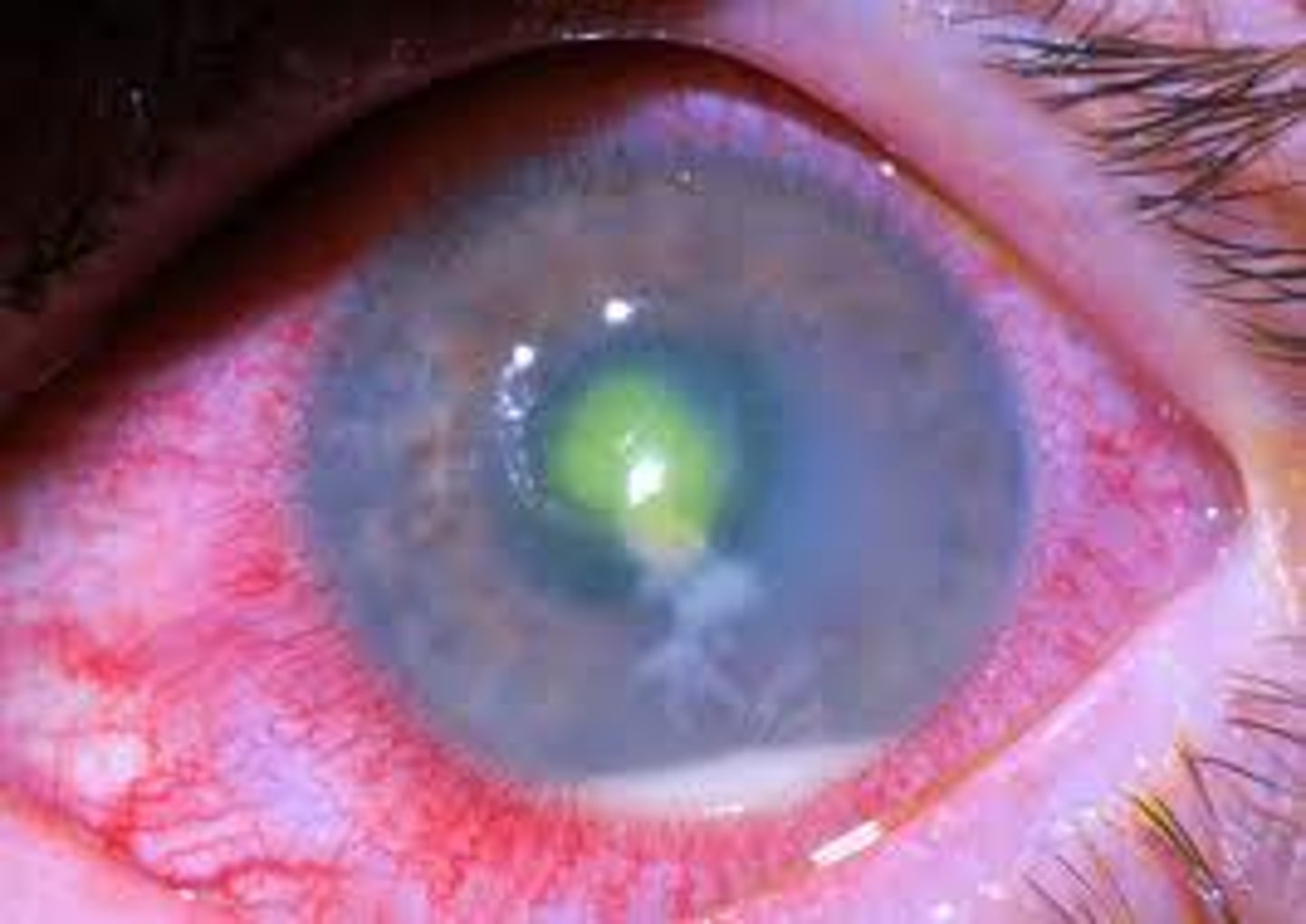
describe the management of keratitis
refer
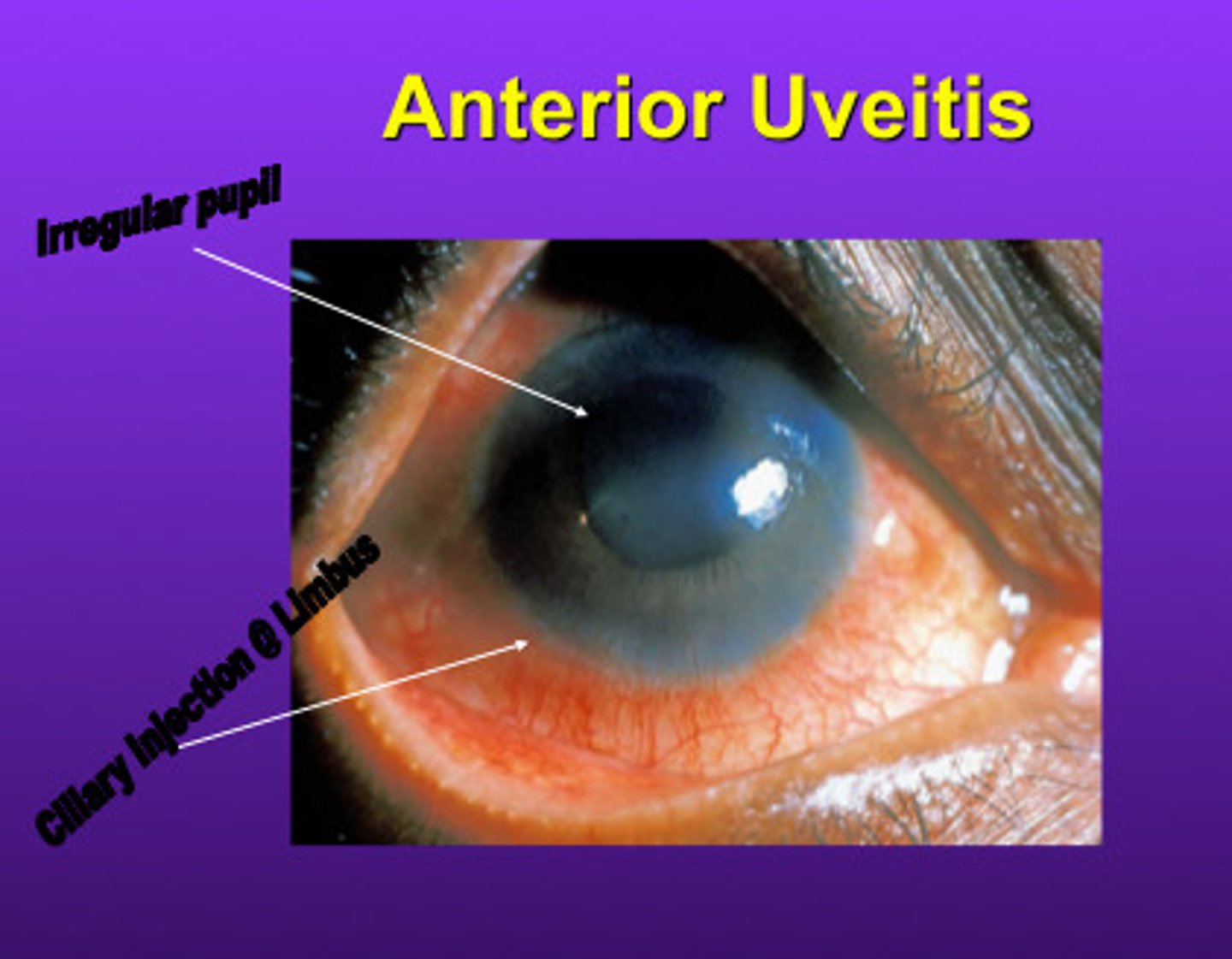
describe uveitis
redness
watery discharge
photophobia
changes in vision
what does a stye look like
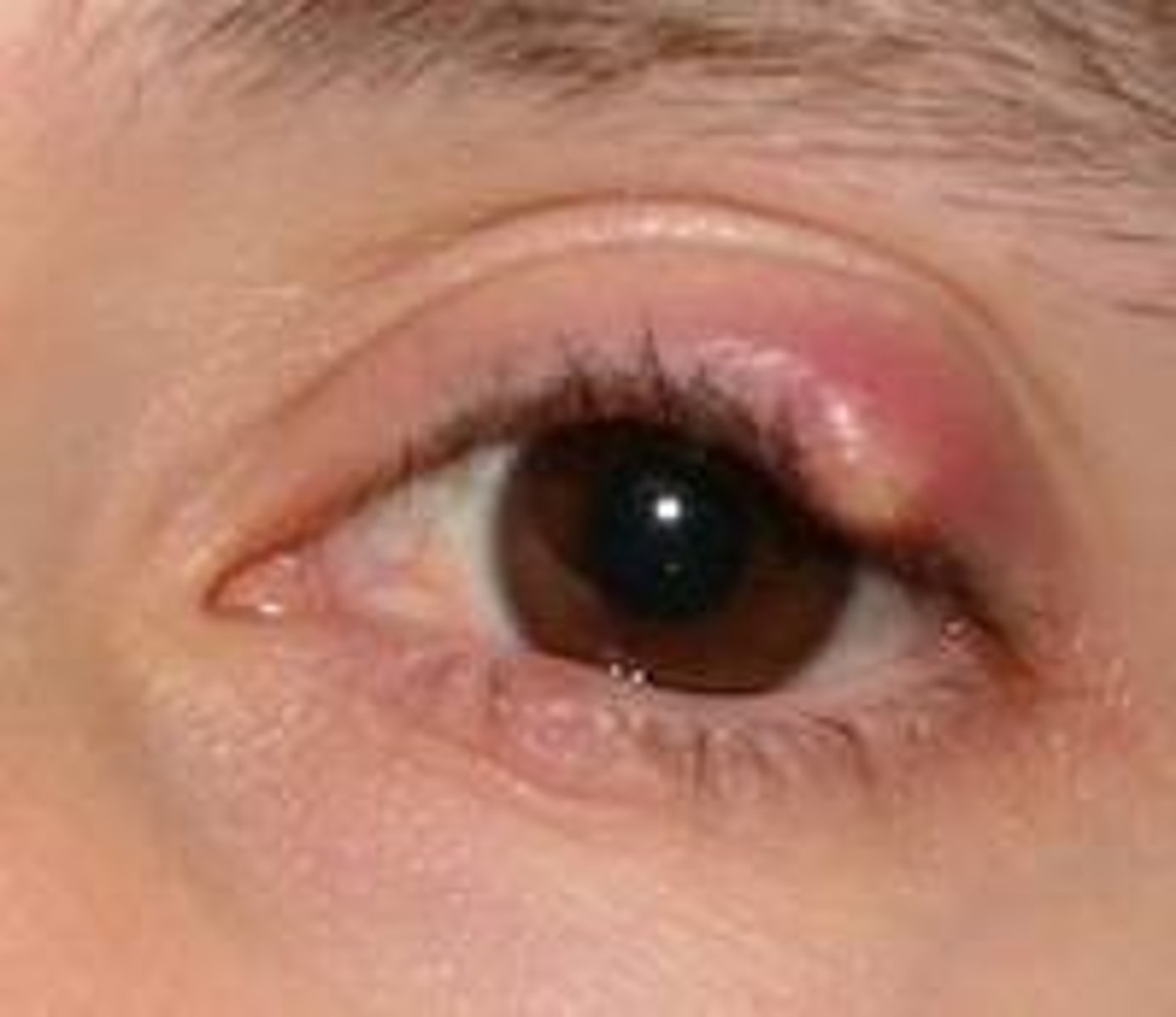
how do you manage styes?
-reassure patient that they are self limiting and symptoms will resolve once stye has ruptured
-advise to not pick or squeeze
-warm compress for 5-10mins, 2-4 times a day, will bring it to a head quicker
-refferal only needed if it doesn't resolve
what does blepharitis look like
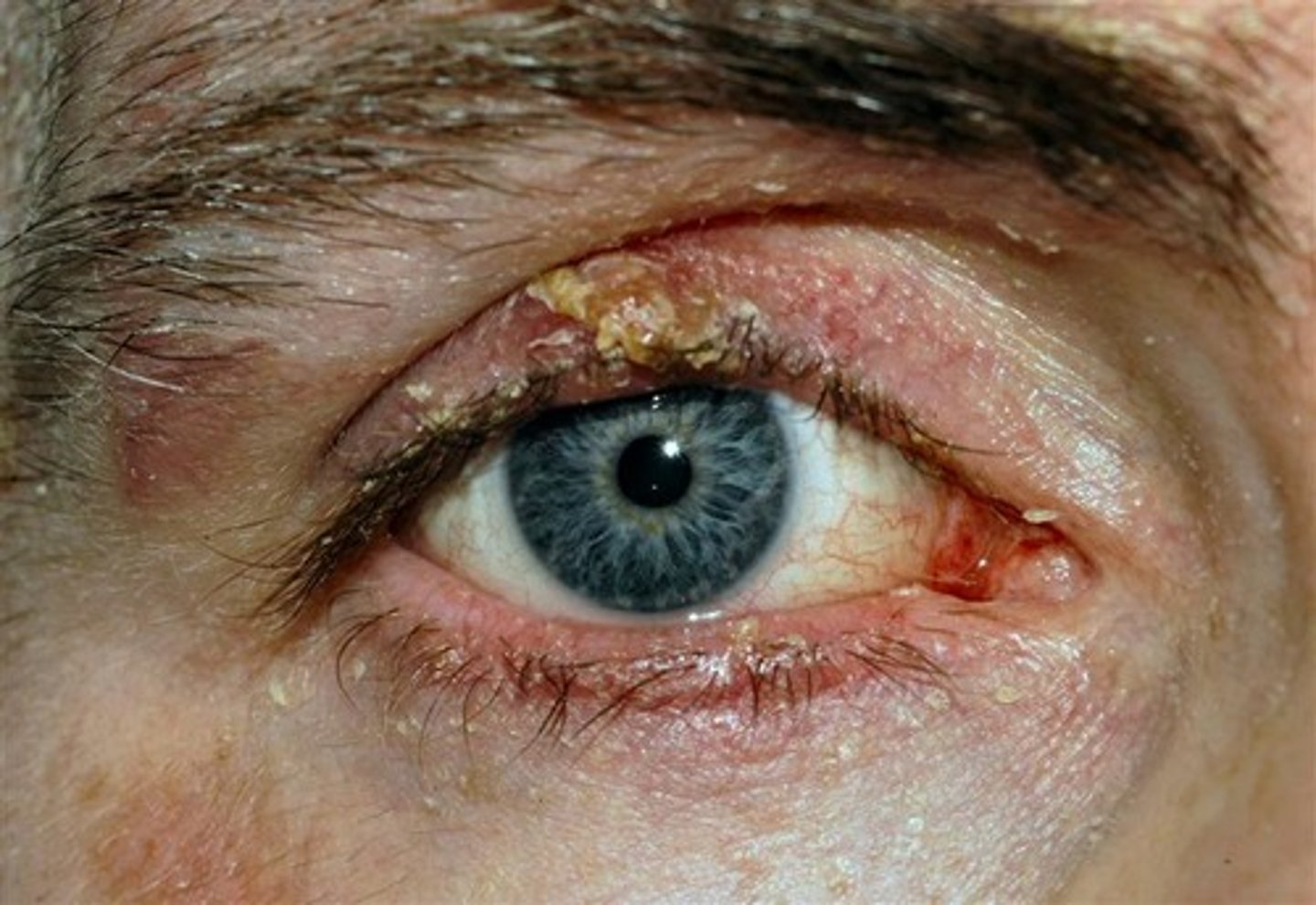
describe the management of blepharitis
advise good eyeliud hygiene , clean twice a day
apply warm compress to closed eyes for 5-10mins 1 or 2 times a day
baby shampoo diluted 1-10 with water and wipes on eyelids with cotton bud or cloth twice daily, reducing to once when symptoms improve
refer if no improvement in 7-14 days
what are the symptoms of dry eyes
burning, tired eyes
itching, irritated, gritty
lack of ocular redness
long standing history of symptoms
what are the 1st and 2nd line treatments for cystitis
1st line, paracetamol or ibuprofen plus fluids
2nd line, cymalon, canesOasis (not recommended by NICE)
I would recommend d mannose
what are the 1st and 2nd line treatments for vaginal candiasis
1st line fluconazole 150mg oral capsule
2nd line clotrimazole pessaries (internal cream or internal and external, or plus tablet)
ALL not liscenced in pregnancy
what should be noted about internal preparations
only use at night
what is a common side effect of fluconazole
GI disturbances
risk factors
pregnancy, undiagnosed diabetic, increasing age, sexual activity
possible causes in men
underlying bladder or prostate infection
obstruction/ tumour
enlarged prostate