FORENSIC 6 BALLISTICS
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Ballistics
refers to the science that deals with the study of the motion of projectiles and the conditions affecting such motion.
Ballo or Ballein
Greek word which means "to throw".
Ballista
an early Roman War machine, which means a gigantic bow or catapult which used to hurl missiles or large objects at a particular distance.
Projectile
refers to the metallic or non metallic object propelled from the firearm by means of heated gas coming from the burning gun powder.
Caliber
the diameter of the bore measured from land to land
Ballistic fingerprinting
involves analyzing firearm, ammunition and tool mark evidence in order to establish whether a certain firearm or tool was used in the commission of a crime.
Calvin H. Goddard
"Father of Modern Ballistics" and he also invented the "Bullet Comparison Microscope"
Jhon M. Browning
known as the Wizard of Modern Firearms
Alexander John Forsyth
Father of the percussion ignition
Branches of Ballistics (IETF)
1. Internal/Interior Ballistics
2. External/Exterior Ballistics
3. Terminal Ballistics
4. Forensic Ballistics
Internal Ballistics
it is the study of the motion of the projectile while still inside the gun barrel, this covers from the time the firearm is loaded with the cartridge, the explosion and the movement of the bullet towards the muzzle end of the gun.
Misfire
refers to the failure of the cartridge to explode after the firing pin strikes the primer
Hang-Fire
refers to the delay of the explosion of the gunpowder after the firing pin hits the primer
Gyroscopic Stability/Gyroscopic Action
it is the stability of the flight of the bullet within the effective range due to the twist of the lands and grooves from the breech end to the muzzle end.
Yaw
refers to the rotation of the nose of the bullet away from the line of flight or unsteadiness
External Ballistics
it is the study of the motion and traits of projectiles, after it has left from the muzzle of the gun, which includes the condition of the bullets movement and flight up to the target.
Muzzle Blast
a sound or noise created at the muzzle point of the gun
Muzzle Energy
energy generated at the muzzle end whenever the cartridge explodes from the firearm
Trajectory
refers to the curved path in the horizontal flight of the bullet which usually occurred a few meters away from the muzzle of the firearm.
Range
is the straight distance from the muzzle of the gun to the target.
Accurate/Effective Range
refers to the distance within which the shooter or the firer has control of his shot.
Maximum Range
refers to the farthest distance that a projectile can be propelled from a firearm, up to final vertical drop to the ground.
Velocity
it is the speed of the bullet per unit of the time, which is expressed in foot per second
Air Resistance
the resistance encountered by the bullet in flight which is clearly experience by the bullet few meters away from the muzzle of the gun.
Pull of Gravity
It is the downward reaction of the bullet towards the earth surface due to its weight.
Penetration
is the point where the bullet hits the target
Terminal Ballistics
this refers to the study of the effect of the impact of the bullet on the target
Terminal Accuracy
this refers to the size of the bullet grouping on the target
Terminal Energy
the energy of the bullet when it strikes the target. This refers to the fatal equivalent of a bullet when it struck the victim.
Terminal Velocity
this refers to the speed of the bullet upon hitting the target which is express in foot per second.
Terminal Penetration
refers to the depths of the entry of the bullet on the target
Forensic Ballistics
refers to the investigation and identification of firearms by means of ammunitions fired from the submitted suspected firearms.
Field Investigation
refers to the work of an investigation in the field. It concerns mostly with the collection, marking, preservation, packing and transmission of firearms evidences.
Technical Examination
refers to the examiners who examine bullets/ or shells, whether fired from also whether or not cartridges were loaded and ejected made by the suspected firearms submitted. Reports are made by the examiners and testify in court regarding their report
Legal Proceedings
Court Trials - wherein the ballistics report of the firearm
examiner and the ballistics exhibits are presented during the trial of the case in a court justice.
Firearms
refers to any handheld or portable weapon, whether a small arm or light weapon, that expels or is designed to expel a bullet, shot, slug, missile or any projectile, which is discharged by means of expansive force of gases from burning gunpowder or other form of combustion or any similar instrument or implement. For purposes of this Act, the barrel, frame or receiver is considered a firearm.
RA 10591
Comprehensive Firearms and Ammunition Regulation Act
Forfeited firearm
refers to a firearm that is subject to forfeiture by reason of court order as accessory penalty or for the disposition by the FEO of the PNP of firearms considered as abandoned, surrendered, confiscated or revoked in compliance with existing rules and regulations
Loose firearm
refers to an unregistered firearm, an obliterated or altered firearm, firearm which has been lost or stolen, illegally manufactured firearms, registered firearms in the possession of an individual other than the licensee and those with revoked licenses in accordance with the rules and regulations.
Imitation firearm
refers to a replica of a firearm, or other device that is so substantially similar in coloration and overall appearance to an existing firearm as to lead a reasonable person to believe that such imitation firearm is a real firearm.
Tampered, obliterated or altered firearm
refers to any firearm whose serial number or other identification or ballistics characteristics have been intentionally tampered with, obliterated or altered without authority or in order to conceal its source, identity or ownership.
Authority to Issue License
The Chief of the PNP, through the FEO of the PNP, shall issue licenses to qualified individuals and to cause the registration of firearms.
Type 1 license
allows a citizen to own and possess a maximum of two (2) registered firearms
Type 2 license
allows a citizen to own and possess a maximum of five (5) registered firearms
Type 3 license
allows a citizen to own and possess a maximum of ten (10) registered firearms
Type 4 license
allows a citizen to own and possess a maximum of fifteen (15) registered firearms
Type 5 license
allows a citizen, who is a certified gun collector, to own and possess more than fifteen (15) registered firearms
Use of an Imitation Firearm
An imitation firearm used in the commission of a crime shall be considered a real firearm as defined in this Act and the person who committed the crime shall be punished in accordance with this Act
Airsoft Rifle/Pistol
includes battery operated , spring and gas type powered rifles/pistol which discharge plastic or rubber pellets only as bullets or ammunition. This differs from replica as the latter does not fire plastic or rubber pellet.
Is Airsoft Rifle/Pistol considered as firearm?
No, because it does not discharge projectile by means of expansive force of gases.
Registration of Airsoft Rifle/Pistol
The one time registration for airgun shall be applied to airsoft rifle/pistol.
Transport of Airsoft Rifle/Pistol
A Permit To Transport (PTT) airsoft rifle/pistol shall be required for the transport of all airsoft rifles/pistols from the place of residence to any game or exhibition site.
General Classes of Firearms
I. According to the Mechanical Internal Constructions of Gun Barrel
II. According to the Projectiles Propelled
III. According to Mechanical Constructions
Rifle Bore Firearms
are those types of firearms wherein the bore is cut longitudinally with a number of spiral grooves from the breech end to the muzzle end of the barrel.
Lands
the elevated portions inside the bore of the barrel
Grooves
the depressed portions inside the bore of the barrel
Smooth Bore Firearms
those that have no riflings inside the gun barrel for the breech end up to the muzzle of the firearm. Such as the following: Shotguns - Muskets
Artillery
are those types of firearms that propel projectile that is more than one inch in diameter
Small arms
any firearms designed to fire projectiles that is less than one inch in diameter
Single Shot Firearm
those firearms designed to fire only one shot for every loading which have to be reloaded for each shot
Repeating Firearm
firearm designed to fire several rounds of cartridges in one loading
Automatic Firearm
A firearm that will load and fire automatically and continuously with a single pull and hold of the trigger until the magazine is empty. Automatic firearms can be full automatic or semi-automatic.
Bolt Action Type
firearms that are provided with a box magazine under the bolt but some of them have tubular magazine like a trombone action firearm
Automatic Loading Type
After the first shot is fired, automatic loading or chamber takes place as long as the trigger of the gun is squeezed by the shooter.
Slide/Pump Action Type
this type of firearm can be opened by grasping the forearm which is usually a wooden part of the gun, located under the barrel. This firearm is designed to slide back and forth.
Lever Action Type
the trigger guard of this type of firearm is hinged (attached) at the front end, which is connected with the breech mechanism. After firing, the finger lever is moved downward so as to cause the trigger guard to pivot on its hinged and its forward extension is to move back.
German Gustav Gun
largest gun ever used in combat
Zip Gun
homemade handgun, this class of gun found to have a clever mechanism most are effective weapon
Ammunition/Cartridge
It is a complete unfired unit consisting of bullet, cartridge case, gunpowder and primer.
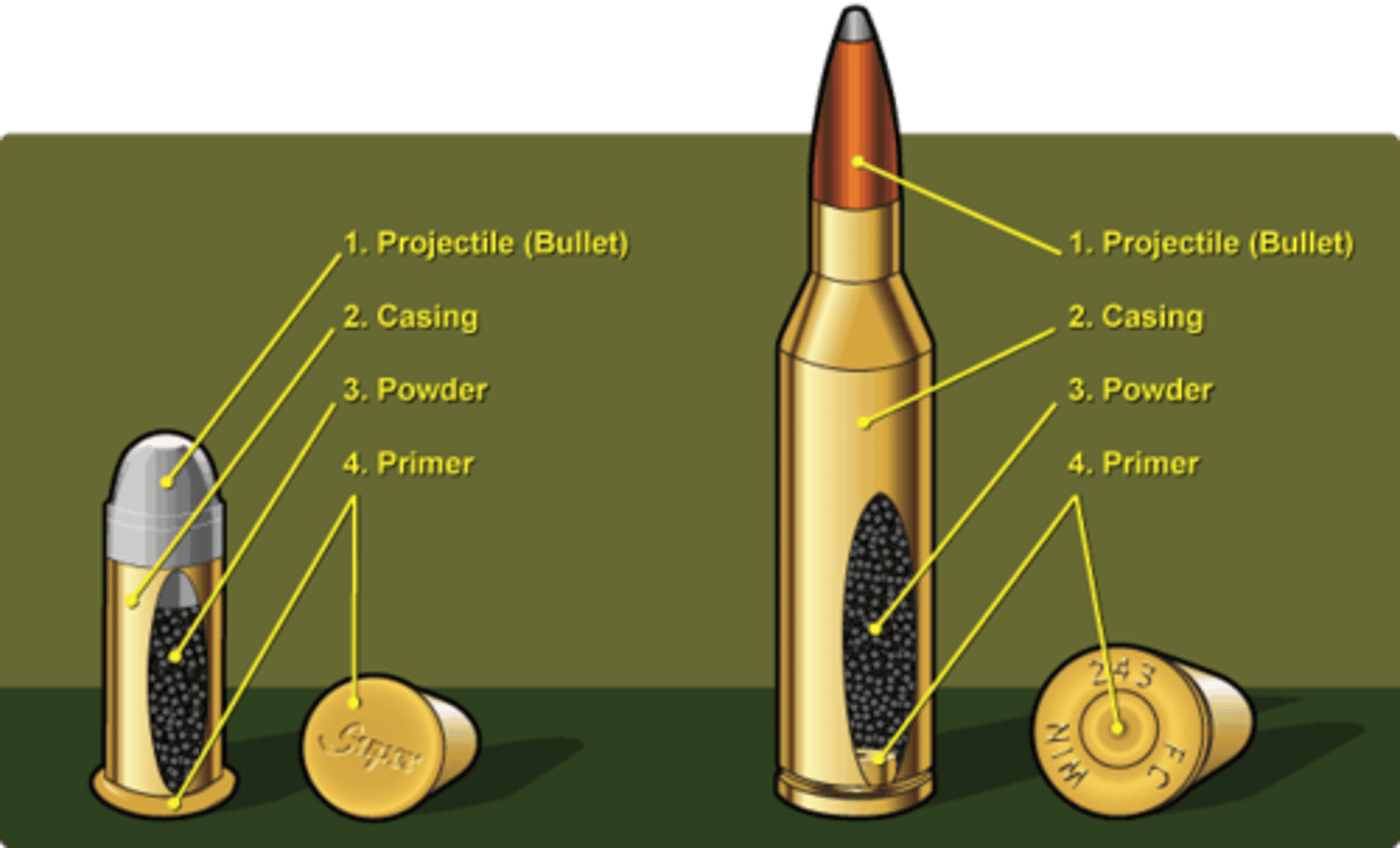
Parts of cartridge/ammunition
bullet, cartridge case, gun powder, primer
Bullet
a projectile propelled through the barrel of a firearm by means of an expansive force of gases coming from a burning gun powder. It is also called as ball, or shot.
Classifications of Bullet
a. Lead Bullet
b. Jacketed Bullet
Lead Bullet
A bullet formed from a lead alloy
Jacketed Bullet
The soft lead is surrounded by another metal, usually copper, that allows the bullet to penetrate a target more easily.
Ball bullets
have soft lead core inside a jacket and are used against person
Armor piercing bullet
A bullet consisting of a hardened core or wholly composed of a substance other than lead or lead alloy. Used to penetrate armored cars and vehicles.
Tracer bullet
sets on fire when the bullet is projected. The flash of light and smoke from the burning, permits flight of the tracer bullet to be seen, especially at night time.
Incendiary Bullet
A projectile containing a chemical compound which ignites upon impact with the intended purpose of starting fires.
Explosive/Fragmentary Bullet
contain a high charge of explosive
Dum-Dum Bullet
It consists of a service ball that has an exposed nose due to trimmed jacket at the back. At present, the term is loosely used in describing any expanding bullet. These are now known as Hallow Point bullet and Soft Point bullet.

Gas Check Bullet
A lead alloy projectile with a copper or gilding metal cup pressed over the base. This metal cup is used to protect the base of the bullet from deformation due to the hot gases produced during firing.
Wad Cutter Bullet
the front of the bullet is flattened. Used mainly for target practice.

Wax Bullet
A projectile made from paraffin and/or other wax preparations, usually used for short range indoor target shooting.
Shots/Pellets
these are projectiles designed for shotguns
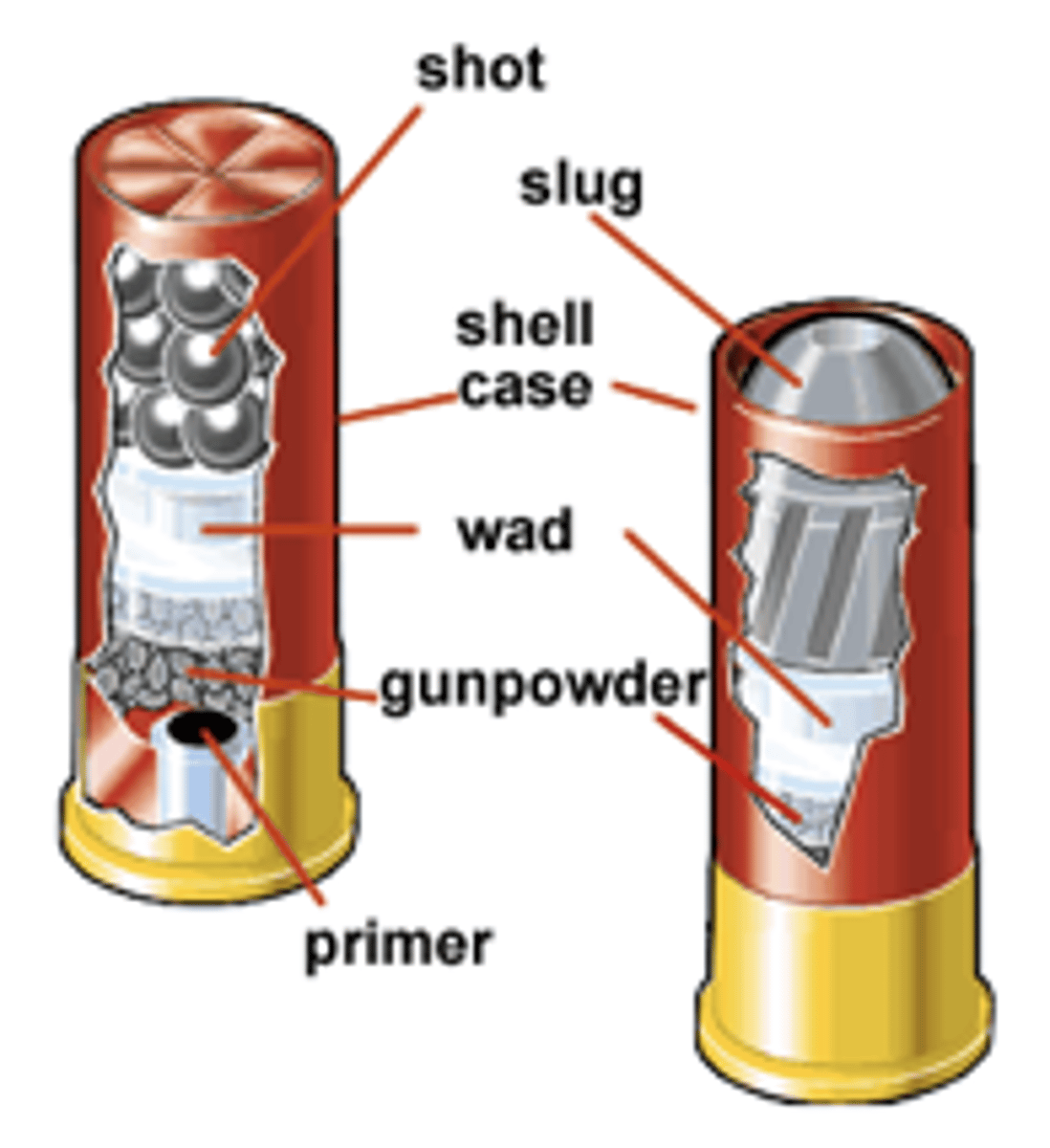
Slug
a single shot or bullet in a shotgun shell.
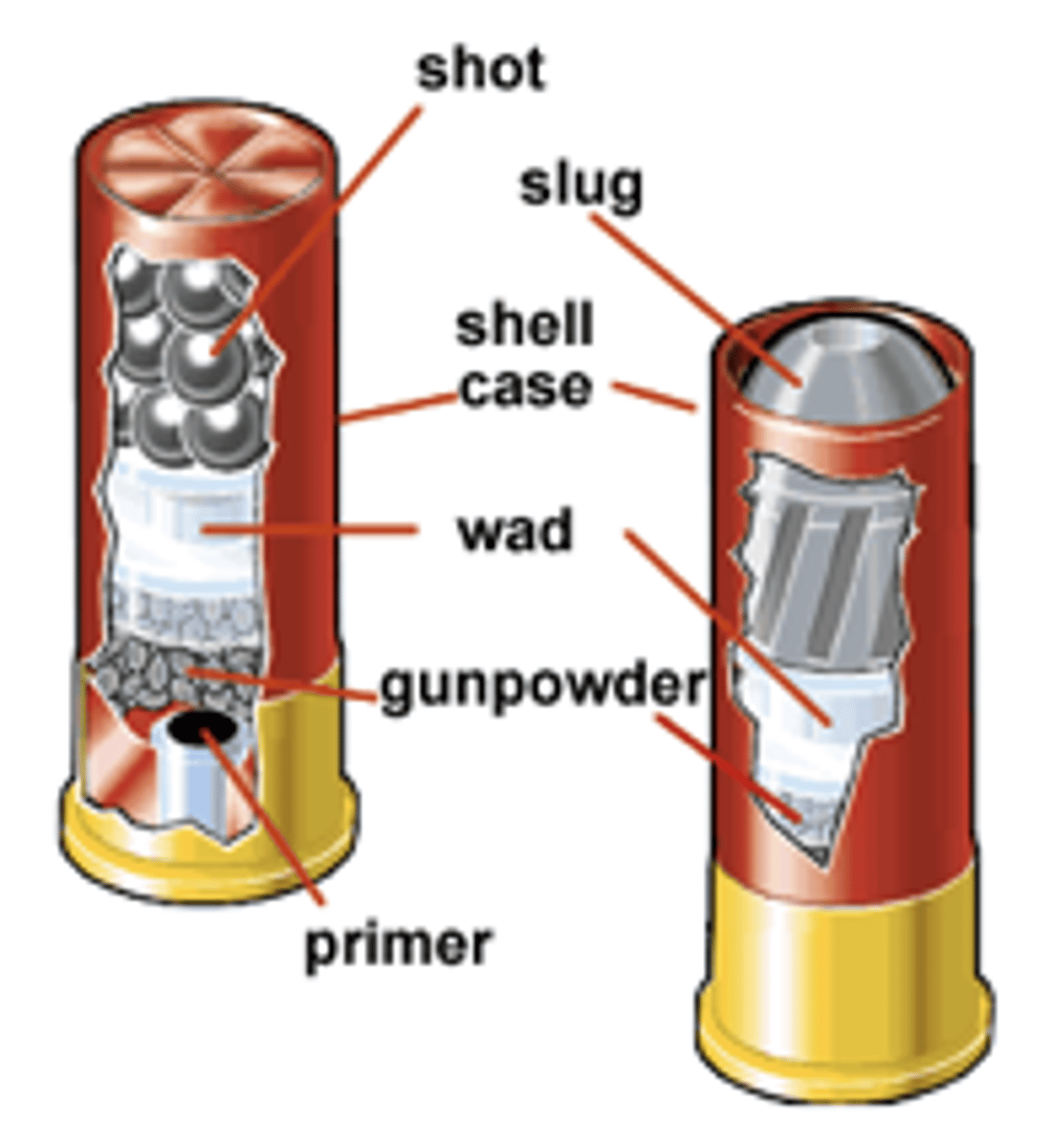
Cartridge Case/Shell/Casing
the tubular metallic container for gun powder. It holds together the primer, gunpowder, and bullet.
Gunpowder
a propellant or powder charge which when ignited by the primer flash, is converted into heated gas under high pressure and propels the bullet or shots through the barrel.

Roger Bacon
and english monk and scientist invented the gunpowder known as Black Powder.
Paul Vieille
Invented smokeless gunpowder
Ingredients of Black Powder (PCS)
potassium nitrate 75%, charcoal 15%, sulfur 10%
Primer
the metal cup containing the highly sensitive priming mixture of chemical compound which when hit by a firing pin would ignite or detonate. It is the complete assembly of priming mixture, paper disk, anvil, vent.
Composition of a Primer (PAF)
Potassium Chlorate 45%
Antimony Sulfide 23%
Fulminate of Mercury 32%
Berdan Primer
A primer/case system, designed by Col. Hiram Berdan, having two or more flash holes consisting of a cup, explosive mixture and covering foil. The anvil is an integral part of the cartridge case head in the bottom of the primer pocket. Although widely used throughout the world, this system has never been popular in the U.S., due largely to the difficulty in reloading Berdan cases.
Boxer Primer
One flash hole. Has a cup shaped igniting system having the anvil and flash built in.
Rim
an edge, border, or margin on or around anything
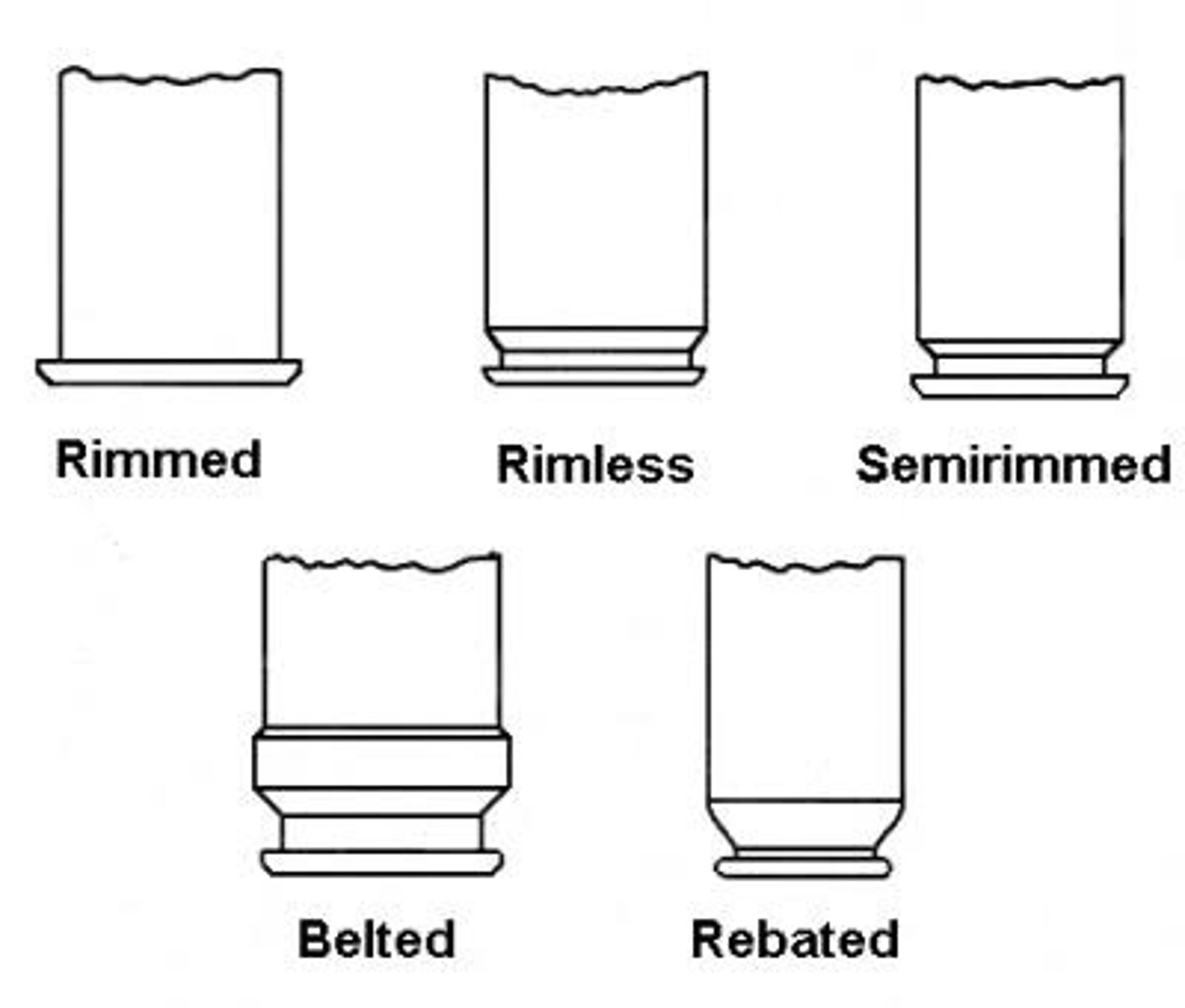
Classification of Cartridge According to Rim
1. Rimmed
2. Semi-Rimmed
3. Rimless
4. Rebated
5. Belted
Rimmed Type
The diameter of the rim is greater than the diameter of the body of the cartridge case.
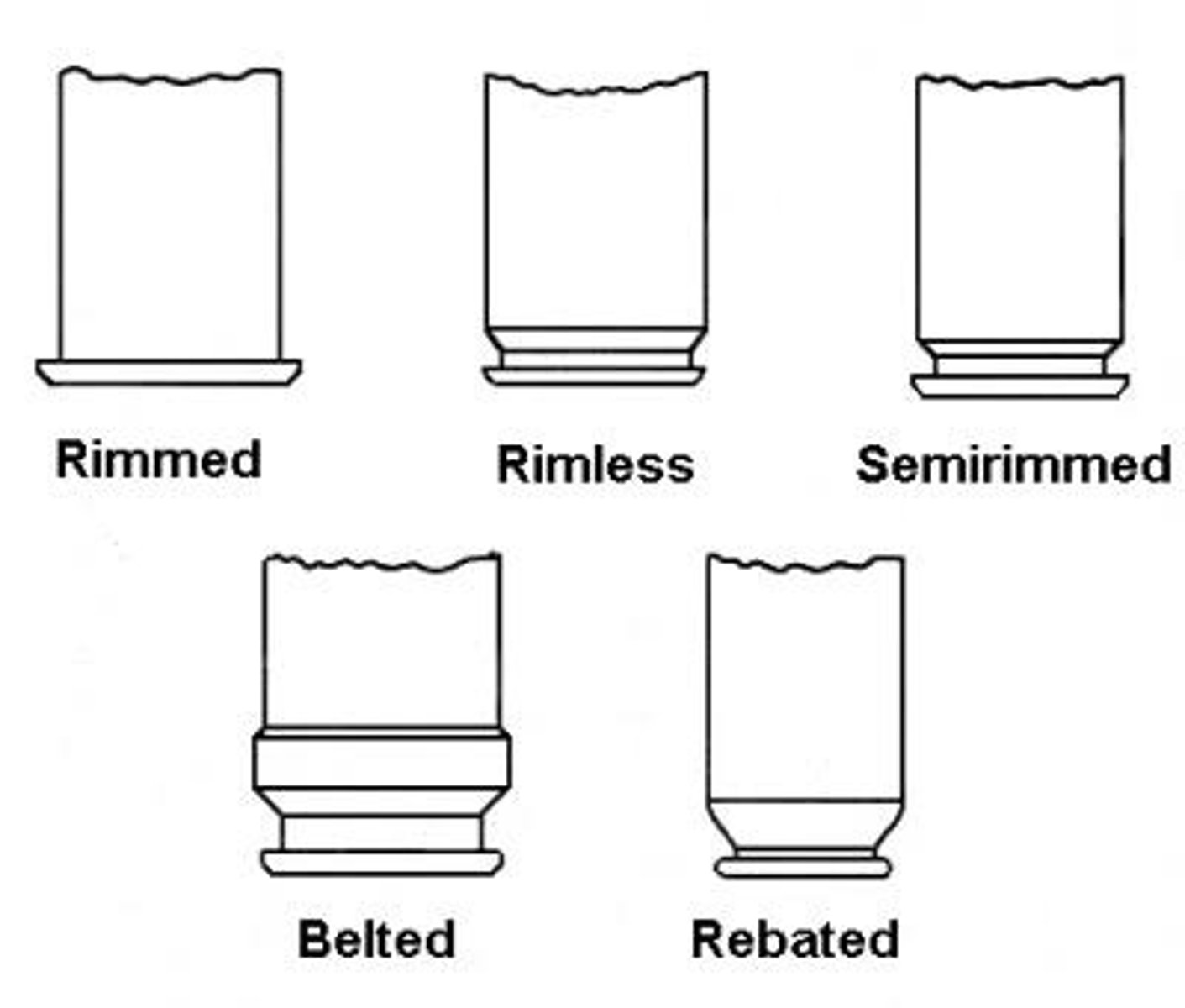
Semi-Rimmed Type
the diameter of the rim is slightly greater than the body of the cartridge case
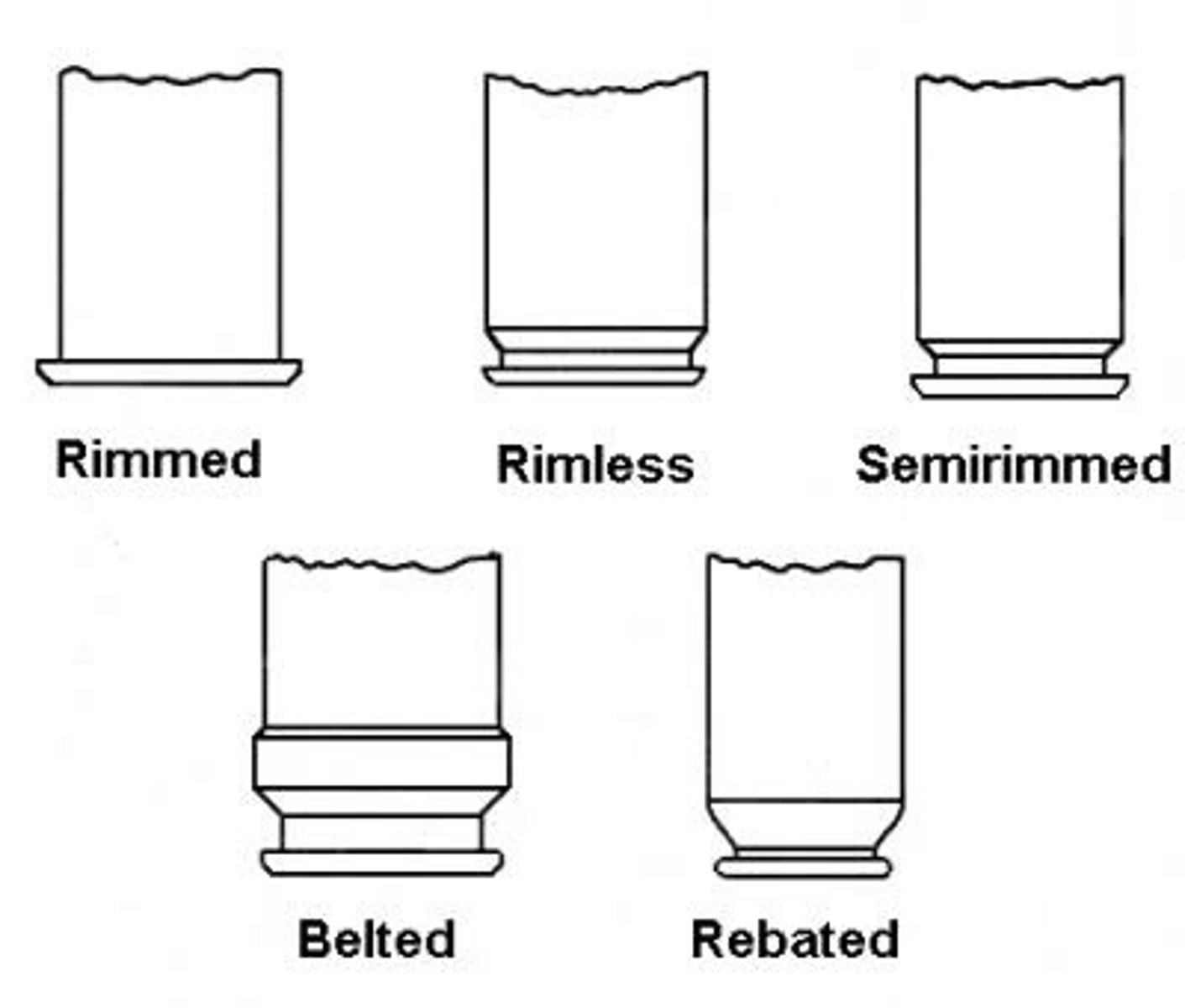
Rimless Type
The diameter of the rim is equal with the diameter of the body of the cartridge case.

Rebated Type
the diameter of the rim is smaller than the body of the cartridge case