Y9 Science electrical energy exam revision
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Electrical current
Generated by the movement of electrons repelling one another in a chain reaction in a closed circuit.
Conductor
A material that allows an electrical current to run through it. Eg. metals, sea water
Insulator
A material that is very resistant to electrons flowing through it (doesn’t let the current pass through it). Eg. rubber, glass, oil, diamond, wood
Voltage
The measure of push each electron feels or the strength of the electromagnetic force. It is measured in Volts (V) using a voltmeter.
Resistance
The degree of difficulty for an electron to get past the atoms that make up a material.
Amperage
The frequency of an electron, how many electrons pass a particular spot in the wire per second. It is measured in Amperes / Amps (A) with an ammeter.
Circuit diagram symbols
.
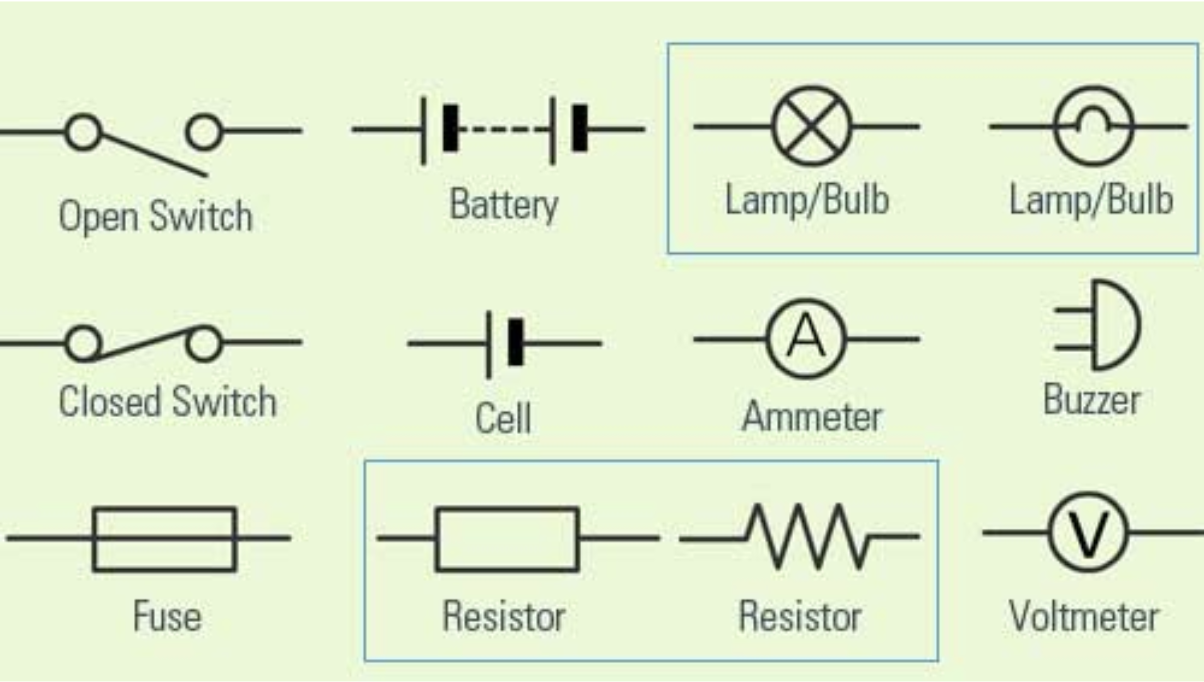
Series circuit
A circuit in which all components are connected by a single loop. All devices are controlled by the same switch, the total supply voltage is shared between devices (more globes = duller light) and a blown device will break the entire circuit.
Parallel circuit
A circuit that is arranged into different sections or branches. Each device receives a full supply of voltage, meaning that adding a device on its own branch will not affect the brightness of another device. Device blowouts only affect one branch and each branch can have its own switch.