5) The adaptive immune system
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
In which compartment of the body do B-cells predominantly act?
Extracellular: blood, intersitial fluid or cell membrane surface
In which compartment of the body do T-cells predominantly act?
Intracellular: Vesicles or cytoplasm
Linear epitopes
Consecutive amino acids within peptide recognised by antibodies.
Conformational epitopes
Only formed when protein adopts normal or native 3D structure
What cells recognise the constant region of antibodies?
Dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, complement
What is the function of the Fc portion of antibodies?
Recruit effector function
Functions of antibodies
-Opsonisation
-Neutralisation
-Complement activation
Where are T-lymphocytes produced?
Bone marrow
Where do T-lymphocytes mature?
Thymus
What does the TCR recognise?
Processed antigen (degraded peptide) in complex with specific MHC - which makes its action MHC restricted
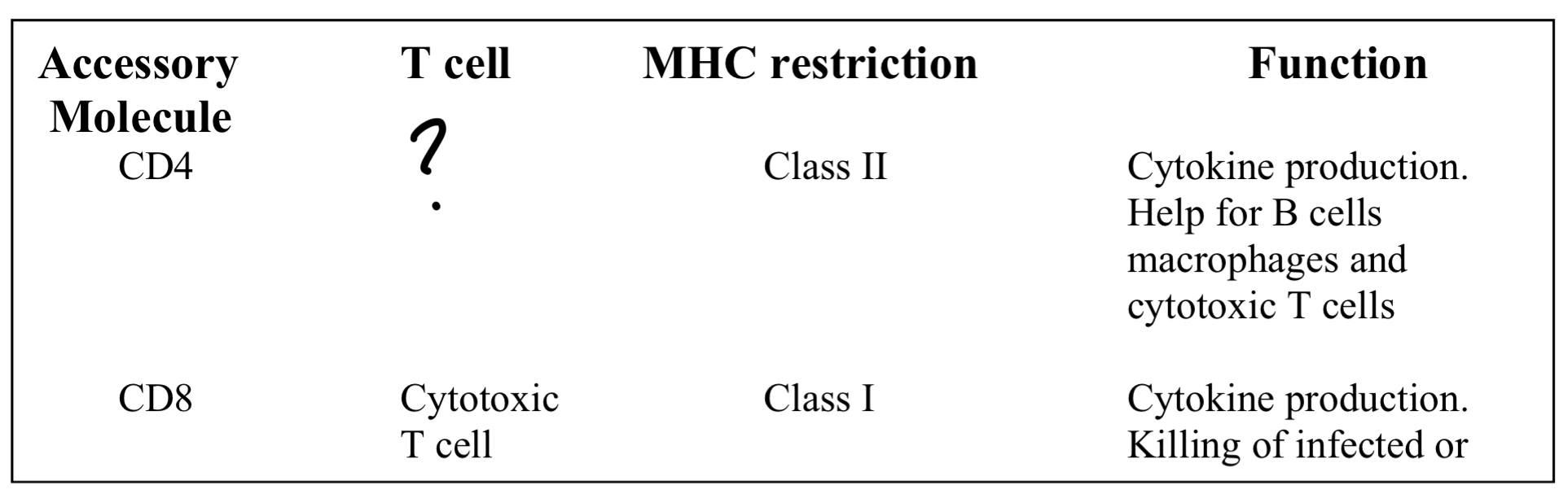
T helper cell
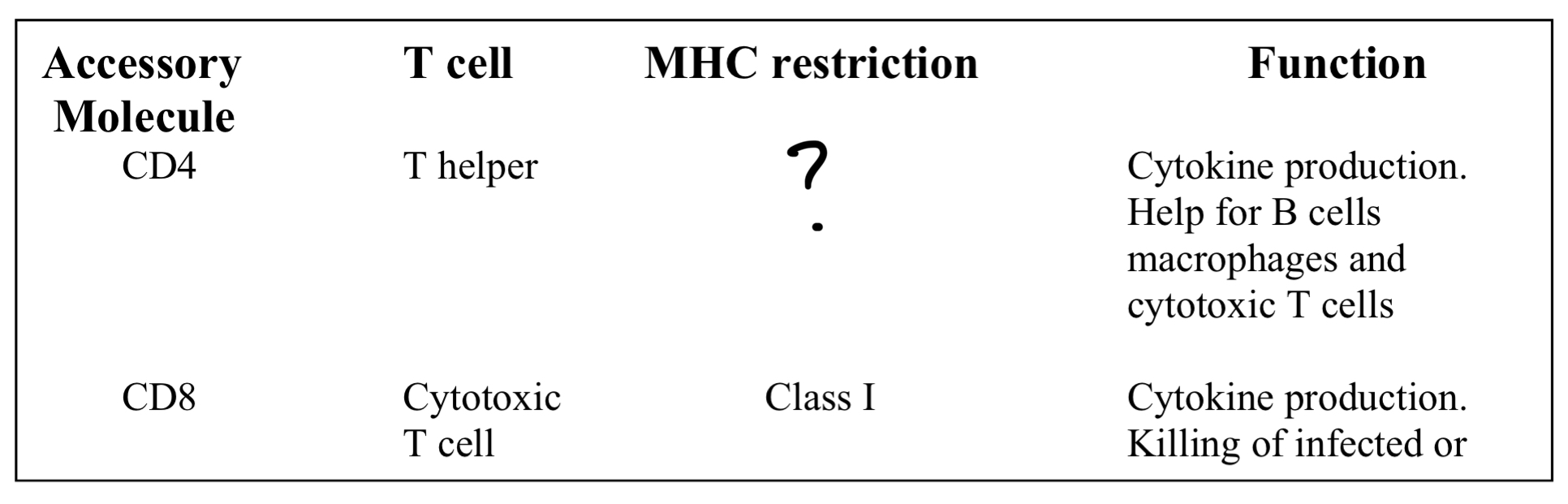
MHC2

-Cytokine production
-Help for B-cells, macrophages and cytotoxic T cells

Cytotoxic T cell
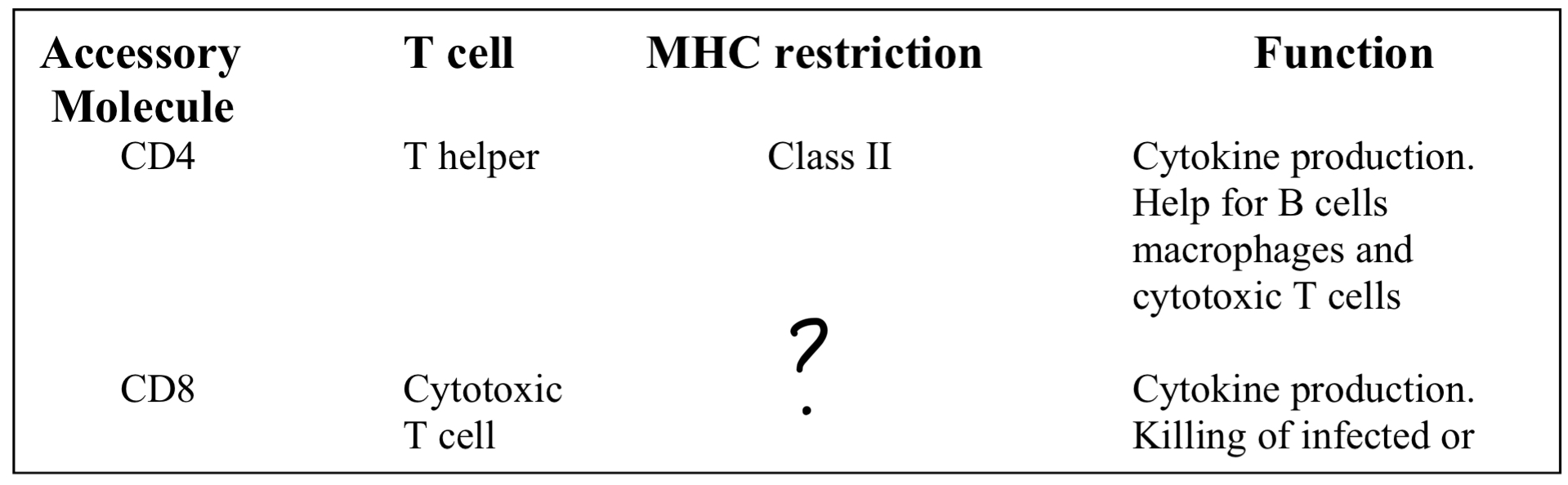
MHC1

-Cytokine production
-Killing of infected cells
What types of peptides does MHC 1 express?
Intracellular- cytosolic proteins
What types of peptides does MHC 2 express?
Extracellular proteins
What is a naive lymphocyte?
These are the lymphocytes that have yet to interact with antigens- so typically in it’s inactive form.
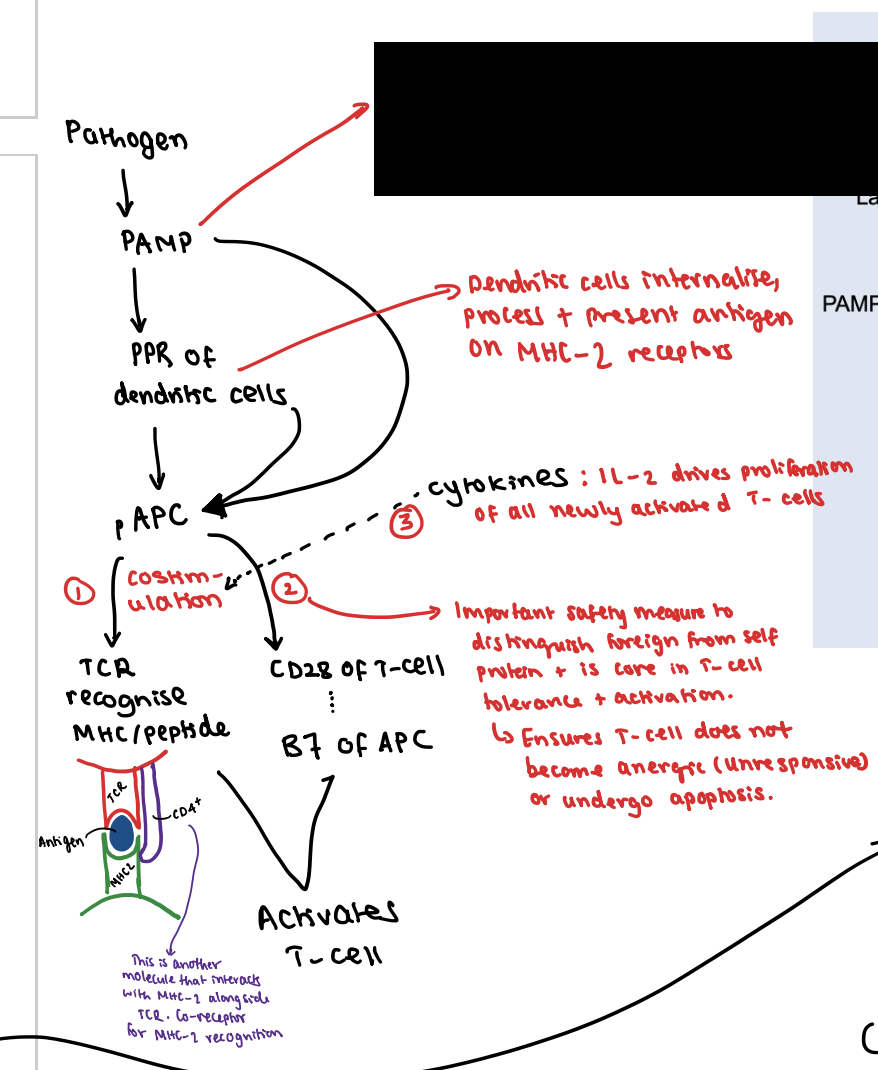
This PAMP triggers activation of the pAPC which initiates expression of B7 receptor.
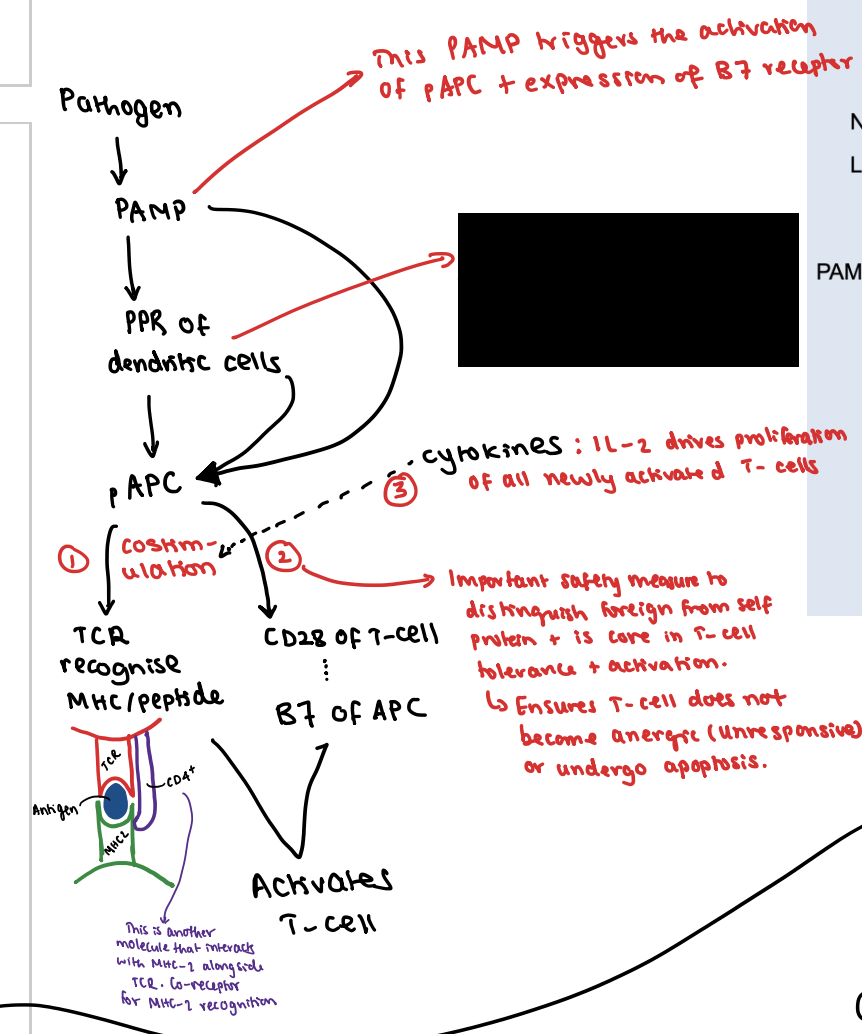
Dendritic cells internalise, process and present the antigen on the MHC-2 receptors.
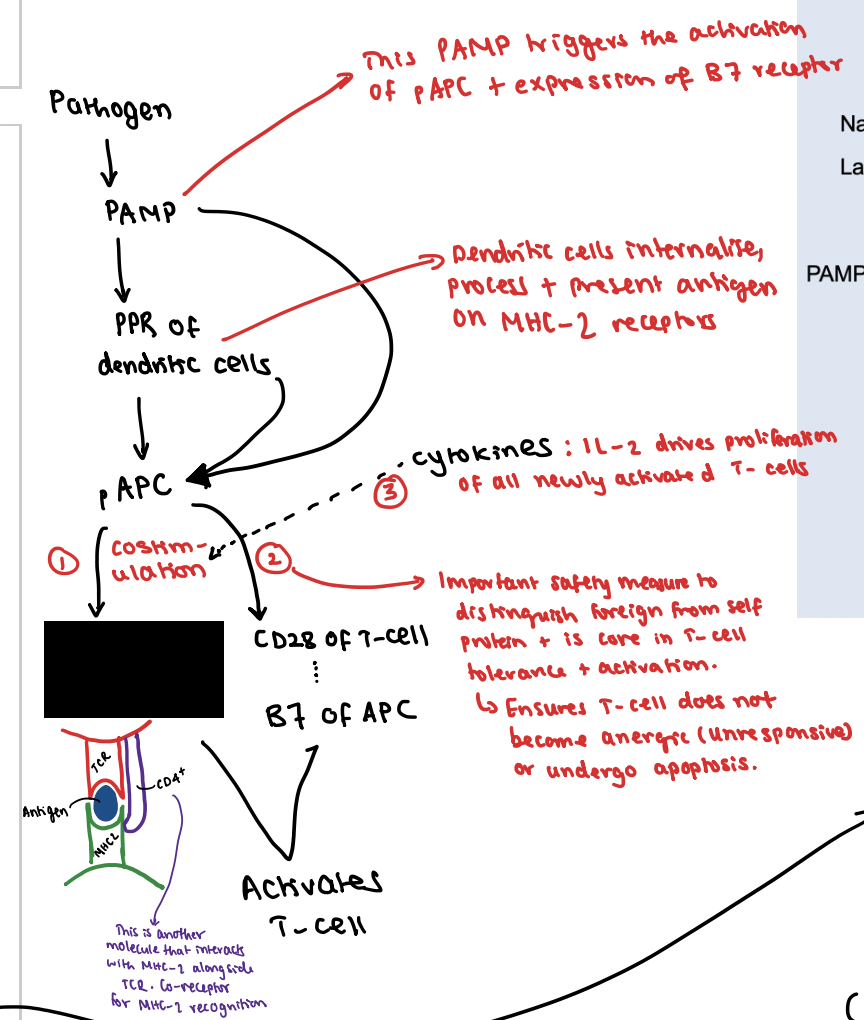
What is the first signal?
TCR interacts with antigen + MHC1/2 (side note: for T-cell to interact with MHC this relies on TCR and CD4/8+ receptors to co-interact)
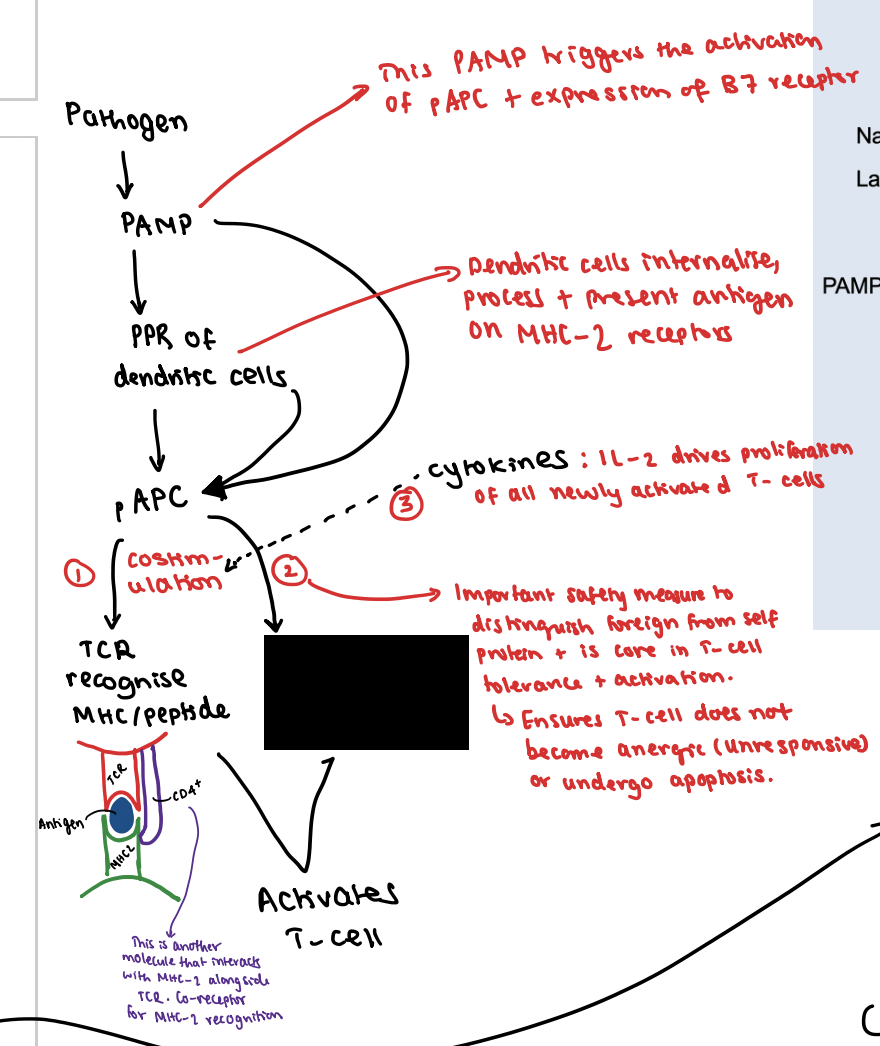
What is the second signal?
CD28 receptor on T-cell interacts with B7 receptor on pAPC
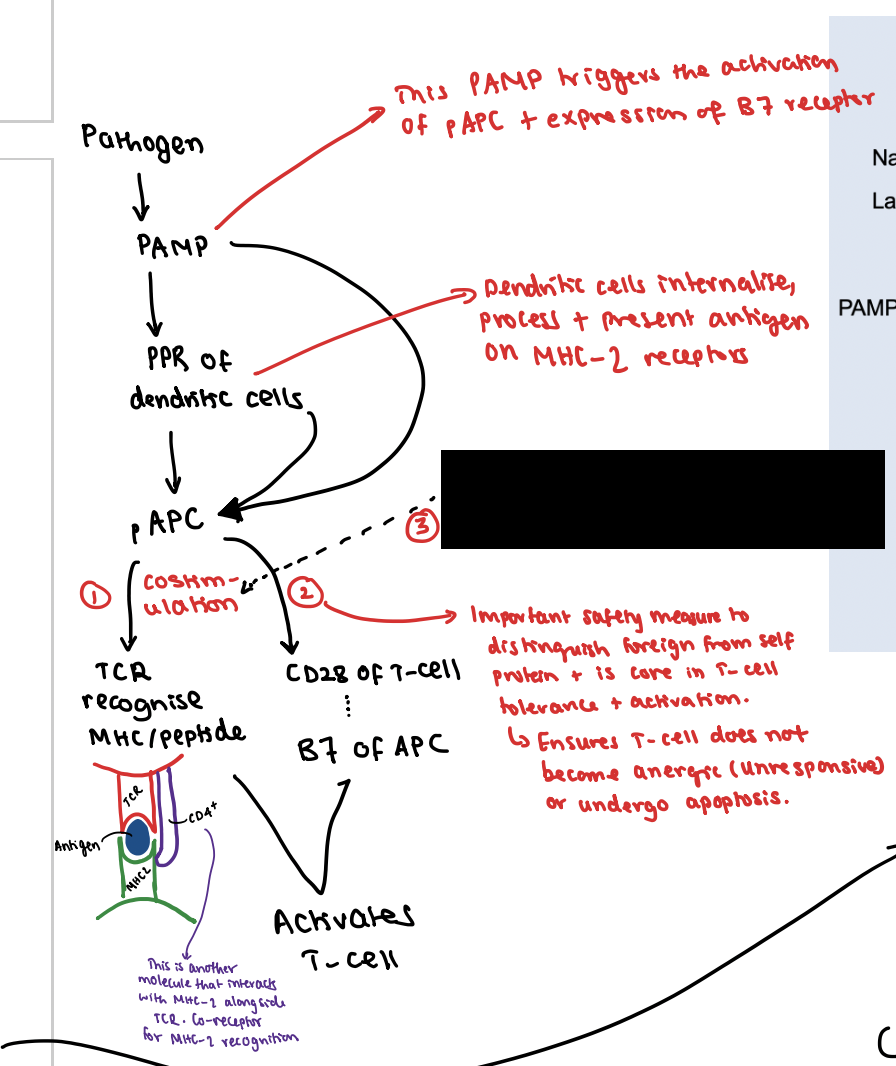
What is the third signal?
This co-stimulatory interaction activates the T-cell to secrete IL-2 which drives the proliferation of all newly activated T-cells
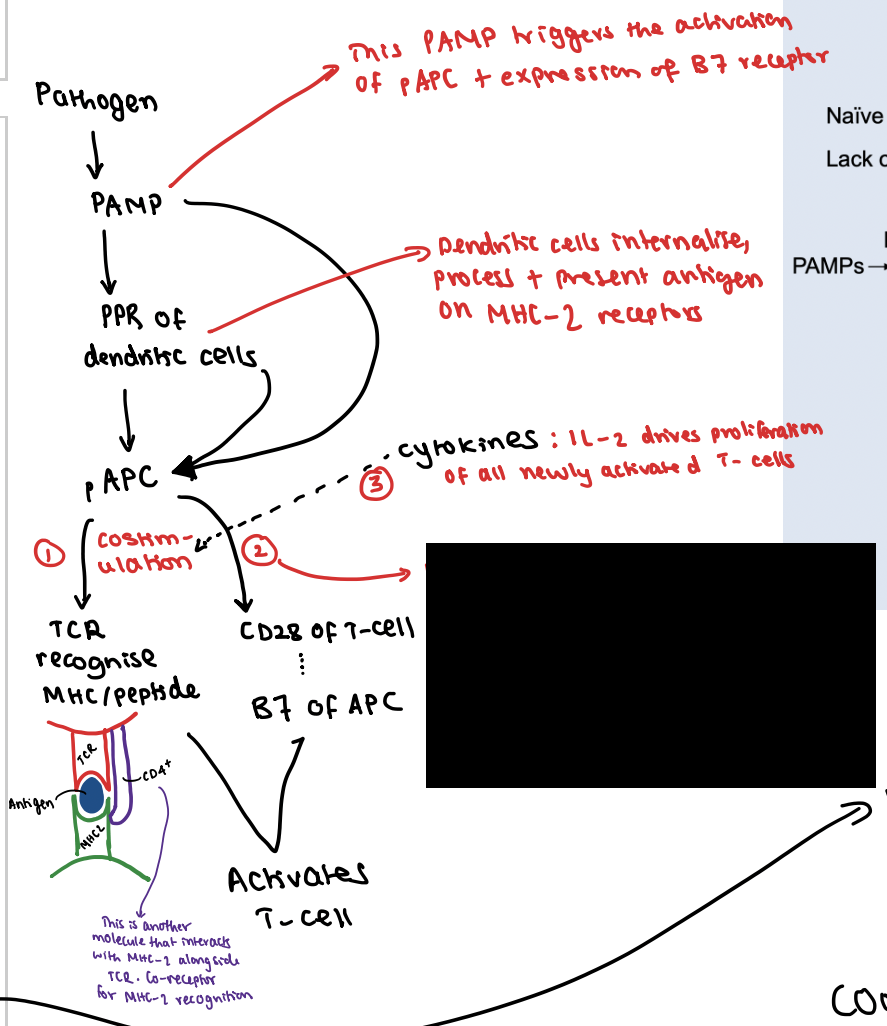
What is the importance of signal 2?
It’s an important safety measure to distinguish between foreign and self proteins and is core in T-cell tolerance and activation.
Plus it ensures the T-cell does not become anergic (unresponsive) or undergo apoptosis.
Which requires stronger activation CD8 or CD4 T-cells?
Naive CD8 T-cells
What is the precursor T-helper cell known as?
THP or TH0
What does TH1 do?
Helps activate macrophages
Suppress intracellular infections
Help activate CTLs
What cytokines drive TH1?
IL-12 and INF-gamma
What does TH2 do?
Helps basophils,mast cells,eosinophils and B-cells deal with parasitic infections
What cytokines drive TH2?
IL-4
What does TH17 do?
Help promote neutrophil control of extracellular bacterial and fungal infections
What cytokines drive TH17?
IL-6, TGF-beta, IL-23
What does TFH do?
Help B-cells become activated
Help switch B-cells from producing low to high affinity antibodies
What cytokines drive TFH?
IL-6, IL-21
What does Treg do?
Suppress activity of other effector T-cell populations
What cytokines drive Treg?
TGF-beta
Where does affinity maturation occur?
In the germinal centres of lymphoid tissue
Why are TFH cells important for B-cells?
-Required for affinity maturation
-Required for B-cell activation
What is the difference between short and long-lived plasma cells?
Short lived cells have effector functions and secrete large amounts of antibodies whilst long-lived take up residence in the bone marrow and maintain continuous low level supply of antibody.