Biology: Quiz 7
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
a system which consists of endocrine glands and tissues which secrete hormones in an organism
endocrine system
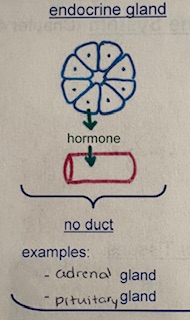
a gland which secretes certain substances directly into the blood stream, possesses no duct or tube
endocrine gland
what are two examples of endocrine glands? What do they not contain?
adrenal and pituitary
do not contain ducts
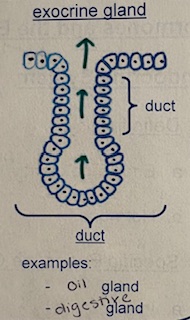
what are two examples of exocrine glands? what does it contain?
oil and digestive glands
contains a duct
What is an example of a gland that contains both endocrine and exocrine glands?
heterocrine gland
chemical substance produced in an endocrine gland or tissue secreted into the blood stream and carried to a target cell upon which it has a physiological effect
classical definition of a hormone
chemical substance produced in specialized cells, travels in body fluids and acts on a target cell, changing it functioning
modified definition of a hormone
chemical composition meaning water-soluble ex. proteins, peptides, amino acid derivatives
hydrophilic
chemical composition meaning lipid-soluble ex. steroids
lipophilic/ hydrophobic
hormones are effective in ____ ____ quantities
extremely small
hormones govern _____ of a reaction and don’t initiate the reaction
the rates
What are the functions of hormones?
influence reactions with aid in homeostasis
have a morphogenic action
regulate autonomic activity, central nervous system, and behavior
What does it mean that hormones have a morphogenic action?
influence an animal’s form or shape of its tissues and organs
signal transduction pathways link ____ to ____
signal transduction pathways link signal reception to response
a process in which a cell converts and amplifies an extra curricular signal into an intracellular signal that affects the same function in the cell (response)
signal transduction
Describe the process: Mechanism of Action
hormone or environmental stimulus goes to a receptor
Reception → the receptor receives signal and the stimulus goes through a conformational change through the plasma membrane
Transduction → signal is turned into relay proteins or transferred to second messengers
Response → the relay proteins and second messengers activate a cellular response
What is the response the occurs from Signal Transduction?
Transcriptional Regulation (DNA → RNA) and
Post-translational modification (RNA → Protein)
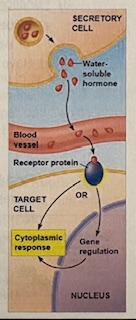
Describe the process of a hydrophilic hormone
secretory cell releases the water soluble hormone into the extracellular fluid
the water soluble hormone diffuses into the bloodstream and goes throughout the body
the water soluble hormone diffuses back out of the blood and into a receptor protein on the target cell
the hormone can then go directly and create a cytoplasmic response OR go into the nucleus for gene regulation, back out of the nucleus, and then create a cytoplasmic response
Describe the process of a lipophilic hormone
secretory cell releases the lipid-soluble hormone
the lipid soluble hormone diffuses into the bloodstream and is carried by transport proteins throughout
eventually, the lipid-soluble hormone diffuses out of the bloodstream and goes directly into the target cell
within the target cell, the lipid-soluble hormone connects with a receptor protein in the nucleus OR cytoplasm
The hormone then works with the receptor protein and triggers a cytoplasmic response
The brain hormone (PTTH) produces…
ecdysteroid (ecdysone)
ecdysteroid (ecdysone) stimulates …
molting and metamorphosis
The juvenile hormone continues ___, maintains ___, and prevents ___.
continues juvenile molts
maintains larval growth
prevents maturation
Endocrine gland contains
pineal gland, hypothalamus, and posterior pituitary
what is the hormone produced by the pineal gland?
melatonin
participates in regulation of biological rhythms
melatonin (pineal gland)
What hormones does the hypothalamus contain?
releasing and inhibiting hormones
regulate anterior pituitary
releasing and inhibiting hormones (hypothalamus)
What hormones do the posterior pituitary contain?
oxytocin and vasopressin
secretion of milk by mammary glands and uterine muscle contraction
oxytocin (posterior pituitary)
also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), promotes retention of water by kidneys; influences social behavior and bonding
vasopressin (posterior pituitary)
what is the target of the hormone ADH?
kidney tubules
What is the target of oxytocin?
mammary glands and uterine muscles
The anterior pituitary contains what hormones?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin
Growth Hormone (GH)
GH
growth hormone
ACTH
adrenocorticotropic hormone
TSH
Thyroid stimulating hormone
LH
liteinizing hormone
FSH
follicle stimulating hormone
What are the steps of a follicle maturing through the ovary?
primary follicle is stimulated by FSH (anterior pituitary)
the primary follicle then produces estrogen
the primary follicle then matures developing a secondary ovum and mature follicle
FSH and LH (anterior pituitary) cause the follicle to rupture and release (ovulation)
The follicle then develops into the corpus luteum
the corpus luteum is yellow and produces progesterone
the progesterone then causes the corpus luteum to turn into the corpus albicans which then disintegrates
what is the regulator of the ovulation system that signals the rest of the process to happen?
estrogen
What stimulates the release of the anterior pituitary hormones?
the hypothalamus
FSH and LH target what?
testes or ovaries
TSH targets what?
thyroid
Prolactin targets what?
mammary glands
MSH targets
melanocytes
GH targets what?
liver, bones, other tissues
Which hormones from the anterior pituitary have tropic effects only?
FSH and LH, TSH, and ACTH
Which hormones from the anterior pituitary have nontropic effects only?
Prolactin, MSH
Which hormone from the anterior pituitary have both tropic and nontropic effects?
GH
The posterior pituitary has?
long hormones
the anterior pituitary has?
short hormones (with capillary bed within the hypothalamus)
the endocrine gland contains?
thyroid glands, parathyroid glands, adrenal (medulla and cortex) glands
What hormone does the thyroid gland contain?
thyroid hormones T1 and T2 and calcitonin
T1 and T2 (thyroid gland)
stimulates and maintains metabolic processes
lowers blood calcium levels
calcitonin (thyroid gland)
what hormone does the Parathyroid gland contain?
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
raises blood calcium levels
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Adrenal gland the adrenal medulla contains?
epinephrine and norepinephrine
raise blood glucose levels, increase metabolic activities, constrict certain blood vessels
epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenal medulla)
Adrenal gland the adrenal cortex contains what hormone?
glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
raise blood glucose levels
glucocorticoids (adrenal cortex)
promotes reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of K+ in kidneys
mineralocorticoids (adrenal cortex)
Pancreas contains what hormones?
insulin and glucagon
lowers blood gluecose
insulin (pancreas)
raises blood glucose
glucagon (pancreas)
Ovaries contain what hormone?
estrogens and progestins
stimulates uterine lining growth, promotes developments and maintenance of female secondary sex characteristics
estrogen (ovaries)
promote uterine lining growth
protestins (ovaries)
Testes contain what hormones?
androgens
support sperm formation; promotes development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristics
androgens (testes)
tropic hormones
stimulates other endocrine glands to produce their hormone
pituitary gland is often called the ____ of the endocrine system
master gland
gondotropins
found in both male and females
FSH and LH
Females: stimulates follicle development and produces estrogen
males: aids in production of sperm and produces inhibin
FSH → Follicle stimulating hormone
Females: stimulates ovulation and development of corpus luteum and produces progesterone
males: stimulates secretion of male sex hormones
LH → luteinizing hormone
what increases Ca2+ levels in blood?
parathyroid hormone (parathyroid gland)
Describe the control of calcium homeostasis feedback loop
blood Ca2+ levels fall
blood going through the parathyproid glands stimulates the gland based on how much Ca2+ is in the blood
parathyroid glands release PTH if Ca2+ is too low
PTH stimulates Ca2+ uptake and promotes vitamin D in the kidneys (doesn’t allow Ca2+ and vitamin D to leave the body via urination)
the active vitamin D then increases Ca2+ uptake in the intestines
PTH also stimulates Ca2+ release in the bones by triggering the osteoclast to break it down off the bone
because of the bones, kidneys, and intestines increasing Ca2+ and vitamin D in the blood, the Ca2+ levels rise
what lowers the Ca2+ levels in blood by triggering the opposite of PTH?
calcitonin (thyroid gland)
What is the regulator in the control of calcium homeostasis feedback loop?
calcium (Ca2+)
Describe the blood glucose feedback loop
blood glucose levels rise because of eating
the beta cells of the pancreas secretes insulin which goes to the cells and the liver
cells transport glucose into body cells and store it as glycogen in the liver causing blood glucose levels to fall
when blood glucose levels fall too much, the alpha cells of the pancreas secretes glucagon
glucagon causes the breakdown of glycogen and release of glucose into the blood, causing the blood glucose levels to rise
What is the stimulator in the blood glucose feedback loop?
glucose levels
hyposecretion of growth hormone in a child/ adolecant causes?
(too little GH)
causes dwarfism
hypersecretion of growth hormone child/adolecent causes?
(too much)
giantism
hypersecretion of growth hormone in an adult causes?
acromegaly (bones keep growing and have excess bony material)
hyposecretion and hypersecretion of thyroxine cause?
goiter and other complications
(growth on neck)
hyposecretion of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) causes
(too little) diabetes insipidus
hyposecretion of insulin causes?
diabetes mellitus
What are the two types of diabetes mellitus?
type 1
Type 2
insulin dependant (they don’t make any insulin)
type 1
non-insulin dependant and insulin resistance (their insulin isn’t effective and they have reduced sensitivity of target tissues to actions of insulin
type 2
what are the functions of a transport system?
carry nutrient + O2 to cells
remove CO2 and other wastes
carry regulatory materials (hormones)
transport system functions must be delivered where?
to cells either suspended or dissolved in water
contains interstitial fluid that is squeezed through spaces around cells as the animal moves, usually a muscular pump that facilitates movemens
contains hemolymph in sinuses surrounding organs, tubular heart
open circulatory system
blood circulates through vascular system by a pump, vascular system keeps circulating blood that s seperate from the extracellular fluid, there is an exchange of materials between blood and cells occurring across capillaries
contains dorsal vessels (main heart), auxiliary hearts, and ventral vessels
close circulatory system
what are two examples of open circulatory systems?
arthropods (insect) and molluscs (clams)
What is an example of a close circulatory system?
annelids (earthworms)
carries blood away from the heart
artery
carries blood to the heart
veins
The insect hormone that stimulates molting and metamorphosis of a larva into a butterfly is?
ecdysteriod
In the ovary, FSH stimulates the development of the primary follicle which releases what hormone?
estrogen