Synapses and NTs
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 8 and 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Describe a synapse
junction between two neurons allowing signals to pass from one to the other
Compare and contrast the key features, functions, and capabilities of chemical vs. electrical synapses
Both:
are ‘plastic’ (i.e., can be modified), but chemical synapses probably more so
allow summing up inputs by the post-synaptic neuron
Most synapses are chemical synapses
Describe the main steps of chemical neurotransmission and how these steps are regulated
Package NTs into vesicles at the axon terminal
Action potential arrives 🡪 voltage-gated Ca2+ influx
Ca2+ influx 🡪 vesicles fuse via SNAREs
NTs bind to receptors on postsynaptic side
NTs removed from synaptic cleft
What is synaptic transmission?
process of signalng via synapses
Where does the word synapse come from?
from Greek, ‘syn’ = together, ‘haptein’ = to fasten, join (coined by Sherrington in 1897)
How many synapses does the brain have? How does this compare to the nb of neurons?
~100 trillion (1014) synapses
~100 billion (1011) neurons so 1000 synapses per neuron
How was the disagreement over distinct neurons or a continuous net of fibres resolved?
Golgi stain (Ramón y Cajal, late 1800s)
Physiological evidence from study of reflexes (Sherrington, around 1900)
Final evidence from electron microscopy (1950s)
What’s the neuron doctrine vs the reticular theory?
existence of distinct neurons vs continuous net of fibres
How do neurons allow flexibility in complex organisms vs in very simple animals?
thanks to integration of inputs from interneurons, sensory neurons etc = output through motor neurons = behaviour // sensory input = stereotypic behaviour
What structures allow electrical synapses to function correctly and how? What are their subtypes?
gap junctions to let current pass between neurons
connexons made up of connexins
What’s the diameter of a gap junction? What flows through them?
1 - 2 nm
ions = current passing through
How are electrical changes in one neuron passed directly to the other? What types of currents are transmitted?
gap junctions !
hyperpolarisation and depolarisation
How can we block hyper.depolarisation from being passed from one neuron to the next?
by deleting a connexin gene (shakB2 mutant)
How was communication between neurons shown visually?
through a red dye, turning the green neurons yellow - this made adjacent neurons yellow too
What are 2 main advantages of synapses?
fast communication
synchronising neurons
What was the first evidence of chemical synapses? Who did this experiment?
using two isolated frog hearts that nerves release a chemical which slows the heartbeat - ACh!
Otto Loewi, 1921
What are types of post-synaptic cells?
neuron in a neuron-neuron synapse
skeletal muscle in a motor neuron
hormonal gland, smooth muscle, heart in an autonomic neuron
What are secretory granules?
dense and large vesicles carrying peptide NTs and used once
What are the 5 stages of chemical synaptic transmission?
NT put in vesicles at pre-synaptic terminal
AP arrives, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open
Ca2+ influx 🡪 vesicles fuse to membrane, NTs released
NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft, activate Rs on the postsynaptic cell
NTs removed from cleft
What are the main differences between synaptic vesicles and dense-core secretory granules?
size and density: ‘clear’ small (40 - 50 nm) // dense and large (100nm)
content: small molecule NTs // peptide NTs
Filling: by transporter proteins at presynaptic `terminal // ER/Golgi secretory apparatus
Termination: recycled // one and done
What are 2 ways that NTs can be packaged to be brought to the presynaptic terminal?
in synaptic vesicles or in dense-core secretory granules
When using a calcium-sensitive fluorescent protein, what does more fluorescence translate?
more calcium
How does AP affect calcium channels in presynaptic terminals?
opens the channels = influx of calcium
Is the synaptic cleft of electrical or chemical synapses larger?
chemical
How does a sudden influx of calcium in presynaptic terminals affect vesicles and their content?
vesicles fuse to membrane, NTs released
After a chemical synapse, the vesicle was recycled through endocytosis, this means the vesicle contained…?
small molecules, NOT peptides
What structures allow vesicle fusion? What ion is involved in this interaction and what role does it play?
SNAREs
calcium binds to synaptotagmin = conformational change so SNAREs ‘zipper’ together, forcing the vesicle to fuse to the plasma membrane
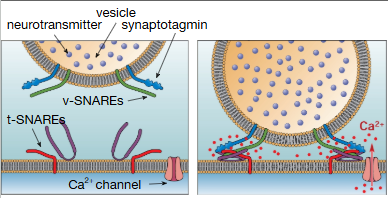
What are SNAREs targeted by?
toxins (botulinum toxin, tetanus toxin)
What types of postsynaptic receptors can NTs bind to after their release into the synapse?
ligand gated ion channels and GPCRs eg
What type of receptor leads to direct de.hyper.polarisation of the postsynaptic cell?
ligand-gated ion channels
How does a NT affect the postsynaptic neuron? (does it enter the cell?)
by binding to receptors which lead to ion influxes or downstream effects like phosphorylation of target effectors
DOES NOT ENTER CELL
What types of channels do NTs go through?
ones allowing their uptake, NEVER pores in postsynaptic neurons
What are 3 ways in which NTs can be removed from the synaptic cleft, terminating their communication?
diffuse away
actively taken up by transporters for recycling (into presynaptic neuron or glia)
destroyed in the cleft by enzymes
What is the issue with NTs always only diffusing away as a method of termination?
passive and slow, unreliable bc would mean prolonged communication when no longer necessary
What are common points between electrical and chemical synapses?
both are plastic but chemical synapses a bit more
allow summing up inputs by the post-synaptic neuron
Are most synapses chemical or electrical?
chemical
What distinguishes electrical vs chemical synapses in terms of their direction, their transformation and their speed?
both directions // only in one
passed directly, can only be attenuated // can be radically transformed (inverted, amplified, modulated)
fast (under 0.3 ms) // slow (0.3 - 5 ms)
What types of action potentials do motor neuron APs cause?
always muscle cell APs
What is the speed of transmission in the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and the NT used? Does failure/attenuation of AP occur?
fast and reliable
ACh
no!
What is a neuromuscular junction?
junction between motor neuron and muscle cell
How do presynaptic neurons contribute to the efficiency of the NMJ?
large nb of active zones
How do postsynaptic (motor end-plate) contribute to the efficiency of the NMJ?
Contains junctional folds, densely filled with NT receptors
How are active zones and junctional folds relatively located in the NMJ?
precisely aligned
What is the qualitative size of the NMJ?
one of largest synapses in the body
How was it understood that NTs are released from vesicles?
release always produced the same amplitude so must be a repeatable way of releasing the same amount every time
no halves, not irregular or continuous, always multiples = NTs come in quantal packets
What are different varieties of CNS synapses and what informs on this?
dendrosomatic
dendrodendritic
axosomatic
axodendritic
axoaxonic
the morphology of the synapse
Why does botulinum toxin cause paralysis?
targets SNAREs
= no fusion of vesicles with neuron membrane = no NT release
= no synapse so no motor mvt/no contraction
If you block vesicle endocytosis, how would this affect release of small molecule vs. peptide neurotransmitters?
small molecule vesicles would be affected bc they are recycled so we would run out // peptide would be fine bc they are a one use anyway
What is the Nernst potential of Ca2+ at 37 ºC, if the concentration outside is 1 mM and the concentration inside is 0.0001 mM? Why does this explain the movement of calcium ions when calcium channels open?
+122 mV
calcium moves out into IC down concentration/chemical gradient + towards the negative membrane potential bc is a positive ion (-65mV inside so defo mvt in considering nernst equation)
What is a quantum?
one vesicle full of neurotransmitter
What makes a molecule a NT?
present in a presynaptic terminal
released in response to stimulation
acts on the postsynaptic neuron
its inhibition should prevent synaptic transmission
What are 4 ways of determining if a molecule acts as a NT experimentally?
immunostaining = presence of NT
in situ hybridisation = enzyme/transporter expression?
collect fluid around neuron = release?
drugs, delete genes encoding enzymes/transporters/receptors = block it to study it
What are 3 origins from which NTs can come from?
amino acids
amines
peptides
What are 3 characteristics of NTs that come from amino acids and amines?
small (100-200 Da)
stored in synaptic vesicles
bind to ligand gated ion channels or GPCRs
What are 3 characteristics of NTs that come from peptides?
large (1K - 3K Da)
stored in secretory granules
bind to GPCRs
What will peptide-releasing neurons also release alongside the NT?
small molecule transmitter, called a ‘co-transmitter’
What type of receptor will lead to direct depolarisation/hyperpolarisation of the postsynaptic cell?
ligand-gated ion channels (ionotropic receptors)
How many transmitters, receptors and effectors are involved in divergence?
1 // multiple receptors and effectors
How many transmitters and effectors are involved in convergence?
multiple transmitters and receptors // 1
What’s the major excitatory NT, its role, mode of action and how is it synthesised then degraded/removed?
amino acid glutamate
EPSP, coincidence detector
binds to 3 different types of ionotropic Rs + mGLuRs
found everywhere
selective uptake into presynaptic terminals and glia
What types of receptors does glutamate bind to?
ionotropic receptors:
AMPA
NMDA
Kainate
metabotropic receptors:
mGluR1, mGluR2, etc
What’s the function of glutamate AMPA receptors?
fast excitatory transmission
sodium and potassium currents = EPSP
Can AMPA and NMDA glutamate receptors co-exist? When do NMDA receptors open?
yes!
voltage-dependent magnesium block, magnesium blocks the gate at resting potential, evacuates and opens up the gate at -30mV eg, so only open when the neuron is already depolarised
What’s the function of NMDA receptors?
let calcium in, leading to downstream signalling
coincidence detector: when a neuron is activated right after it was already activated 🡪 important for learning
In what case can glutamate be inhibitory?
when binding to some metabotropic receptors like in the retina
What’s the major inhibitory NT, its role, mode of action and how is it synthesised then degraded/removed?
GABA, amino acid but never used to make proteins
IPSPs
binds to ionotropic and metabotropic receptors
synthesised from glutamate
selective uptake into presynaptic terminals and glia
Which enzyme is responsible for synthesising GABA from glutamate?
glutamic acid decarboxylase
How does GABA produce IPSPs?
GABA-gated chloride channels
In what condition do GABA channels open?
when GABA binds
What’s the major modulatory NT, its role, mode of action?
glycine
inhibits neurons via glycine receptors + binds to glutamate receptors
Name disorders where NT systems are impaired. How are these systems linked to the identified disorders?
too much GABA = coma/loss of consciousness
too little = seizures
Why does it matter how excitatory and inhibitory synapses are arranged spatially?
if an inhibitory synapse is closer to the soma, it can inhibit the excitatory synapse/EPSP
When could a GABA receptor not produce an IPSP? Why?
e.g. if Vm is near chloride’s Nernst potential (-65mV)
instead of chloride exiting, it would flow out of the cell to stay closer to -65mV, instead of coming in and causing hyperpolarisation
When does inhibition often occur? What are mechanisms for this?
presynaptically
inactivating calcium channels = reduced calcium = fewer NTs = reduced effect/inhibition
What is runaway excitation? What avoids this and what type of neuron can this role be compared to?
too much excitation!
like interneurons - they balance excitation and inhibition here
What does shunting inhibition mean?
reduction in membrane resistance caused by the opening of membrane pores = decrease in neuronal activity acting as CNS-wide inhibition
How do GABA receptors leak current out of the membrane? What does this cause?
Opening chloride conductance decreases the membrane resistance
When other chemicals bind to GABA-Rs, what is their effect and a condition to this?
modulate the response to GABA binding ie no effect if GABA is not already bound - termed an allosteric drug
What are examples of chemicals that can bind to GABA receptors?
ethanol (alcohol), benzodiazepines (diazepam for anxiety), barbiturates (sedatives/anti-convulsant), neurostreroids (progesterone)
What’s an example of inhibition caused by alcohol binding to GABA-Rs? What does continuous then absent stimulation of these receptors cause (like sobering)?
not being able to walk in a straight line
withdrawal - will need more stimulation to work bc of this continuous stimulation = big adjustment needed
What are examples of ways in which metabotropic GABA Rs work in different cells?
open K+ channels
close Ca2+ channels
trigger other second messengers like cAMP
Are metabotropic GABA Rs pre or postsynaptic? Are they inhibitory or excitatory?
presynaptic and/or autoinhibitory
Give examples of pharmacological agents that modify neurotransmission in a variety of ways and explain how they work
modulate GABA effect so can be positive or negative modulators, those leading to relaxation increase will increase GABA affinity
alcohol (+ GABA agonist), diazepam (+ GABA affinity), sedatives, anti-convulsants, progesterone (natural regulators?)
What is an allosteric drug?
bind to specific sites on proteins distinct from the active site modulating protein activity and offering advantages like enhanced selectivity