7. Psychological Disorders (4%)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Biomedical Approach
Biomedical vs. Biopsychosocial Approach
Therapy includes interventions that rally around symptom-reduction of psychological disorders
Assumes that any disorder has roots in biomedical disturbances, and thus the solution should also be of a biomedical nature
Fails to take into account many of the other sources of disorders
Biopsychosocial Approach
Biomedical vs. Biopsychosocial Approach
This method assumes that there are biological, psychological, and social component's to an individual's disorder
Goal is to provide both direct therapy and indirect therapy
Direct Therapy
Direct vs. Indirect Therapy
Acts on the patient
Examples include medications and counseling
Indirect Therapy
Direct vs. Indirect Therapy
Consists of increasing social support for the individual by educating the family and friends of the patient
psychotic disorders
a general class of disorders marked by the following symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thought, disorganized behavior, catatonia, and negative symptoms
Schizophrenia
Name the Psychotic Disorder
Marked by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thought, disorganized behavior, catatonia and negative symptoms
Characterized by a break between an individual and reality
Positive Symptoms
Schizophrenia - Positive vs. Negative Symptoms
Symptoms of behaviors, thoughts, or feelings added to normal behavior
EX: delusions or hallucinations.
Negative Symptoms
Schizophrenia - Positive vs. Negative Symptoms
The absence of normal behaviors
EX: disturbance of affect and avolition
Delusions
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
False beliefs discordant with reality and not shared by others in the individual's culture that are maintained in spite of strong evidence to the contrary
Delusions of Reference
Schizophrenia - Delusions of Reference vs. of Persecution vs. of Grandeur
The belief that common elements in the environment are directed toward the individual
A positive symptom
Delusions of Persecution
Schizophrenia - Delusions of Reference vs. of Persecution vs. of Grandeur
The belief that the person is being deliberately interfered with, discriminated against, plotted against, or threatened
A positive symptom
Delusions of Grandeur
Schizophrenia - Delusions of Reference vs. of Persecution vs. of Grandeur
The belief that the person is remarkable in some significant way
A positive symptom
Thought Broadcasting
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
The belief that one's thoughts are broadcast directly from one's head to the external world
Thought Insertion
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
The belief that thoughts are being placed in one's head
Hallucinations
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
Perceptions that are not due to external stimuli but have a compelling sense of reality
Most common type is auditory
Disorganized Thought
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
The loosening of associations that may be exhibited as speech in which ideas shift from one subject to another or as if their speech has no structure
Neologisms
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
Sometimes schizophrenics create new words
A variation of disorganized thought
Disorganized Behavior
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
A person's inability to carry out activities of daily living such as paying bills, maintaining hygiene, and keeping appointments
Catatonia
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
Refers to certain motor behaviors characteristic of some people with schizophrenia
The patient’s spontaneous movement and activity may be greatly reduced or the patient may maintain a rigid posture, refusing to be moved
At the other extreme, behavior may include useless and bizarre movements not caused by an external stimuli, echolalia, or echopraxia
Echolalia
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
Repeating other people's words
A specific type of catatonic behavior
Echopraxia
Schizophrenia - Positive Symptoms
Imitating other people's actions
A specific type of catatonic behavior
Affect
Schizophrenia
Refers to the experience and display of emotion
Disturbance of this is a negative symptom
Blunting
Schizophrenia - Disturbance of Affect/Negative Symptoms
A lack of emotional responsiveness, seen through limited facial expressions, flat vocal tone, and reduced gestures
Emotional Flattening (aka Flat Affect)
Schizophrenia - Disturbance of Affect/Negative Symptoms
Where a person shows a reduced or absent outward expression of emotion, even if they feel it internally
Inappropriate Affect
Schizophrenia - Disturbance of Affect/Negative Symptoms
When a person's emotional expression doesn't match the situation or their words
EX: laughing hysterically while describing a parent’s death
Avolition
Schizophrenia - Disturbance of Affect/Negative Symptoms
Marked by decreased engagement in purposeful, goal-directed actions
A severe lack of motivation or inability to initiate and persist in goal-directed activities, making everyday tasks like hygiene, chores, or social interaction difficult to start or finish
depressive disorders
a general class of disorders characterized by feelings of sadness that are severe enough, in both magnitude and duration, to meet specific diagnostic criteria
depressive disorders
What class of disorders are these symptoms of?
sadness, sleep, loss of interest (anhedonia), guilt, low energy, concentration, appetite, psychomotor symptoms, suicidal thoughts
(mnemonic = Sadness + SIG E. CAPS)
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Depressive Disorders
A type of depressive disorder characterized by at least one major depressive episode
Classified by severity
Major Depressive Episode
Depressive Disorders
A period of at least two weeks with a depressed mood, loss of interest in life, appetite disturbances, substantial weight changes, sleep disturbances, low energy, difficulty concentrating, etc...
(at least 5/9 of the depressive symptoms are encountered, which must include either depressed mood or anhedonia & the symptoms must be severe enough to impair one’s daily social or work-related activities)
Anhedonia
Depressive Disorders
The loss of interest in formerly enjoyed activities
Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD)
Depressive Disorders
A type of depressive disorder diagnosed to patients who lack the severity of major depressive disorder
When an individual experiences a period, lasting at least 2 years, in which they experience a depressed mood on the majority of days
Classified by duration
Dysthymia
Depressive Disorders
a depressed mood that is not on the scale of major depressive disorder.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Depressive Disorders
A type of major depressive disorder with season onset
The dark winter months are believed to be the source of depressive symptoms
Bipolar Disorders
a general class of disorders characterized by both depressive and manic symptoms, which if severe and persistent enough can be labelled as episodes
Manic Symptoms
Bipolar Disorders
symptoms thought of as prolonged and exaggerated emotion of happiness or joy
bipolar disorders
(***these are the MANIC symptoms)
What class of disorders are these symptoms of?
distractibility, irresponsibility, grandiosity, flight of thoughts, activity or agitation, sleep, talkative
(mnemonic = DIG FAST)
Hypomanic Episodes
Bipolar Disorders - Manic vs. Hypomanic Episodes
When manic symptoms are present for at least 4 days and include at least 3 or more of the 7 defined manic symptoms, yet the symptoms are not severe enough to impair the person’s social or work activities
Manic Episodes
Bipolar Disorders - Manic vs. Hypomanic Episodes
when manic symptoms (3 or more of the defined 7) are severe enough to impair a person’s social or work activities and persist for at least 7 days
Bipolar I Disorder
Bipolar Disorders
A type of bipolar disorder characterized by the presence of manic episodes
Depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes may also occur but are not a requirement for diagnosis
Bipolar II Disorder
Bipolar Disorders
A type of bipolar disorder characterized by the presence of both a major depressive episode and a hypomanic episode, but NOT a manic episode
Cyclothymic Disorder
Bipolar Disorders
A type of bipolar disorder characterized by the presence of less-severe manic and depressive symptoms for the majority of time over a 2-year (or longer) period
Monoamine/Catecholamine Theory of Depression
Bipolar Disorders
theory stating that too much norepinephrine or serotonin in the synapse leads to mania while too little leads to depression.
Anxiety Disorders
A general class of disorders characterized by irrational and excessive fear or anxiety that affects an individual’s daily functioning
They each are classified by the situation or stimulus that induces anxiety
Specific Phobias
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder in which anxiety is produced by a specific object or situation
The most common type of anxiety disorder
Social Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder in which anxiety is brought about by social situations with the belief that the individual will be exposed, embarrassed, or simply negatively perceived by others
Avoidant behavior to the point of social or occupational impairment is necessary for diagnosis
Panic Disorder
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder characterized by repetitive panic attacks
Diagnosis requires the recurrence of unexpected panic attacks wherein there is no clear trigger and the panic attacks are seemingly random
Agoraphobia
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder in which anxiety brought about by being in places where escape would be difficult
People tend to be uncomfortable leaving their homes, using public transportation, being in open spaces, waiting in lines, or simply being in crowds
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder defined as disproportionate and persistent worry about various things for at least 6 months
In addition, the worrying is difficult to control, even in cases where the individual knows that their worrying and fear is irrational
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder characterized by obsessions, which bring about tensions and compulsions that relieve tension but cause significant impairment to a person’s life
The relationship between the two is key → obsessions raise the individual’s stress level, and the compulsions relieve that stress
A diagnosis requires that the compulsions impair one’s daily activities
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Anxiety Disorders
A type of anxiety disorder in which person has an unrealistic negative evaluation of their personal appearance and attractiveness, usually directed toward a certain body part (this is known as preoccupation, a type of worry which lacks the disastrous ideation that accompanies obsessions)
The belief persists even with clear evidence to the contrary
trauma- and stressor-related disorders
A general class of disorders characterized by a traumatic event being the source of symptoms
Typical responses include fear, helplessness, and anxiety but uniquely also include maladaptive symptoms such as anhedonia, dysphoria, aggression, or dissociation
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Trauma- & Stressor-Related Disorders
A type of trauma- and stressor-related disorder that occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event
Consists of intrusion symptoms, arousal symptoms, avoidance symptoms, and negative cognitive symptoms
To meet diagnostic criteria, a particular number of these symptoms must be present for at least one month
Avoidance Symptoms
PTSD - Avoidance vs. Intrusion vs. Negative Cognitive vs. Arousal Symptoms
Deliberate attempts to avoid the memories, people, places, and activities associated with the trauma.
Intrusion Symptoms
PTSD - Avoidance vs. Intrusion vs. Negative Cognitive vs. Arousal Symptoms
Recurring reliving of the event such as flashbacks and nightmares.
Negative Cognitive Symptoms
PTSD - Avoidance vs. Intrusion vs. Negative Cognitive vs. Arousal Symptoms
An inability to recall key features of the event.
Arousal Symptoms
PTSD - Avoidance vs. Intrusion vs. Negative Cognitive vs. Arousal Symptoms
An increased startle response, irritability, and anxiety.
Dissociative Disorders
a general class of disorders in which the person avoids stress by escaping from parts of their identity but otherwise still have an intact sense of reality
Dissociative Amnesia
Dissociative Disorders
a type of dissociative disorder characterized by an inability to recall past experiences due to trauma, not a neurological disorder
Dissociative Fugue
Dissociative Disorders - Dissociative Amnesia
A sudden, unexpected move or purposeless wandering away from one's home or location of daily activities
Individuals are confused about their identity and can even assume a new identity — they may actually believe they are someone else, with a complete backstory
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)
Dissociative Disorders
A type of dissociative disorder where there are two or more personalities that recurrently take control of a person's behavior
Results when the components of identity fail to integrate
In most cases, patients have suffered from severe physical or sexual abuse as young children
Depersonalization/Derealization Disorder
Dissociative Disorders
A type of dissociative disorder wherein a person feels detached from their own mind and body, or from their surroundings
These feelings cause significant impairment of regular activities, but even during these times such patients do not display psychotic symptoms like delusions or hallucinations
somatic disorders
a general class of disorders characterized by somatic (bodily) symptoms that cause significant stress or impairment
Somatic Symptom Disorder
Somatic Disorders
A type of somatic disorder characterized by having at least one somatic symptom, which may or may not be linked to an underlying medical condition, and that is accompanied by disproportionate concerns about its seriousness, devotion of an excessive amount of time and energy to it, or elevated levels of anxiety
Illness Anxiety Disorder
Somatic Disorders
A type of somatic disorder characterized by being consumed with thoughts about having or developing a serious medical condition
Most patients were previously classified under hypochondriasis in the DMS-IV-TR
Conversion Disorder
Somatic Disorders
A type of somatic disorder characterized by unexplained symptoms affecting voluntary motor or sensory functions that are incompatible with the patient’s neurophysiological condition
EX: paralysis or blindness without evidence of neurological damage
Was historically called hysteria
Personality Disorder
a general class of disorders characterized by a pattern of behavior that is inflexible and maladaptive, causing distress or impaired functioning in at least two of the following → cognition, interpersonal functioning, or impulse control
Ego-Syntonic
Ego-Syntonic vs. Ego-Dystonic
A psychological disorder is considered this when a person believes that their behavior is correct, normal, or in harmony with their goals
EX: Personality disorders
Ego-Dystonic
Ego-Syntonic vs. Ego-Dystonic
A psychological disorder is considered this when a mentally ill person believes their illness was thrust upon them
EX: most of the disorders covered in this chapter EXCEPT for personality disorders
Paranoid, Schizotypal, Schizoid
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
name the 3 personality disorders found in Cluster A (all marked by behavior that is labeled as odd or eccentric by others)
Antisocial, Borderline, Histrionic, Narcissistic
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
name the 4 personality disorders found in Cluster B (all marked by behavior that is labeled as dramatic, emotional, or erratic by others)
Avoidant, Dependent, Obsessive-Compulsive
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
name the 3 personality disorders found in Cluster C (all marked by behavior that is labeled as anxious or fearful by others)
Paranoid Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster A personality disorder
Marked by pervasive distrust of others and suspicion regarding their motives
In some cases, these patients may actually be in the prodromal phase of schizophrenia
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster A personality disorder
Refers to a pattern of odd or eccentric thinking
They may have minor delusions of reference, or magical thoughts and superstitious beliefs
Schizoid Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster A personality disorder
Involves a pervasive pattern of detachment from social relationships and a restricted range of emotional expression.
Antisocial Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster B personality disorder
Marked by a pattern of disregard for and violations of the rights of others
3x more common in males
Displayed by many serial killers and career criminals
People with this disorder make up ~ 20-40% of prison populations
Borderline Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster B personality disorder
Marked by a pervasive instability in interpersonal behavior, mood, or self-image
Interpersonal relationships are often intense and unstable
May use splitting as a defensive mechanism, in which they view others as either all good or all bad
2x more common in females
Histrionic Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster B personality disorder
Characterized by constant attention-seeking behavior;
Weird clothes, dramatic behavior, extremely extroverted
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster B personality disorder
One has a grandiose sense of self-importance or uniqueness, preoccupation with fantasies of success, a need for constant admiration and attention, and characteristic disturbances in interpersonal relationships such as feelings of entitlement
They often have very fragile self-esteem and are constantly concerned with how others view them
Avoidant Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster C personality disorder
The affected individual has extreme shyness and fear of rejection
Dependent Personality Disorder
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster C personality disorder
Characterized by a continuous need for reassurance from others
Tend to remain dependent on one person to take action and make decisions
Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD)
Personality Disorders
WORD BANK: Paranoid, Antisocial, Borderline, Avoidant, Dependent, Schizotypal, Schizoid, Obsessive-Compulsive, Histrionic, Narcissistic
——
A type of Cluster C personality disorder
Where the individual is perfectionistic and inflexible, tending to like rules and order
Sometimes they are unable to discard worn-out objects, lack a desire to change, and excessively stubborn
Unlike OCD this is lifelong and ego-syntonic → (“I just like rules and order!” as opposed to “I can’t stop washing my hands because of the germs!”)
dopamine, neuroleptics, dopamine, neuroleptic, nerve, antipsychotics
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is highly associated with an excess of __________ in the brain. Many medications used to treat schizophrenia, such as ____________, block ____________ receptors. The term ____________ means that these medications depress ________ function. These drugs are also known as ________________.
Depressive Disorders
What are these biomarkers of? - Depressive vs. Bipolar Disorders
High glucose metabolism in the amygdala.
Hippocampal atrophy after a long duration of illness.
Abnormally high levels of glucocorticoids.
Decreased norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
Bipolar Disorders
What are these biomarkers of? - Depressive vs. Bipolar Disorders
Increased norepinephrine and serotonin.
Higher risk if a parent has it.
Higher risk for a person with multiple sclerosis.
Alzheimer’s Disease
A type of dementia characterized by gradual memory loss, disorientation to time and place, problems with abstract thought, and a tendency to misplace things
Later stages are associated with changes in mood or behavior, changes in personality, difficulty with procedural memory, poor judgement, and loss of initiative
Alzheimer’s Disease
What are these biomarkers of? - Alzheimer’s vs. Parkinson’s Disease
Diffuse atrophy of the brain on CT or MRI.
Flattened sulci in the cerebral cortex.
Enlarged cerebral ventricles.
Deficient parietal lobe blood flow (correlated with cognitive decline)
Acetylcholine reduction.
Choline acetyltransferase reduction (the enzyme that produces acetylcholine).
Reduced metabolism in the temporal and parietal lobes.
Beta-amyloid plaques.
Neurofibrillary tangles of hyperphosphorylated tau protein.
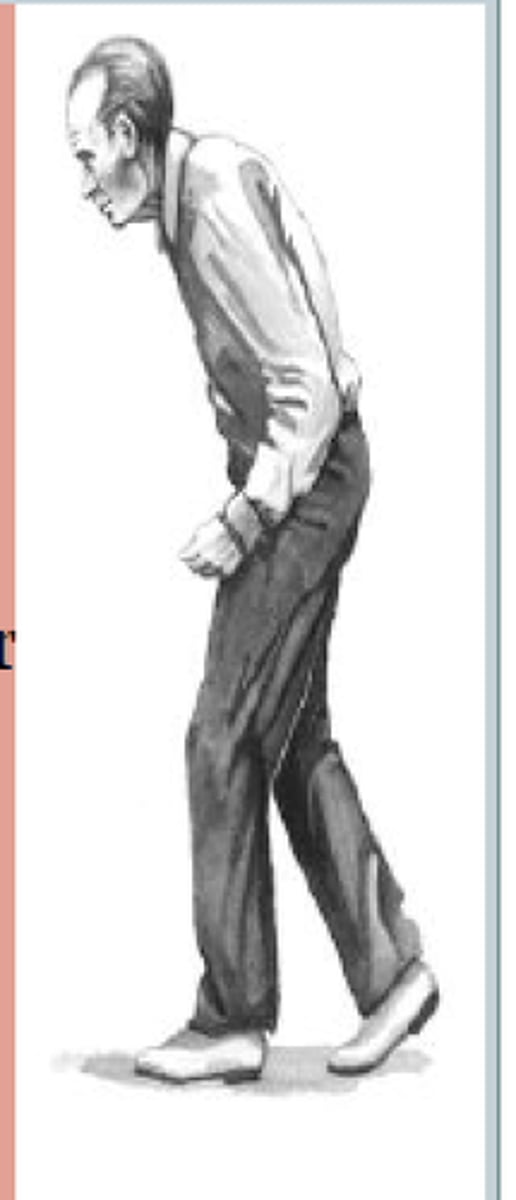
Parkinson's Disease
A neurological disease characterized by bradykinesia, resting tremor, pill-rolling tremor, masklike facies, cogwheel rigidity, and a shuffling gait
Resting Tremor
Parkinson’s Disease - Resting vs. Pill-Rolling Tremor
A tremor that appears when the muscles aren't being used.
Pill-Rolling Tremor
Parkinson’s Disease - Resting vs. Pill-Rolling Tremor
Flexing and extending the fingers while moving the thumb back and forth.
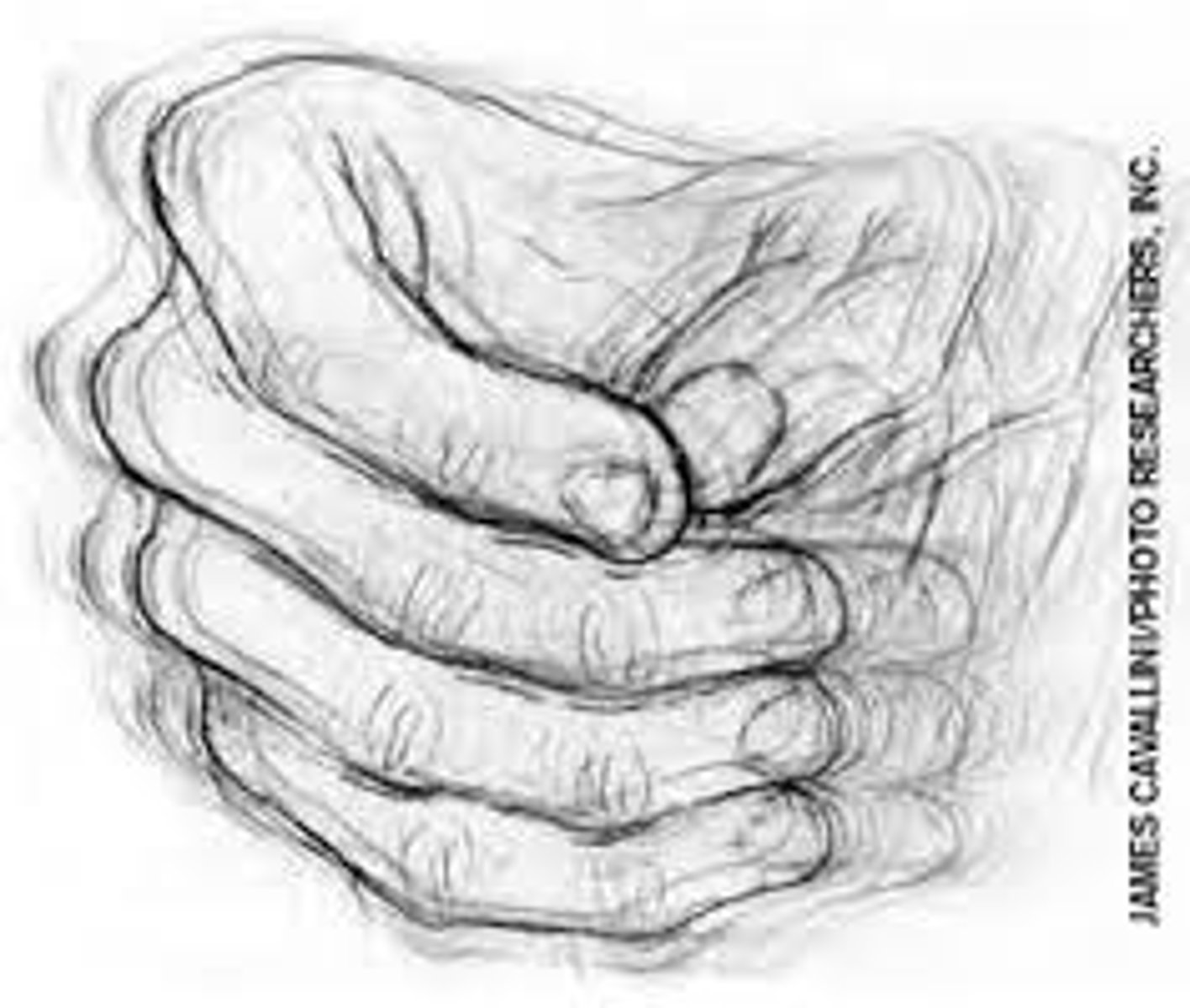
Masklike Faces
Parkinson’s Disease
A facial expression consisting of static and expressionless facial features.
Cogwheel Rigidity
Parkinson’s Disease
Muscle tension that intermittently halts movement as an examiner attempts to manipulate a limb.
Shuffling Gait
Parkinson’s Disease
Stooped posture with small shuffling steps of low ambulatory efficiency.

Parkinson's Disease
What are these biomarkers of? - Alzheimer’s vs. Parkinson’s Disease
Decreased dopamine production in the substantia nigra, which is a layer of cells in the brain that produces dopamine to permit proper functioning of the basal ganglia.
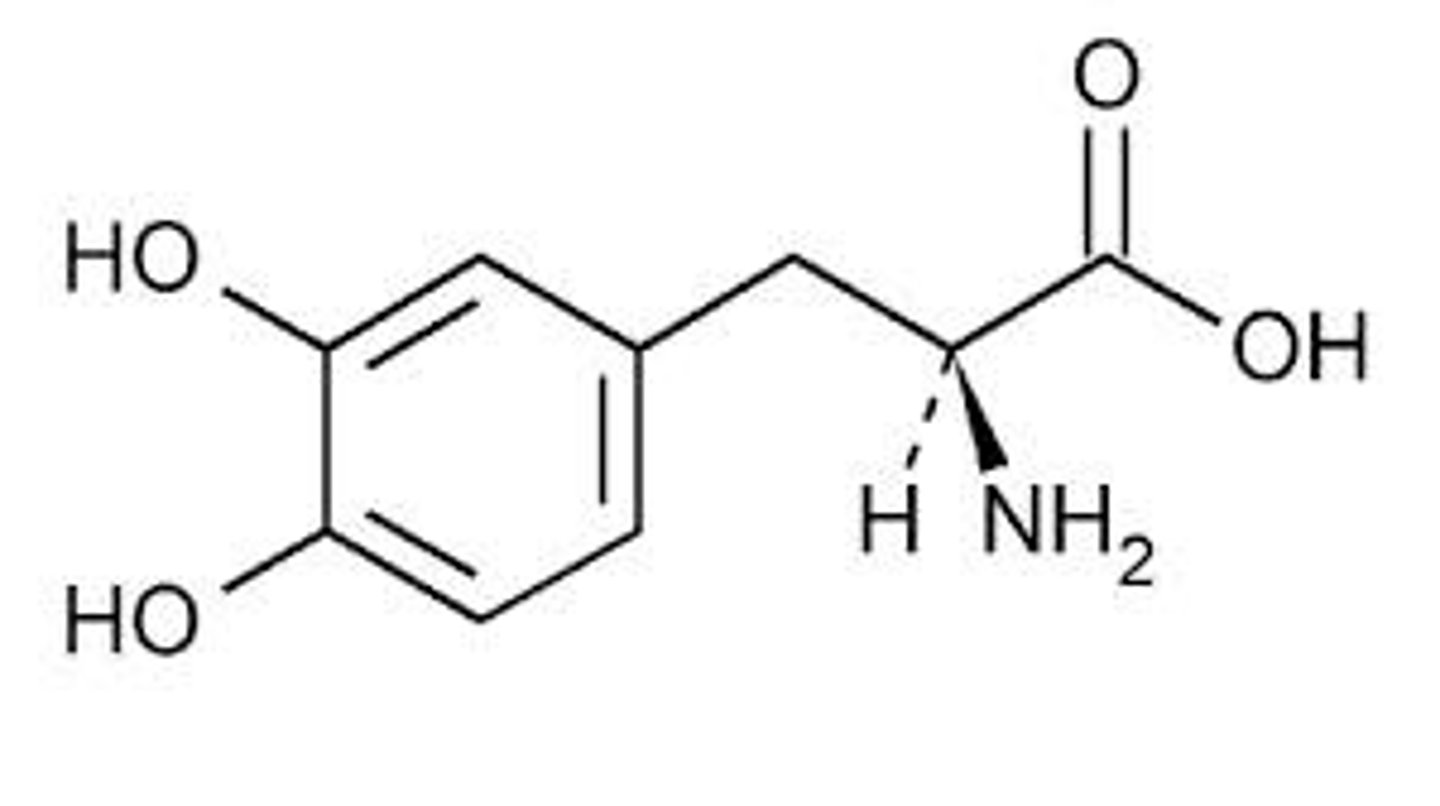
L-DOPA, dopamine
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease can be partially managed with _______, a precursor that is converted to __________ once in the brain, replacing that which is lost due to Parkinson’s Disease.
Antipsychotic
Parkinson’s Disease
_____________ medications often lead to “parkinsonian” side effects, like muscle rigidity and flattened affect.
Parkinson’s Disease
Medications used in ____________ __________ often lead to psychotic side effects, such as hallucinations and delusions.