Quiz 2: Shoulder Complex, Dysfunctions, & Brachial Plexus
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
GH Flexion
Brady: biceps brachii
Pats: pectoralis major
CORAs: coracobrachialis
Ass: anterior deltoid
GH Extension
Pull: pec major
That: triceps brachii
LATtuce: LATtissimus dorsi
Tere: teres major
GH Abduction
Brady: biceps brachii
Drugs: deltoids
Suprina: supraspinatus
GH Adduction
Tere: teres major
Puts: pectoralis major
tere jr's: teres minor
LATtuce: latissimus dorsi
IN: infraspinatus
CORA's: coracobrachialis
Tummy: triceps brachii
GH internal rotation
Tere: teres major
Puts: pectoralis major
LATtuce: LATissimus dorsi
Around: anterior deltoid
SUBS: SUBScapularis
GH external rotation
TERE jr: teres minor
INvades: INfraspinatus
POland: posterior deltoids
Shoulder Complex Bones
-scapula
-humerus
-clavicle
-sternum
Articulation of shoulder complex
-scapulothoracic
-acromioclavicular
-sternoclavicular
-glenohumeral
Scapulothoracic joint
Articulation btwn. scapula and thorax (rib cage)
-not a TRUE joint
ST joint motions
elevation/depression
protraction/retraction
upward/downward rotation
Acromioclavicular Joint
Articulation btwn. acromion and clavicle
-plane joint
acromioclavicular joint motions
small amount of movement
-anterior/posterior translation
-superior/inferior translation
acromioclavicular important ligaments
coracoclavicular and acromioclavicular ligaments
-keep AC joint in place
sternoclavicular joint
Articulation between the clavicle and the sternum
-complex saddle joint
-3 degrees of freedom
sternoclavicular joint motions
elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, axial rotation
sternoclavicular stability
-sternoclavicular ligaments
-articular discs: fibrocartilage (shock absorptions, stability)
-costoclavicular and interclavicular ligament: keep bones from dislocating and distribute forces
Glenohumeral Joint
Articulation btwn. head of humerus and glenoid fossa
-ball and socket joint
-3 degrees of freedom
glenohumeral joint motions
flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, internal/external rotation, horizontal abduction/adduction, and scaption
scaption
30º anterior to frontal plane
other planar motions
horizontal abduction and adduction
scapulohumeral rhythm
when GH and scapula move at the same time
-ST contributes 60º upward rotation
-GH contributes 120º flexion
ST + GH motion = full ROM of shoulder
ratio: 2:1 for GH:ST motion
GH joint stability
GH sacrifices stability for mobility
static stability in GH joint
-capsular ligaments
-coracohumeral ligaments: resists inferior displacement of humeral head
-glenoid labrum: increases surface area
dynamic stability of GH joint
-rotator cuff muscles: SItS
-long head of biceps tendon: when contracts contributes to dynamic stability
coracoacromial arch
roof of GH joint formed by
-coracoacromial ligaments
-acromion
-coracoid process
subacromial space
underneath roof, includes:
-supraspinatus muscle and tendon
-infraspinatus tendon only
-subacromial bursae
-biceps long head
-superior capsule
structures giving dynamics stability
-compresses humeral head into glenoid fossa when carrying weight
-depress humeral head during elevation
-primary movers for shoulder motions (SItS, biceps, and triceps)
dysfunction results from
-structural deficits (congenital, injury)
-overuse/trauma
-nervous system damage
-physiological causes
rotator cuff tear
partial thickness or full thickness tear of SItS muscles
risk factors of RC tear
-repetitive OH activities
-trauma/FOOSH
-weak scapular muscles
-previous impingement
-age, sex, arm dominance
signs and symptoms of RC tear
-pain with active motion
-decreased AROM
-decrease strength, muscle atrophy
clincial evaluation for RC tear
AROM and PROM eval: lack of active abduction past 90º predicts RC tear
diagnostic eval for RC taer
-ultrasound
-MRI
special test for RC tear
jobe (empty can) test
adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
axillary pouch and posterior capsule gets tighter and cause decreased ROM
two types of adhesive capsulitis
primary: unknown
secondary: freq. associated w/ prev UE injuries, hemiplegia (CVA), or conditions where shoulder motion is limited
risk factors of adhesive capsulitis
-female
-thyroid disease
-diabetes
-other autoimmune disease
-CVA
signs and symptoms of adhesive capsulitis
-decrease AROM and PROM
-tight capsule
-pain
-functional challenges
three phases of adhesive capsulitis
phase 1: freezing (weeks to months)
phase 2: stiffness (4-12 months)
phase 3: thawing (5-26 months)
clinical evaluation
-physical exam
-AROM and PROM eval
-differential diagnosis to rule out other conditions
-assess functional limitations and pain
shoulder instability
shallow glenoid fossa- lack of bony stability
other impairment of structures can cause
-capsular laxity
-muscle weakness/imbalance
-nervous system damage
weakness of trapezius can cause
Loss or impairment of elevation, upward rotation, retraction, depression
weakness of serratus anterior can cause
-loss of protraction and upward rotation
-causes winging of scapula
shoulder subluxation
head of humerus comes PARTIALLY out of glenoid fossa; may reduce on its own
dislocation
head of humerus comes COMPLETELY out of glenoid fossa; needs to be reduced back
causes of subluxation
-trauma
-weakness or paralysis of muscles that help hold head of humerus in fossa due to CVA
signs and symptoms of subluxation
-instability at shoulder joint
-pain
-decrease AROM
-have >2cm of subacromiaol space
special test for subluxation
sulcus sign
impingement syndrome
irritation of structures in the subacromial space
risk factors of impingement
-structural causes that narrow space
-muscle imbalance/weakness/tightness
-overuse/excessive OH movements
-shoulder bursitis
-shoulder tendinitis
-posture
-variations in shape of acromion
signs and symptoms of impingement syndrome
-pain (esp. w/ OH activities, sleeping)
-weakness
-possible loss of AROM
evaluations for impingement syndrome
-PROM and AROM
-identify compensation patterns during ROM
-functional eval of occupations (posture/ergonomics)
special tests for impingement
-neer test: sensitive
-hawkins test: sensitive
-painful arc test: limited evidence to support use
brachial plexus formed from
ventral rami C5, C6, C7, C8, & T1
ventral rami nerve travel
C1-C8 travel ABOVE T1
T1 travels BELOW T2
bony contents located near brachial plexus
clavicle and 1st rib
muscular contents located near brachial plexus
-anterior and middle scalenes
-pectoralis minor
artery and veins located near brachial plexus
subclavian vein → axillary vein
subclavian artery → axillary artery
brachial plexus composed of
-5 rami (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1)
-3 trunks (upper, middle, lower)
-6 divisions coming from trunks (3 anterior and 3 posterior)
-3 cords (lateral, posterior, medial)
-branches (musculocutaneous (C5-C7), axillary (C5-C6), radial (C5-T1), median (C5-T1), ulnar (C7-T1)
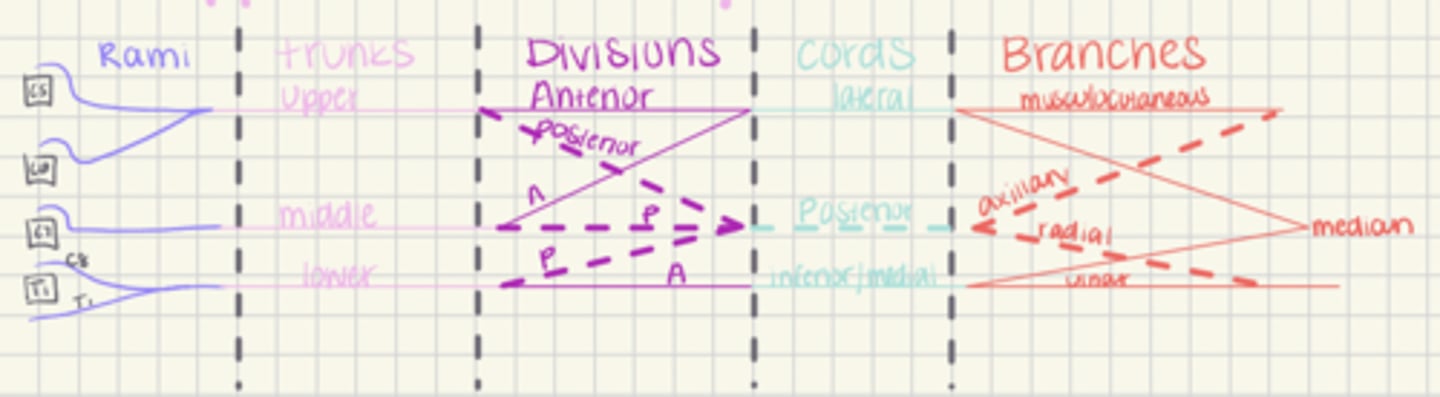
brachial plexus supplies
motor and sensory information to UE
prefixed variaton
STRONG contribution from C4, WEAK contribution from T2
postfixed variation
WEAK contribution from C5, STRONG contribution from T12
upper plexus lesion
-Erb's palsy most common - shoulder is internally rotated, adducted, elbow extension, forward flex
-Happens during birth
muscles affected by erb's palsy
-proximal UE muscles (RC, scapular, triceps, supinator)
lower plexus lesion
Klumpke's Palsy (C8 -T1); less common
muscles affected by klumpke's palsy
distal UE muscles (loss of finger extension, thumb motions, wrist motions)
adult injury to brachial plexus
-trauma to head, neck, shoulder
-MVA
-GSW
-post anasthesia
thoracic outlet borders
Scalene muscles, first rib, and clavicle
thoracic outlet contains
-subclavian artery and vein
-brachial plexus
thoracic outlet syndrome
compression of brachial plexus/vascular structures within thoracic outlet
entrapment occurs
-scalene triangle
-costoclavicular interval
-axillary interval (under pec minor)
risk factors of TOS
-Anatomical Variations of the cervical rib
-Head or neck trauma
-large pectoral muscles
-tumors
-repetitive OH activity/trauma
-poor posture
-female
neurogenic TOS
-atrophy of UE muscles
-loss of discriminative touch/proprioception
-parasthesia
-dull pain/discomfort
Vascular TOS → compression of vein
-edema of UE
-blueness (cyanosis)
-stiffness
vascular TOS → compression of artery
-paleness
-coolness
-decreased pulse/BP
nonspecific TOS
mixed symptoms of both neurogenic and vascular TOS
motor symptoms
-weakness
-atrophy
-loss of AROM
sensory symptoms
-loss of proprioception
-parasthesia
-loss of discriminative touch
-pain
clinical evaluations for TOS
-physical exam
-sensory and motor testing
-BP or pulse
-ergonomice evals
special test for TOS
Roos test
ST retraction
Make: middle trap
Them: traps (upper and lower)
Retract: rhomboids
ST depression
LATs: latissimus dorsi
Party: pectoralis minor
Like: lower trapezius
Sarra: Serratus anterior
ST downward rotation
Please: pectoralis minor
Lower: levator scapulae
Rolls: rhomboids
ST elevation
Umbrella: upper trapezius
Likes: levator scapulae
Rain: rhomboids
ST upward rotation
Let: lower trapezius
Us: upper trapezius
Spin: serratus anterior
ST protraction
Protract: pectoralis minor
the
Scap: serratus anterior