Human Body Orientation and Organization
1/29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is gross anatomy?
Large structures that are easy observable
What is the study of anatomy?
Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts. Observation is used to see the sizes and relationships of parts.
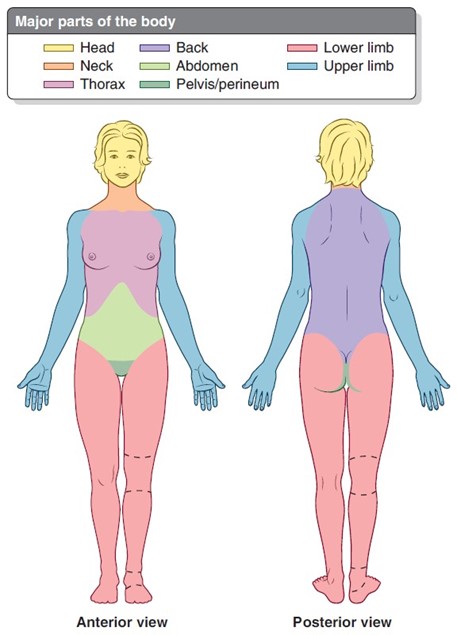
Major regions of the body (8)
Head
Neck
Thorax
Abdomen
Back
Pelvis/perineum
Upper extremities
Lower extremities
Systemic Anatomy
Organized by organ systems to carry out complex functions.
Body Systems (9)
Integumentary
Skeletal
Articular
Muscular
Nervous
Digestive/Alimentary
Urinary
Reproductive
Endocrine
Clinical Anatomy
Especially important for medicine, dentistry, and allied health sciences.
Regional and systematic study of anatomy and stresses clinical application.
Anatomical position
The standard position of the body used as a reference in anatomy, where the body is standing upright, facing forward, with arms at the sides and palms facing forward.
Superior (cranial or cephalic)
Toward the head or upper part of a structure or the body; ABOVE
Inferior (caudal)
Away from the head or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; BELOW
Anterior (ventral)
Toward or at the front of the body; IN FRONT OF
Posterior (dorsal)
Toward or at the backside of the body; behind
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body; ON THE INNER SIDE OF
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body; ON THE OUTER SIDE OF
Intermediate
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure
Proximal
Close to the origin of the body part or point of attachment to a limb to the body trunk.
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Superficial (external)
Toward or at the body surface
Deep (internal)
Away from the body surface; more internal
Sagittal place
Divides into left and right
Median, or midsagittal section dives the body into equal left and right.
Frontal (coronal) section
Divides into anterior and posterior parts
Transverse (cross) plane
Divides the body into superior and inferior sections.
Dorsal body cavity
The cavity that houses the brain and spinal cord, providing protection and support.
Cranial: Protected by skull
Spinal: Protected by vertebrae
Ventral body cavity
The cavity that houses the thoracic and abdominopelvic organs, providing a space for their function and protection.
Separated by the diaphragm
Thoracic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
Thoracic cavity
Superior to the diaphragm
Houses heart, lungs, and organs
Mediastinum, the central region, houses heart, trachea, and other organs.
Protected by the rib cage
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Cavity inferior to the diaphragm
Superior abdominal cavity: liver, stomach, protected only by trunk muscles
Inferior pelvic cavity: reproductive organs, bladder, rectum. Protected somewhat by bony pelvis
Axial Skeleton (4)
Bones from skull, laryngeal skeleton, vertebral column, rib cage.
Appendicular skeleton
Bones from the upper and lower extremities, shoulder girdle, and pelvis
Sagittal plane movements
Flexion and extension
Frontal plane movements
Abduction and adduction
Transverse plane movements
Internal and external rotation