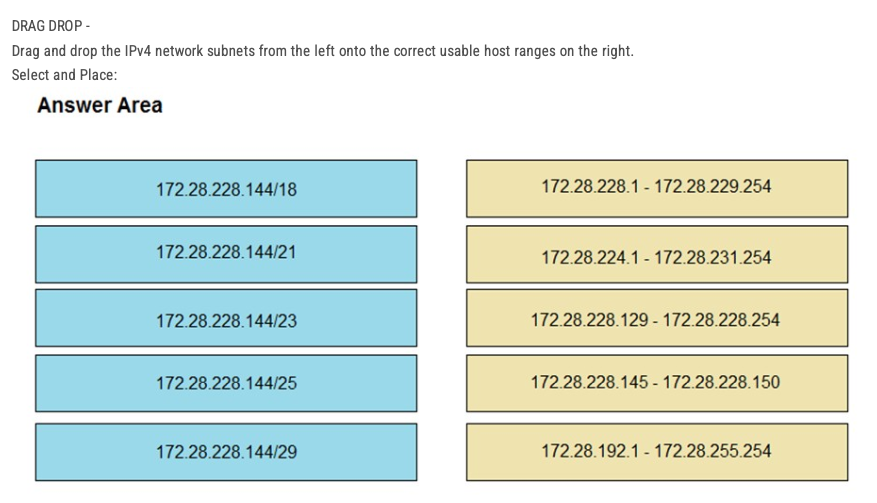
CCNA 1000
1/999
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1000 Terms
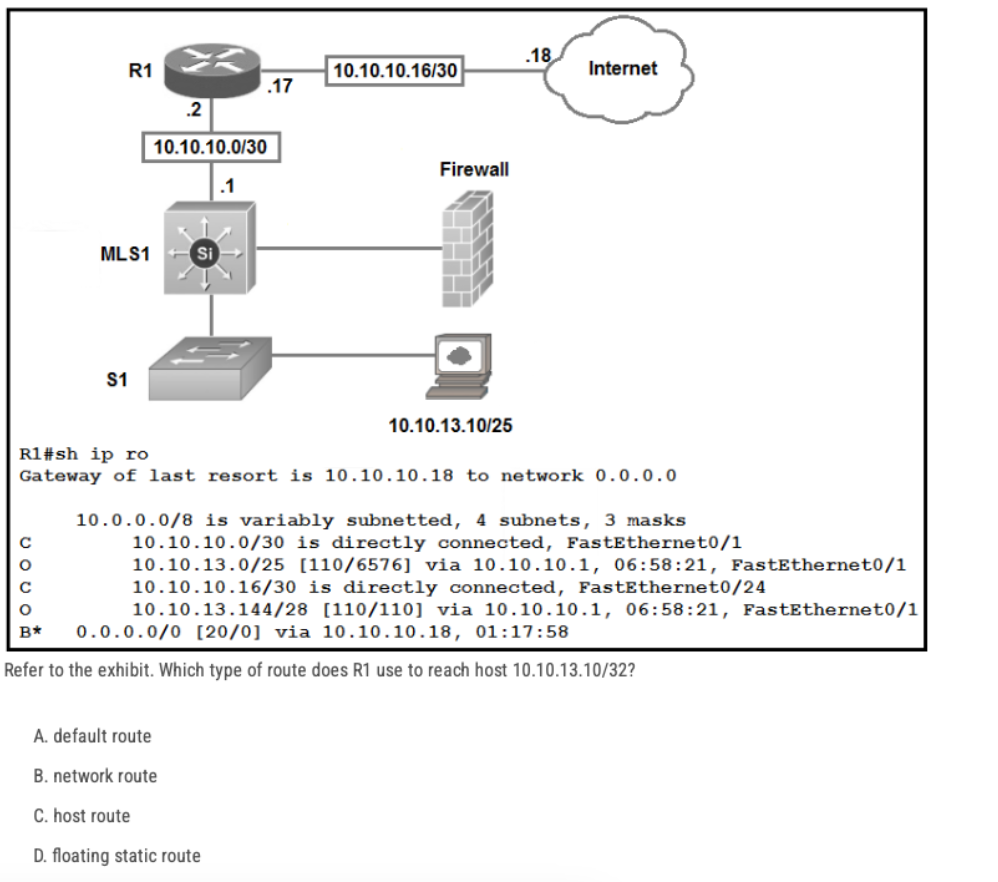
Refer to the exhibit. Which type of route does R1 use to reach host 10.10.13.10/32?
A. default route
B. network route
C. host route
D. floating static route
B. network route
A. default route
The default route is 0.0.0.0/0, it is used to reach all destinations not included in the routing table. But the router already has a route to 10.10.13.10/32. The default route is not needed.
Wrong answer.
B. network route
The routing table includes a route to 10.10.13.0/25. This subnet has these characteristics:
7 bits in the host ID = (2^7 – 2) = 126 IP addresses
1st IP address = 10.10.13.1
Last IP address = 10.10.13.126
This route includes address 10.10.13.10 and is an OSPF route (see the leading O).
Correct answer.
C. host route
There’s no host route in the routing table.
Wrong answer.
D. floating static route
A floating static route is used as a “backup” route to reach a subnet when the “main” route fails. But here the route to the host’s subnet is already in the routing table, and it is working.
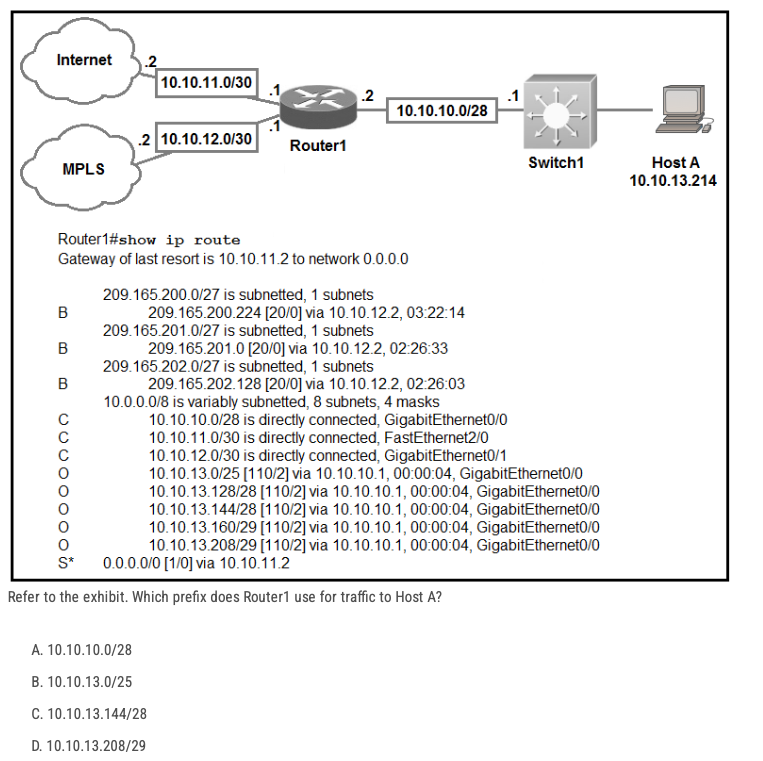
Refer to the exhibit. Which prefix does Router1 use for traffic to Host A?
A. 10.10.10.0/28
B. 10.10.13.0/25
C. 10.10.13.144/28
D. 10.10.13.208/29
D. 10.10.13.208/29
10.10.13.208/29 gives .208 for network, hmin 209, hmax 214, bcast 215. The correct answer will be D as this route gives the correct range.
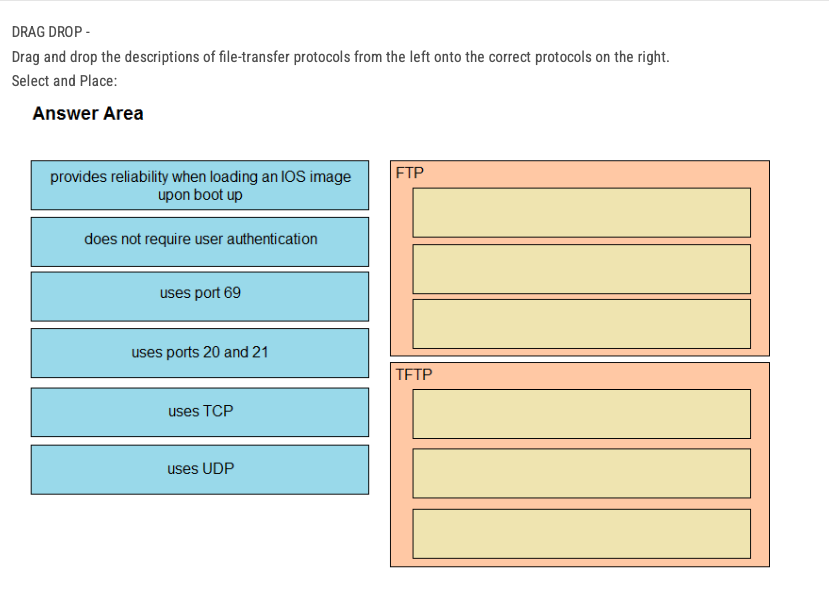
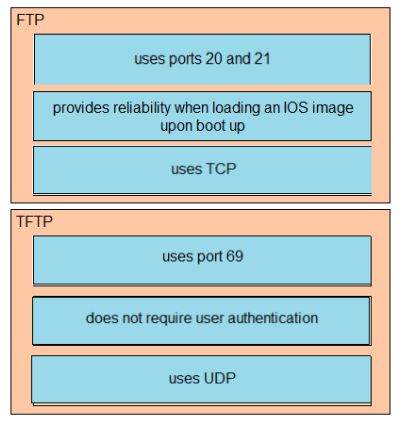
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simple protocol that provides basic file transfer function with no user authentication.
A frame that enters a switch fails the Frame Check Sequence. Which two interface counters are incremented? (Choose two.)
A. input errors
B. frame
C. giants
D. CRC
E. runts
A. input errors
D. CRC
input errors: total of many counters, including all below
frame: Frames on illegal format. Can be caused by collisions
giants: Frames that exceeded the maximum size (1518 bytes)
CRC: Received frames that did not pass the FCS math runts: Frames that did not meet the minimum size (64 bytes). Can be caused by collisions
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way that they establish a connection between two endpoints?
A. TCP uses the three-way handshake, and UDP does not guarantee message delivery.
B. TCP uses synchronization packets, and UDP uses acknowledgment packets.
C. UDP provides reliable message transfer, and TCP is a connectionless protocol.
D. UDP uses SYN, SYN ACK, and FIN bits in the frame header while TCP uses SYN, SYN ACK, and ACK bits.
A. TCP uses the three-way handshake, and UDP does not guarantee message delivery.
Which 802.11 frame type is Association Response?
A. management
B. protected frame
C. action
D. control
A. management
In which way does a spine-and-leaf architecture allow for scalability in a network when additional access ports are required?
A. A spine switch and a leaf switch can be added with redundant connections between them.
B. A spine switch can be added with at least 40 GB uplinks.
C. A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch.
D. A leaf switch can be added with a single connection to a core spine switch.
C. A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch.
What identifies the functionality of virtual machines?
A. The hypervisor communicates on Layer 3 without the need for additional resources.
B. Each hypervisor supports a single virtual machine and a single software switch.
C. The hypervisor virtualizes physical components including CPU, memory, and storage.
D. Virtualized servers run efficiently when physically connected to a switch that is separate from the hypervisor.
C. The hypervisor virtualizes physical components including CPU, memory, and storage.
Which command automatically generates an IPv6 address from a specified IPv6 prefix and MAC address of an interface?
A. ipv6 address dhcp
B. ipv6 address 2001:DB8:5:112::/64 eui-64
C. ipv6 address autoconfig
D. ipv6 address 2001:DB8:5:112::2/64 link-local
B. ipv6 address 2001:DB8:5:112::/64 eui-64
When configuring IPv6 on an interface, which two IPv6 multicast groups are joined? (Choose two.)
A. 2000::/3
B. 2002::5
C. FC00::/7
D. FF02::1
E. FF02::2
D. FF02::1
E. FF02::2
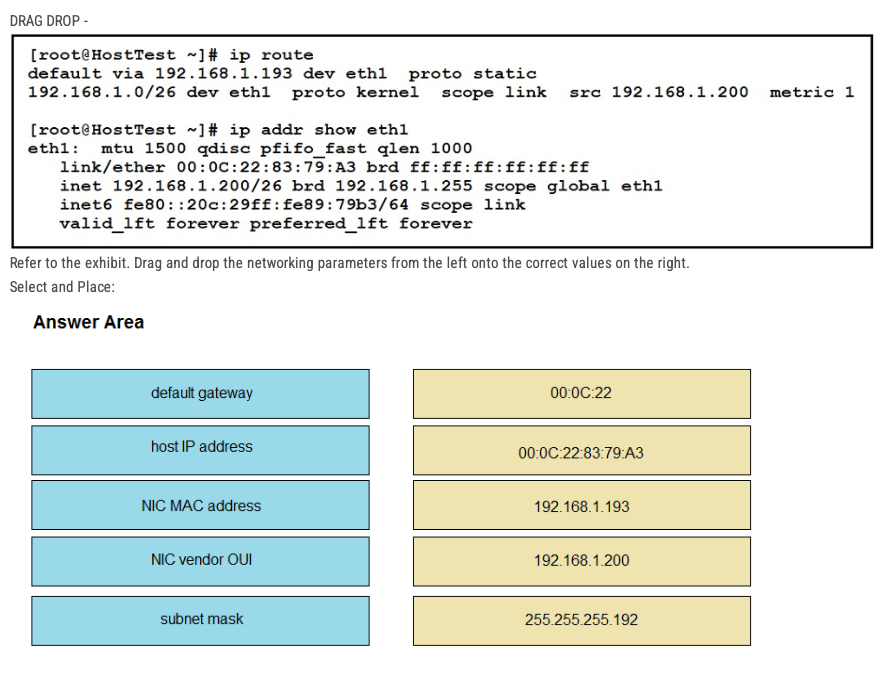
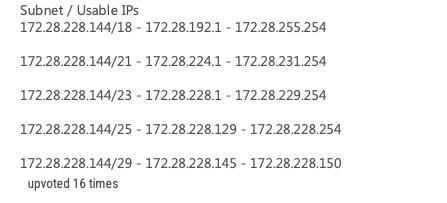
Refer to the exhibit. Drag and drop the networking parameters from the left onto the correct values on the right. Select and Place:
- default gateway = 192.168.1.193
- host IP address = 192.168.1.200
- NIC MAC address = 00:0C:22:83:79:A3
- NIC vendor OUI = 00:OC:22
- subnet mask = 255.255.255.192
The first 24 bits represent Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI)
What is the default behavior of a Layer 2 switch when a frame with an unknown destination MAC address is received?
A. The Layer 2 switch forwards the packet and adds the destination MAC address to its MAC address table.
B. The Layer 2 switch sends a copy of a packet to CPU for destination MAC address learning.
C. The Layer 2 switch floods packets to all ports except the receiving port in the given VLAN.
D. The Layer 2 switch drops the received frame. Reveal Solution Discussion 23
C. The Layer 2 switch floods packets to all ports except the receiving port in the given VLAN.
An engineer must configure a /30 subnet between two routes. Which usable IP address and subnet mask combination meets this criteria?
A. interface e0/0 description to XX-AXXX:XXXXX ip address 10.2.1.3 255.255.255.252
B. interface e0/0 description to XX-AXXX:XXXXX ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.248
C. interface e0/0 description to XX-AXXX:XXXXX ip address 172.16.1.4 255.255.255.248
D. interface e0/0 description to XX-AXXX:XXXXX ip address 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252
D. interface e0/0 description to XX-AXXX:XXXXX ip address 209.165.201.2 225.255.255.252
10.2.1.3 is a private IP (from the 10.0.0.0/8 range), which is typically used for internal networks rather than WAN links.
The up in A is a broadcast
The address range for 209.165.201.0/30 is:
Network address: 209.165.201.0
Usable IP addresses: 209.165.201.1 and 209.165.201.2
Broadcast address: 209.165.201.3
let's analyze the IP address 10.2.1.3 within the context of a /30 subnet:
For a /30 subnet:
Network address: 10.2.1.0
Usable IP addresses: 10.2.1.1 and 10.2.1.2
Broadcast address: 10.2.1.3
Which network allows devices to communicate without the need to access the Internet?
A. 172.9.0.0/16
B. 172.28.0.0/16
C. 192.0.0.0/8
D. 209.165.201.0/24
B. 172.28.0.0/16
Class A private IP address ranges from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 Class B private IP address ranges from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 Class C private IP address ranges from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
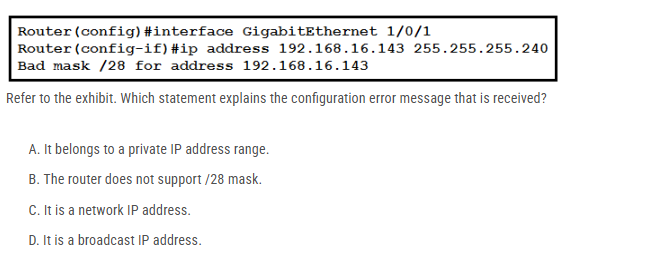
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement explains the configuration error message that is received?
A. It belongs to a private IP address range.
B. The router does not support /28 mask.
C. It is a network IP address.
D. It is a broadcast IP address.
D. It is a broadcast IP address.
D is correct.
If list out the subnet for /28
It will be like
192.168.16.0
192.168.16.16
..
192.168. 16.128
-------> here the last IP is 192.168. 16.143 is a broadcast
192.168.16.144
192.168.16.160..
Last 192.168. 16.240
!Which IPv6 address type provides communication between subnets and cannot route on the Internet?
A. link-local
B. unique local
C. multicast
D. global unicast
B. unique local
Which IPv6 address block sends packets to a group address rather than a single address?
A. 2000::/3
B. FC00::/7
C. FE80::/10
D. FF00::/8
D. FF00::/8
What are two reasons that cause late collisions to increment on an Ethernet interface? (Choose two.)
A. when Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection is used
B. when one side of the connection is configured for half-duplex
C. when the sending device waits 15 seconds before sending the frame again
D. when a collision occurs after the 32nd byte of a frame has been transmitted
E. when the cable length limits are exceeded
B. when one side of the connection is configured for half-duplex
E. when the cable length limits are exceeded
What is a benefit of using a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller?
A. It eliminates the need to configure each access point individually.
B. Central AP management requires more complex configurations.
C. Unique SSIDs cannot use the same authentication method.
D. It supports autonomous and lightweight APs.
A. It eliminates the need to configure each access point individually.
Which action is taken by switch port enabled for PoE power classification override?
A. If a monitored port exceeds the maximum administrative value for power, the port is shutdown and err-disabled.
B. When a powered device begins drawing power from a PoE switch port, a syslog message is generated.
C. As power usage on a PoE switch port is checked, data flow to the connected device is temporarily paused.
D. If a switch determines that a device is using less than the minimum configured power, it assumes the device has failed and disconnects it.
A. If a monitored port exceeds the maximum administrative value for power, the port is shutdown and err-disabled.
What occurs to frames during the process of frame flooding?
A. Frames are sent to all ports, including those that are assigned to other VLANs.
B. Frames are sent to every port on the switch that has a matching entry in MAC address table.
C. Frames are sent to every port on the switch in the same VLAN except from the originating port.
D. Frames are sent to every port on the switch in the same VLAN.
C. Frames are sent to every port on the switch in the same VLAN except from the originating port.
Which function does the range of private IPv4 addresses perform?
A. allows multiple companies to each use the same addresses without conflicts
B. provides a direct connection for hosts from outside of the enterprise network
C. ensures that NAT is not required to reach the Internet with private range addressing
D. enables secure communications to the Internet for all external hosts
A. allows multiple companies to each use the same addresses without conflicts
Which action must be taken to assign a global unicast IPv6 address on an interface that is derived from the MAC address of that interface?
A. explicitly assign a link-local address
B. disable the EUI-64 bit process
C. enable SLAAC on an interface
D. configure a stateful DHCPv6 server on the network
C. enable SLAAC on an interface
SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration) is used in IPv6 to automatically assign an address to an interface
Several new coverage cells are required to improve the Wi-Fi network of an organization. Which two standard designs are recommended? (Choose two.)
A. 5GHz provides increased network capacity with up to 23 nonoverlapping channels.
B. 5GHz channel selection requires an autonomous access point.
C. Cells that overlap one another are configured to use nonoverlapping channels.
D. Adjacent cells with overlapping channels use a repeater access point.
E. For maximum throughput, the WLC is configured to dynamically set adjacent access points to the channel.
A. 5GHz provides increased network capacity with up to 23 nonoverlapping channels.
C. Cells that overlap one another are configured to use nonoverlapping channels.
Option A and C are both fundamental design principles for deploying multi-cell Wi-Fi networks.
How do TCP and UDP differ in the way they provide reliability for delivery of packets?
A. TCP does not guarantee delivery or error checking to ensure that there is no corruption of data, UDP provides message acknowledgement and retransmits data if lost.
B. TCP provides flow control to avoid overwhelming a receiver by sending too many packets at once, UDP sends packets to the receiver in a continuous stream without checking.
C. TCP is a connectionless protocol that does not provide reliable delivery of data; UDP is a connection-oriented protocol that uses sequencing to provide reliable delivery.
D. TCP uses windowing to deliver packets reliably; UDP provides reliable message transfer between hosts by establishing a three-way handshake.
B. TCP provides flow control to avoid overwhelming a receiver by sending too many packets at once, UDP sends packets to the receiver in a continuous stream without checking.
!!What are two differences between optical-fiber cabling and copper cabling? (Choose two.)
A. A BNC connector is used for fiber connections
B. The glass core component is encased in a cladding
C. The data can pass through the cladding
D. Light is transmitted through the core of the fiber
E. Fiber connects to physical interfaces using RJ-45 connections
B. The glass core component is encased in a cladding
D. Light is transmitted through the core of the fiber
The data can pass through the cladding: The cladding is designed to reflect light back into the core, not to transmit data.
1.There are 3 kind of wiring mainly when we talk about networking: Fiber, Coaxial cable, twisted pair. The last 2 are Copper wiring
2. BNC Connector is for Coaxial Cable, so A is wrong
3.the structure of fiber is: Jacket encase Buffer, Buffer encase Cladding, Cladding encase core. We uses light to transmit data through the core. Therefore B and D are right, C is wrong
4. RJ45 is a connector is for twisted pair, so E is wrong
How does CAPWAP communicate between an access point in local mode and a WLC?
A. The access point must not be connected to the wired network, as it would create a loop
B. The access point must be connected to the same switch as the WLC
C. The access point must directly connect to the WLC using a copper cable
D. The access point has the ability to link to any switch in the network, assuming connectivity to the WLC
D. The access point has the ability to link to any switch in the network, assuming connectivity to the WLC
In CAPWAP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points) communication, the access point (AP) in local mode can be connected to any switch in the network, as long as there is proper connectivity to the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC)
Which IPv6 address block forwards packets to a multicast address rather than a unicast address?
A. 2000::/3
B. FC00::/7
C. FE80::/10
D. FF00::/12
D. FF00::/12
————————————————————————
FF <- easiest way to remember multicast.
What is the difference regarding reliability and communication type between TCP and UDP?
A. TCP is reliable and is a connectionless protocol; UDP is not reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol.
B. TCP is not reliable and is a connectionless protocol; UDP is reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol.
C. TCP is not reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol; UDP is reliable and is a connectionless protocol.
D. TCP is reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol; UDP is not reliable and is a connectionless protocol.
D. TCP is reliable and is a connection-oriented protocol; UDP is not reliable and is a connectionless protocol.
What are two descriptions of three-tier network topologies? (Choose two.)
A. The distribution layer runs Layer 2 and Layer 3 technologies
B. The network core is designed to maintain continuous connectivity when devices fail
C. The access layer manages routing between devices in different domains
D. The core layer maintains wired connections for each host
E. The core and distribution layers perform the same functions
A. The distribution layer runs Layer 2 and Layer 3 technologies
B. The network core is designed to maintain continuous connectivity when devices fail
A correct because distribution layer has multilayer switches (L2 and L3 technologies)
B correct oore provides reliability
C incorrect because it must be core layer, not access
D incorrect because it must be access layer, not core
E incorrect because core & distribution only perform same functions in 2-tier model (since they are aggregated)
Which type of IPv6 address is publicly routable in the same way as IPv4 public addresses?
A. multicast
B. unique local
C. link-local
D. global unicast
D. global unicast
Global unicast addresses (GUAs), also known as aggregatable global unicast addresses, are globally routable and reachable in the IPv6 Internet. They are equivalent to public IPv4 addresses. They play a significant role in the IPv6 addressing architecture
What is the expected outcome when an EUI-64 address is generated?
A. The interface ID is configured as a random 64-bit value
B. The characters FE80 are inserted at the beginning of the MAC address of the interface
C. The seventh bit of the original MAC address of the interface is inverted
D. The MAC address of the interface is used as the interface ID without modification
C. The seventh bit of the original MAC address of the interface is inverted
A corporate office uses four floors in a building.
✑ Floor 1 has 24 users.
✑ Floor 2 has 29 users.Floor 3 has 28 users.
✑ Floor 4 has 22 users.Which subnet summarizes and gives the most efficient distribution of IP addresses for the router configuration?
A. 192.168.0.0/24 as summary and 192.168.0.0/28 for each floor
B. 192.168.0.0/23 as summary and 192.168.0.0/25 for each floor
C. 192.168.0.0/25 as summary and 192.168.0.0/27 for each floor
D. 192.168.0.0/26 as summary and 192.168.0.0/29 for each floor
C. 192.168.0.0/25 as summary and 192.168.0.0/27 for each floor /32 1 /31 2 /30 4 /29 8 /28 16 /27 32 /26 64 /25 128 /24 256 /23 512 /22 1024 /21 2048
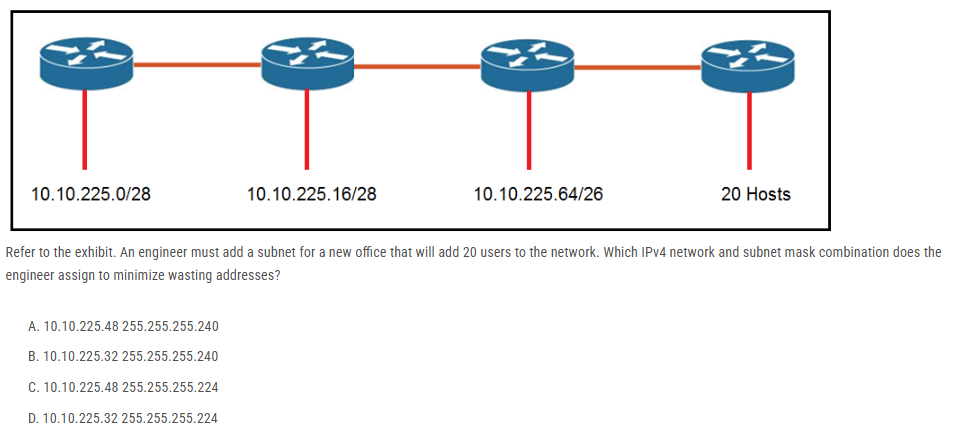
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer must add a subnet for a new office that will add 20 users to the network. Which IPv4 network and subnet mask combination does the engineer assign to minimize wasting addresses?
A. 10.10.225.48 255.255.255.240
B. 10.10.225.32 255.255.255.240
C. 10.10.225.48 255.255.255.224
D. 10.10.225.32 255.255.255.224
D. 10.10.225.32 255.255.255.224
Find the subnet mask *To have 20 User in a subnet We have to use /27 prefix
So Host count for /27 prefix is (2^5-2)=30
Subnet Mask for /27 prefix is (sum of Network bits (128+64+32)=224 , so 255.255.255.224
Find the network ID *As per the /27 prefix each subnet has 30 host and 32 including network ID & Broadcast ID
so first network ID is 10.10.255.0 and the second will be 10.10.255.32
For C Subnet ID 00001010.00001010.11111111.00110000
Subnet mask 11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000
And Result 00001010.00001010.11111111.00100000 = 32 not equal to 48
Decimal 10.10.255.32
This is not the subnet ID. Wrong answer.
D. 10.10.225.32 255.255.255.224
What is a characteristic of spine-and-leaf architecture?
A. Each link between leaf switches allows for higher bandwidth.
B. It provides greater predictability on STP blocked ports.
C. It provides variable latency.
D. Each device is separated by the same number of hops.
D. Each device is separated by the same number of hops.
An office has 8 floors with approximately 30-40 users per floor. One subnet must be used. Which command must be configured on the router Switched VirtualInterface to use address space efficiently?
A. ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0
B. ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0
C. ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.128
D. ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.224
B. ip address 192.168.0.0 255.255.254.0
8 floors and 40 user per floor means 320 users (approx.). How many bits do you need to have 320 IP addresses? 8 bits = (2^8 - 2) =254 IP addresses, and it's not enough. 9 bits = (2^9 - 2) = 510 IP addresses, and this is enough. You have a class C subnet (192.168.0.0). This means a subnet mask like this: 255.255.255.0 But you need 9 bits for the hosts, so you've got left with a subnet mask like this: 255.255.1111111x.xxxxxxxx =255.255.254.0
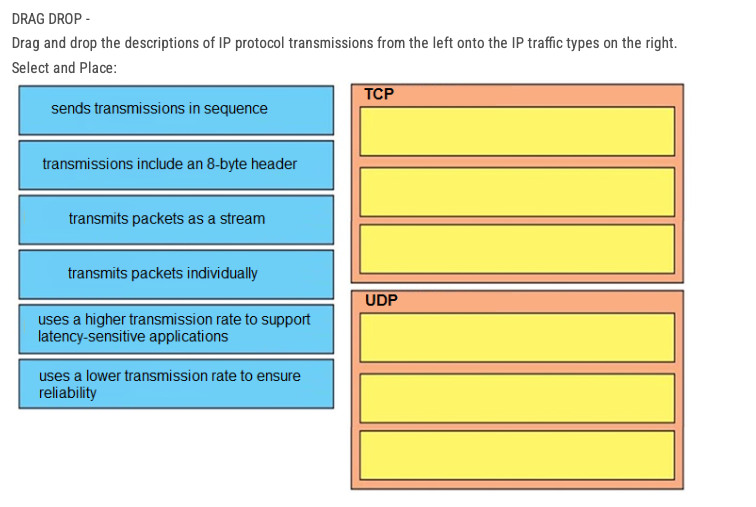
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the descriptions of IP protocol transmissions from the left onto the IP trac types on the right. Select and Place:
A device detects two stations transmitting frames at the same time. This condition occurs after the first 64 bytes of the frame is received. Which interface counter increments?
A. runt
B. collision
C. late collision
D. CRC
C. late collision
Collision happens after 512 bits =64 byte =late collision
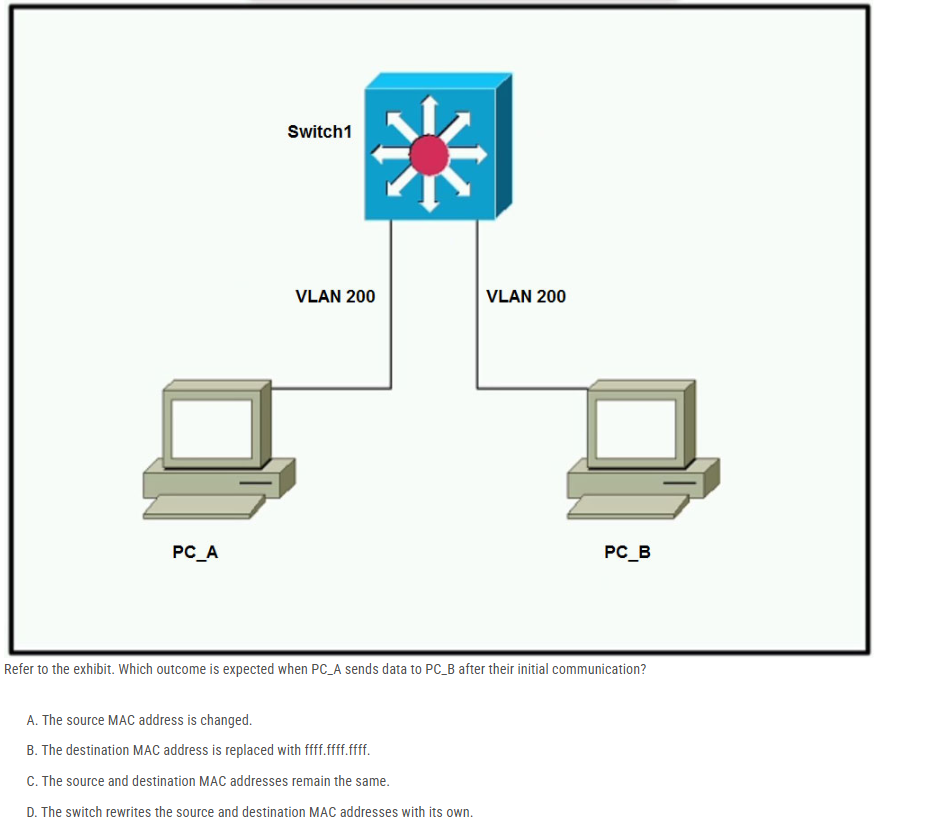
Refer to the exhibit. Which outcome is expected when PC_A sends data to PC_B after their initial communication?
A. The source MAC address is changed.
B. The destination MAC address is replaced with ffff.ffff.ffff.
C. The source and destination MAC addresses remain the same.
D. The switch rewrites the source and destination MAC addresses with its own.
C. The source and destination MAC addresses remain the same.
————————————————————————————
after their initial communication
-> before answer is B
after answer is C
C correct
Using direct sequence spread spectrum, which three 2.4-GHz channels are used to limit collisions?
A. 5, 6, 7
B. 1, 2, 3
C. 1, 6, 11
D. 1, 5, 10
C. 1, 6, 11
!!How do TCP and UDP differ in the way they guarantee packet delivery?
A. TCP uses retransmissions, acknowledgment, and parity checks, and UDP uses cyclic redundancy checks only
B. TCP uses two-dimensional parity checks, checksums, and cyclic redundancy checks, and UDP uses retransmissions only
C. TCP uses checksum, acknowledgements, and retransmissions, and UDP uses checksums only
D. TCP uses checksum, parity checks, and retransmissions, and UDP uses acknowledgements only
C. TCP uses checksum, acknowledgements, and retransmissions, and UDP uses checksums only
A wireless administrator has configured a WLAN; however, the clients need access to a less congested 5-GHz network for their voice quality. Which action must be taken to meet the requirement?
A. enable Band Select
B. enable DTIM
C. enable RX-SOP
D. enable AAA override
A. enable Band Select
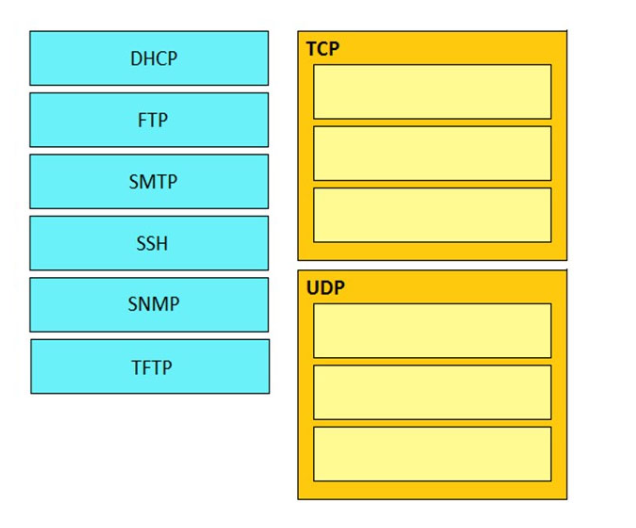
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the application protocols from the left onto the transport protocols that it uses on the right. Select and Place:
What is the destination MAC address of a broadcast frame?
A. 00:00:0c:07:ac:01
B. ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
C. 43:2e:08:00:00:0c
D. 00:00:0c:43:2e:08
E. 00:00:0c:ff:ff:ff
B. ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
For what two purposes does the Ethernet protocol use physical addresses?
A. to uniquely identify devices at Layer 2
B. to allow communication with devices on a different network
C. to differentiate a Layer 2 frame from a Layer 3 packet
D. to establish a priority system to determine which device gets to transmit first
E. to allow communication between different devices on the same network
F. to allow detection of a remote device when its physical address is unknown
A. to uniquely identify devices at Layer 2
E. to allow communication between different devices on the same network
B. to allow communication with devices on a different network:
This is not correct for Ethernet addresses. Communication with devices on a different network requires IP addresses and routing, which happens at Layer 3 (Network Layer), not Layer 2.
Physical address is MAC address
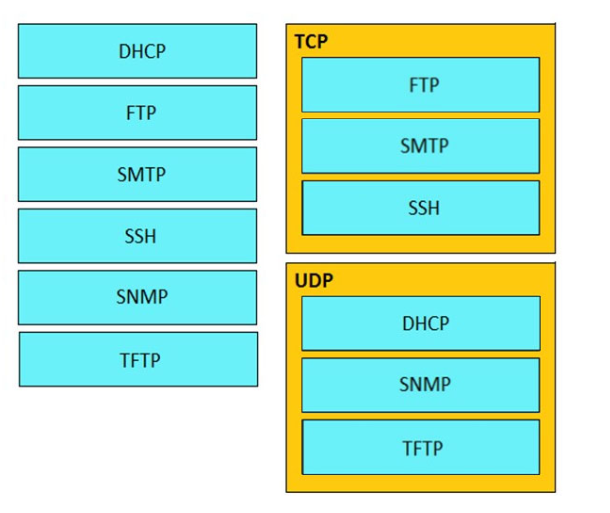
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the networking parameters from the left on to the correct values on the right. Select and Place:
Which component of an Ethernet frame is used to notify a host that traffic is coming?
A. start of frame delimiter
B. Type field
C. preamble
D. Data field
C. preamble
You are configuring your edge routers interface with a public IP address for Internet connectivity. The router needs to obtain the IP address from the service provider dynamically.Which command is needed on interface FastEthernet 0/0 to accomplish this?
A. ip default-gateway
B. ip route
C. ip default-network
D. ip address dhcp
E. ip address dynamic
D. ip address dhcp
Which two statements about the purpose of the OSI model are accurate? (Choose two.)
A. Defines the network functions that occur at each layer
B. Facilitates an understanding of how information travels throughout a network
C. Changes in one layer do not impact other layer
D. Ensures reliable data delivery through its layered approach
A. Defines the network functions that occur at each layer
B. Facilitates an understanding of how information travels throughout a network
Which three statements about MAC addresses are correct? (Choose three.)
A. To communicate with other devices on a network, a network device must have a unique MAC address
B. The MAC address is also referred to as the IP address
C. The MAC address of a device must be configured in the Cisco IOS CLI by a user with administrative privileges
D. A MAC address contains two main components, the first of which identifies the manufacturer of the hardware and the second of which uniquely identifies the hardware
E. An example of a MAC address is 0A:26:B8:D6:65:90
F. A MAC address contains two main components, the first of which identifies the network on which the host resides and the second of which uniquely identifies the host on the network
A. To communicate with other devices on a network, a network device must have a unique MAC address
D. A MAC address contains two main components, the first of which identifies the manufacturer of the hardware and the second of which uniquely identifies the hardware
E. An example of a MAC address is 0A:26:B8:D6:65:90
Which technique can you use to route IPv6 traffic over an IPv4 infrastructure?
A. NAT
B. 6 to 4 tunneling
C. L2TPv3
D. dual-stack
B. 6 to 4 tunneling
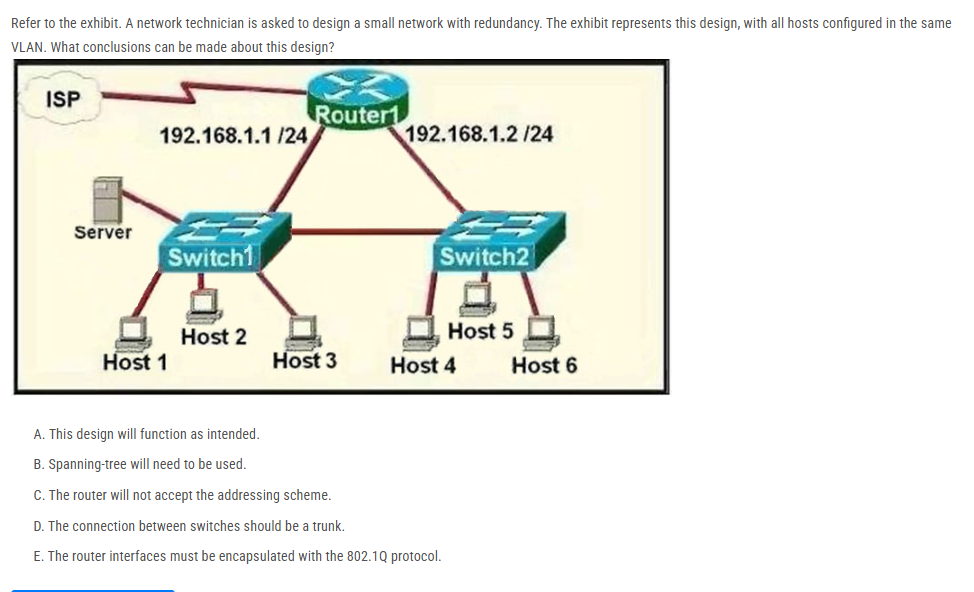
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is asked to design a small network with redundancy. The exhibit represents this design, with all hosts configured in the same VLAN. What conclusions can be made about this design?
A. This design will function as intended.
B. Spanning-tree will need to be used.
C. The router will not accept the addressing scheme.
D. The connection between switches should be a trunk.
E. The router interfaces must be encapsulated with the 802.1Q protocol.
C. The router will not accept the addressing scheme.
Router won't accept that addressing scheme because each router's active interface must be in a different subnetwork
The proposed addressing scheme is on the same network. Cisco routers will not allow you to assign two different interfaces to be on the same IP subnet.
Which two statements are true about the command ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4? (Choose two.)
A. It establishes a static route to the 172.16.3.0 network.
B. It establishes a static route to the 192.168.2.0 network.
C. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination to the 172.16.3.0 network.
D. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination out the interface with the address 192.168.2.4.
E. It uses the default administrative distance.
F. It is a route that would be used last if other routes to the same destination exist.
A. It establishes a static route to the 172.16.3.0 network.
E. It uses the default administrative distance.
What are two benefits of private IPv4 IP addresses? (Choose two.)
A. They are routed the same as public IP addresses.
B. They are less costly than public IP addresses.
C. They can be assigned to devices without Internet connections.
D. They eliminate the necessity for NAT policies.
E. They eliminate duplicate IP conflicts.
B. They are less costly than public IP addresses.
C. They can be assigned to devices without Internet connections.
What are two benefits that the UDP protocol provide for application traffic? (Choose two.)
A. UDP traffic has lower overhead than TCP traffic
B. UDP provides a built-in recovery mechanism to retransmit lost packets
C. The CTL field in the UDP packet header enables a three-way handshake to establish the connection
D. UDP maintains the connection state to provide more stable connections than TCP
E. The application can use checksums to verify the integrity of application data
A. UDP traffic has lower overhead than TCP traffic
E. The application can use checksums to verify the integrity of application data
In networking, overhead is the extra time, processing, or resources required to transmit data
Which two goals reasons to implement private IPv4 addressing on your network? (Choose two.)
A. Comply with PCI regulations
B. Conserve IPv4 address
C. Reduce the size of the forwarding table on network routers
D. Reduce the risk of a network security breach
E. Comply with local law
B. Conserve IPv4 address
D. Reduce the risk of a network security breach
Which WAN access technology is preferred for a small office / home office architecture?
A. broadband cable access
B. frame-relay packet switching
C. dedicated point-to-point leased line
D. Integrated Services Digital Network switching
A. broadband cable access
Which two WAN architecture options help a business scalability and reliability for the network? (Choose two.)
A. asychronous routing
B. single-homed branches
C. dual-homed branches
D. static routing
E. dynamic routing
C. dual-homed branches
E. dynamic routing
What is the binary pattern of unique ipv6 unique local address?
A. 00000000
B. 11111100
C. 11111111
D. 11111101
B. 11111100
Which two options are the best reasons to use an IPV4 private IP space? (Choose two.)
A. to enable intra-enterprise communication
B. to implement NAT
C. to connect applications
D. to conserve global address space
E. to manage routing overhead
A. to enable intra-enterprise communication
D. to conserve global address space
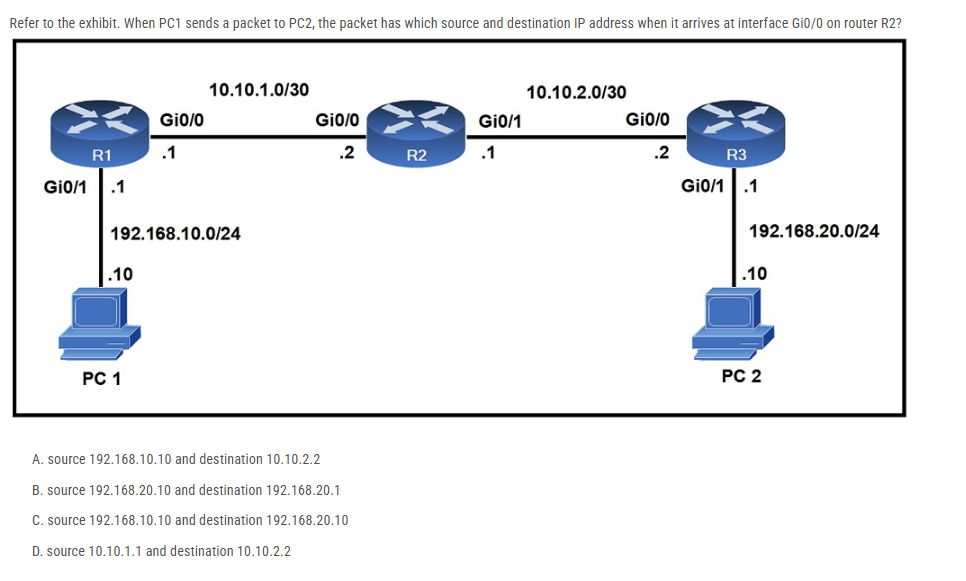
Refer to the exhibit. When PC1 sends a packet to PC2, the packet has which source and destination IP address when it arrives at interface Gi0/0 on router R2?
A. source 192.168.10.10 and destination 10.10.2.2
B. source 192.168.20.10 and destination 192.168.20.1
C. source 192.168.10.10 and destination 192.168.20.10
D. source 10.10.1.1 and destination 10.10.2.2
C. source 192.168.10.10 and destination 192.168.20.10
The source and destination IP addresses of the packets are unchanged on all the way. Only source and destination MAC addresses are changed.
What is the same for both copper and fiber interfaces when using SFP modules?
A. They support an inline optical attenuator to enhance signal strength
B. They accommodate single-mode and multi-mode in a single module
C. They provide minimal interruption to services by being hot-swappable
D. They offer reliable bandwidth up to 100 Mbps in half duplex mode
C. They provide minimal interruption to services by being hot-swappable
What are two functions of a server on a network? (Choose two.)
A. handles requests from multiple workstations at the same time
B. achieves redundancy by exclusively using virtual server clustering
C. housed solely in a data center that is dedicated to a single client achieves redundancy by exclusively using virtual server clustering
D. runs the same operating system in order to communicate with other servers
E. runs applications that send and retrieve data for workstations that make requests
A. handles requests from multiple workstations at the same time
E. runs applications that send and retrieve data for workstations that make requests
!Which function is performed by the collapsed core layer in a two-tier architecture?
A. enforcing routing policies
B. marking interesting traffic for data policies
C. applying security policies
D. attaching users to the edge of the network
A. enforcing routing policies
D. attaching users to the edge of the network: User attachment occurs at the access layer, not the collapsed core.
What is the primary function of a Layer 3 device?
A. to transmit wireless traffic between hosts
B. to analyze traffic and drop unauthorized traffic from the Internet
C. to forward traffic within the same broadcast domain
D. to pass traffic between different networks
D. to pass traffic between different networks
Layer 3 = different network Layer 2 = same network
Which two functions are performed by the core layer in a three-tier architecture? (Choose two.)
A. Provide uninterrupted forwarding service
B. Inspect packets for malicious activity
C. Ensure timely data transfer between layers
D. Provide direct connectivity for end user devices
E. Police traffic that is sent to the edge of the network
A. Provide uninterrupted forwarding service
C. Ensure timely data transfer between layers
Verified
What is a recommended approach to avoid co-channel congestion while installing access points that use the 2.4 GHz frequency?
A. different nonoverlapping channels
B. one overlapping channel
C. one nonoverlapping channel
D. different overlapping channels
A. different nonoverlapping channels
A manager asks a network engineer to advise which cloud service models are used so employees do not have to waste their time installing, managing, and updating software that is only used occasionally. Which cloud service model does the engineer recommend?
A. infrastructure-as-a-service
B. platform-as-a-service
C. business process as service to support different types of service
D. software-as-a-service
D. software-as-a-service
What are two functions of a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two.)
A. acts as a central point for association and authentication servers
B. selects the best route between networks on a WAN
C. moves packets within a VLAN
D. moves packets between different VLANs
E. makes forwarding decisions based on the MAC address of a packet
C. moves packets within a VLAN
E. makes forwarding decisions based on the MAC address of a packet
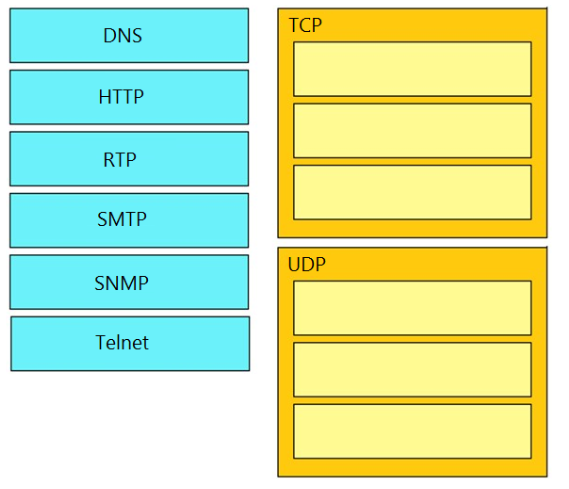
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the TCP/IP protocols from the left onto their primary transmission protocols on the right. Select and Place:
TCP- HTTP, SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), Telnet
UDP- DNS, RTP, SNMP
An engineer observes high usage on the 2.4GHz channels and lower usage on the 5GHz channels. What must be configured to allow clients to preferentially use5GHz access points?
A. Client Band Select
B. Re-Anchor Roamed Clients
C. OEAP Spilt Tunnel
D. 11ac MU-MIMO
A. Client Band Select
Which networking function occurs on the data plane?
A. processing inbound SSH management traffic
B. sending and receiving OSPF Hello packets
C. facilitates spanning-tree elections
D. forwarding remote client/server traffic
D. forwarding remote client/server traffic
Verified
Under which condition is TCP preferred over UDP?
A. UDP is used when low latency is optimal, and TCP is used when latency is tolerable.
B. TCP is used when dropped data is more acceptable, and UDP is used when data is accepted out-of-order.
C. TCP is used when data reliability is critical, and UDP is used when missing packets are acceptable.
D. UDP is used when data is highly interactive, and TCP is used when data is time-sensitive.
C. TCP is used when data reliability is critical, and UDP is used when missing packets are acceptable.
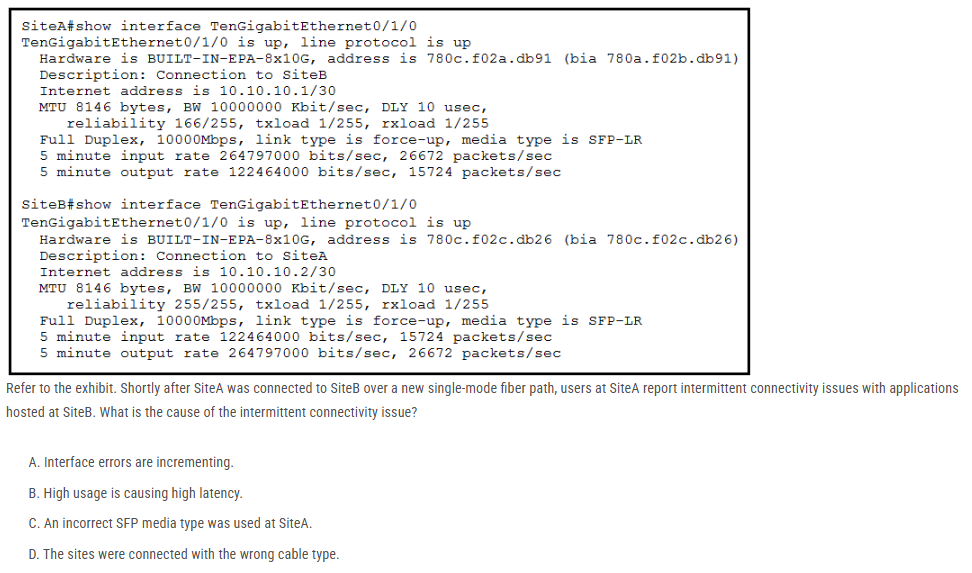
Refer to the exhibit. Shortly after SiteA was connected to SiteB over a new single-mode fiber path, users at SiteA report intermittent connectivity issues with applications hosted at SiteB. What is the cause of the intermittent connectivity issue?
A. Interface errors are incrementing.
B. High usage is causing high latency.
C. An incorrect SFP media type was used at SiteA.
D. The sites were connected with the wrong cable type.
D. The sites were connected with the wrong cable type.
applied, the engineer must compress the address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0500:000a:400F:583B. Which command must be issued on the interface?
A. ipv6 address 2001::db8:0000::500:a:400F:583B
B. ipv6 address 2001:db8:0::500:a:4F:583B
C. ipv6 address 2001:db8::500:a:400F:583B
D. ipv6 address 2001:0db8::5:a:4F:583B
C. ipv6 address 2001:db8::500:a:400F:583B
0000 is replace by :
Only leading zero (not trailing zeros) are removed
What is a network appliance that checks the state of a packet to determine whether the packet is legitimate?
A. Layer 2 switch
B. LAN controller
C. load balancer
D. firewall
D. firewall
What is a role of access points in an enterprise network?
A. integrate with SNMP in preventing DDoS attacks
B. serve as a first line of defense in an enterprise network
C. connect wireless devices to a wired network
D. support secure user logins to devices on the network
C. connect wireless devices to a wired network
An implementer is preparing hardware for virtualization to create virtual machines on a host. What is needed to provide communication between hardware and virtual machines?
A. router
B. hypervisor
C. switch
D. straight cable
B. hypervisor
How does a Cisco Unified Wireless Network respond to Wi-Fi channel overlap?
A. It allows the administrator to assign the channels on a per-device or per-interface basis.
B. It segregates devices from different manufactures onto different channels.
C. It analyzes client load and background noise and dynamically assigns a channel.
D. It alternates automatically between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz on adjacent access points.
C. It analyzes client load and background noise and dynamically assigns a channel.
Verified
In which situation is private IPv4 addressing appropriate for a new subnet on the network of an organization?
A. The network has multiple endpoint listeners, and it is desired to limit the number of broadcasts.
B. The ISP requires the new subnet to be advertised to the Internet for web services.
C. There is limited unique address space, and traffic on the new subnet will stay local within the organization.
D. Traffic on the subnet must traverse a site-to-site VPN to an outside organization.
C. There is limited unique address space, and traffic on the new subnet will stay local within the organization.
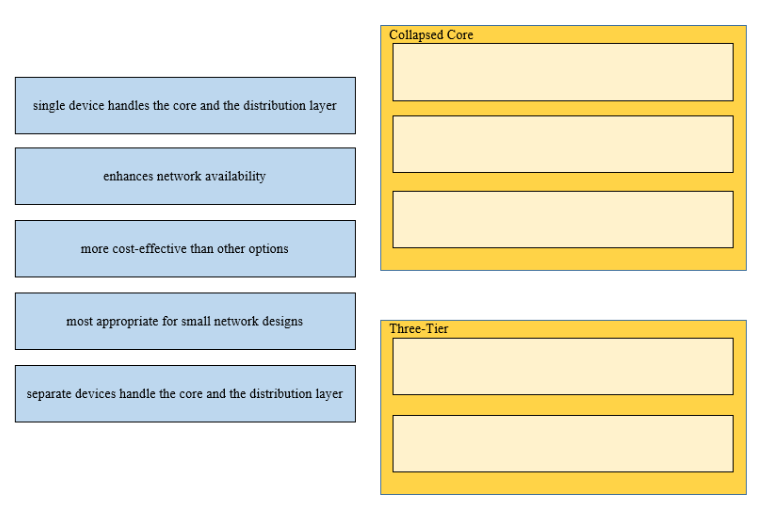
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the characteristics of network architectures from the left onto the type of architecture on the right. Select and Place:
Which 802.11 frame type is indicated by a probe response after a client sends a probe request?
A. data
B. management
C. control
D. action
B. management
Management frames: Used for joining and leaving a wireless cell. Management frame types include association request, association response, and reassociation request, just to name a few. (See Table 7-2 for a complete list.)
Control frames: Used to acknowledge when data frames are received.
Data frames: Frames that contain data.
What is the difference in data transmission delivery and reliability between TCP and UDP?
A. TCP transmits data at a higher rate and ensures packet delivery. UDP retransmits lost data to ensure applications receive the data on the remote end.
B. TCP requires the connection to be established before transmitting data. UDP transmits data at a higher rate without ensuring packet delivery.
C. UDP sets up a connection between both devices before transmitting data. TCP uses the three-way handshake to transmit data with a reliable connection.
D. UDP is used for multicast and broadcast communication. TCP is used for unicast communication and transmits data at a higher rate with error checking.
B. TCP requires the connection to be established before transmitting data. UDP transmits data at a higher rate without ensuring packet delivery.
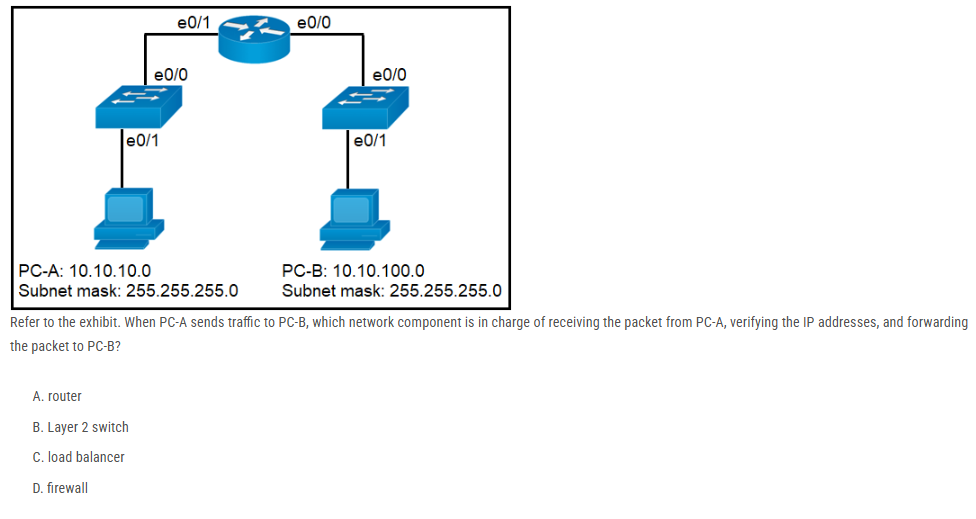
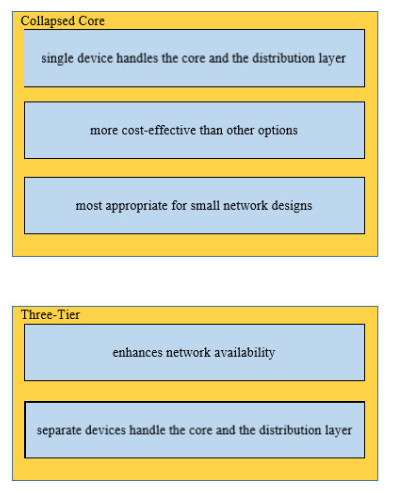
Refer to the exhibit. When PC-A sends traffic to PC-B, which network component is in charge of receiving the packet from PC-A, verifying the IP addresses, and forwarding the packet to PC-B?
A. router
B. Layer 2 switch
C. load balancer
D. firewall
A. router
What is the maximum bandwidth of a T1 point-to-point connection?
A. 1.544 Mbps
B. 2.048 Mbps
C. 34.368 Mbps
D. 43.7 Mbps
A. 1.544 Mbps
A. T1 B. E1 C. E3 D. T3
What are two similarities between UTP Cat 5e and Cat 6a cabling? (Choose two.)
A. Both support speeds up to 10 Gigabit.
B. Both support speeds of at least 1 Gigabit.
C. Both support runs of up to 55 meters.
D. Both support runs of up to 100 meters.
E. Both operate at a frequency of 500 MHz.
B. Both support speeds of at least 1 Gigabit.
D. Both support runs of up to 100 meters.
UTP Cables CAT 5e: Frequency: 100 MHz Max. Bandwidth: 1 Gbps Max. Distance: 100 m UTP Cables CAT 6a: Frequency: 500 MHz Max. Bandwidth: 10 Gbps Max. Distance: 100 m
What is a characteristic of cloud-based network topology?
A. onsite network services are provided with physical Layer 2 and Layer 3 components
B. wireless connections provide the sole access method to services
C. physical workstations are configured to share resources
D. services are provided by a public, private, or hybrid deployment
D. services are provided by a public, private, or hybrid deployment
Which network action occurs within the data plane?
A. reply to an incoming ICMP echo request
B. make a configuration change from an incoming NETCONF RPC
C. run routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, BGP)
D. compare the destination IP address to the IP routing table
D. compare the destination IP address to the IP routing table Reveal Solution
A. Reply to an incoming ICMP echo request → This is handled in the control plane because the router must generate a new ICMP response, which is not just simple packet forwarding.
B. Make a configuration change from an incoming NETCONF RPC → Configuration changes are processed in the management plane, not the data plane.
C. Run routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, BGP) → Routing protocols operate in the control plane, as they are responsible for building and maintaining the routing table.
![<p class="card-text">Refer to the exhibit. R1 has just received a packet from host A that is destined to host B. Which route in the routing table is used by R1 to reach host B?</p><ul><li><p><span>A. </span>10.10.13.0/25 [1/0] via 10.10.10.2</p></li><li><p><span>B. </span>10.10.13.0/25 [108/0] via 10.10.10.10</p></li><li><p><span>C. </span>10.10.13.0/25 [110/2] via 10.10.10.6</p></li><li><p><span>D. </span>10.10.13.0/25 [110/2] via 10.10.10.2</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c3d08e12-d947-4c2d-939a-76ecefb70fc3.png)
Refer to the exhibit. R1 has just received a packet from host A that is destined to host B. Which route in the routing table is used by R1 to reach host B?
A. 10.10.13.0/25 [1/0] via 10.10.10.2
B. 10.10.13.0/25 [108/0] via 10.10.10.10
C. 10.10.13.0/25 [110/2] via 10.10.10.6
D. 10.10.13.0/25 [110/2] via 10.10.10.2
B. 10.10.13.0/25 [108/0] via 10.10.10.10
A is not even listed in the routing table.
B is correct; it uses the lowest AD out of all the routes presented that go to the 10.10.13.0/25 subnet. A is a default route and would only be
there wasn't a route to that subnet in the routing table.
Which two network actions occur within the data plane? (Choose two.)
A. Run routing protocols.
B. Make a configuration change from an incoming NETCONF RPC.
C. Add or remove an 802.1Q trunking header.
D. Match the destination MAC address to the MAC address table.
E. Reply to an incoming ICMP echo request.
C. Add or remove an 802.1Q trunking header.
D. Match the destination MAC address to the MAC address table.
The data plane is also called the forwarding plane
What are network endpoints?
A. support inter-VLAN connectivity
B. a threat to the network if they are compromised
C. act as routers to connect a user to the service provider network
D. enforce policies for campus-wide traffic going to the Internet
B. a threat to the network if they are compromised
Verified
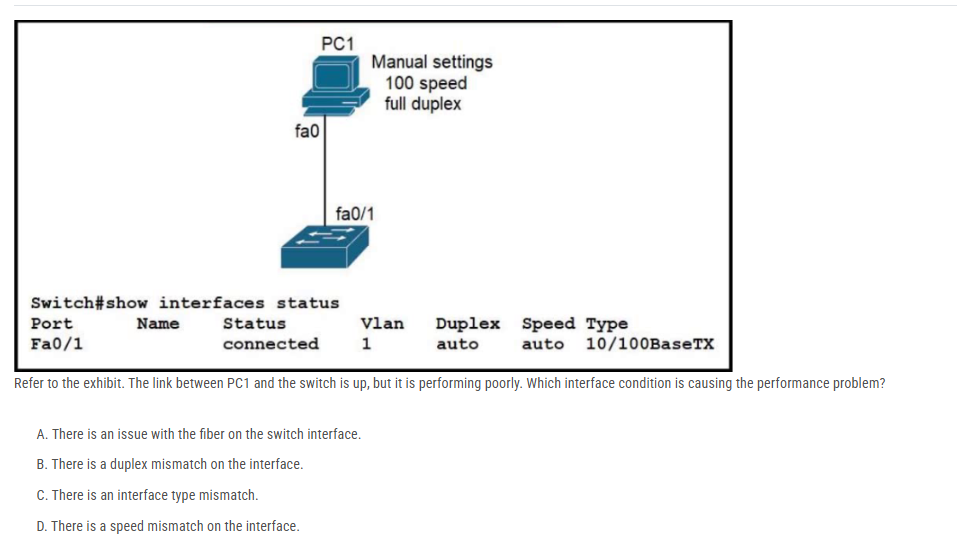
Refer to the exhibit. The link between PC1 and the switch is up, but it is performing poorly. Which interface condition is causing the performance problem?
A. There is an issue with the fiber on the switch interface.
B. There is a duplex mismatch on the interface.
C. There is an interface type mismatch.
D. There is a speed mismatch on the interface.
B. There is a duplex mismatch on the interface.
Why was the RFC 1918 address space defined?
A. conserve public IPv4 addressing
B. support the NAT protocol
C. preserve public IPv6 address space
D. reduce instances of overlapping IP addresses
A. conserve public IPv4 addressing
ipv6 doesnt need any preservation or conservation. It's got a metric fuck ton to the power of bazillion addresses. Whereas ipv4 is essentially already depleted.
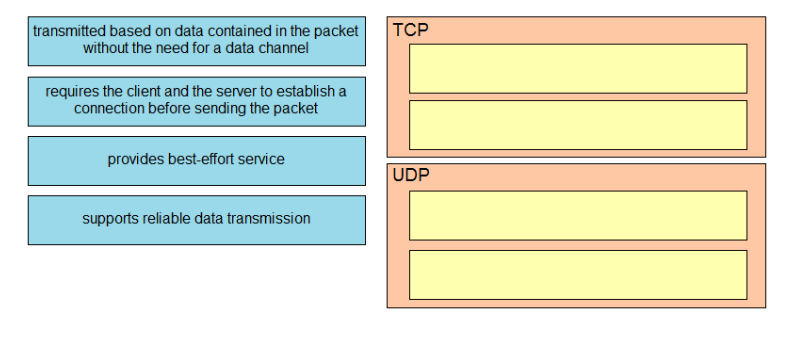
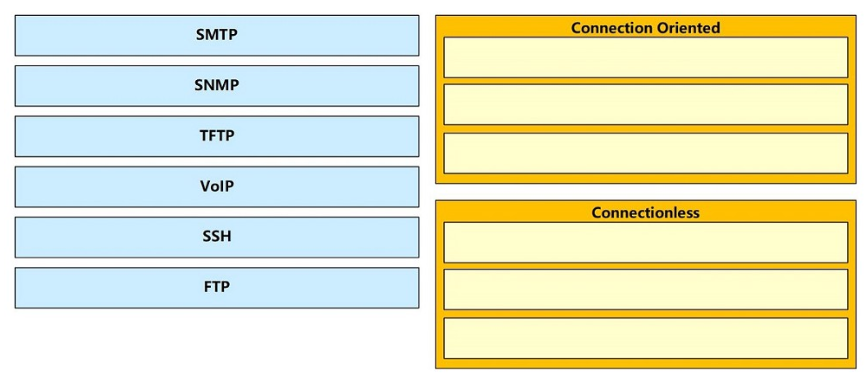
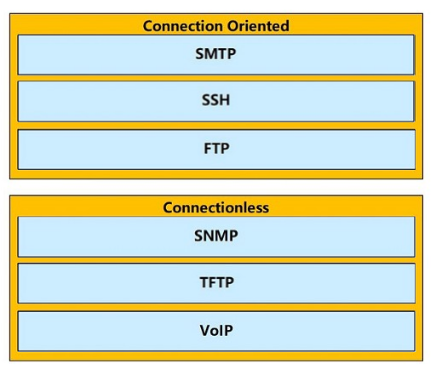
DRAG DROP -
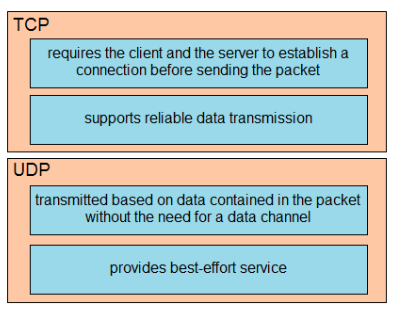
Drag and drop the TCP or UDP details from the left onto their corresponding protocols on the right. Select and Place:
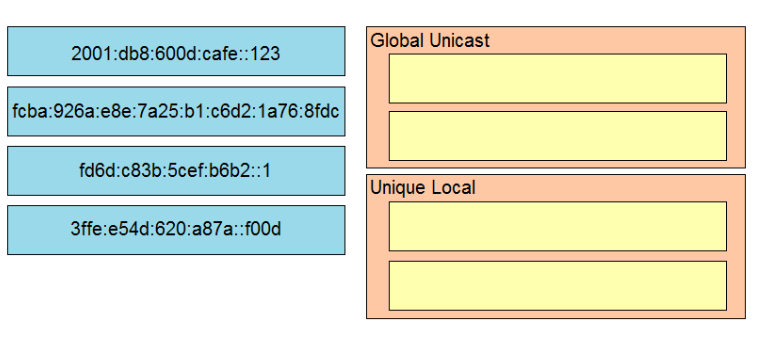
DRAG DROP -
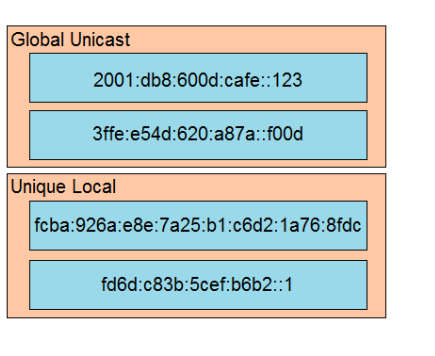
Drag and drop the IPv6 addresses from the left onto the corresponding address types on the right. Select and Place:
The FC00::/7 prefix is reserved for unique local addresses, however when you implement this you have to set the L-bit to 1 which means that the first two digits will be FD
Which type of organization should use a collapsed-core architecture?
A. small and needs to reduce networking costs
B. large and must minimize downtime when hardware fails
C. large and requires a flexible, scalable network design
D. currently small but is expected to grow dramatically in the near future
A. small and needs to reduce networking costs
A network administrator is setting up a new IPv6 network using the 64-bit address 2001:0EB8:00C1:2200:0001:0000:0000:0331/64. To simplify the configuration, the administrator has decided to compress the address. Which IP address must the administrator configure?
A. ipv6 address 2001:EB8:C1:22:1::331/64
B. ipv6 address 21:EB8:C1:2200:1::331/64
C. ipv6 address 2001:EB8:C1:2200:1:0000:331/64
D. ipv6 address 2001:EB8:C1:2200:1::331/64
D. ipv6 address 2001:EB8:C1:2200:1::331/64
0000 is replace by :
Only leading zero (not trailing zeros) are removed
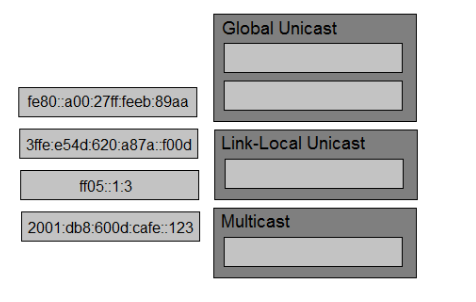
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the IPv6 addresses from the left onto the corresponding address types on the right. Select and Place:
Link-Local Unicast Always starts with FE80::/10
Multicast Address Prefix: Always starts with FF00::/8
Global Unicast Address Prefix: Typically starts with 2000::/3
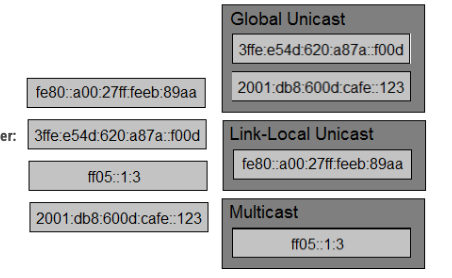
What is an appropriate use for private IPv4 addressing?
A. to allow hosts inside to communicate in both directions with hosts outside the organization
B. on internal hosts that stream data solely to external resources
C. on the public-facing interface of a firewall
D. on hosts that communicate only with other internal hosts
D. on hosts that communicate only with other internal hosts