Entomology Final Exam
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
1. Insects do not belong to which of the following higher taxonomic groups?
Radiolaria
Which of the following classifications contains the smallest number of species? (Hint: remember that classifications are hierarchical)
All insects that have complete metamorphosis: Holometabola
Although all of the Neoptera share a common insect ancestor that had folding wings, some species have lost those wings. Therefore, this characteristic cannot be considered _________, but is better classified as __________.
synapomorphy symplesiomorphy
Which of the following best describes the term “bug”?
It is a common term used loosely for many different types of arthropods
Insects are ________________.
a.) the most biodiverse group of organisms on earth and C.) a valid taxonomic group including all of the descendants from a common ancestor.
Chelicerata
This group includes spiders and mites.
Myriapoda
This group includes both the centipedes and millipedes.
Crustacea
An outdated classification representing a paraphyletic assemblage of lineages closely related to Hexapoda.
Collembola
A member of the group Hexapoda but not Insecta, they have modified appendages that act as a springtail.
Which of the following is the most accurate statement about insect wings?
They represent the earliest origin of flight among the Metazoa (animals)
Which of the following is the most accurate statement about the insect fossil record?
The fossil record for insects is fragmentary but gives us a reliable partial record of the group’s history on earth.
The first arthropods in the fossil record ___________.
appeared during the “Cambrian explosion” about the same time as other complex animals like annelids, chordates and mollusks.
Someone asks you if an insect has a heart. Which of the following would be the most accurate response?
They have multiple pulsatory organs along a dorsal vein and sometimes accessory pulsatile organs at the base of antennae and wings.
Malphigian tubules
This organ is analogous to the human kidney and can be found at the junction of the midgut and hindgut.
Ommatidia
A small, simple organ for light perception.
Sacromere
An individual unit that makes up muscles.
Tympanum
An organ for auditory input analogous to the human ear.
What is the primary function of the insect hindgut?
to reabsorb water and thus limit dehydration
Both the insect antennae and insect mouthparts ________.
evolved from the same early appendages as insect legs, just on different segments
Complex eyes evolved three times in the history of the Metazoa (animals): mollusks, vertebrates and arthropods. What feature makes arthropod eyes distinct from the other two types?
They are compound: made up of many individual lenses.
Which of the following is the best description of mouthparts across the Insecta?
Although many insects still have the standard ancestral components (labrum, mandibles, maxilla and labia), in different groups they are highly specialized for different methods of obtaining and processing food.
Which of the following best describes our current understanding regarding the origin and evolution of the insect wing?
There is still a degree of uncertainty, although it may be a combination of pleural and tergal components. More work needs to be done to make a conclusive determination.
1. Which of the following features is the least important when trying to explain why insects are more diverse than all the other arthropods?
exoskeleton
1. Which of the following phenomena is created by diffraction of light and reflection from different microscopic layers of chitin?
iridescence
1. Which of the following is not a part of the insect head?
a. Aedeagus
1. Most insect species lay eggs that develop outside their mother’s body. What is the best term for this?
oviparity
1. What are the three tagmata the make up the insect “body plan”? (mark all three correct answers)
Head, Thorax, and Abdomen
1. The hair-like, sensory structures found on many different parts of the insect body are called ________.
setae
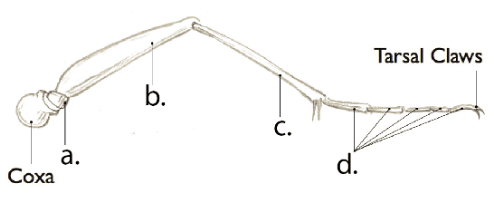
femur
B
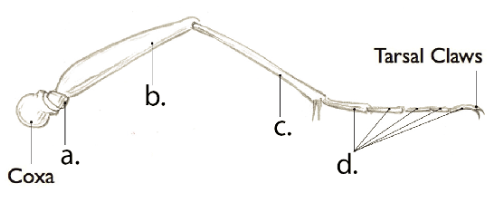
Tibia
C
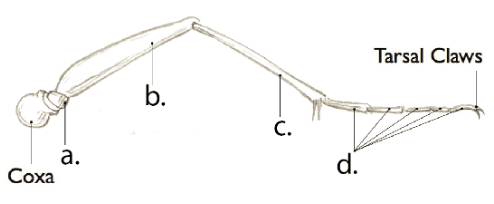
Tarsal Segments
D
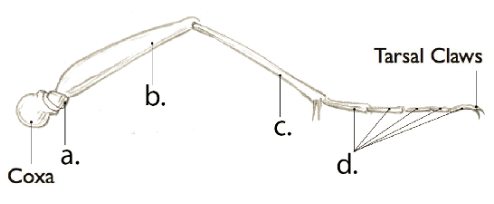
Trochanter
A
1. Which of the following is not a component of the insect respiratory system?
Alveoli
1. At the molecular level, chitin is similar to _________.
peptidoglycan and cellulose
1. In which of the following locations are you most likely to find resilin?
The leg joint of a flea
1. A juvenile insect that looks very different from the adult stage is called a ____ and indicates that that insect belongs to the group ______.
larva, Holometabola
1. What is an ootheca?
a. A bundle of eggs with a protective substance wrapped around them.
Cerci
a. Paired appendages on the posterior part of the abdomen.
Pleuron
the lateral sides of insect exoskeleton
1. Imaginal primordium
a. Small bundles of tissue found in larvae that serve as centers of organization during the pupal stage.
What would happen if you held a grasshopper’s head under the water and why?
Probably not much as their primary intake of oxygen is through openings along the thorax and antennae.
Wriggling is a common mode of locomotion among insects associated with _______.
soft-bodied larvae with a hydrostatic skeleton
Which of the following occurs during apolysis?
Release of enzymes that begin to digest the portion of the exoskeleton closest to the epidermis.
Sexual dimorphism is when one sex looks markedly different than the other and is caused when natural selection forces are different for males compared to females.
true
1. The proleg is a feature found along abdominal segments of the larval stages of Hymenoptera (wasps), Lepidoptera (butterflies) and some other insects. It is most crucial in which of the following modes of locomotion?
crawling
Why is Drosophila not the best choice as a model organism for the study of insect metamorphosis?
Drosophila, like other Diptera, has highly simplified larvae that are different from the ancestral type larvae.
Ephemeroptera (Mayflies)
Aquatic nymphs and short-lived adults that cannot fold their wings.
Diplura (Diplurans)
This group is classified as a hexapod, but not an insect.
Archeaognatha (Jumping Bristletails)
Along with the Zygentoma represents one of two extant branches of insects that diverged prior to the origin of wings.
Dermaptera (Earwigs)
Enlarged, pincer like cerci at the end of the abdomen; a small number of species are specialized ectoparasites.
Exam 2
You survey a species of insect and find only females; additionally, tests show that this species is much less genetically diverse than other closely related species. Which of the following would be the most likely statement about this species?
This species is parthenogenetic and reproduces asexually.
Most species of insects reproduce ________ and have _______ maternal care.
sexually and little to no
Strepsiptera males have many features typical of other adult insects, however the females maintain larval characteristics even after they reach maturity and are able to reproduce. Which terms fit this condition? (mark all correct answers)
Neoteny and Sexual dimorphism
Ecdysosteroid
a. A hormone that plays a role in the cycle of molting the exoskeleton of insects.
Diapause
The ability to temporarily stop or slow down development to deal with less-than-ideal environmental conditions.
Eclosion
The process of transitioning from one life stage to the next by shedding the exoskeleton.
Katatrepsis
A stage of embryonic development where the position of the embryo inside of the egg shifts.
What is the main advantage of asexual reproduction?
a. Rapid population growth because there are no individuals producing only sperm gametes.
1. What is the main disadvantage of asexual reproduction?
a. Decreased genetic diversity among the population due to no meiotic recombination.
1. Some ants make their home in the canopy of large trees. Trees without ant colonies are morphologically the same as trees with ant colonies and there is no evidence to suggest any advantage or disadvantage to either condition for the trees.
Commensalism
1. Leaf cutter ants raise a particular type of fungus that provides all the food for the colony.
Mutualism
1. Some crickets live inside ant colonies; they chemically mimic baby ants and receive nearly all their food from worker ants.
Antagonism
1. Some flowers create a noxious scent that mimics rotting flesh, this attracts flies that then pollinate these flowers.
Antagonism
1. Cordyceps fungi grow inside insects, they drastically change the behavior of their host and consume them from the inside.
Antagonism
Univoltine
Anthocharis cardamines, a butterfly that has one generation each year.
Multivoltine
Danaus plexippus, monarch butterflies migrate across North America and have several generations each year.
Semivoltine
a. Magicicada tredecim, a cicada that grows as a nymph underground and only emerges to reproduce once every thirteen years.
What drove the Lord Howe Island stick insect to near extinction?
a. Introduction of invasive species, like rats, onto their small home island.
1. Which of the following is not a strategy that insects use to survive periods of cold?
a. Homeothermy
1. Why are insects so susceptible to changes in temperature?
a. They are small, poikilothermic organisms.
1. Which of the following is not an insect order with eusocial systems?
a. Mantodea (praying mantids)
1. Which of the following is most likely the most important behavioral trait contribution to the evolution of social and eusocial systems?
maternal care
1. How many times has eusociality evolved in insects?
many different times
Trophallaxis
a. Termite adults regurgitate some of their gut content and feed it to their nymphs.
Inquiline
a. Some crickets mimic the pheromones of ants and live inside their colonies.
Repletes
a. Some ant species have castes with enlarged abdomens and they act as storage vessels for food collected by the workers.
1. Which of the following would be least likely in a fungivorous insect?
a. Nymphs found in an aquatic environment.
1. Which group of insects has some species with a specialized soldier caste that can expel acid out of a nozzle like structure on the head?
termites
1. The phylogeny of leaf cutter ants closely matches that of the fungi that they rely on for food. This is a clear example of ___________.
cospeciation
1. Which of the following best explains the evolution of eusociality in the Hymenoptera (ants, bees and wasps)?
a. It has evolved many different times within this group due to the high degree of relatedness amongst sisters. This is caused by a haplodiploid form of reproduction.
1. Which of the following is the most important factor in the ability of termites to take advantage of wood as a primary source of energy?
a. They have mutualistic gut microbes that help them to access the carbohydrates and proteins in wood that are difficult to enzymatically break down.
1. “Bt cotton” comprises the majority of cotton grown today. What is the distinguishing feature of Bt cotton?
a. It is a transgenic organism and has a bacterial gene inserted into its genome
1. Why might a bacterial, or fungal biocontrol agent be a better approach than a chemical pesticide?
a. It is more species specific
b. Less long-term residue in the environment
c. More cost effective
1. Why is reproductive manipulation an advantage for some endosymbionts?
a. They are transmitted vertically from mother to offspring
1. Most obligate symbionts have greatly reduced genomes. Which of the following is not a force that helps to explain this reduction in genome size?
a. Genetic drift, particularly on the third position in the reading frame of symbiont genes
1. Wolbachia bacteria have complex interactions with their various insect hosts. Some are best categorized as mutualists, others as antagonists, and others may be in a gray area where ecological interactions are difficult to categorize.
true
1. Most pollination interactions between plants and insects can best be classified as a _________ interaction.
mutualistic
Gall
a. Cynips quercusfolii is a wasp that lays its eggs in oak leaves, the oak forms a structure around the wasp larvae that protects and feeds it during development.
Monophage
a. Pipevine swallowtails always lay their eggs on one plant and the larvae rely completely on their leaves for all their nutrition.
Phytotelmata
a. Bromeliads are plants that have small pool of water and can act as a mini aquatic ecosystem in the canopy of rain forests.
Myrmecochory
a. Acacia extensa is a species of tree that generates seeds with special “handles” the help ants pick them up, some stick insect eggs mimic seeds and also benefit from this behavior.
1. Some pitcher plants have evolved away from an antagonistic relationship with insects. Which of the following observations would provide evidence that a pitcher plant fell into this category?
a. A small ecosystem of living insects in its reservoir of water
1. Which of the following would be evidence of a plant mounting an indirect chemical response to phytophagy?
a. Production of a chemical that signals to a wasp parasitoid of the phytophagous insect.
1. Which of the following is the best description of the relationship between Blattodea (roaches) and Isoptera (termites)?
a. Termites are a highly specialized, eusocial branch of Blattodea and should not be considered as a separate group.
1. Members of which of the following orders of insects is most likely to be a phytophagous fluid feeder?
a. Hemiptera (true bugs)
1. You notice a domatia structure on a plant, which of the following is the best statment regarding this situation?
a. The plant and the insects inside the domatia have a mutualistic relationship.
1. Grylloblattodea “Ice Crawlers”
a. Adapted to cool or very cold habitats, many species are found associated with glaciers or ice caves.
1. Mantodea “Praying Mantids”
a. Forelimbs modified into raptorial claws.
Orthoptera “Crickets and Grasshoppers”
a. Hind legs modified and enlarged for jumping.