(5) Measurement - Inflation
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Economic growth
Ability of economy to produce increasing quantities of goods/services
The increase in real GDP or real GDP per capita over time
Long-run = rising productivity increases average standard of living
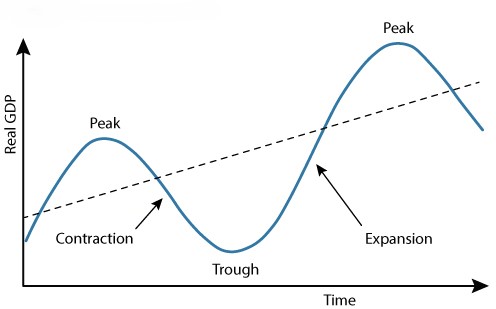
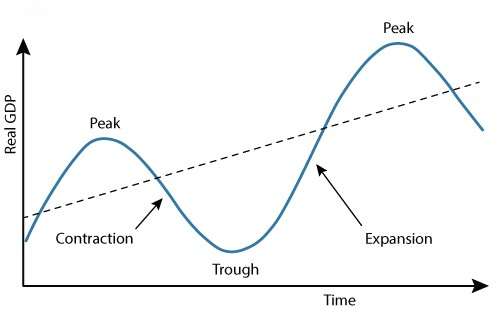
Business Cycle
Alternating periods of economic expansion and economic contraction relative to the long-term trend rate of economic growth
Real GDP per capita
A measure of average output per person, adjusted for inflation; the best indicator of living standards
(Real GDP/population)
Rule of 70
The number of years required for a variable (like GDP) to double = 70 ÷ annual growth rate
70 comes from a formula
Labour Productivity
The quantity of goods and services produced per hour of labour’
Determined by…
Increases in capital per hour worked
Technological change
Potential GDP
The level of real GDP the economy can produce at full employment (firms are producing at capacity
The Business Cycle - when economy EXPANDS
Production increases - more output
Unemployment decreases - businesses need people for output
Wage increases - attract and keep workers by offering higher wages
Consumer spending increases - people spend more because they earn more
Prices increases - consumers spend more (inflation)
The Business Cycle - when economy CONTRACTS
Production decreases - businesses produce fewer output
Unemployment increases - businesses need fewer workers
Wages decrease - businesses are doing less well
Consumer spending decreases - people spend less because they earn less
Prices decreases - consumers spend less (deflation)
Physical capital
The stock of equipment, buildings, and tools used to produce goods and services (manufactured goods)
Human capital
The knowledge and skills acquired through education, training, and experience from workers
Technological progress
Change in ability of firm to produce a given level of output with given input
Improvements in knowledge that enhance production efficiency and output
Financial system
The network of institutions that match savers’ funds with borrowers’ investment needs
Investment
Expenditure on new capital goods that add to future productive capacity
Public saving
Taxes minus government spending (T – G)
Private saving
Disposable income minus consumption
(national income - consumption - net taxes)
National saving
Sum of private and public saving; funds available for investment
Closed economy formula for GDP
Y = C + I + G
Investment in a closed economy
I = Y – C – G = national saving
Crowding out
A decline in private investment due to increased government borrowing or higher interest rates
Foreign direct investment
Investment by foreign firms in domestic capital or operations
Catch-up effect
The tendency for poorer countries to grow faster than richer ones when similar policies are adopted
Policies promoting growth
Increasing saving, investment, education, research, trade, and stable institutions
Institutions
Economic and political rules that shape incentives and govern behaviour
Recession
Significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, visible in industrial production, employment, real income and wholesale-retail trade
If an economy’s growth rate is 3.5% per year, its GDP will double in approximately:
B) 14 years
Which of the following contributes most to long-run economic growth?
C) Growth in labour productivity
Which of the following policies best encourages long-run economic growth?
B) Subsidising education and research
Which of the following is an example of crowding out?
B) Government borrowing raising interest rates, reducing private investment
The catch-up effect predicts that:
B) Poor countries will grow faster than rich ones, holding other factors constant
During expansions, inflation rate…
increases
exception: if expansion is due to rising productivity levels and an expansion of potential GDP
During contractions, inflation rate…
decreases
exception: if recession is caused by a supply shock
Unemployment rate will RISE even after a recession because…
firms delay hiring and more people re-enter the labour force to look for work as conditions improve.