A3.2- Classifications and Cladistics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
The need for classification of organisms
Because of the immense diversity of species
Species
Basic level of classification
Taxon
Any classificatory group (plural: taxda)
Difficulty of classifying orgnaisms into traditional hierarchy of taxa
Traditional hierarchy of kingdom, phylum, class, order family, genus and species do not always correspond to patterns of divergence by evolution
Divergence
Evolutionary process where population diverges /splits) into 2+ descendant species and are gradually becoming dissimilar
Advantages of classification corresponding to evolutionary relationships
Ideal classification follows evolutionary relationships
All members in taxonomic group evolved from a common ancestor
Characteristics of organisms can be predicted because of shared clade
Examples of species of bat
Bats are classified as mammals, some predictions can be made then:
New species of bat will have:
a four-chambered heart
hair
mammary glands
placenta
navel/belly button
Examples of species of daffodils
Some types of daffodil produce galanthamine
Used for treatment of Alzheimer's disease, there is strong evidence that all species in the genus Narcissus evolved from a common ancestor
Reasonable to predict that alkaloids are synthesised by Narcissus species
Evidence for placing organisms in the same clade
Base sequences of genes or amino acid sequences of proteins
State what is used instead when sequence data is not available to provide/present as evidence
Morphological traits
Clade example drawing
(draw and label)
Smaller clases are nested within larger ones
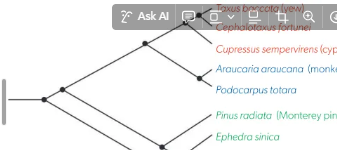
Molecular Clock
Method of estimating times since two species diverged from a common ancestor
Reason why molecular clocks can only give estimates
Mutation rates are affected by:
Length of generation time
Population size
Intensity of selective pressure
Etc
How are cladograms constructed
Sequence Analysis
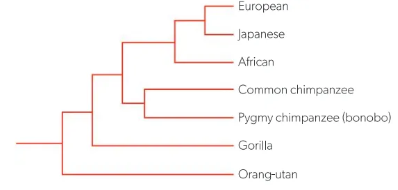
Cladogram + sample drawing for humans and primates
A branching diagram that represents ancestor-descendant relationships
(draw and label)
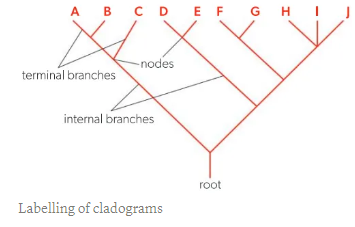
Analysing cladograms
Cladogram is a tree diagram with a number of branches
Root → Base of a cladogram
Node → Branching points that represent hypothetical common ancestor
Terminal Branch → Ends that represent individual clades
The new 3 major categories of organsisms
Eubacteria
Archae
Eukaryota
Why is classification not regarded as appropriate anymore
Because prokaryotes are so diverse