IB Geography Oceans and Coastal Landforms
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are the causes and patterns of ocean currents
They are cause by the influence of prevailing winds blowing steadily across the sea
The main pattern is roughly circular.
Clockwise in northern hemisphere
Anti-clockwise in southern hemisphere
What are upwelling currents
Ocean currents move cold, nutrient rich water from the ocean floor to the surface. Eg. Found off the coast of Peru.
This supports fisheries, however the upwelling off the coast of Peru disappears during El Nino
What is El Nino
The reversal of normal atmospheric circulation in the Southern Pacific Ocean. This warms the East Pacific.
What is El Nina
The intensification of normal conditions, strong easterly winds push cold, upwelling water off the coast of South America into the Western Pacific
What are the normal conditions in the Pacific Ocean
Near South America, winds blow offshore causing upwelling. Warm surface water is pushed into the Western Pacific. This causes high pressure, low temperature and low rainfall in South America. And causes low pressure, high temperatures and high rainfall in the Western Pacific.
What are the conditions in El Nino
High pressure over western pacific, and low rainfall
Low pressure over South America, causes high rainfall
What are the features of a hurricane
Intense low pressure systems which bring heavy rainfall, strong winds, and high waves. This can cause flooding and mudslides. They usually originate over tropical seas.
What are the conditions for a hurricane to form
Sea temperatures over 27 degrees
Warm water must have a greater depth than 60m
The area must be far enough from the equator that the coriolis effect takes place.
What is the oceans role in the carbon cycle
The largest Co2 sink
Photosynthesis turns carbon dioxide into organic material. This material, over time, settles into the deep ocean.
How does ocean acidification occur
Caused by man-made sources. Oceans absorb carbon which becomes carbonic acid. This lowers the pH of the ocean. This can kill off coral reefs and shellfish beds by reducing calcification. This results in slower growth and weaker skeletons
How are waves an influence on coastal landscapes
Constructive waves
Depositional
Long wavelength, low height
Low frequency
Swash greater than backwash
Destructive waves
Erosional
Short wavelength, high height
High frequency
Backwash greater than swash
How does weathering affect coastal landscapes
Salt weathering
salt compounds expand in joints and cracks, weakening rock structures
Freeze-thaw weathering
Water freezes, expands and degrades jointed rocks
Biological weathering
Carried out by molluscs, sponges and urchins
How do tides affect coastal landscapes
Tidal range controls vertical range of erosion, deposition and biological activity. It can also have a scouring effect.
How does sediment affect coastal landscapes
Mass movement
Provides large amounts of material which can bury beaches and protect cliffs
Rivers
Carry sediment to coast
Periglacial processes
Provide frost-shattered shingle for beaches
Erosion of cliffs
Provides material for beach building, may also protect the cliff from further erosion
Wind erosion and transport can carry fine sand
Volcanic activity can produce dust and ash for beaches.
What does the profile of a cliff depend on
A low resistance rock will make a weak coast as they are easily eroded and won’t support an overhang. Jointing may also cause weakness. The amount of undercutting, and sub-aerial processes also affect the cliff profile.
What are wave cut platforms and how are they formed.
Steep cliffs are replaces by a lengthening platform which then lowers cliff angles. This can be caused by sub-arial processes, erosion and weathering.
How are stacks formed
Lines of weakness can be eroded to form enlarged caves, if this breaks through a headland it is called an arch. Then if the roof of the arch collapses due to weathering and erosion it becomes a stack. The eventual erosion of the stack makes a stump
How are spits formed
A spit is a beach of sand/shingle which is connected at one end to land. They have a thin attached end (distal end) and a larger (distal) end, which may be curved due to wave refraction. These occur as a result of longshore drift.
What is eustatic change
A global change in sea level. Sea levels change in connection with the growth and decay of ice sheets.
What is isostatic change
The localised change in the level of the land relative to the level of the sea. This could be caused by tectonic uplift.
How are isostatic and eustatic change linked in the ice sheet degradation and formation cycle
Temperatures decrease, glaciers and ice sheets advance and sea level falls eustatically
Ice thickness increases so land is lowered isostatically
Temperatures rise, ice melts, sea levels rise eustatically
Melting releases pressure on the land so land rises isostatically
What does retreating coasts mean
Where the rate of erosion exceeds the rate of deposition
Includes submerged coasts
What does advancing coasts mean
When deposition is rapid
Includes emerged coastlines
What are some features of emerged coastlines
Raised beaches
Coastal plains
Relict cliffs
Raised mudflats
What are some features of submerged coastlines
drowned river valleys
fjords
drowned glacial lowlands
What are the order of names in the development of dunes
Embryo dune → Yellow dune
Yellow dune → Semi-fixed dune
Semi-fixed dune → fixed (gray) dune
How do dunes develop
Sea couch grass can colonies a small embryo dune formed by wind blowing sand up the beach, above the seaweed strand line.
Once the dune starts growing, marram grass can colonise which can grow it into a yellow dune.
When the dune is very high, less sand builds up behind, so marram grass dies and soil begins to form which means other plants can grow, this creates the semi-fixed dune.
As time goes on and soil becomes richer and more developed, lichens, mosses etc form a continuous layer over the dune forming a gray dune.
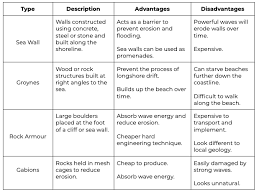
What are some hard engineering tactics and their advantages and disadvantages
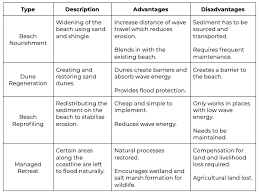
What are some soft engineering tactics and their advantages and disadvantages
What are the biological and economic importances of coral reefs
They protect coasts against erosion and provide a habitat for many different species of fish. They generate large profits in tourism, for diving and adventure.
How can coral reefs be managed
Marine protected areas, which can restrict harmful activities such as oil drilling, fishing and mining. Another major harmful impact is fishing vessels which need to be restricted.
What are mangrove swamps
Salt-tolerant forests of trees and shrubs which grow in tidal estuaries and coastal zones of tropical areas. The muddy waters are rich in nutrients.
Why are mangroves important and how can they be managed
They provide fuelwood, charcoal, dyes, poisons and shellfish. Many species of fish use mangroves as nurseries.
Management strategies include restoration and afforestation, managed realignment allowing mangroves to migrate inland. And general protection.
What is an exclusive economic zone
An area in which a coastal nation have sovereign rights over all the economic resources in the sea, up to 200 nautical miles from the coast.
What are hydrates and how are they used.
Compounds which usually consist of methane molecules trapped in water. Some scientists believe they contain more energy than all known fossil fuel deposits.
Where are oil and gas deposits often found
In the continental shelf. Most oil and gas reserves are in the Persian gulf
How has the worlds aquaculture production changed
The worlds supply of fish has dramatically increased. Africa was the lowest consumer, and Asia the greatest.
What are the main sources of oceanic pollution
Fishing industry, the use of boats for shipping, offshore mining and extraction and illegal dumping.
What are the main sources of oceanic litter
Discharge from stormwater drains, industrial outfalls, untreated sewage, littering and landfills.
How does radioactive waste pollute water systems
It comes from nuclear power and industrial uses. After the explosion of the nuclear power station at Fukushima, nuclear waste was carried across the northern pacific ocean to USA and Canada. Nuclear waste remains radioactive for decades.
How does plastic pollute water systems
Great pacific garbage patch- Containing approx. 100 million tones of garbage suspended in two gyres. It can take centuries for plastic to decompose. Marine wildlife inadvertently eat it, which causes death usually.
How does oil pollute water systems
Ships burn bunker oil which causes death from chest and lung infections and cancer. Oil spills cause massive ecological disaster.
What actions have been taken against ocean pollution
UN Law of the Sea implemented regulations on deep sea mining and EEZ’s.
A series of international laws eliminated the discharge of toxic materials into waters around Europe.