Ch. 22 - Communication Mammalogy [Dr.Wood]
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Behavior; Why is it difficult to study?
Hard to study, nocturnal, small, secretive
Neocortex
advance processing of sensory input, coordinate behavior
Display
conveys message from 1 indvl to another
Message
describes the sender's state
Meaning; The importance of another understand in a message?
It must be received by another individual
Signal
physical form in which a message is sent in the environment
Adaptive
signal/response enhances survival,reproduction; controlled by genetics/natural selection
Ritualized
exaggerated, repeated but with minimal amt energy spent
Deceit
Rare, natural selection favors ignoring deceit/punishing deceit
Northern elephant seal
Young males mimic females to sneak copulations
• Females vocalize loudly, so the harem master chases off young male impostors, and the youg male can die
Discrete
signals sent in a simple either/or manner

Equids
•ear position, mouth opening
•Hostility: flat ears; friendliness = raised ears
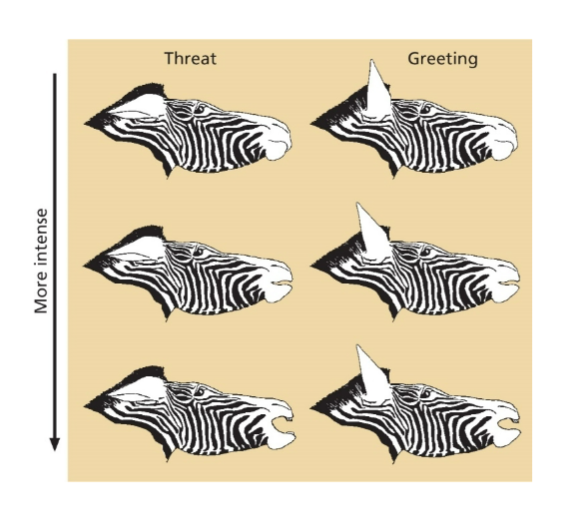
Graded
signals are more variable, different intensities
Composite
signals: more than or equal to 2 signals
Syntax
The order of signals
Context
situation dependent
Odor
•Earliest form (pheromones)
•Mate i.d., attraction, spacing, alarm, terr.
• Nocturnal, persistent
Priming pheromones
cause physiological changes in an animal that ultimately result in a behavioral response.
Signaling pheromones
immediate motor response (mounting)

Flehmen
Retract the upper lip after/during olfaction
Sound
• flexible traits
• Frequency, modulation changes
Sound window
ideal frequency range for a species. Blue monkeys high pitch, Howler monkeys low frequency.
Echolocation
Found in bats
Extra cred: Noctoid Moth
•tympanic membrane for hearing, but don't vocalize
• Listen for sound waves from bats/evade
• Also jamming sounds
foot drumming
Banner-tailed kangaroo rats use for territoriality
Elephant Rumbles
Elephants' 14-35 Hz can be heard over several km
Visual displays
location in space-time in Daylight, short-distance signaling
Flagging behavior example
white-tailed deer
Flagging Behavior Functions
1. Distract the predator from others
2. warn herd
3. Confuse the predator with group display
4. loss of surprise
5. elicit premature pursuit
6. intraspecific social signal
Lion's mane
Females prefer males w/darker mane, rival males avoid darker-maned males
Touch: tactile grooming
• Remove ectoparasites, enhance social bonding in social species
• Try to groom individuals of higher rank
• Groom kin over non-kin
Tactile stimulation
can initiate ovulation, positioning for copulation
Spacing signals
1. distance-increasing
2. distance-maintaining (home ranges)
3. distance-reducing
4. proximity-maintaining (grooming)
Species recognition
reduce infertile matings with other species
Kin recognition
reduces inbreeding by knowing familly
Phenotype matching
visual, but most likely olfactory recognition (rodents)
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
immune system recognition of self/non-self
Grivet monkeys: Case Study
Use different calls for different predators. Look in different strata for different predators (snakes, eagles, leopards), and their ID improves with age
rally
African wild dogs: rally before hunt to synchronize behavior
Agonistic behavior
offensive/defensive behaviors given
Agonistic behavior Functions:
1. territoriality
2. dominance
3. sexual
4. parental
Exploitation
deprive others of resources
Home range
range covered by a mammal over its lifetime
Core area
heavy use area w/in the Home range
Territory
defended area w/in Home range
Economic defensability
benefits outweigh costs, or must reduce HR/T size
Lek
topis, males congregate, display, females visit the lek to find a mate
Dominance
social groups, access limited by dominance displays
Dominance 4 possibilities:
1. linear dominance hierarchy
2. 1 dominant indvl, others equally subordinate
3. circular dominance
4. coalitions/alliances
Physiological consequences of dominance
Subordinates have poor condition, malnourished/diseased
What is the effect on Subordinates from a dominant male
high levels of glucocortical hormones than the dominants
Infanticide
Ex: hanuman langur monkeys
• New male kills older male, infants
• Females enter estrus when they lose their young
• New male breeds females
creches
Females form ______to protect young
Facultative siblicide
Found in spotted hyenas
• Poor food supplies, siblings fight, often to death, especially if same sex
• If food supplies are good, no siblicide, but instead form strong bonds