all of biochem
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
molecule
substances composed of two or more covalently bonded atoms
elements that make up the chemical foundation of life
CHNOPS - carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur
intramolecular forces
forces within molecules that hold atoms together: covalent bonds or ionic bonds
electronegativity
property of how strong an atom attracts electrons,
polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons
non-polar covalent bond
when two atoms of similar electronegativities equally share electrons
intermolecular forces
between molecules and determine how same type molecules interact, weaker than intramolecular forces, responible for attracting molecules but will break with enough force
hydrogen bond
involves hydrogen atom and oxygen/nitrogen atoms, aqueous environments, hyrdophilic
hydrophobic
non-polar that don’t form hydrogen bonds
functional group
cluster of atoms that always behave in a certain way, contains ONPS
structural formulas
show how the atoms are bonded together
macromolecule
large complex molecules composed of repeating units of smaller molecuels, linked by covalent bonds
polymers
long chain like substances that make up macromolecules
monomers
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
types of macromolecules
carbs, lipids, protien, nucleic acids
carbohydrates
contain CHO, (CH2O)#carbon atoms, usually polar, sugars and starches
monosaccharides
single carbon based monomer stuctures, simple sugar with 3 to 7 carbon atoms, glucose, fructose, galactose, energy
disacchardies
two monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage, surose, lactose, energy
glycosidic linkage
a type of ether bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate
condensation reaction
forms glycosidic linkage, one monomer gives up hydroxyl group and other hydrogen, requires energy
hydrolysis reaction
how glycosidic linkage is broken, water is split into hydroxyl group and hydrogen, releases energy
polysaccharides
long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides, glycogen, starch, cellulose, storage, support/structure
function of carbs
energy, storage, support/stucture
functional groups of carbs
hydroxyl and carbonyl
triglycerides
lipid molecules formed from one glucerol molecule bonded by ester linkages to three fatty acid molecules
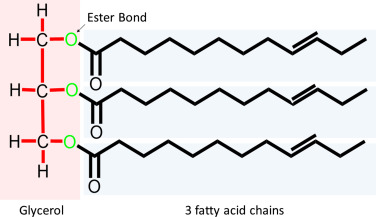
ester linkage
formed between the oxygen molecules of glycerol and the hydroxyl molecules of fatty acids
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain ending in a carboxyl group
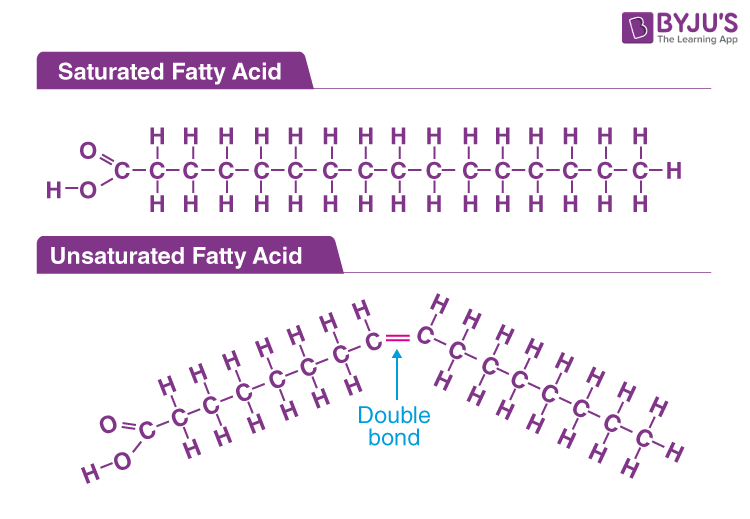
saturated
no double bonds between carbon, straight line, solid
unsaturated
monounsaturated (one double bond between carbond) or polyunsaturated (more than one double bond), bent, liquid
phospholipids
main components of cell membranes, similar to triglycerides but phosphate group replaces third fatty acid

steriods
lipids composed of four attached carbon based rings, used for sending signals and membrane fluidity, differ based on functional groups
waxes
lipids made of long carbon based chains, used for protection, solid
functions of lipids
long term energy(tri), membranes(phospho), sending signals(steriods), protection(wax)
functional groups of lipids
hydroxyl, carboxyl,
dual nature of phospholipids
they have a polar head and non polar tail which creates a hydrophobic interior and the basics of a cell membrane when placed in water. the tails move together and the hydrophilic heads move outwards facing the water
proteins
macromolecules composed of amino acids and linked by covalent bonds, made of polypeptides
amino acid
orgainic molecules composed of central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, variable R group
functions of protein
transport
structural support
mobility
signals/hormones (regulating cellular processes)
defence (antibodies)
speed up reaction
type of linkage in proteins
covalent bonds called peptide bonds, form between carboxyl group and amino group
polypeptides
polymers composed of many amino acids linked by colvant bonds, protiens are composed of one or many polypeptides, vary in number and sequence of amino acids
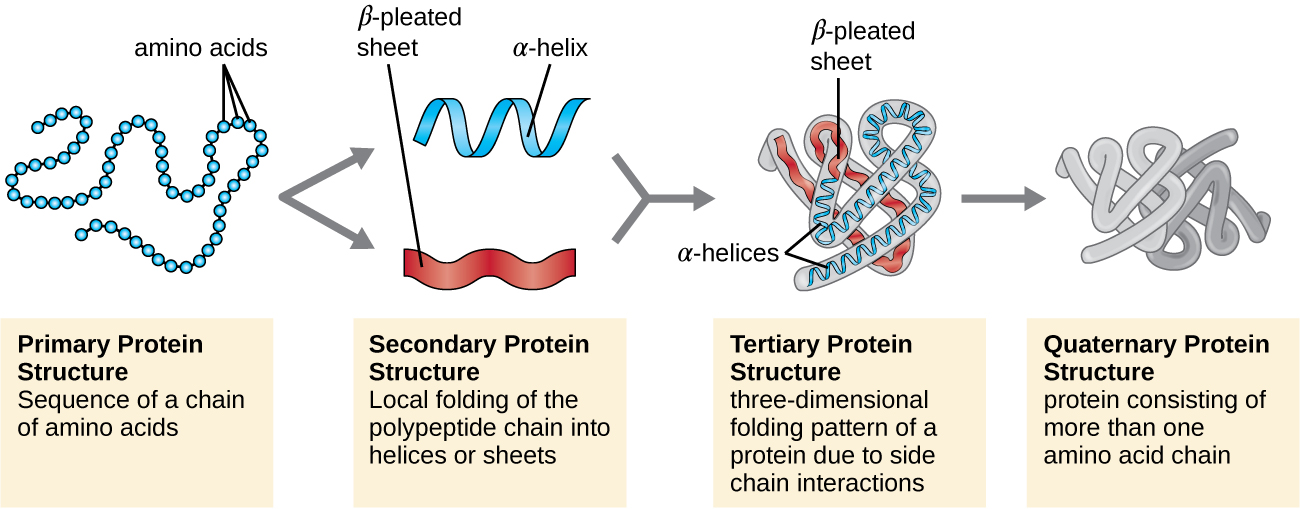
levels of organization in proteins
primary - linear sequence of amino acids
secondary - hydrogen bonding contributes to an alpha helix or beta pleated structure
tertiary - 3D folding based on hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions
quaternary - multiple polypeptides joining more than one polymer chain of amino acids
denaturation
breaking of many of the weak linkages, or bonds (e.g., hydrogen bonds), within a protein molecule that are responsible for the highly ordered structure of the protein in its natural state and is caused by extreme temp changes and chemical exposure.
functional group of proteins
hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino
monomers of nucleic acids
nucleotides
polymers of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
4 main types of chemical reactions
neutralization, oxidation-reduction, condensation, hydrolysis
acid
substance that produces hydrogen ions (pH under 7)
base
substance that produces hydroxide ions (pH over 7)
neutralization reaction
acid and base react together, base accepts hydrogen ions, produces salt and water
normal range of human pH
7.35 fo 7.45 (below 7 or aboive 7.8 is fatal)
alkalosis
blood pH over 7.5, dizziness and agitation, caused by breathing quickly or taking too many antiacids
acidosis
low blood pH, kidney disease or vomiting
buffers
substances the minimize changes in pH, give H2 when basic and take H2 when acidic
oxidation reactions
when a molecule loses electrons and becomes oxidized
OIL
reduction reactions
when a molecule accepts electrons and is reduced
RIG
example of a buffer system
carbonic acid - hydrogen carbonate ion buffer system is used when the blood is too basic.
example of redox reaction
cellular respiration used redox to oxidze sugar through small steps to slow the release of energy - stored in chemical bonds
condensation reaction
joins molecules covalently, produces water, requires energy
hydrolysis reaction
breaks apart large molecules, uses water, releases energy
activation energy
energy requires to begin a chemical reaction, large activation energy means slow reaction
catalysts
substances that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy, proteins
enzymes
specifics proteins that acts as catalysts in organisms, made of long chains of amino acids, globular shapes with indents called active sites
active sites
pockets or indents on the surface of an enzyme
enzyme substrate complex
when active sites and substate join together
induced fit
slight cahnge to the shape of the enzyme to fit the substate
catalytic cycle
cycle of a enzyme
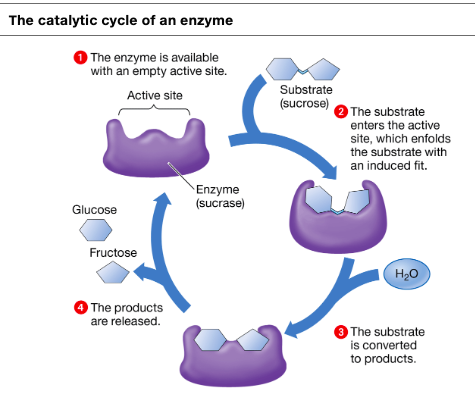
addtional moleules needed to catalyze a reaction
coenzymes and cofactors
what affects enzyme activity
temperature and pH change and how much substate is present because enzymes encouter them less frequently
inhibitors
molecules that interact with enzymes, they reduce the activity of the enzyme by interfering with its interaction with the substrate
activators
molecules that can bind to an allosteric site to cause an increase in enzyme activity
feedback inhibition
process where biochemical reaction are grouped and regulated
competitive inhibitior
interfers with the active sites so substrate cannot bind to enzyme
noncompetitive inhibitor
changes the shape of the enzyme so substrate cannot bind
nucleus
manages or controls all the cell functions in eukaryotic cell, membrance bound
cytoplasm
fills the interior of the cell except for nucleus
cytosol
liquid of the cytoplasm
nucleoplasm
fills the nucleus
nuclear membrane
phospholipid membrane bilayer barrier around the nucleus
nuleolus
site where ribosomes are made
ER
connects to the nucleus and has 2 parts
rough ER
membrane bound tubules and sacs associated with ribosomes, sites of protein synthesis, transports materials within the cell
ribosome
synthesises proteins for export from the cell or membrane formation
smooth ER
synthesises lipids and lipid containing molecules, packages proteins
endomembrane system
system for transortation and product processing, proteins are synthesized and modified
golgi apparatus
sorts packages and distributes lipids, manufactures macromolecules, produced lysosomes/pectin, closely packed and flattened sacs
peroxisomes
manufacture cholesterol and bile acids, off the ER
vesicles
transort materials ouside of cell and temportary storage of substances
vacuoles
large vesicles in plant cells, store water ion sugar amino acids and macromolecules
lysosomes
digests worn-out cell parts, food particles, and invading viruses or bacteria
mitrochondria
break down energy-rich molecules to convert stored energy into useable energy
cell wall
provides protection and supprt in plants and fungi, made of cellulose
cytoskeleton
innner network of protein fibres which provide structure and anchoring to cell membrane and organelles
microtubules
maintain shape, facilitate movement of organelles, cell division (spindle formation)
intermediate filaments
maintain shape, anchor organelles, form internal scaffolding of nucleus
microfilaments
maintain shape, muscle contractions, assits in cell division (cleavage furrow)
nuclear pores
regulate transport in and out of nucleus
cilia
move cells by a wave lengh movement, can sense things, sweep out debirs in respirary tract
flagella
tails and move cells with a whip like motion
fluidity of the cell membrane is affected by
temperature (more mallable w/ temp)
presence of double bonds (more double bonds more fluid)
length of fatty acid tail (longer length less fluid)
presence of cholesterol (more choesterol less fluid)
what does the fluid mosaic model feature in a cell membrane
semi-fluid phospholipid bilayer with proteins, non-polar proteins and non-polar bilayer come in contact with each other, other proteins and molecules float in/on bilayer, made of two leaflets that slide across each other