Microbiology: Oral Microbiology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are Soft Tissue Lesions of Oral Cavity?
•Candida albicans
•Hairy Oral leukoplakia
•Herpes simplex virus
•Coxsackie A virus
–Herpangina
–Hand, foot, mouth disease
What are the clinical findings of Candida albicans?
Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
•Aka “thrush”
•White plaques on buccal mucosa, palate, tongue, oropharynx
--Wipe off leaves a red, raw painful surface --> Make Hyphae which dig into the skin
•Can progress to esophagitis in AIDS pts
Neonates often get
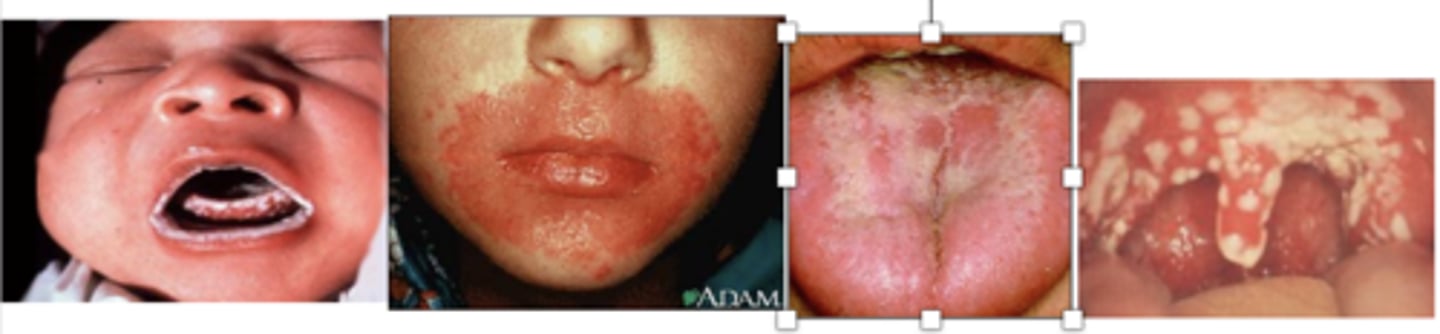
How do you get Candida?
overgrowth
What is the lab dx for Candida?
Microscopy
•Will stain Gram-positive (40X)
•Yeast, budding hyphae, pseudohyphae
•Few PMNs
•Germ tubes for Candida albicans
Growth on Sabouraud dextrose agar
What is the tx for Candida?
•Topical nystatin (Binds directly)
•Oral fluconazole for AIDS pts (binds to ergosterol enzyme to inhibit synthesis)
--For esophagitis
What is Hairy Oral Leukoplakia?
Caused by reactivated EBV infection (in B cells)
•Opportunistic infection in AIDS pts
--Productive infection of epithelial cells
--Characterized by lesions of the mouth
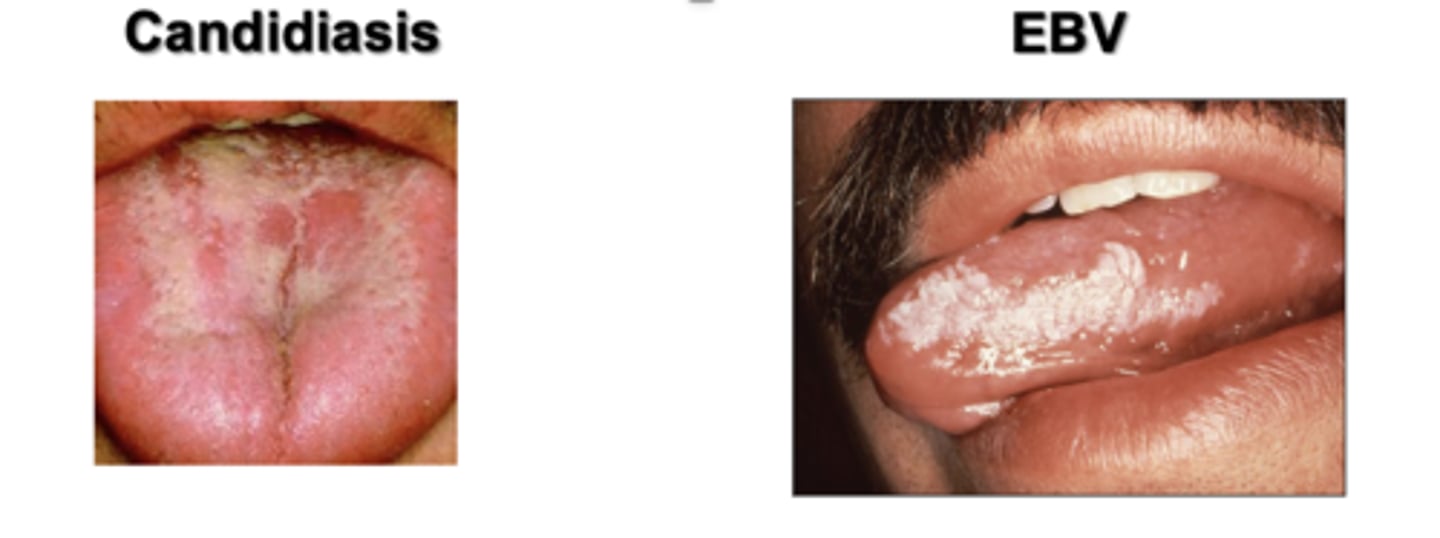
What is EBV characteristics?
Herpes DS DNA virus with nuclear envelope
What are CF of Herpes simplex virus 1?
-Flu-like symptoms
-Virus goes latent
-Cold sore
-Herpetic whitlow
When does the primary infection of HSV-1 occur?
•1o infection ~1 wk after contact
How does HSV-1 go latent and what happens after reinfection?
Virus goes latent in trigeminal ganglia
•2o infection after reactivation
•Immune suppression
What are you concerned with a cold sore in HSV-1?
•Still concerned w/ TL encephalitis!
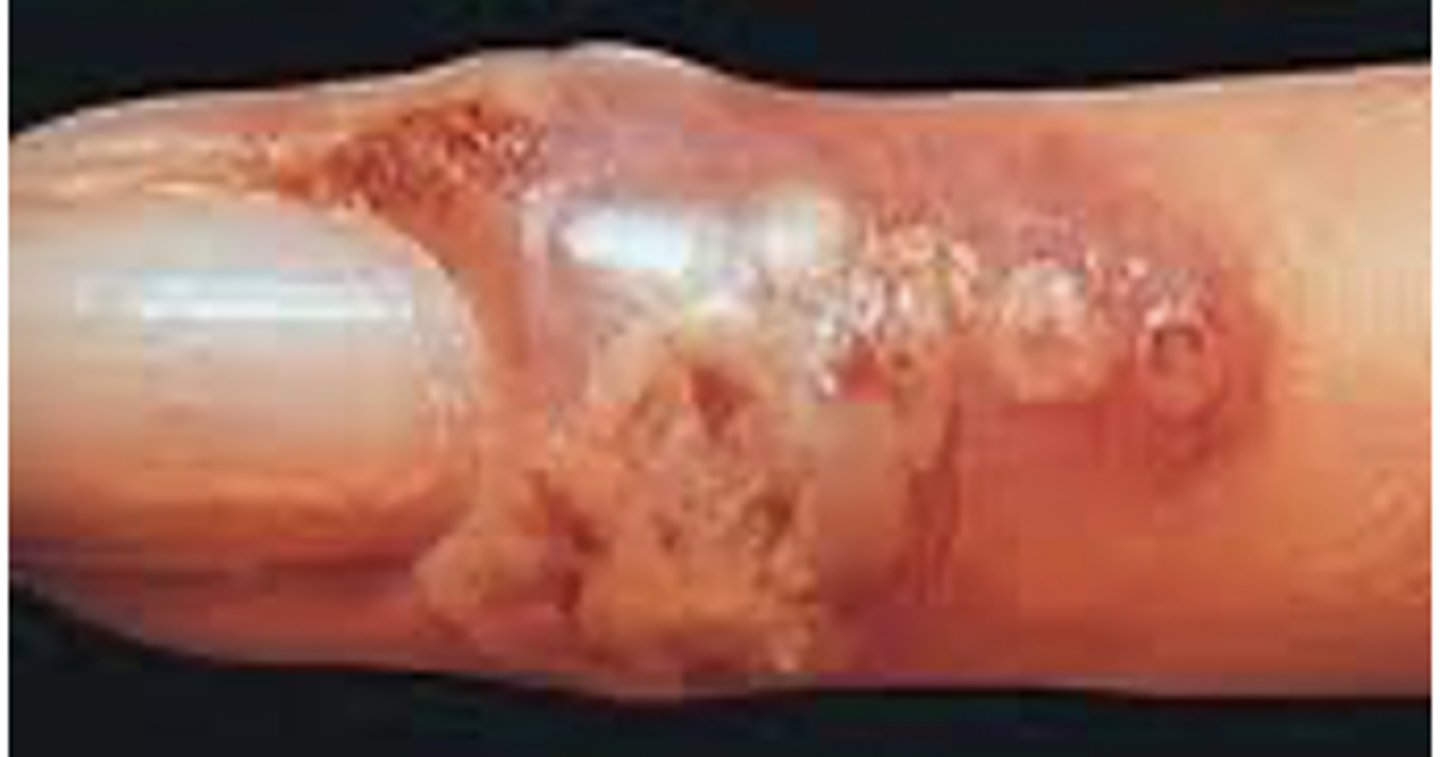
What is herpetic whitlow in HSV-1?
•Primary infection of fingers
•Physicians, nurses, dental personnel
―Child sucking thumb
What is the picornavirus?
Coxsackie Virus
–Naked, positive-stranded RNA, icosahedral
–Fecal-oral transmission
–Childhood illness in late summer/fall
What are the different diseases of picornavirus?
-Herpangina (A2-6)
-Hand foot and mouth (A5, 9, 10, 16)
What is Herpangina?
Highly contagious, 4 d incubation
•Vesicular ulcerated lesions around soft palate and uvula
•Fever, sore throat, anorexia, vomiting

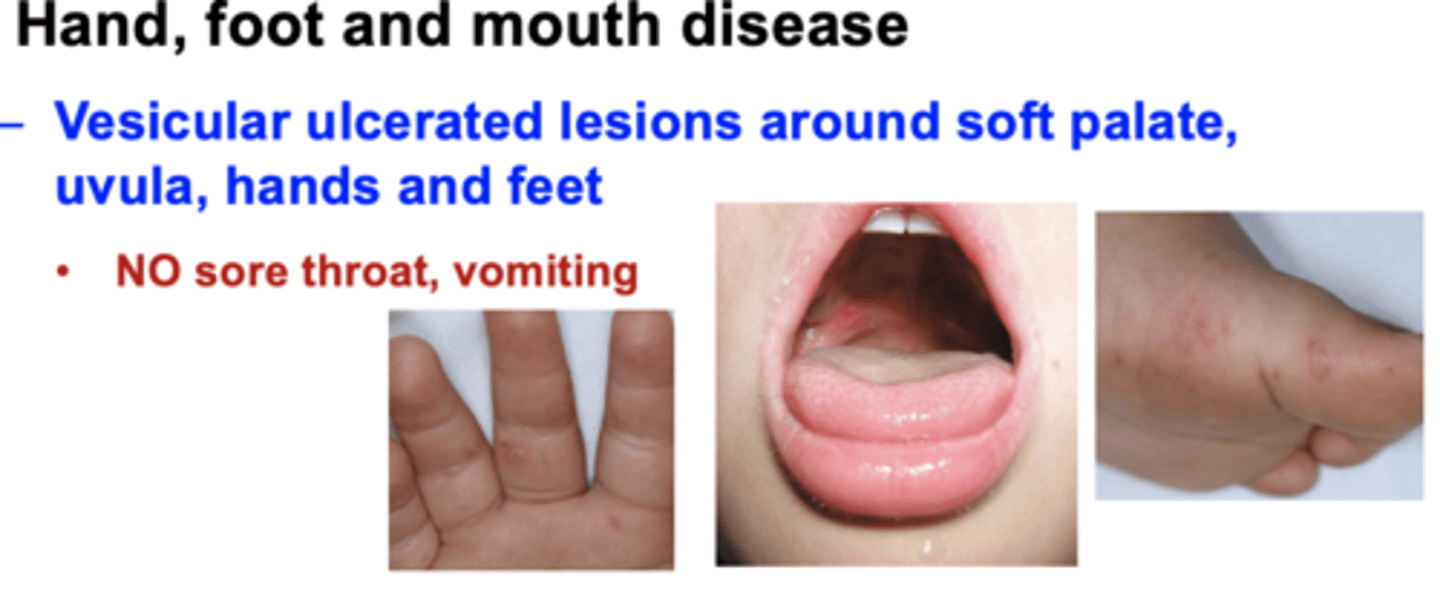
What is Hand, foot and mouth disease?
Vesicular ulcerated lesions around soft palate, uvula, hands and feet
•NO sore throat, vomiting
What are ypical oral cavity infections?
•Typically polymicrobial with obligate anaerobes
What is Dental plaque?
Dental plaque is soft adherent dental deposit
–Forms from bacterial colonization of tooth surfaces
Biofilm is adherent and hard to penetrate. Sugar capsule.
•10^10 – 10^11 bacteria/gram
•Protected from macrophages, antibodies, antibiotics
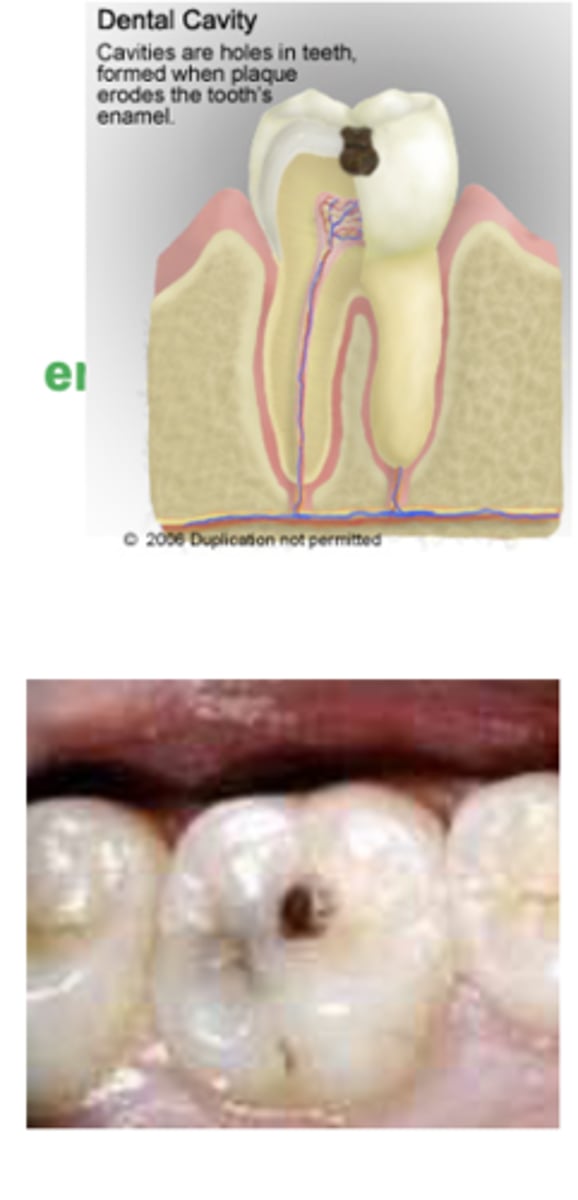
What are dental caries a result of?
Dental caries are result of bacterial metabolism
Sugar is fermented
•Glucose, fructose, sucrose, lactose, maltose
•Acid by-product causes pH decrease
―Demineralization of tooth surface from enamel-coated crown to pulp of tooth
What is the number 1 cause of Dental caries?
Streptococcus mutans is #1 cause
–Viridians group Strep (alpha hemolytic)
•Colonizes tooth surface
•Synthesizes polyglycans (dextrans)
•Promotes aggregation of bacteria
•Endocarditis!
What are Complications of Dental Caries?
Infection of pulp chamber of tooth
1. Necrosis of pulp
2. Extension of infection to adjacent areas
•Intracranial, retropharyngeal, pulmonary
3. Hematogenous dissemination
•Heart valves
•Prosthetic devices
•Osteomyelitis
•Glomeruli
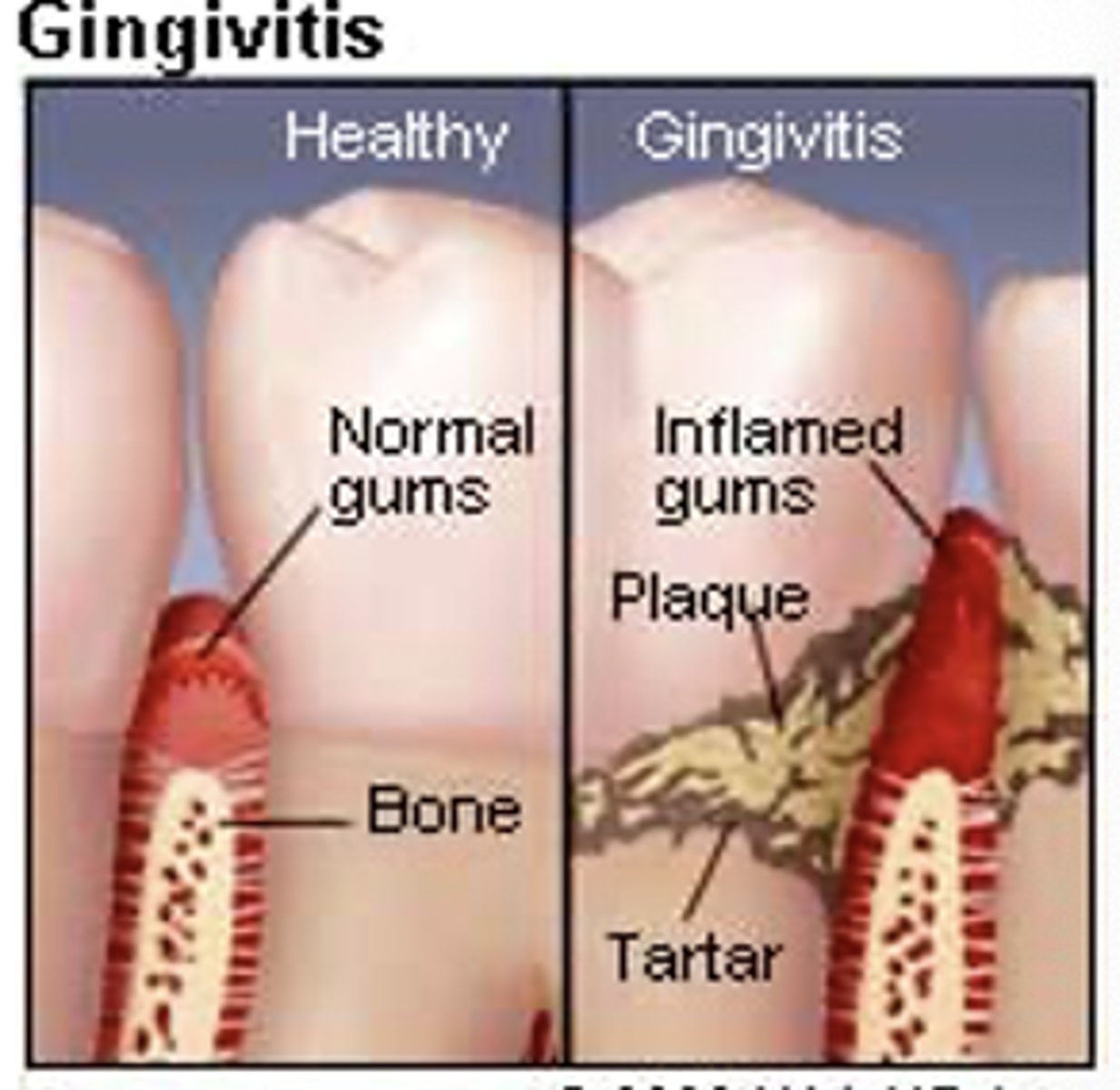
What is the early phase of Periodontal disease?
Early phase – gingivitis
–Acute and chronic inflammation
•Subgingival plaque present
•No pain, gums bleed, mild odor
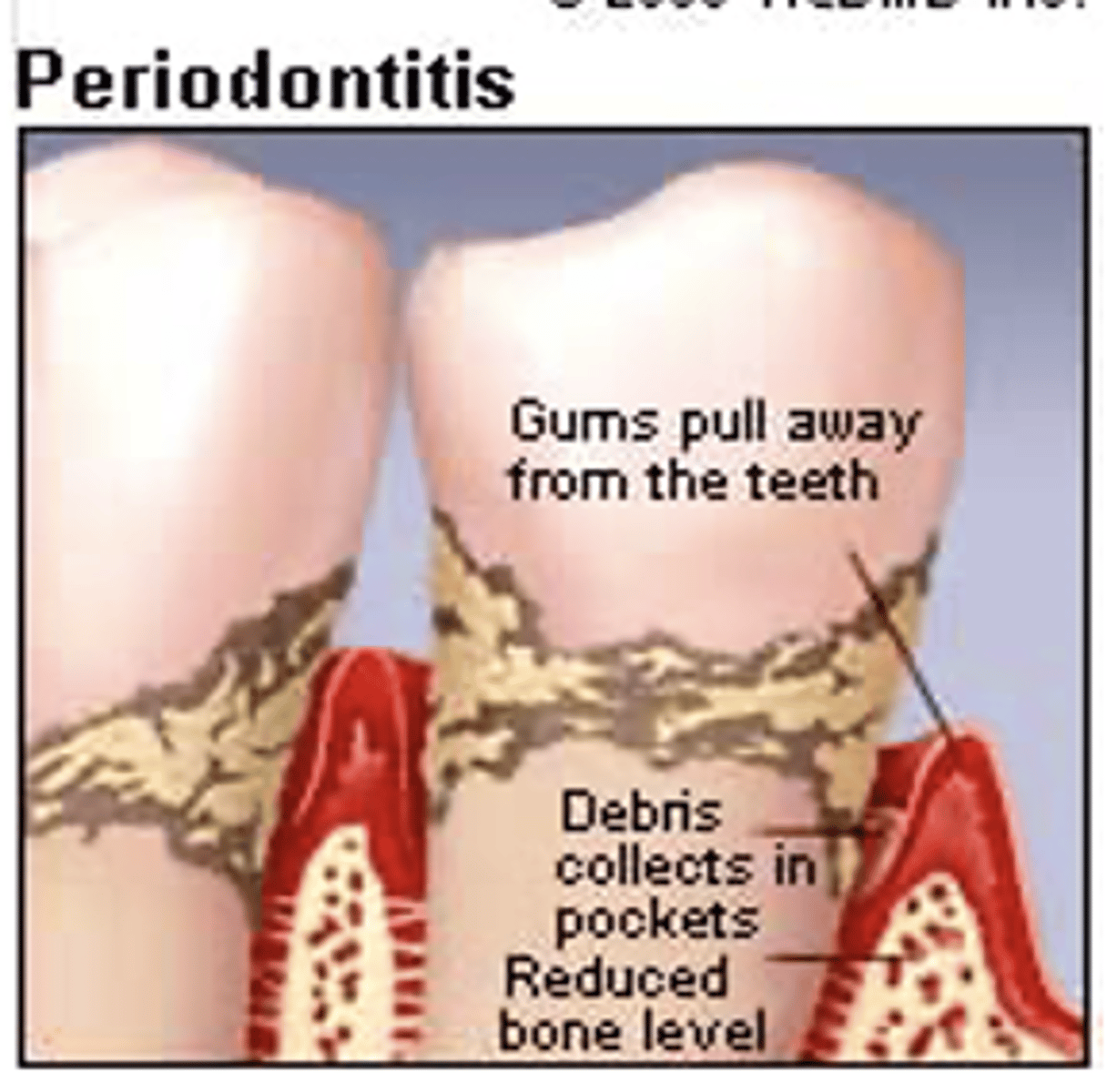
What is the later phase of Periodontal disease?
Later phase – periodontitis
Gingiva inflamed, discolored, bleeds
•Vague pain in jaws
--Reduced bone level
•Pressure – pus expressed
•Support tissues destroyed
--Teeth fall out
What is Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis: Vincent disease?
Vincent disease (trench mouth)
Fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy
•Rapid onset gingival pain
--Necrosis in interdental papilla
•Characteristic halitosis, altered taste
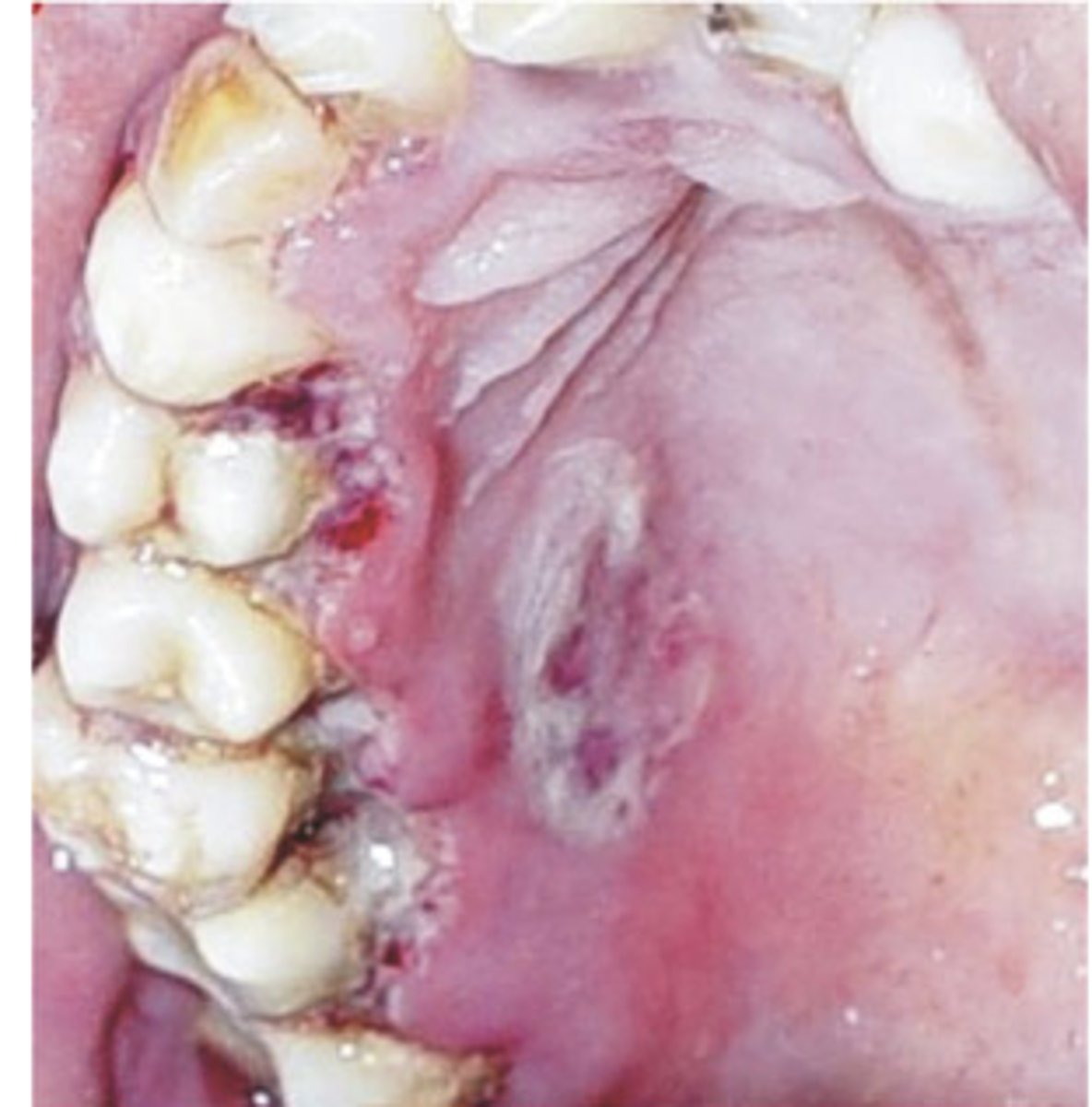
What is Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis: Bacterial etiology?
–Spirochetes
•Treponema denticola
•Borrelia gingivalis
–Prevotella intermedia
What is Periodontitis?
•Chronic inflammation
•Major cause of adult tooth loss
What are the signs of Periodontitis?
Begins in “early adulthood”
•Now finding signs earlier in children
Sign 1: Bleeding
•Bleeding gums during tooth brushing, flossing
Sign 2: Puffiness
•Swollen and bright red gums
Sign 3: Recession
•Gums recede from teeth
•Sometimes roots exposed
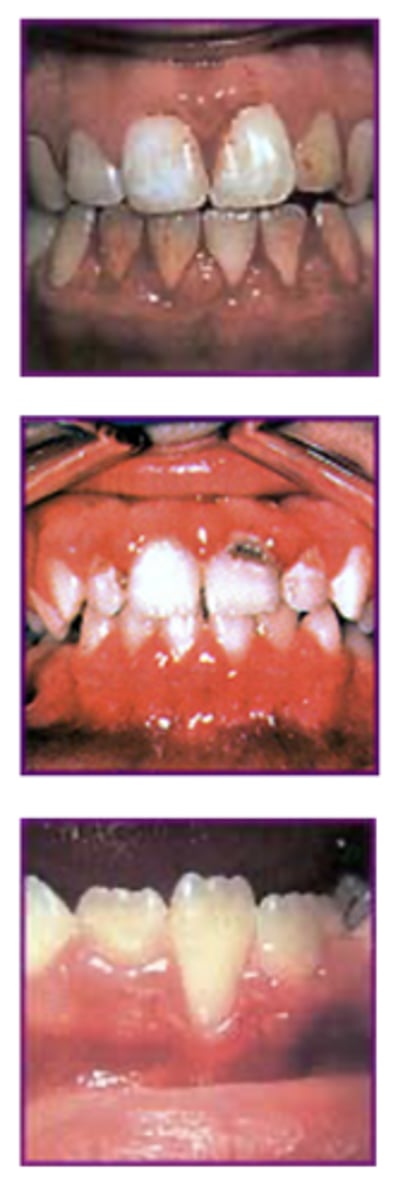
What is Localized Aggressive Periodontitis?
Originally called “juvenile”
–Adolescents
–Rapid vertical bone loss
–First molar, incisor region
•Plaque minimal
–Commonly seen in African-American population
•Autosomal dominant trait
•Neutrophil chemotactic defect
–Presence of high numbers of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
What are the HACEK Organisms?
Fastidious GNR, colonize oropharynx
–Subacute bacterial endocarditis in pts with preexisting heart disease
–Haemophilus parainfluenzae
–Aggregatibacter aphrophilus
•Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
–Cardiobacterium hominus
–Eikenella corrodens
–Kingella kingae
What are lab characteristics of Eikenella corrodens?
--Oxidase-positive
--Bleach-like odor in culture
--See pitting on agar
--IVDU, dental procedures
What are Anaerobic Gram-negative rods?
Fusobacterium spp.
–F. nucleatum, F. necrophorum
Porphyromonas spp.
–P. gingivalis, P. asaccharolytica
Prevotella spp.
–P. intermedia, P. melaninogenica
What are Almost all periodontal infections?
–Mix of Fusobacterium, Prevotella, Porphyromonas (FPP)
Mix of all three
What is Actinomycosis?
Actinomyces israelii
–Filamentous, Gram-positive rods
–Causes cervicofacial actinomycosis
•Lumpy jaw
•Open draining sinus tracts along angle of jaw and neck
•Abscesses may form
•Poor oral hygiene, invasive dental work
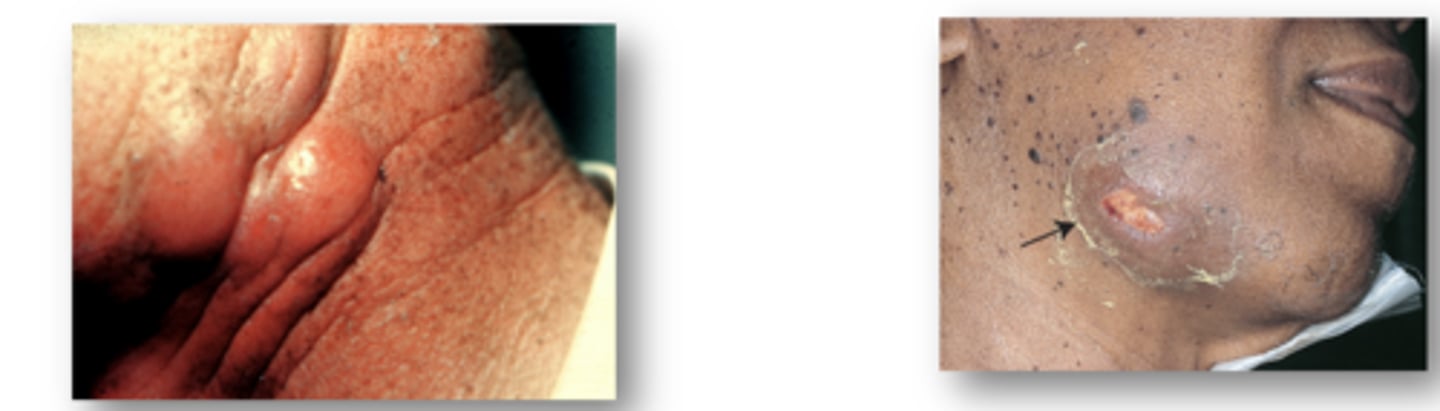
What is Actinomycosis dx?
•Bacteria in sulfur granules
•Culture (≥2 wks) resembles top of a molar
•Need high concertation of CO2 to grow
What is Actinomycosis tx?
•Penicillin or amoxicillin
•Doxy, macrolide alternative

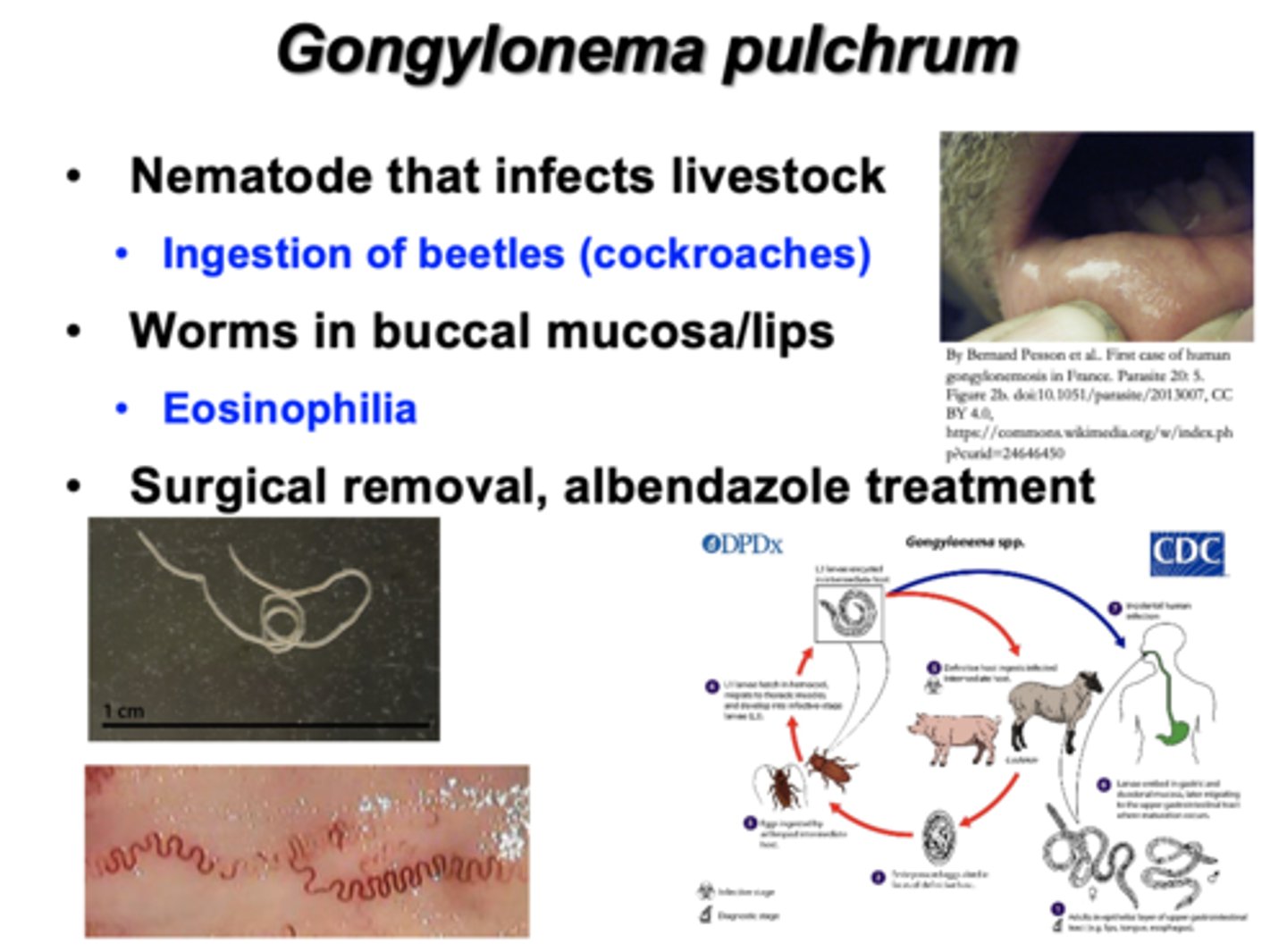
What is Gongylonema pulchrum?
•Nematode that infects livestock
--Ingestion of beetles (cockroaches)
•Worms in buccal mucosa/lips
--Eosinophilia
•Surgical removal, albendazole treatment