MICRO EXAM #2
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
excludable
others can be prevented from use
rivalrous
my use prevents your use
private goods
rivalrous and exclusive
cars, food, most economic goods
common resources
rivalrous and nonexclusive
fish in the ocean, the environment
club goods
nonrivalrous and exclusive
netflix, museum, theme park, sporting events
public goods
nonrivalrous and nonexclusive
fireworks, public radio, vaccines, lighthouses
positive externalities
public goods and club goods
negative externality
common resources → associated with overconsumption
free rider problem
beneficiaries of public goods often don’t need to pay for them, so they won’t do so voluntarily, and the good will be underprovided
explicit costs
on the books → equipment, raw materials, license
implicit costs
opportunity costs → what else one could be doing with money/ time
marginal product of labor
increase in output from hiring 1 additional input of labor
marginal product of labor equation
Δoutput/ Δinputs
diminishing marginal product
marginal product falls as input increases
total cost equation
fixed costs + variable costs
average fixed cost equation
fixed costs/ quantity
average variable costs equation
variable costs/ quantity
average total cost equation
total costs/ quantity or AFC + AVC
marginal cost equation
Δ total cost/ Δ quantity
What does the space between AVC and ATC on SR graph represent?
The average fixed cost
Where does the marginal cost intersect ATC and AVC?
at there minimums
Where are average costs minimized?
where they meet marginal costs
Does diminishing marginal product occur in the long run?
No, because there are no fixed inputs
economies of scale
decreasing long-run ATC, 1 or few firms
constant return
flat long-run ATC, large and small firms
diseconomies of scale
increase in ATC, many small firms
What causes a decrease in LRATC?
specialization
What causes an increase in LRATC?
organizational costs, consequences of not being organized increase
marginal cost
cost of producing an extra unit of output
When is average cost rising and falling?
rising→ marginal costs above AC
falling → marginal costs below AC
Profit equation
total revenue - total costs or (P-ATC)*Q
assumptions of perfect competition
many buyers or sellers → price takers
homogenous product
firms can freely enter and exit the market
Where is profit maximized in perfect competition?
Where marginal revenue meets marginal costs
Average revenue for perfect competition
(total revenue/ quantity) or price
variable costs equation
AVC * Q
fixed costs equation
AFC * Q
marginal revenue for perfect competition
Δtotal revenue/ Δquantity
What does marginal revenue equal in PC only?
price
PC MR>MC
next unit the firm sells will be profitable, so they should produce more
PC MR<MC
last unit a firm produced was a loss, so the firm should produce less
"Stopping point” for profit maximization in PC
marginal cost = marginal revenue
profit in PC SR
P>ATC at Q* where MR = MC
losses in PC SR
P<ATC at Q* where MR = MC
demand curve in PC
perfectly elastic, MR=P=d
P < ATC in LR for PC
firm taking economic losses → exit market
P = ATC in LR for PC
zero economic profits (long run equilibrium) → stay in market
P > ATC in LR for PC
making economic profits → enter
TR > VC in SR for PC
firm will be more profitable by remaining open than shutting down (P > AVC)
TR < VC in SR for PC
firm should shut down because they are taking losses
Where does supply come from?
supply curve is the marginal cost curve above the point where it meets AVC
LR equilibrium for PC gains
P > ATC → profits → entry → increased supply → decrease in price till P = ATC
LR equilibrium for PC losses
P < ATC → losses → exit → decrease supply → increase in price till P =ATC
long run equilibrium characteristics
firms produce at efficient scale (minimum ATC)
firms earn zero economic profit (stay)
LR supply curve in PC
generally flat (relatively more elastic) or flatter than SR supply; it follows efficient scales of the firms
monopoly
controls the entire market, price makers
resource monopoly
control source of a natural resource
std oil, DeBeers, utilities
government-created monopoly
intellectual property
trademark, patent
natural monopoly
naturally occurring, outcompete smaller companies
economies of scale ← LR ATC declining
Where is total revenue maximized for monopoly?
where marginal revenue = 0
Elastic region on monopoly graph
area above isoelastic point (MR > 0)
isoelastic point on monopoly graph
where MR is maximized, where MR hits x-axis
inelastic region on monopoly graph
area below isoelastic point (MR < 0)
Profit maximization for monopoly
maximized where MR = MC
P > ATC
area between ATC and P is profit
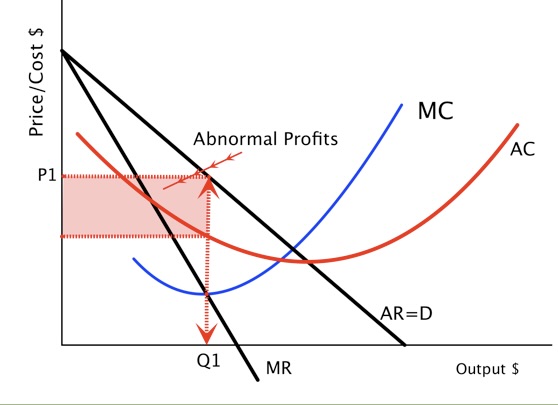
What do monopolies price off of?
the demand curve
Losses in monopoly SR
P < ATC
if losses persist, the monopoly will exit the market
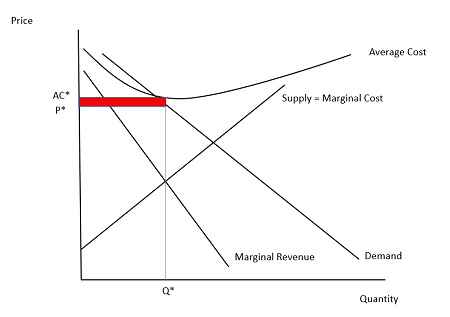
unique characteristics of monopolies
can make profit in the long run
lower consumer surplus and has deadweight loss
less production and higher prices (maximize profits)
Does a monopolist have a supply curve?
Supply is a unique relationship between price and quantity supplied. The optimal quantity supplied and the price for monopolists depends on the demand curve, and it is possible there is the same Q* for 2+ prices or the same P* for 2+ quantities. Meaning monopolists DO NOT have supply curve.
price discrimination
a firm charges different prices to different people or different prices for different quantities
consequences of price discrimination
consumer surplus turns to profit
deadweight loss turns to profit or CS (rare)
requirements for price discrimination
pricing power (non-competitive)
knowledge of WTP varying
segment the market (prevent resale)
examples of price discrimination
student/ senior discounts
airline prices
quantity discounts
coupons
public policy towards monopolies
make monopolies more competitive (break them up)
regulations (marginal cost pricing)
public ownership
no nothing
Monopolistic competition in SR
they are monopolies
Monopolistic competition from SR to LR if making profits
entry to market → decrease demand (new close substitutes increase)
stops when P = ATC
Monopolistic competition from SR to LR if making losses
a firm or competitor leaves market → increase in demand (due to exit of close substitutes)
stops when P = ATC
Monopolistic competition vs Monopoly long run
monopolistic competition unique in that:
barrier to exit and entry are low
close substitutes are available
characteristics of monopolistic competition in the LR
M.Cs produce at less than efficient scale (excess capacity)
mark up over marginal cost: P > MC
has deadweight loss
P = ATC
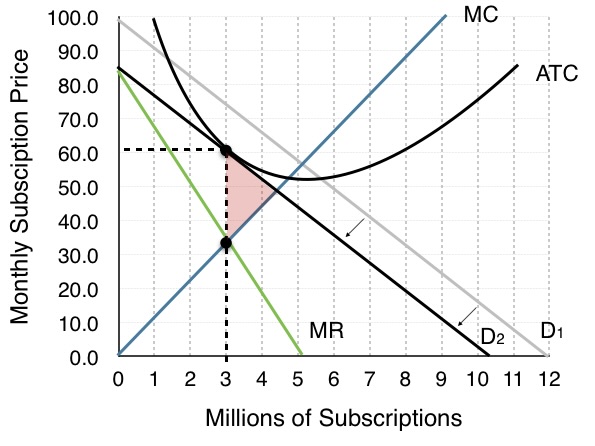
advertising function
help a monopolistic competitor “steal” customers from competitors
reduce transaction costs (information)
inform consumers
brand signalling
Oligopoly
few sellers of identical productions or close substitutes
soda, cigarettes, tech giants
game theory
the study of decision making in strategic situations (outcomes depend on own decisions and decisions of others)
Nash equilibrium
both players best respond to what the other might do ← mutually best response
dominant strategy
the best response is the same irrespective of what other player does