3.3.2 Costs (in the short run)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Definition & Formulae of total cost
Total cost = cost of producing a given level of output
TC = FC + VC
Note that fixed costs only happen in the short run as it can only happen when at least one factor or production is fixed
Variable costs can happen in both short run & long run
What are the 2 types of total costs (every type of cost, there’s a fixed & a variable)
Total fixed costs (TFC)
cost that remains the same as output increases or decreases (ie. rent)
TFC = TC - TVC
Total variable costs (TVC)
cost that changes with the level of output (ie. cost of ingredients)
TVC = TC - TFC
Note: wages (per output produced) so variable
salary (same every month, has a contract) so fixed

Definition & Formulae of average cost
Average (total) cost = cost per unit of output
TC / Q
OR ATC = AFC + AVC
Definition & Formulae of average fixed cost
Average fixed cost = fixed cost per unit of output
AFC = TFC / Q
Definition & Formulae of average variable cost
Average variable cost = variable cost per unit of output
AVC = TVC / Q
Definition & Formulae of marginal cost
Marginal cost = cost of producing one more unit of output
So not affected by a change in FC
affected by a change in level of output so affected by changes in variable cost
MC = change in TC / change in Q
Derivation of short-run cost curves from the assumption of diminishing marginal productivity
The reason that the cost curves are going down and up again like a parabola is because of diminishing marginal productivity :
Fixed factors of production: land of the bakery shop
Variable factors of production: number of workers
Diminishing marginal productivity = for an additional unit of labour, the additional increase in productivity declines
→ MC increase
Example of the law:
ie when making cake: at first, when workers are added, they may become specialized - efficient → an additional unit of labour →increasing marginal productivity → more additional output→ MC falls (less cost to produce one more unit of output)
After some point: diminishing marginal productivity sets in → an additional unit of labour → MP falls → less additional output (as more crowded) → cost more to produce an extra output → MC increases at a faster rate
This only happens in the short run because in the long run, they can expand the space in the shop
The relationship between short-run & long-run average cost curves
In the short run, at least one factor of production is fixed
output only increases when additional units of variable factors (ie. labour) are added to the fixed factor (ie. land) until diminishing marginal productivity sets in where output starts to fall
In the long run, all factors of production are variable, not fixed so won’t experience diminishing marginal productivity. Therefore, the cost curve will be slightly different
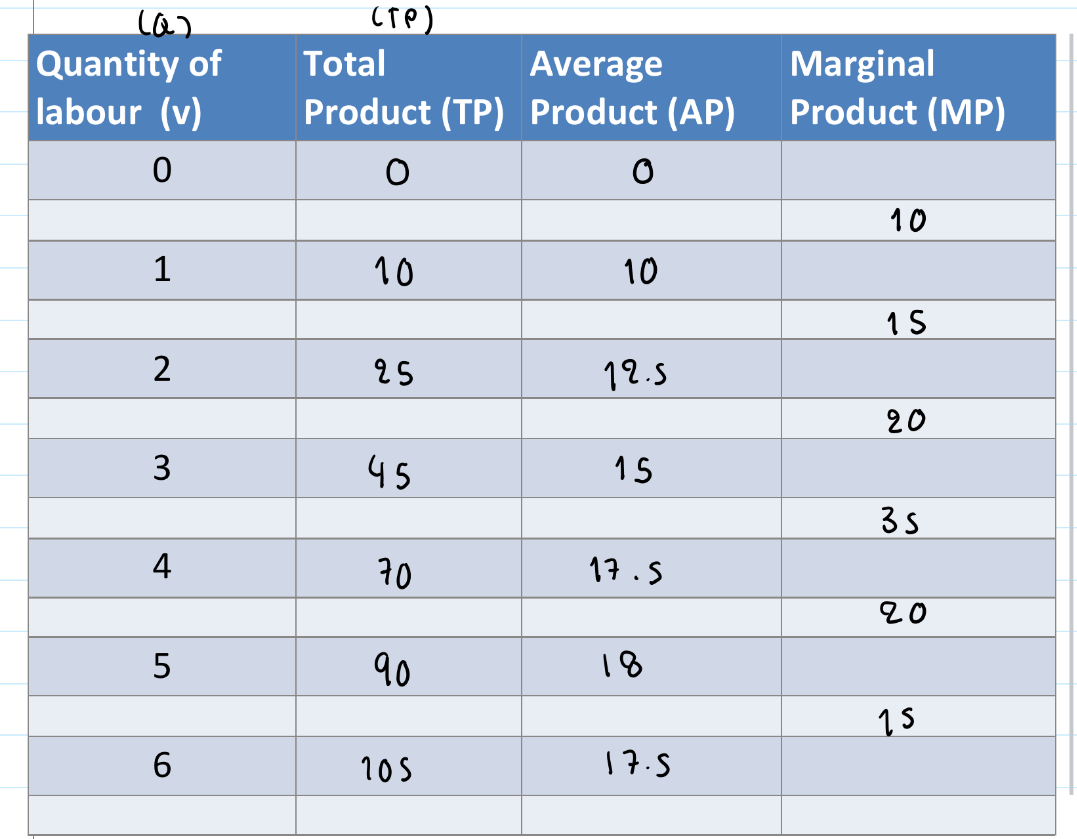
Example of production in the short run shown in a table
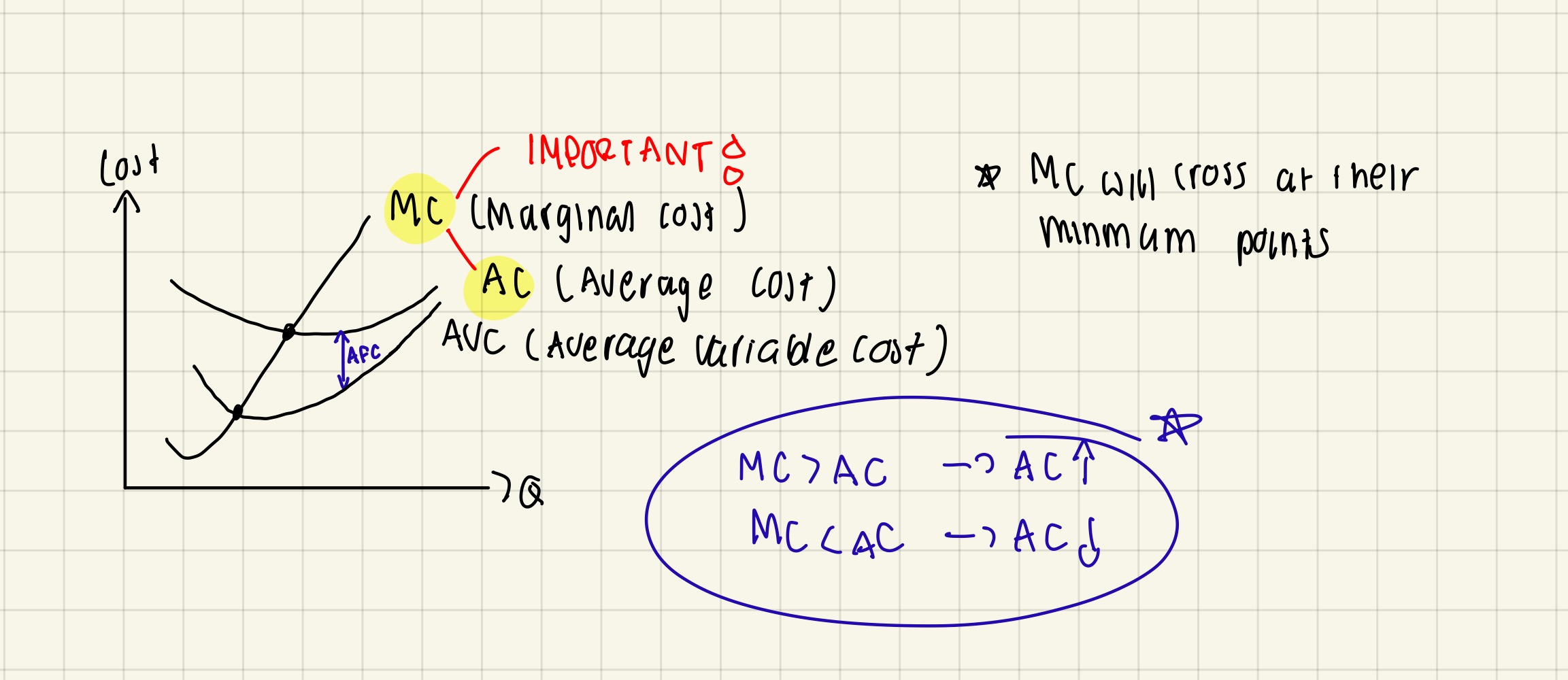
Relationship between average cost & marginal cost & TC
IMPORTANT: MC always cut AC at its lowest point which can be explained by the following:
If marginal cost above average cost → average cost rise → TC increases at a faster rate
If marginal cost below average cost → pulls down average cost → average cost fall
If marginal cost = average cost → average cost stays the same
asks a lot in exam
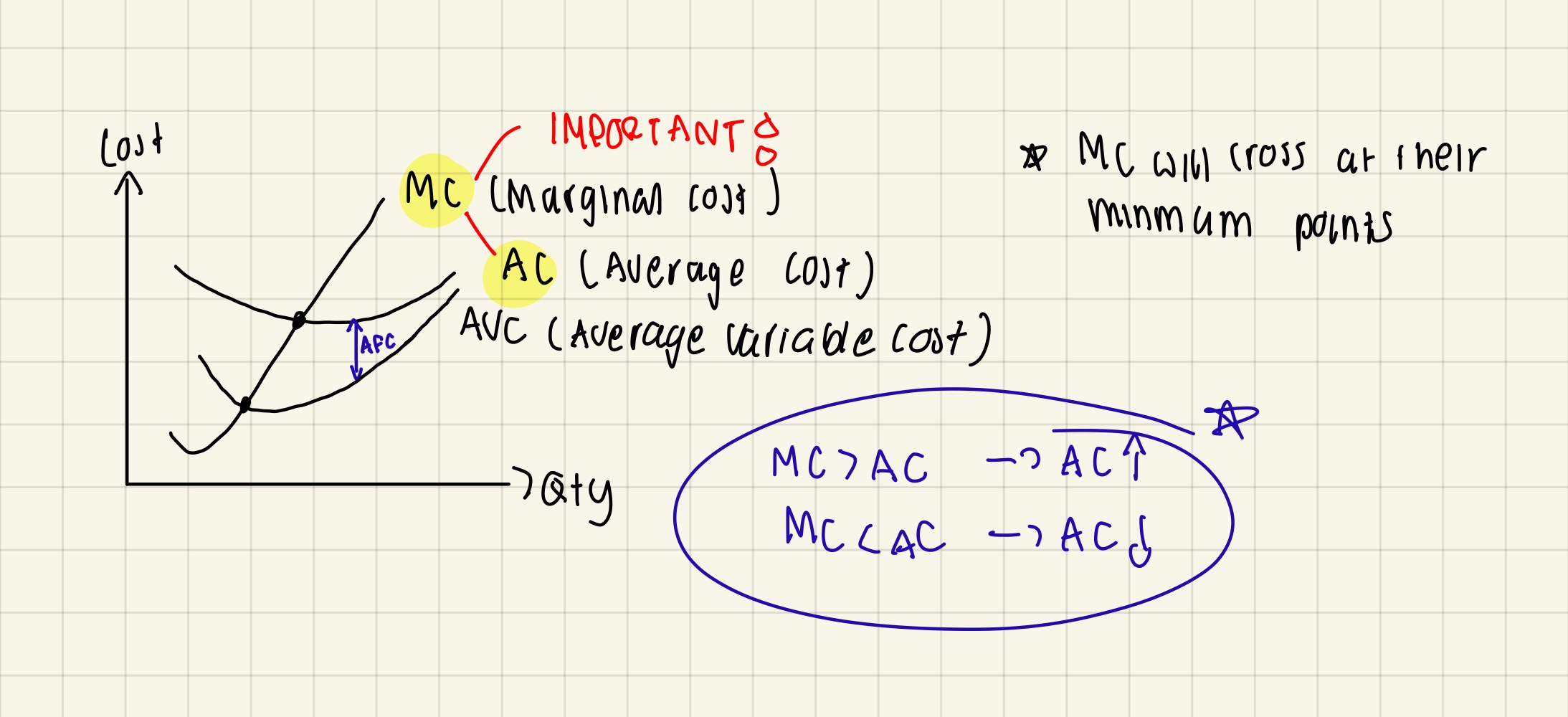
Golden rule when drawing short run average cost curves

Diminishing marginal returns question (3) + mcq
1) Law (use this as definition): As variable factors are added to a fixed factor, MC eventually rise
2) Only happens in the short run only where there is atleast one fixed factor (as in the long run, these these fixed factors can become variable)
2) Definition of MC