domestic uses amd energy transfers
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Power transfers
Power transfer is the rate at which energy is transferred and is directly proportional to the product of the potential difference across a device and the current through it
Explain the relationship between power and voltage or current
This means if either voltage or current increases, the power (and thus the rate of energy transfer) increases.
Power explanation
As electrons flow through wires, they collide with the ions in the wire which causes the ions to vibrate more. This increased vibration of the ions increases the temperature of the wire. Energy has been transferred from the chemical energy store of the battery into the internal energy store of the wire
Energy transfers depend on
how long the appliance is switched on for and the power of the appliance
domestic electricity supply (Uk)
Frequency of 50Hz and about 230V
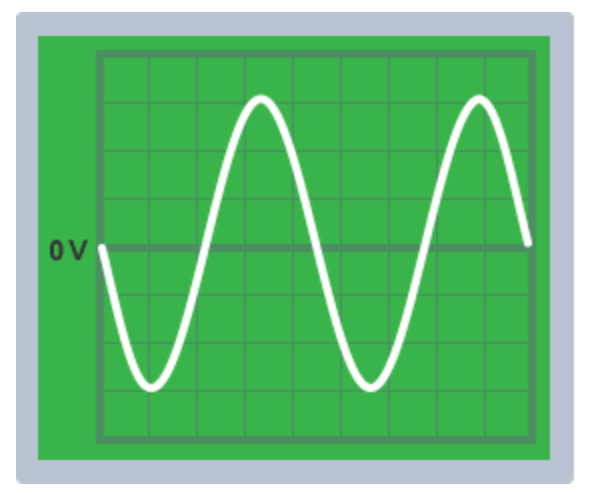
Alternating current
Constantly changing direction, positive and negative voltages indicating direction of flow. Used in uk mains
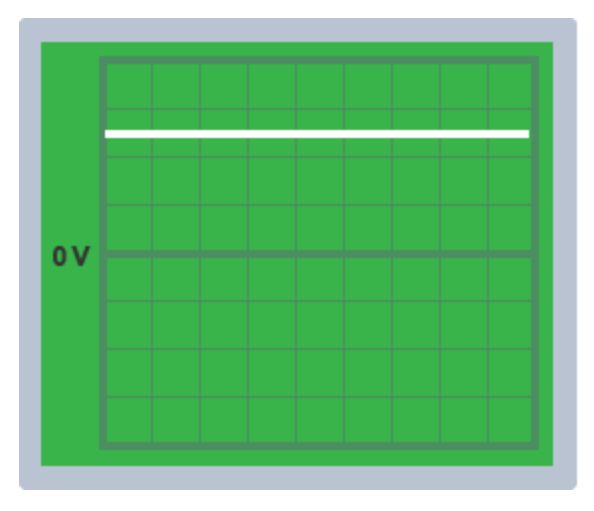
Direct current
Only flows in one direction
Examples of direct current uses
Car batteries
Dry cells
Solar cells
Reasons for being AC used in uk mains
Less of a fire risk- sudden discharge of electricity is less severe
Easy voltage conversions- easier to increase or decrease using transformers, so safer and more efficient
Cost effective- easier and cheaper to generate at high power levels as concert kinetic energy into electrical energy
Live wire
(Brown) brings alternating current from the supply
Neutral wire
(Blue) completes the circuit
Earth wire
(Green and yellow stripes) as safety to stop appliance “going live”, should not carry charge unless faulty
Dangers of live wires
They carry charge and so can electrocute you if you touch it. Even if the circuit is open, it can still carry charge.
Live wire and earth wire touching?
Can create a dangerously short circuit, potentially causing fires or electrocution
When is work done
When charge flows through a circuit
Relationship between power rating and stored energy
higher power rating signifies a faster change in stored energy