Chemistry Exam- Ionic and Covalent Compounds, VSEPR
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
melts at a low temperature
covalent bond
shatters and splinters rather than turns into a powder when hit with a hammer
ionic
conducts electricity when dissolved in water but not as a solid
ionic
some are gases or liquids at room temperature
covalent
lattice structure
ionic
solution is not conductive
covalent
Na^+ has
lost a valence electron
True or False: In an Ionic Compound, a positively charges atom or group of atoms attracts a negatively charged atom or group of atoms
True
1 multiple choice option
True or False: an Ionic Compound, breaks apart when dissolved in water
True
1 multiple choice option
True or False: an Ionic Compound consists of 2 or more bonded atoms of similar electronegativity
False
True or False: In an Ionic Compound, there are several ions that group together in a tightly packed structure
True
If a compound has uniform crystals and has a conductivity of 4213 microS/cm, is it ionic or covalent?
ionic
As atoms bond with each other, they
decrease their potential energy, thus creating more stable arrangements of matter.
3 multiple choice options
A compound doesn't dissolve in water. Is it ionic or covalent?
one cannot tell
3 multiple choice options
A triple bond is ____ compared to a double bond
shorter and stronger
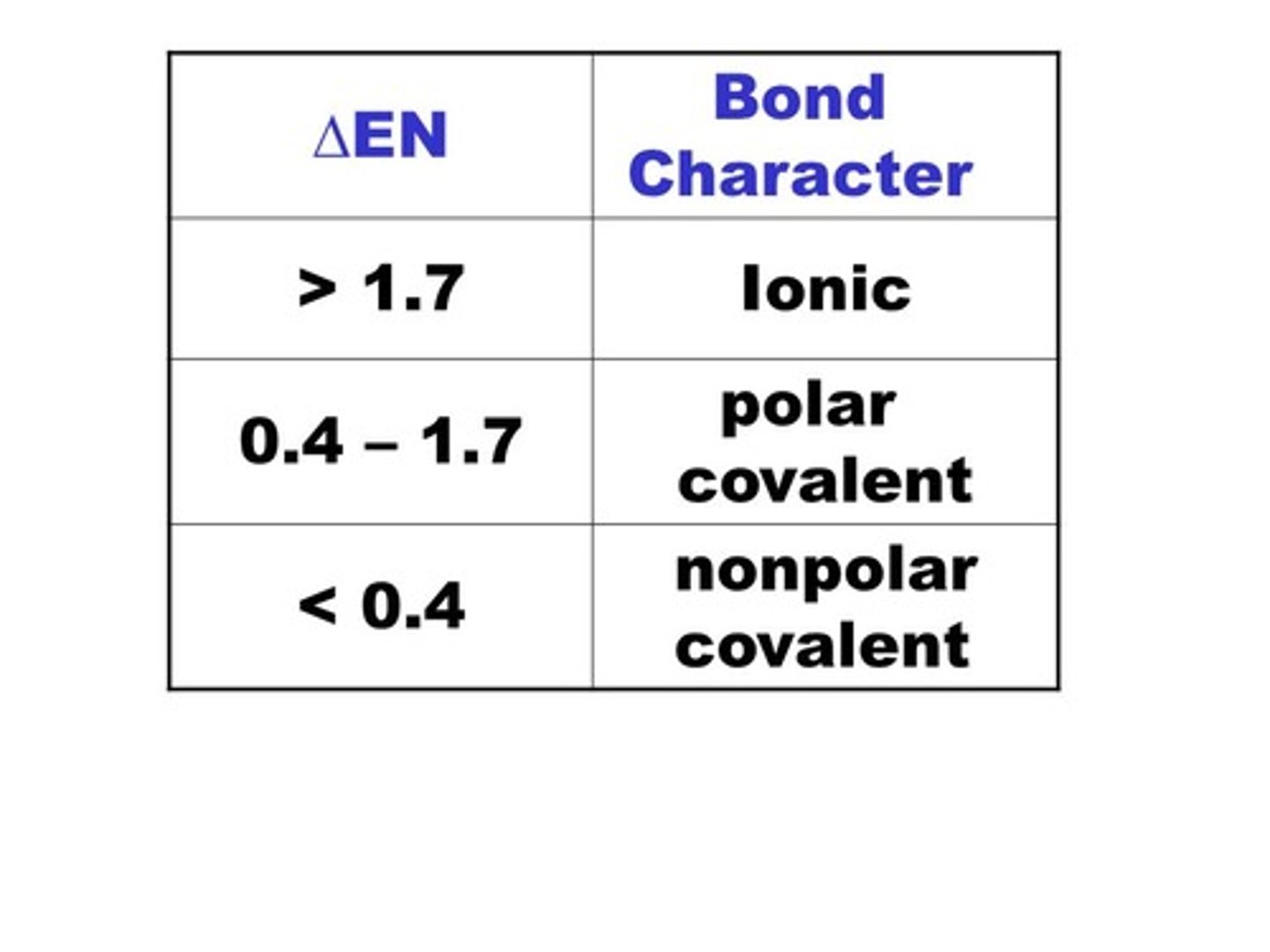
The greater the electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms, the greater the percentage of ____ in the bond.
ionic character
What is the difference in conductivity between ionic and covalent compounds in water and why?
-when ionic compounds dissolve in water, the compounds break apart and the negatively and positively charged ions move around, creating electricity
-electricity: moving of negative charges
-Covalently charges compounds are neutrally charged so when they are dissolved in water, there is no movement of negative charges => not conductivve when dissolved in water
What are potential complications of using tab water on the lab?
-could skew results and give false data
-tap water is treated with certain elements like chlorine (cleans water)
-elements could lower conductivity by having neutral charges and taking up space where negatively charged ions could move (limiting movement)
Which test on lab was the least helpful and why?
determining the solubility of a compound- neither ionic nor covalent compounds can be determined by solubility which varies compound to compound
ionic compound
-a compound composed of positive and negative ions
-metal and nonmetal
covalent compound
-atoms joined by covalent bonds- share electrons
-2 nonmetals
ionic bonds
-give/take of valence electrons
-between ions
covalent bonds
-sharing of valence electrons
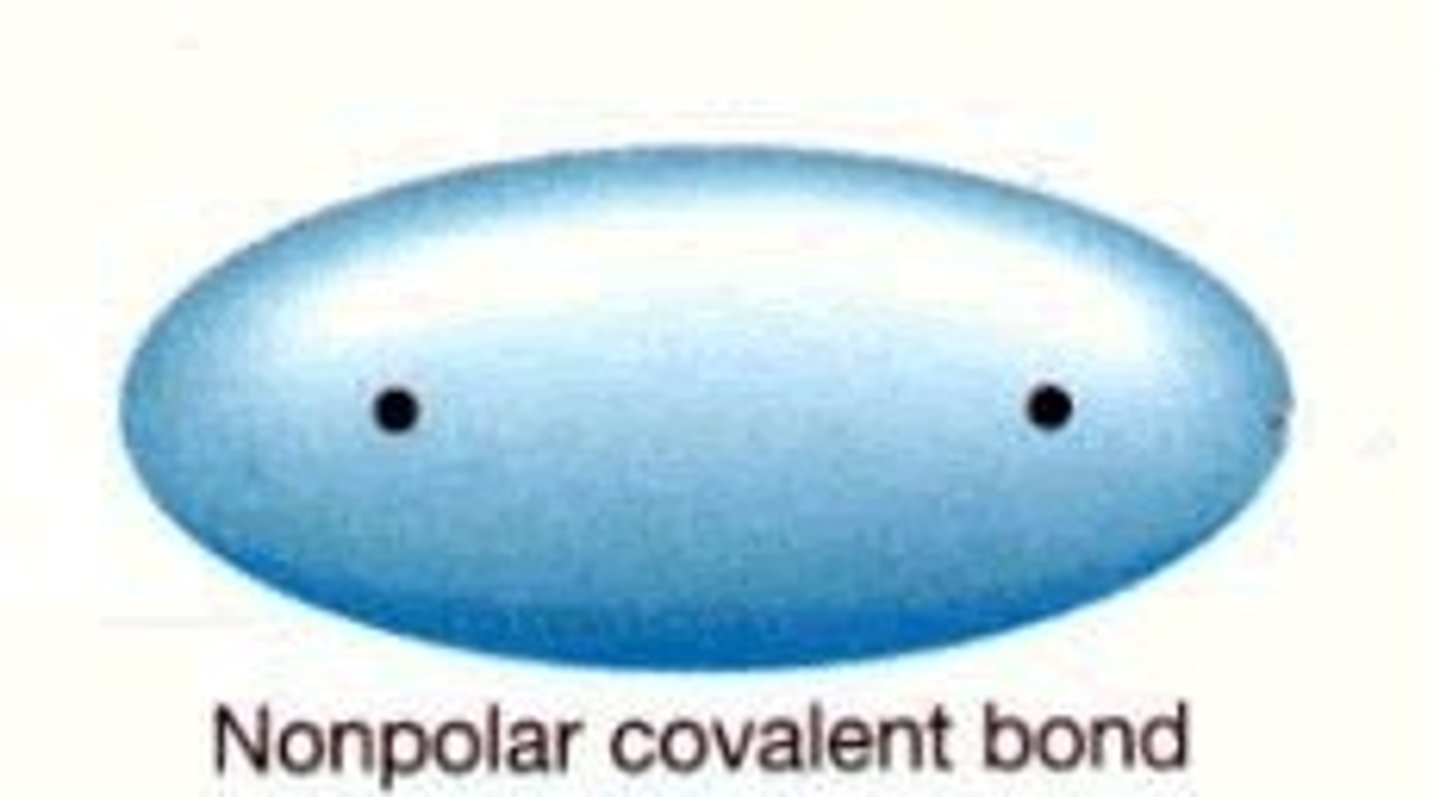
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
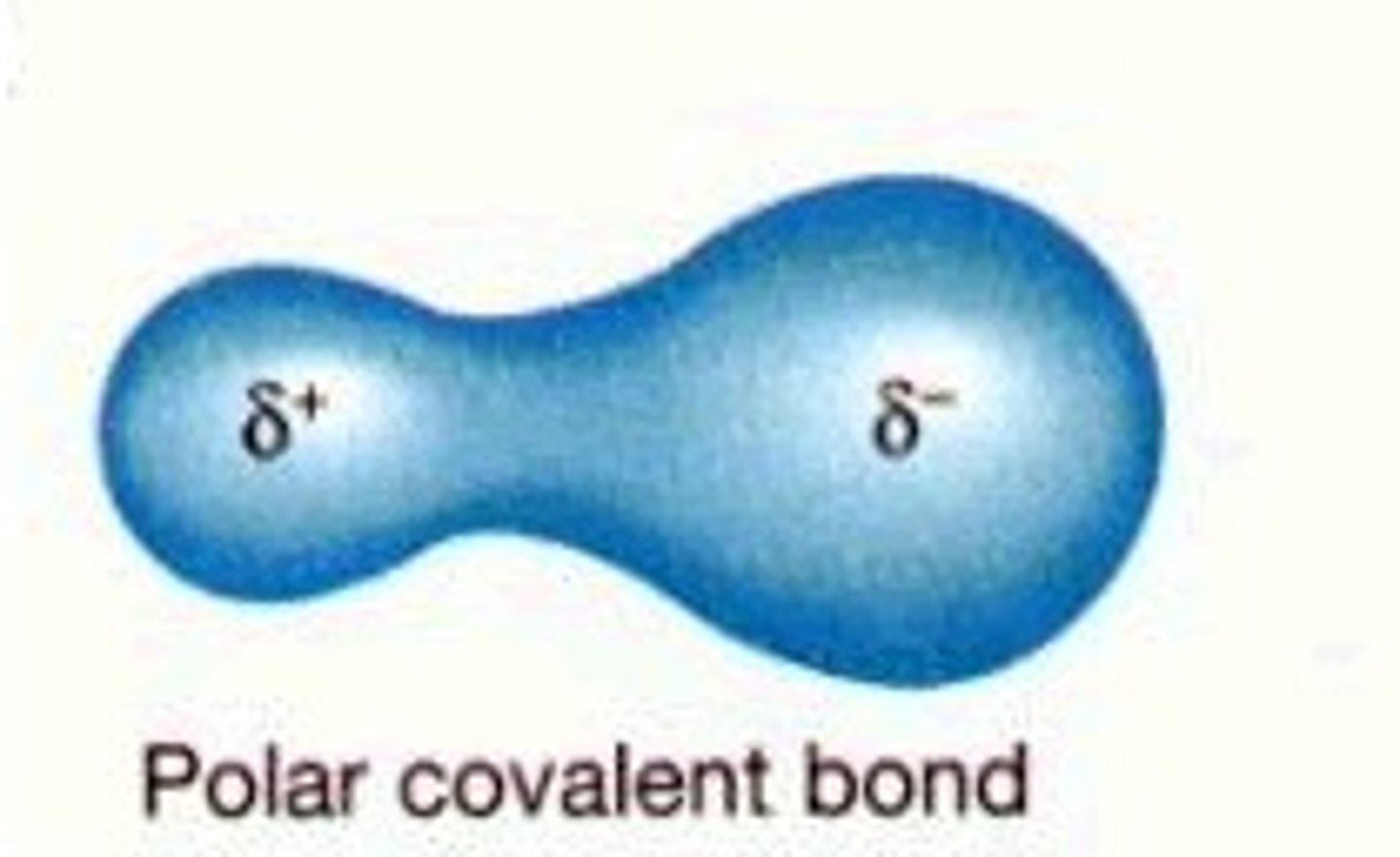
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
lattice energy
the energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions
difference in attraction strength give ionic and molecular compounds
different properties
bond energy
the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms
bond length
the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
excellent conductor as a solid
metallic
has a sea of electrons
metallic
shiny
metallic
malleable
metallic
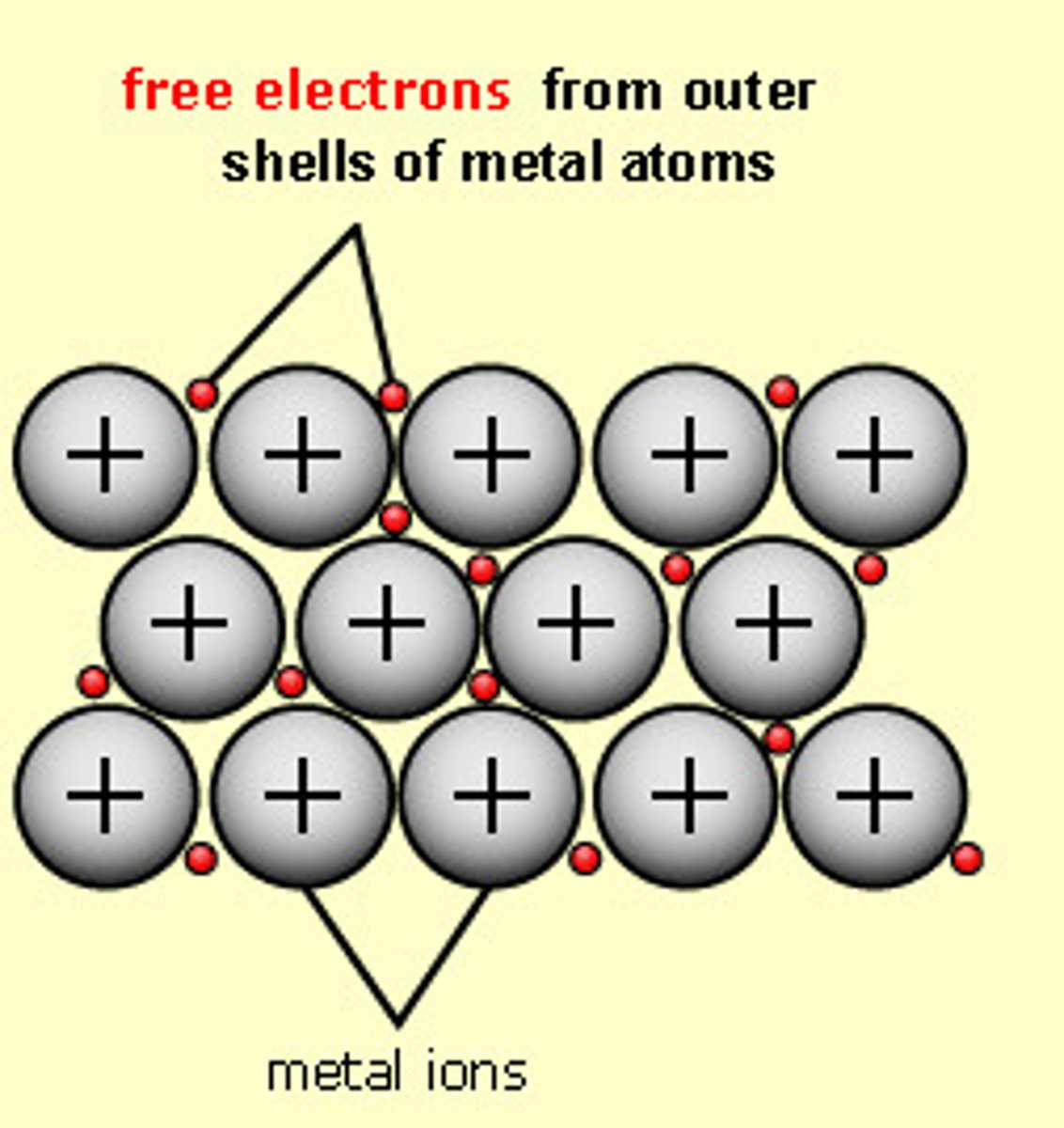
metallic bond
an attraction between a positive metal ion and the electrons surrounding it
VSEPR is short for
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
why do atoms bond?
-if Potential Energy is lowered by doing so
- to have 8 valence electrons- stable
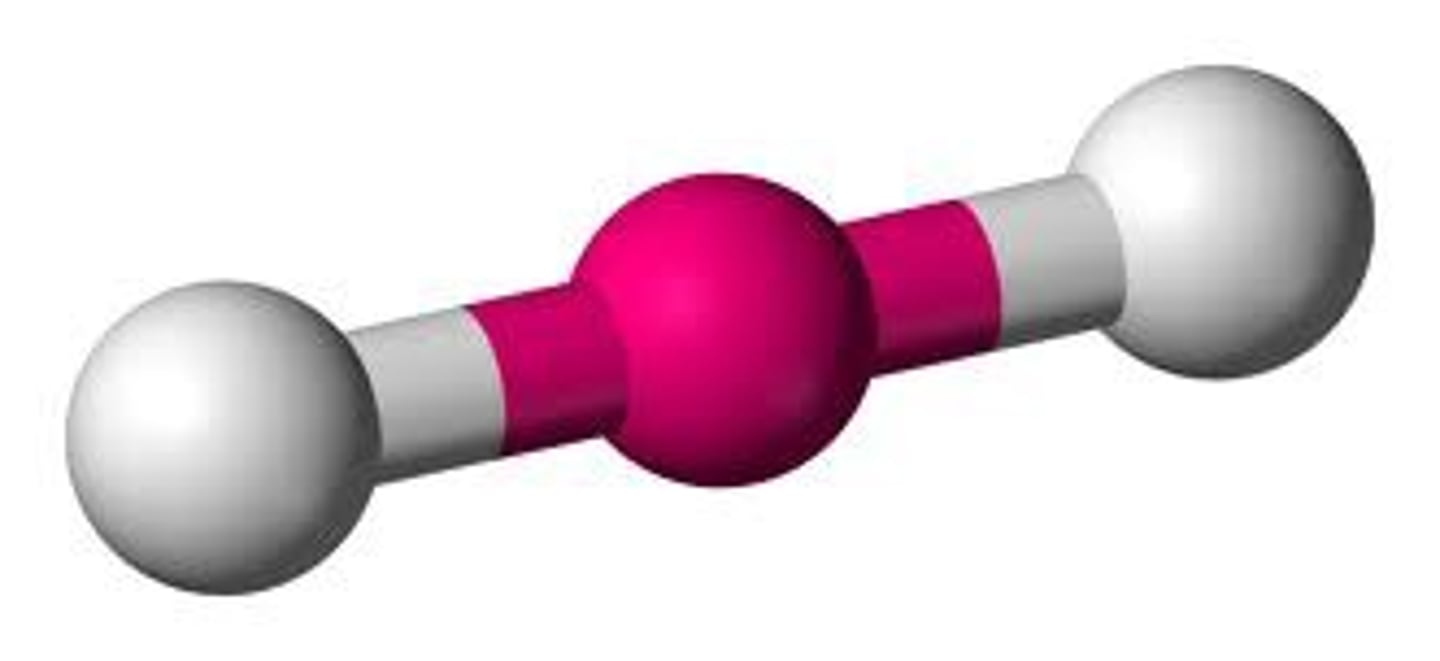
linear bond
trigonal planar bond
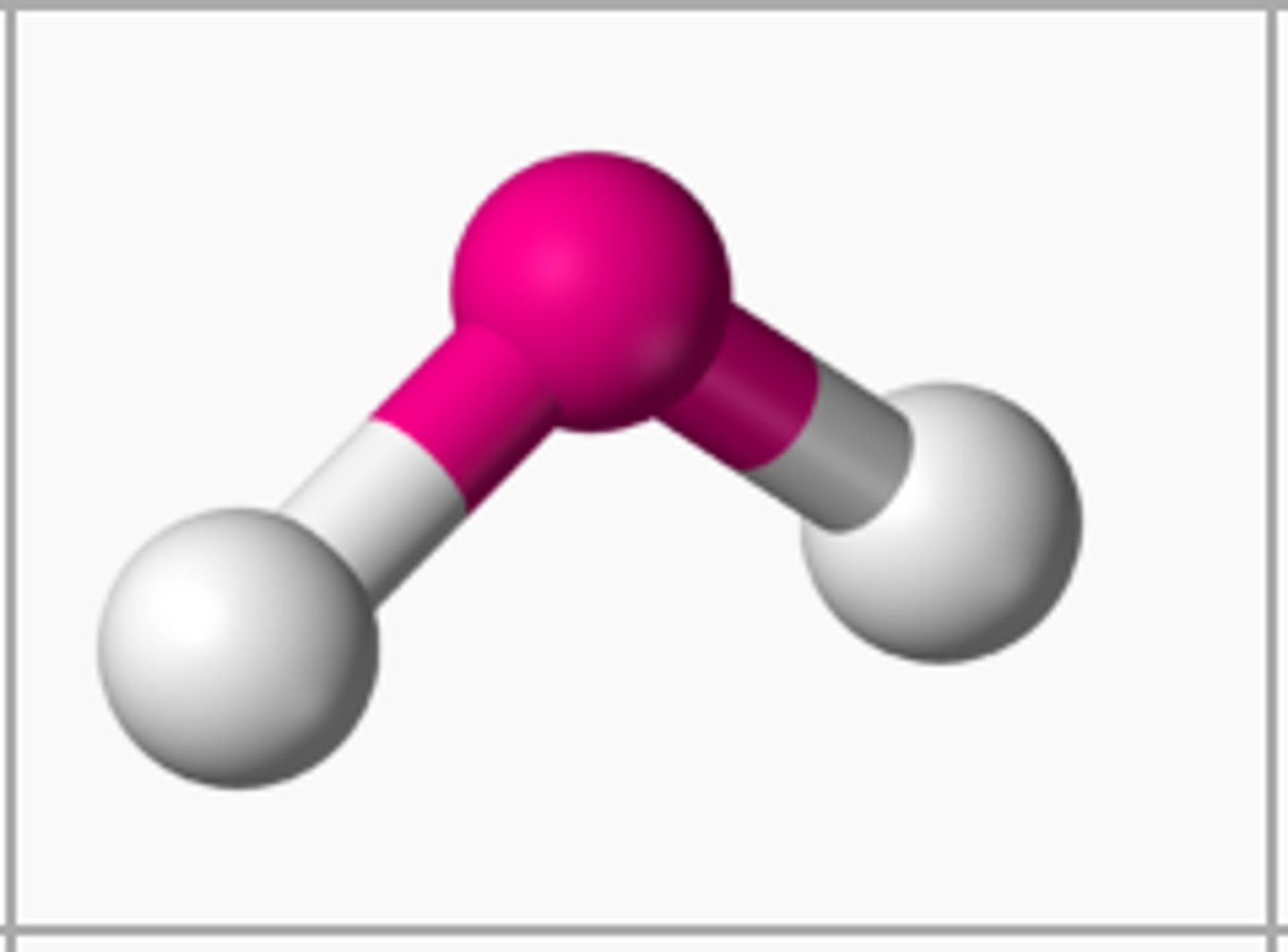
bent bond
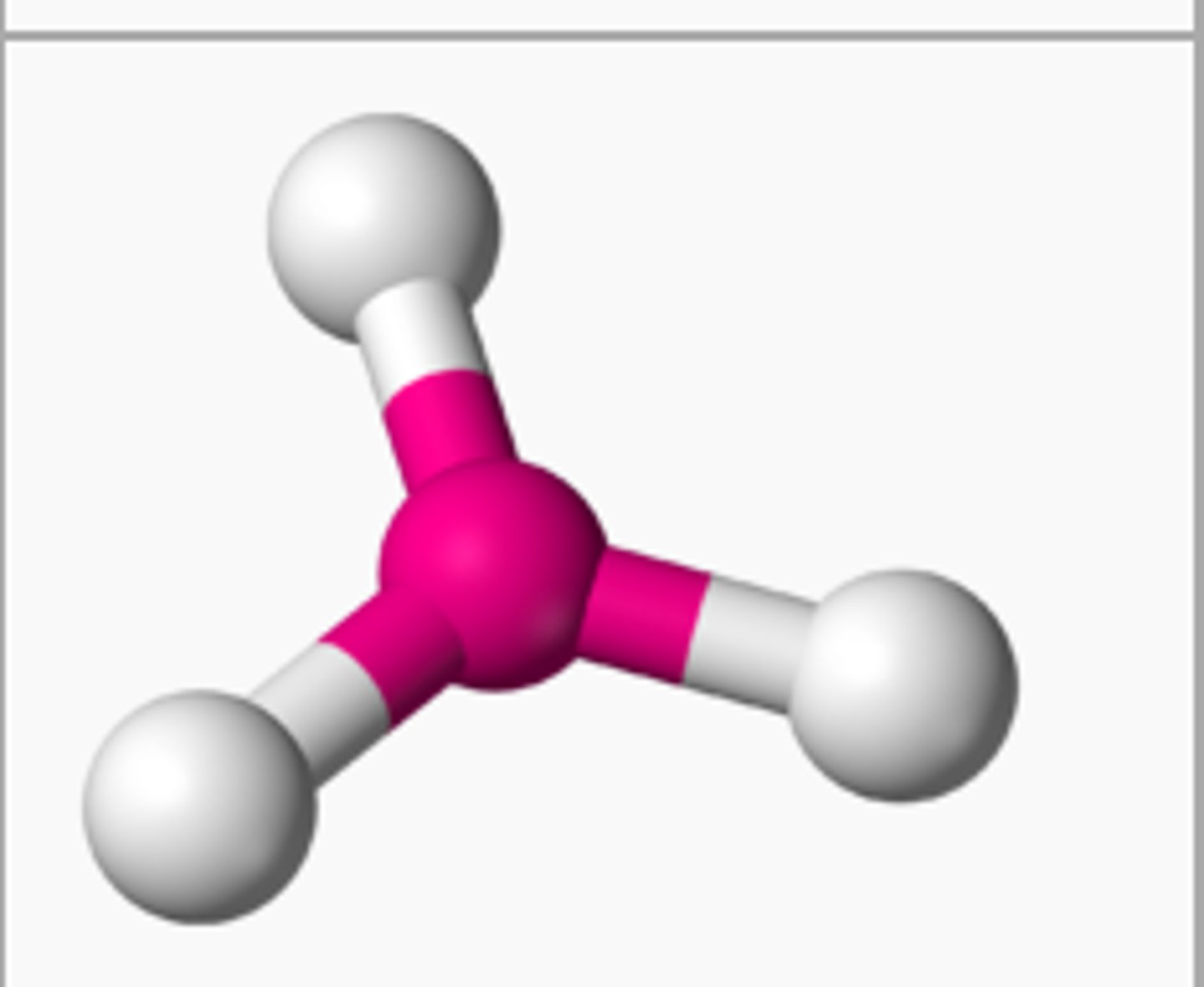
tetrahedral bond
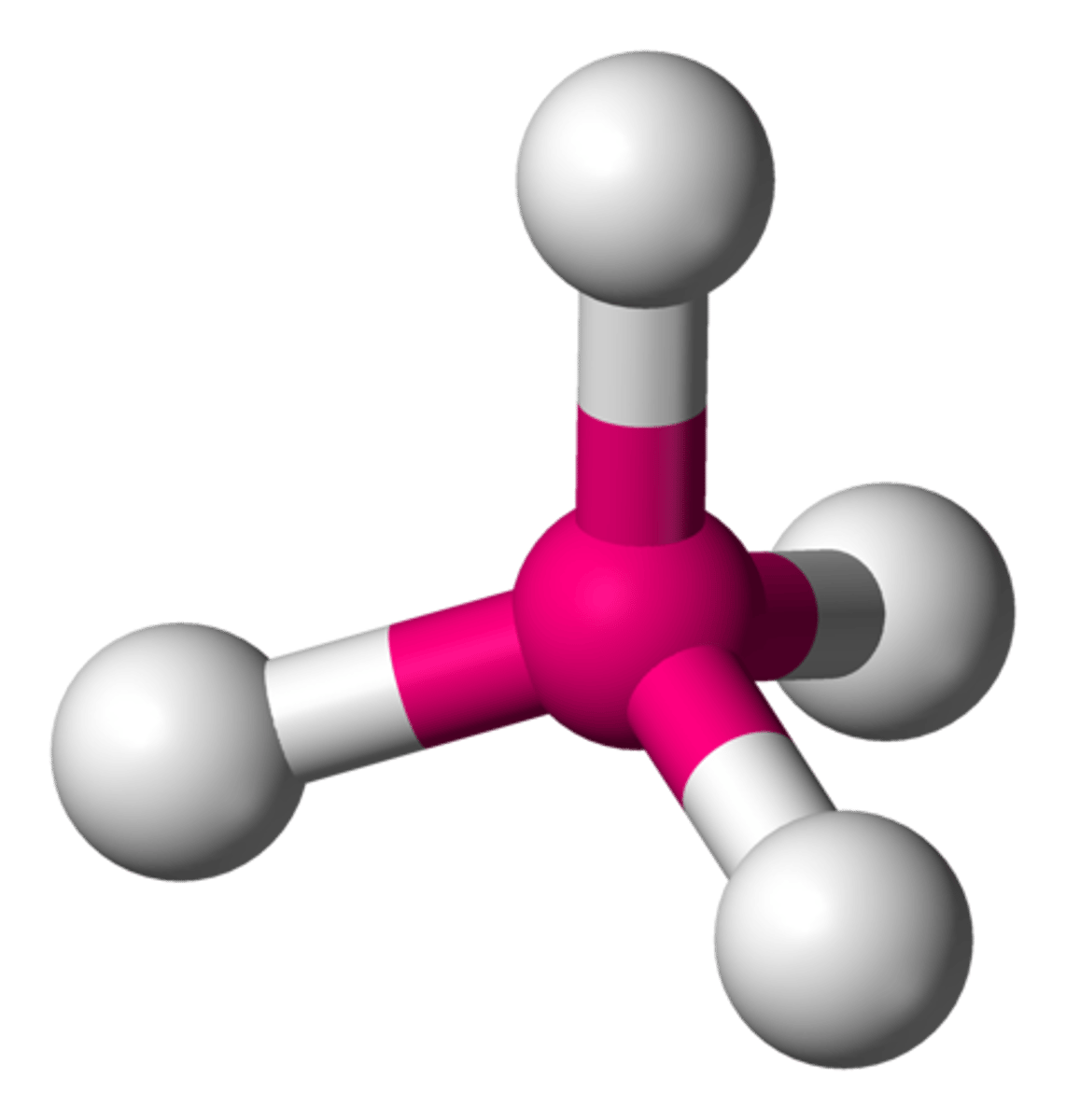
trigonal pyramidal bond
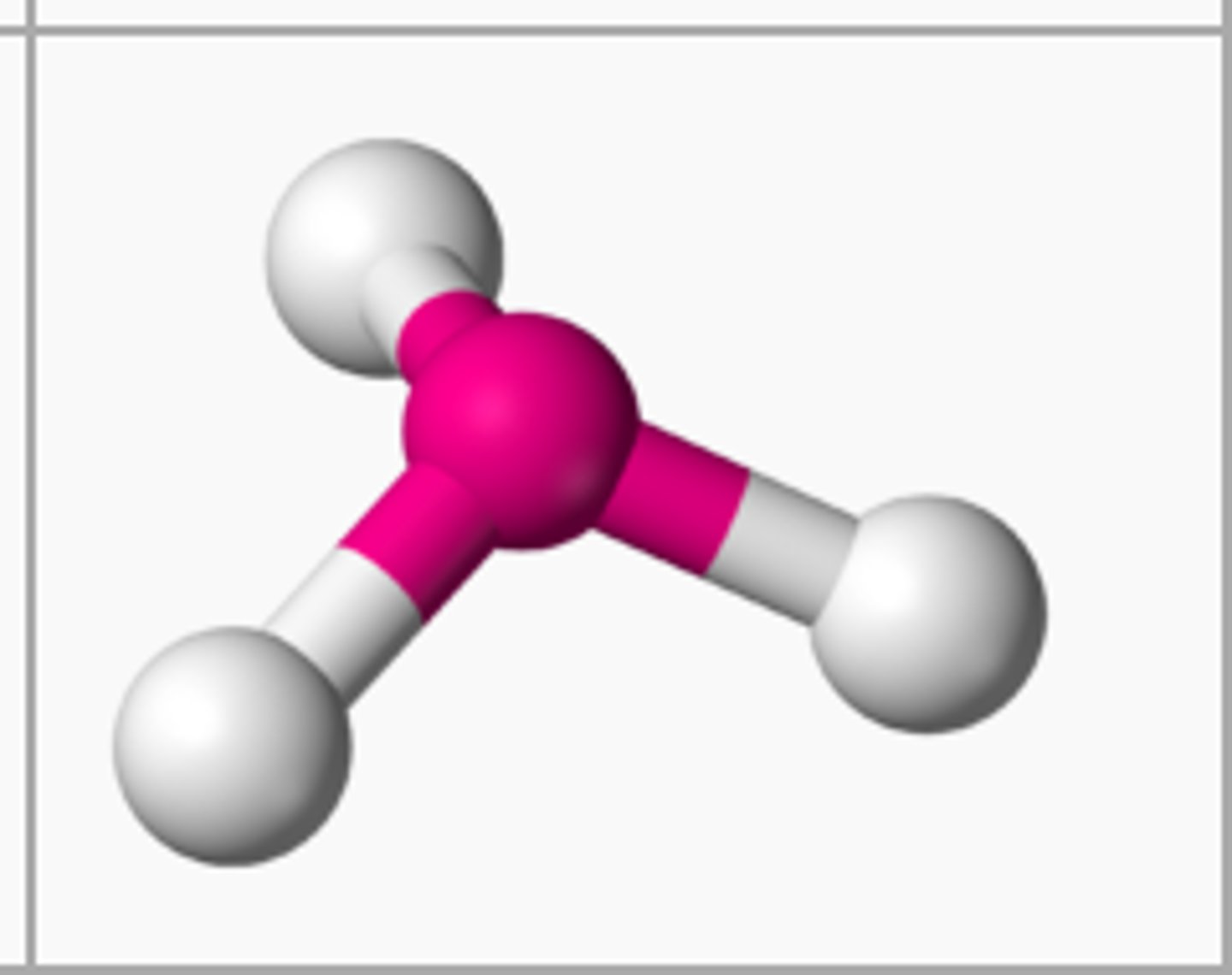
if there are 2 atoms bonded to the central atom and 0 unbonded pairs, then the shape is
linear
if there are 3 atoms bonded to the central atom and 0 unbonded pairs, then the shape is
trigonal planar
if there are 2 atoms bonded to the central atom and 1 unbonded pairs, then the shape is
bent
if there are 4 atoms bonded to the central atom and 0 unbonded pairs, then the shape is
tetrahedral
if there are 3 atoms bonded to the central atom and 1 unbonded pairs, then the shape is
trigonal pyramidal
if there are 2 atoms bonded to the central atom and 2 unbonded pairs, then the shape is
bent
what are the types of forces between molecules?
intermolecular forces
mono
one
di
two
tri
three
tetra
four
penta
five
hexa
six
hepta
seven
octa
eight
nona
nine
deca
ten
What is false about this statement: A hydrogen bond is a covalent bond between H and O in a water molecule.
A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular attraction, not a covent bond.
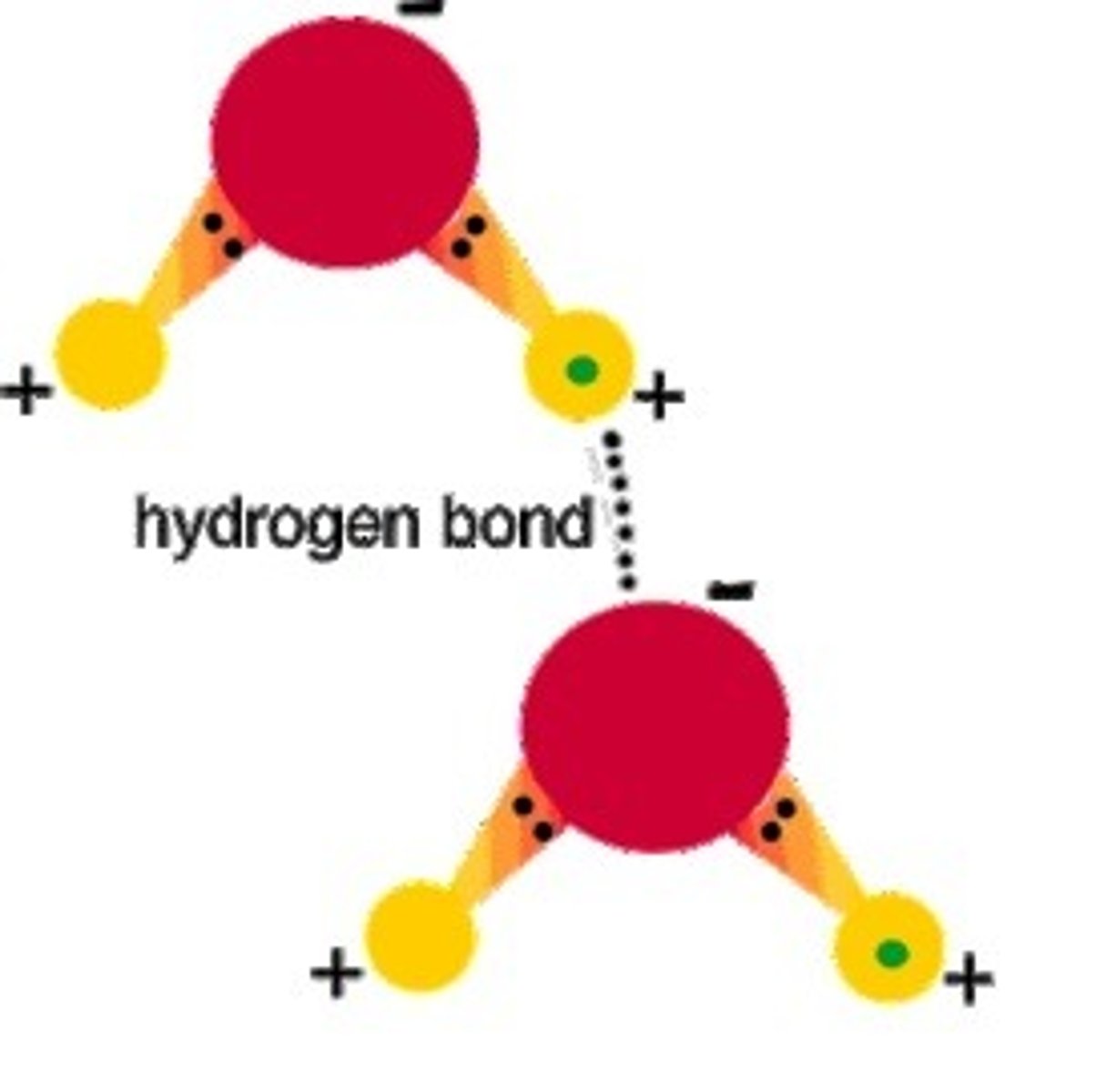
Correct this statement: A hydrogen bond is a covalent bond between H and O in a water molecule.
A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular attraction between hydrogen and the lone pairs of oxygen in H2O molecules
Which is the usually the central atom in a Lewis Structure?
Carbon (or the least electronegative atom)
a higher bond energy corresponds with a
shorter bond length
single bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share one pair of electrons

double bond
A covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms
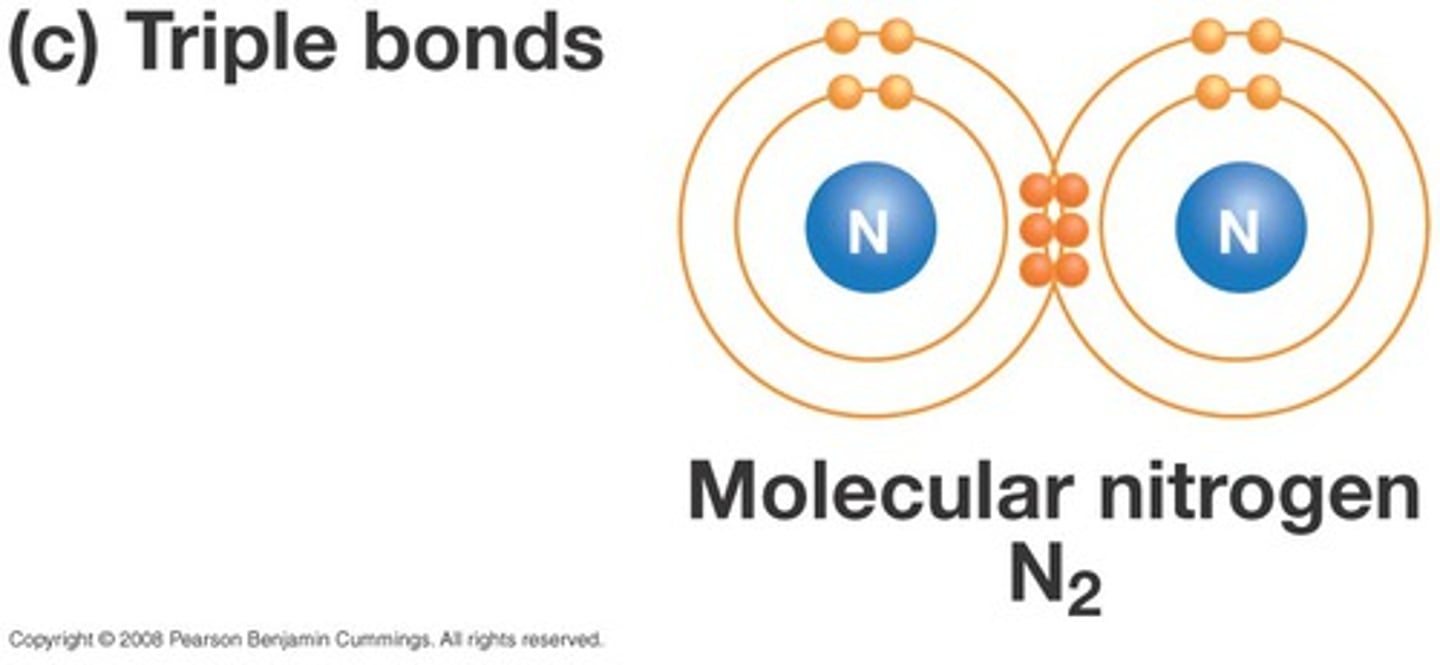
triple bond
A chemical bond formed when atoms share three pairs of electrons
the strongest intermolecular forces exist between
polar molecules
when writing an ionic name, the ____ goes first
cation
cation
positive ion
anion
negative ion
diatomic elements
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
use roman numerals on compounds containing
transition metals, tin, lead, metals that form different ions
when writing covalent names, don't use ____ on the first element
prefixes
when naming both ionic and covalent compounds, add ___ to the second element
-ide
metallic compounds have a ____ structure
lattice