Current Electricity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Define charge. What are the properties of charge?
Electric Charge - it is an intrinsic or fundamental property of matter to attract other materials showing electric and magnetic effects. It is a physical entity which is defined by excess or deficiency of electrons on a body.
It is denoted by Q and the unit used to measure charge is Coulomb
Electric charge is a scalar quantity
There are two types of charges namely Positive and Negative
Positive charge - elementary particle of positive charge is proton or loss of electrons
Negative charge - elementary particle of negative charge ie electron or gain of electrons
The SI Unit of charge is Coulomb
Explain the attraction and repulsion of charges
Like charges repel each other
Unlike charges attract each other
Explain the quantisiation of charge
Quantisation of Charge
Q = ne
Q is the charge
n is the number of electrons
e is the charge of one electron = 1.6 x 10^-19
Inferences from Quantisation of Charge
1.6 x 10^-19 or the charge on one electron is the smallest charge that can be found in the universe.
Charge is always available in an integral form , and an electron cannot be divided into further smaller parts
What can we infer from the quantisation of charge
Inferences from Quantisation of Charge
1.6 x 10^-19 or the charge on one electron is the smallest charge that can be found in the universe.
Charge is always available in an integral form , and an electron cannot be divided into further smaller parts
How do we classify materials based on conductivity of electricity
Conductor - the materials that allow current to pass through them and they have free mobile electrons in their outermost shell.
Insulators - the materials which do not allow current to pass through them as they do not have free mobile electrons in their outermost shells.
Semi-Conductors - the materials that only allow some amount of current to pass through them. Examples - Silicon , Gallium , Arsenic
Write a short note on electric current.

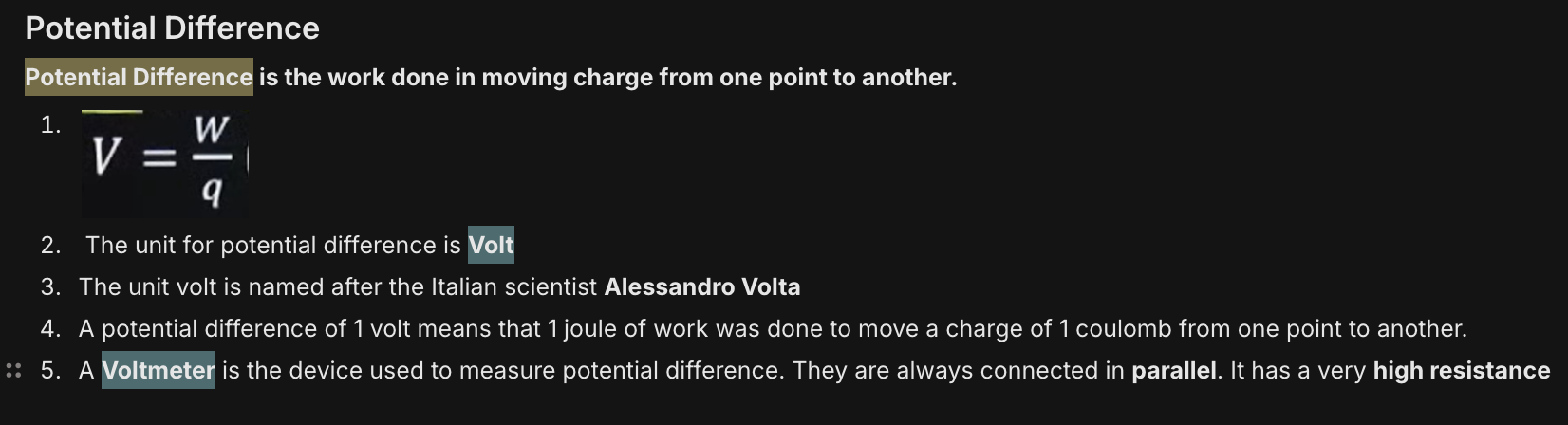
Write a short note on potential difference
Electric Potential is the work done for moving a unit positive charge from infinity to a certain point in the influence of another source charge.
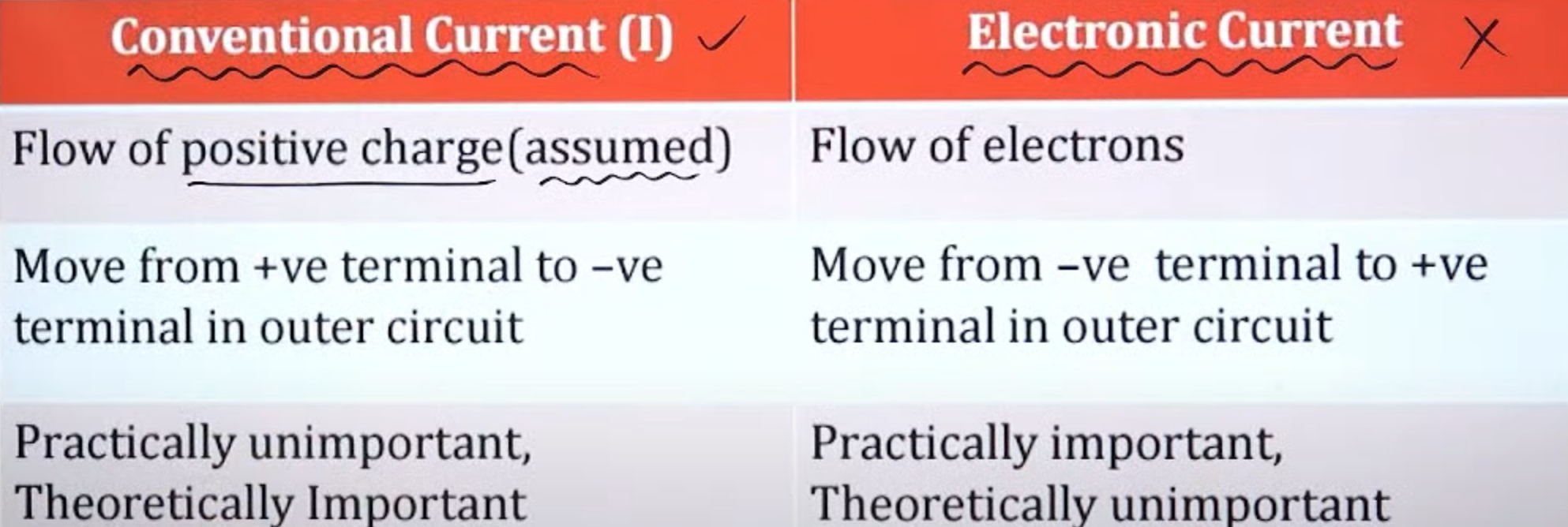
The positive terminal of a battery has a higher potential than the negative terminal of a battery , hence the current always flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. This is known as conventional current
Yet since electrons are negatively charged , they repel the negative terminal hence the electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. This is known as electronic current. Hence we assume that current travels in the opposite direction of electrons.
Differentiate between electronic current and conventional current.
Write a short note on Electric circuit
Electric Circuit
A continuous closed conducting path between the positive and negative terminals of a source of electric energy and other electrical components connected by wires along which the electric current flows is called an electric circuit.
Open Circuit - it is a circuit in which electric contact is broken at some point such that electric current does not flow through all of its components.
Closed Circuit - it is a circuit in which all the components of circuit are joined with one another such there is a continuous current flowing through all of them.
Write the statement of ohms law
The current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference applied across its ends provided physical conditions such as temperature remain unchanged.
What do we understand by 1 ohm of resistance.
If 1 volt of potential difference applied across two ends of a conductor makes a current of 1 ampere flow through it
What do we understand by 1 ampere of current
When 1 coulomb of charge flows through any cross section of a conductor in one second then we can say one ampere of current is flowing through it.
What are the factors on which resistance depends on
Length of Conductor - directly proportional
Area of cross section of the conductor - inversely proportional
Nature of material - resistivity
Temperature- more is the temperature more the resistance
What do you mean by connecting resistors in series? What are the disadvantages of doing so?
When two or more resistors are connected end to end to each other
If any one of the components stops working the circuit breaks and none of the components will work.
It is not possible for its components to have different values of current.
Resistance is maximum in series connections.
What is a parallel connection , what are the advantages of parallel connection?
When two or more resistors are connected simultaneously between two points they are said to be in a parallel connection.