Allied Health - Chapter 5: Cardiac Electrical System
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
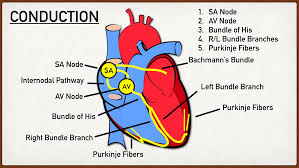
Pathway of Electrical Signal
An electrical impulse from the SA node at the top of the right atrium fires and is transmitted to the AV node, which prolongs the ventricles from contracting, so all blood from the atrium is pumped out. The signal is then sent to the Bundle of His, then the bundle branches, and then into the purkinje fibers. This then causes the ventricles to contract.
Normal BMP Range
60 - 100 BMP
QRS Complex
When the ventricles contract
P Wave
Contractions of both artiums
Sinus
regular/ normal rhythm
What do the impulse make the heart do?
The electrical stimulus travels down through the conduction pathways and causes the heart's ventricles to contract and pump out blood
SA node functions
natural pacemaker
The electrical stimulus travels down through the conduction pathways and causes the heart's ventricles to contract and pump out blood
AV node functions
gatekeeper
delaying the signal to allow for proper ventricular filling
Asystole
Rhythm that has no electrical activity, use CPR
Ventricular Tachycardia
The QRS Complex is irregular, and increased R complexes
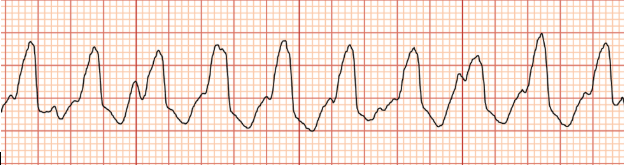
Ventricular Tachycardia
Use AED, chest pain, shortness of breath, shockable rhythm)
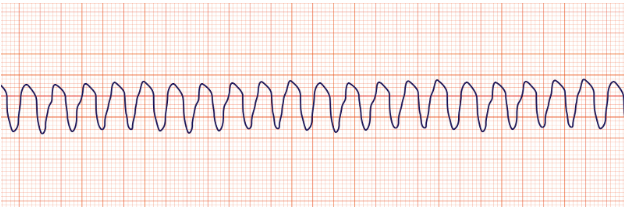
Ventricular fibrillation
quiver, blood is stagnant, cardiac arrest, unconious, shockable rhythm
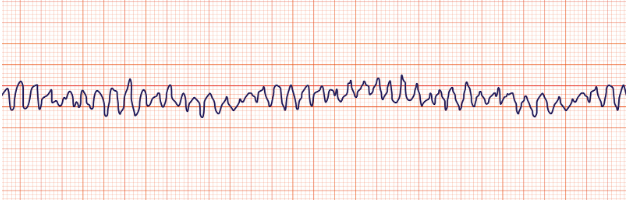
Atrial flutter
saw-toothed” flutter
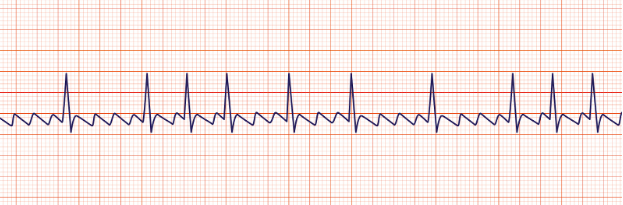
Atrial fibrillation
quivering, blood is stagnant, which can cause clots, then stroke, signal is coming from everywhere) usage of blood thinners
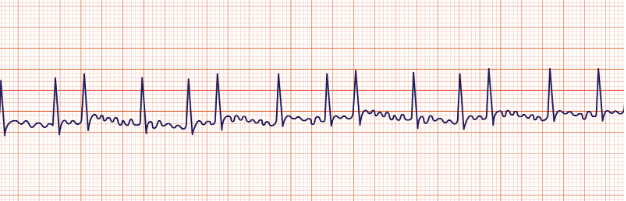
Sinus tachycardia
regular
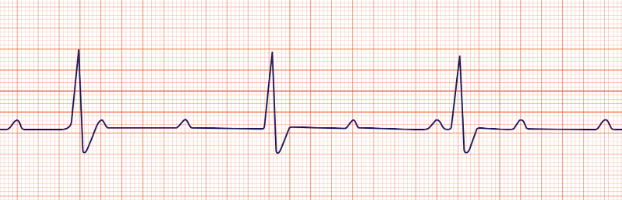
3rd degree heart block or complete heart block
1st degree heart block Wenckebach
longer, longer, longer, longer, drop,
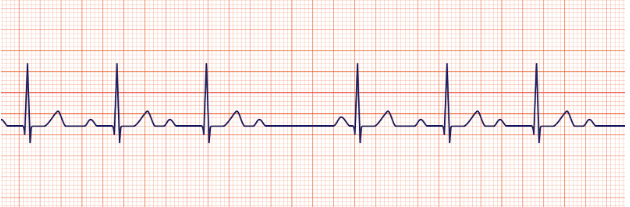
1st degreed heartblock
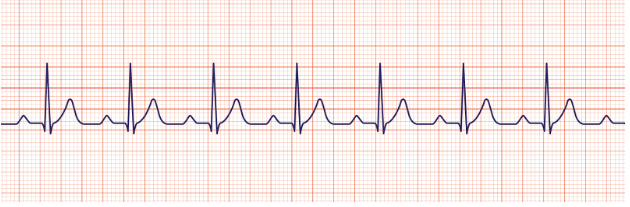
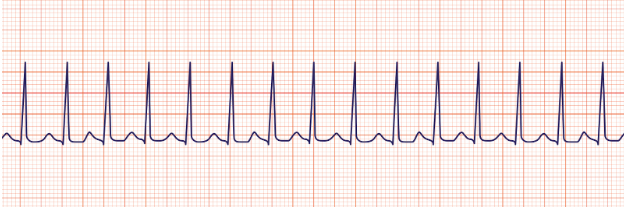
SVT (supraventricular tachycardia)
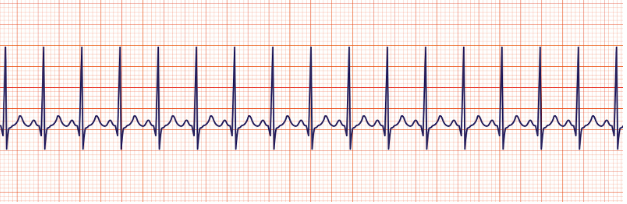
Sinus bradycardia
regular
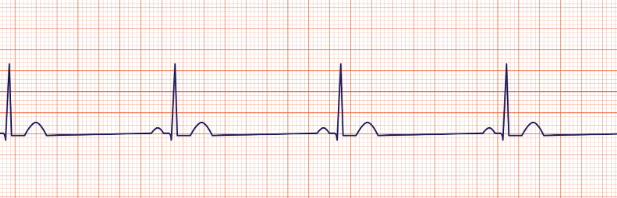
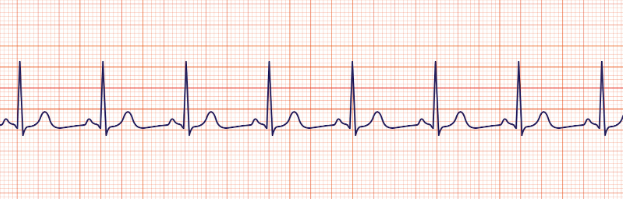
Sinus rhythm
regular regular
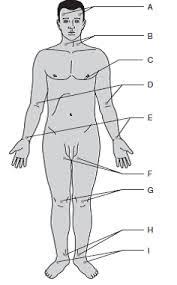
Temporal
A
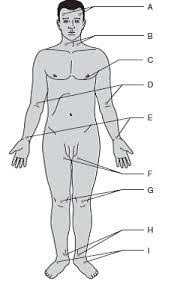
Carotid
B
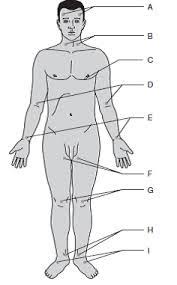
Apical
C
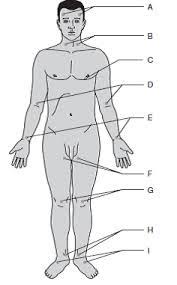
Brachial
D
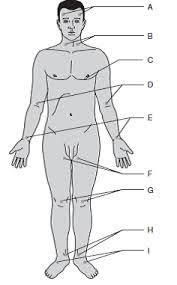
Radial
E (thumb)
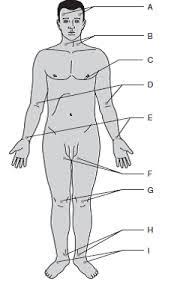
Ulnar
E (pinky)
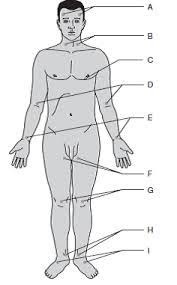
Femoral
F
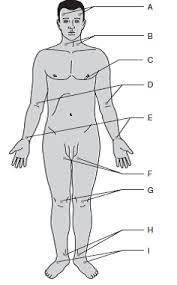
Popliteal
G
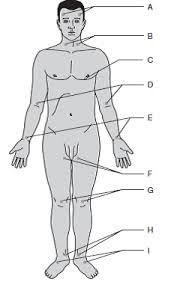
Posterial tibial
H
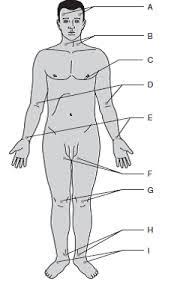
Dorsalis pedis
I
Electrical signal Heart Diagram
AV node blocked
heart rate is slowed leading to heart block, implanted pacemaker is needed
Damage to bundle branches
rhythm will slow to a block, distance between the p-wave and QRS complex
Extra electrical impulses
blood is pumeped ineffecientely due to an increases/ irregular heart rate (a-fib, SVT, a-flutter)