South College AVL Lab Med: Renal Function and Lipids - Lecture 6
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Serum creatinine (SCr)
Waste product of muscle metabolism, proportional to muscle mass and excreted daily by kidneys.
BUN (blood urea nitrogen)
Product of digestion and protein metabolism (takes place in the liver), excreted by the kidneys
urea, creatinine
? - filtered and reabsorbed
? - filtered and secreted
eGFR (glomerular filtration rate)
simple test, calculated with serum creatinine, that estimates how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood - mainly used to check kidney function.
lower eGFR
a higher creatinine level usually means what for eGFR?
kidney function
BUN levels rise when what decreases?
NO! (but BUN levels often change in parallel w/ creatinine)
is eGFR directly calculated from BUN?
NEED TO KNOW HOW KIDNEY IS FUNCTIONING BEFORE PRESCRIBING MEDS!
Why is it important to obtain SCr, BUN, and eGFR?
AKI (acute kidney injury)
Abrupt decrease in renal function
retention of urea, dysregulation of extracellular volume and electrolytes, multiple etiologies can cause this
What is often seen with an AKI?
Increased SCr by >/= 0.3 (mg/dL) within 48 hours OR 50% increase SCr in 7 days
OR
Decrease urine output <0.5 (ml/kg/hr) for >6 hours
How can creatinine levels/urine output help us assess if someone has an Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)?
Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
What is the most common cause of an AKI?
Ischemic ATN (most common)
Nephrotic ATN
What are the two types of ATN?
poor blood flow (shock, sepsis, severe dehydration) or kidneys don't get enough O2 (damaged tubules)
What causes with Ischemic ATN?
toxic substances - drugs (aminoglycosides, contrast dye, cisplatin), myoglobin (rhabdomyolosis), hemoglobin (hemolysis)
What causes with nephrotic ATN?
tubular cells die/slough off - block tubules
filtration impaired - waste builds up in the blood
What happens with an AKI? (INSERT PHOTO)
low urine output (oliguria) or sometimes normal
rising serum Cr and BUN
electrolyte imbalance (ex: hyperkalemia)
What are some symptoms of an AKI?
prerenal, intrarenal, postrenal
What are the three causes of acute renal failure?
prerenal
DECREASED BLOOD FLOW TO KIDNEYS
sudden and severe drop in pressure or interruption of blood flow to kidneys from severe injury or illness
Intrarenal
INTRINSIC KIDNEY DAMAGE
direct damage to the kidneys by inflammation, toxins, drugs, infection, or reduced blood supply
postrenal
OBSTRUCTION PREVENTING MICTURITION
sudden obstruction of urine flow due to enlarged prostate, kidney stones, bladder tumor, or injury
CHF, shock (sepsis, GI bleed), dehydration, vomitting/diarrhea w/ dehydration, ACE/ARBs and NSAIDs
What are some causes of prerenal acute renal kidney failure?
ATN, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, rhabdo, DM, nephrotoxic drugs (contrast, NSAIDS), Anabolic steroids
What are some causes of renal acute renal kidney failure?
prostate (BPH, cancer), nephrolithiasis (bilateral), bladder outlet obstruction, neurogenic bladder, tumor
What are some causes of post-renal acute renal kidney failure?
High Bun:Cr ratio (>20:1 - elevated)
Low Urine Na+ (<20 mmol/L - salt follows water)
What would we expect to see for prerenal Bun:Cr ratio and urine output?
Normal Bun:Cr ratio (10-15:1)
Low Urine Na+ (>20 mmol/L)
What would we expect to see for renal Bun:Cr ratio and urine output?
Variable Bun:Cr
What would we expect to see for post-renal Bun:Cr ratio and urine output?
More Cr produced from muscle metabolism
Why does an increase in muscle mass cause an increase on serum Cr?
muscle breakdown temporarily raises Cr
Why does an intense exercise cause a transient increase on serum Cr?
creatinine like substances absorbed from diet
Why does high protein or cooked meat intake cause a slight increase in serum Cr?
increased GFR (more blood filtered) clears Cr more rapidly
Why does pregnancy cause a decrease in serum Cr?
lower muscle mass = less Cr production
Why does aging cause a decrease/normal serum Cr?
AKI (sudden drop in GFR)
CKD (eGFR <60 mL/min for 3+ months)
Rhabdo (massive muscle breakdown - releases large SCr and myoglobin)
Urinary Tract obstruction (back pressure reduces filtration)
Heart failure or hypovolemia (reduce blood flow to kidneys - impair function)
Nephrotoxic drugs (direct kidney damage - reduces filtration)
Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of glomerulus reduces filtration capacity)
What are some disease processes that increase Serum Cr?
Muscle wasting (ex: malnutrition, muscular dystrophy - less Cr produced)
liver disease (liver makes Cr - if impaired, Cr production may drop)
overhydration (dilutes serum Cr)
What are some disease processes that decreases Serum Cr?
urinary symptoms (increase/decrease urine output, urgency, nocturia, incontinence, weak stream/straining, flank pain w/ gross hematuria, microscopic hematuria and/or proteinuria on urinalysis)
general symptoms (acute HTN or acute worsening HTN, peripheral/periorbital edema, symptoms of infection, arthralgia/myalgia, fever/chills, weight loss, night sweats, fatigue, etc.)
what are some acute reasons as to why we would measure creatinine levels?
CKD, DM, HTN, any autoimmune diseases affecting kidneys (lupus, sarcoidosis), any chronic condition requiring chronic meds
What are some chronic reasons as to why we should measure creatinine levels?
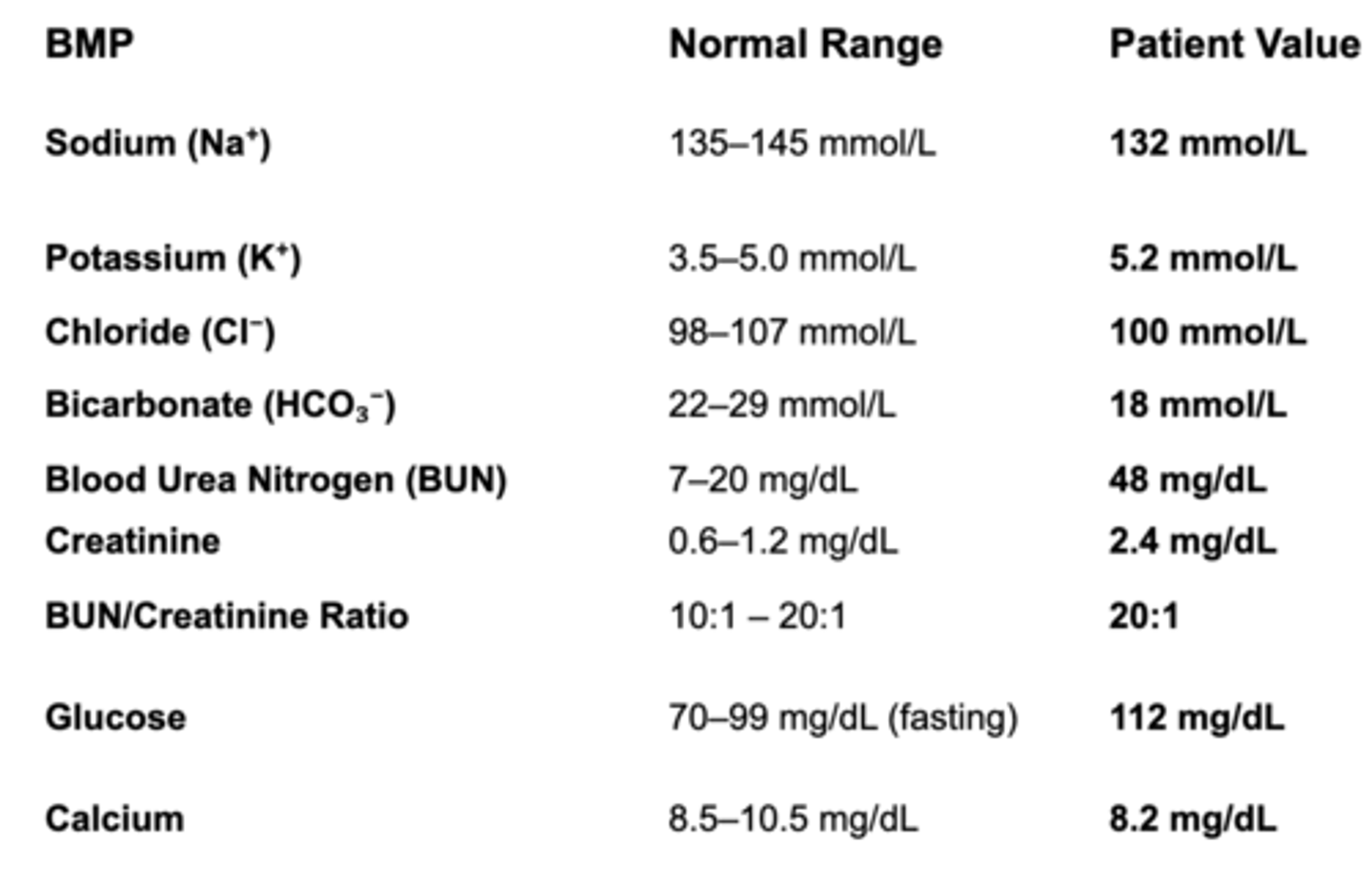
pre-renal AKI
(low Na, high K, normal Cl, low bicarb, high BUN, high BUN:Cr, high glucose, low Ca)
68 YO M patient w/ HTN and type 2 DM presents saying "I've been feeling weak and not peeing as much as usual".
BP: 90/60, HR: 105, dry mucus membranes, BMP: refer to photo
What are you suspecting this patient has?