Molecular Evolution
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What does the evolution of macromolecules involve?
The rates and patterns of changes in the genetic material and its encoded products during evolutionary time, and the mechanisms responsible for such changes
What is molecular phylogeny?
The reconstruction of the evolutionary history of genes and organisms
What does phylogeny involve gathering data on?
Morphology
Development
Metabolic
Biochemical
Genetic
Anything
What does phylogeny refer to?
The ancestry of a biological lineage (also synonymous with phylogenetic tree). Phylogeny is tree-like (or dichotomous) and provides the historical basis to the comparative method
How did taxonomy begin?
By grouping taxa together based on morphology at various structural levels
What does the branching diagram of phylogeny show?
The relationship between species (or higher taxa) based on their shared common ancestors
What is the principle of phylogenetics?
To infer evolutionary relationships among organisms (or genes) by analysing traits or sequences, with a focus on shared derived characteristics (synapomorphies), not just overall similarity
What is homology?
Where similarity is due to common inheritance from an ancestor
What is homoplasy?
Where similarity is due to independent acquisitions of the same or superficially similar character state
What does distance in a phylogenetic tree reflect?
A decreasing number of shared, homologous characteristics (assuming that evolution maximises homology)
What is the basis of molecular systematics?
The accumulation of sequence differences through time
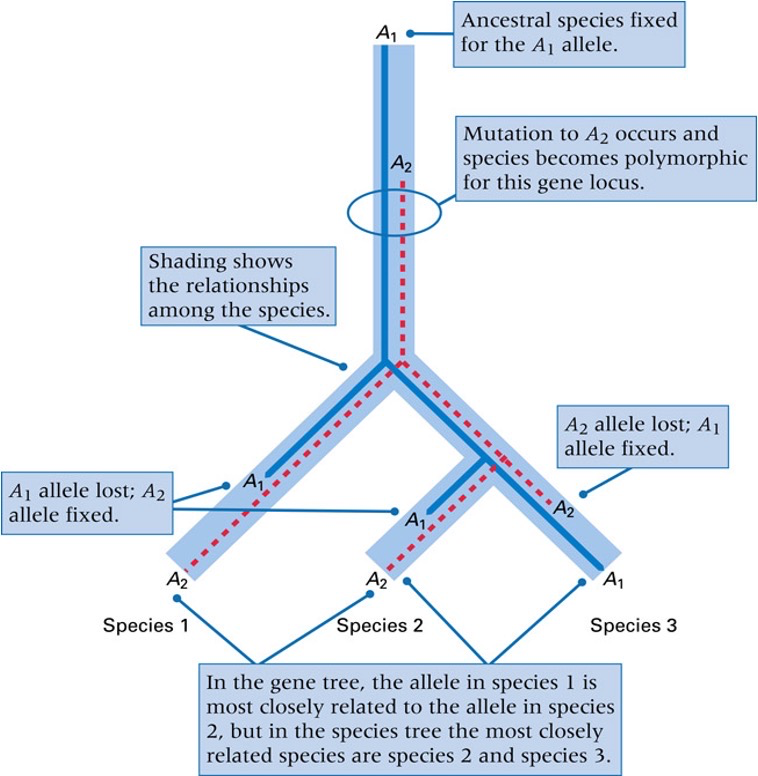
What is a gene tree?
A diagram of the inferred ancestral history of a group of sequences. It is only the estimate of the true pattern of evolutionary relations
What is one of the ways to estimate a gene tree?
Neighbour joining
What is bootstrapping?
A common technique for assessing the reliability of a node in a gene tree
What is a taxon?
The source of each sequence
What does a gene tree not necessarily coincide with?
A species tree, as a gene tree involves the sorting of polymorphic alleles in different lineages
What makes it possible for different parts of the same gene to have different evolutionary histories?
Recombination within genes
What does a gene tree look like?