Pyschology Flashcards chapters 10 and 12
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Motivation
The wants or needs that drive or direct behavior towards a goal
Intrinsic Motivation
Arising from internal factors such as happiness or personal satisfaction, others include autonomy, mastery, purpose
Extrinsic Motivation
Arising from external factors, performed in order to receive or avoid something from others, such as compensation, punishment, or a reward
Overjustification effect
Intrinsic motivation is diminished when extrinsic motivation is introduced
Drive Theory
States that deviations from homeostasis create physiological needs that result in drive states, which direct behavior to the need in order to reattain homeostasis. Emphasizes the roles habits play in behavioral responses and arousal theory
Self-efficacy
Defined as an individual’s belief in their own capacity to complete a task
Triggers for hunger-
Empty stomach contractions, low blood sugar levels
Satiation
Fullness or satisfaction from a meal
Set point theory
Asserts that everyone has an ideal body weight, or set point, which is genetically predetermined and resistant to change. Efforts to move weight significantly are resisted by changes in energy intake or expenditure
Bulimia Nervosa
an individual engages in eating behavior of binging, followed by an attempt to compensate for the large amount of food consumed by purging, usually through vomiting or laxatives
Anorexia Nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by the maintenance of a body weight well below healthy and average ranges through excessive starvation or exercise. Often associated with body dysmorphia.
Sexual Behavior
Limbic system and hypothalamus are associated with sexual motivation
Kinsey’s survey research on sex in 1948 and 1953
Findings:
Women and men are both equally interested in sex, both women and men masturbate without adverse health consequences, relationships and sexual acts between members of the same sex or gender are actually fairly common, also developed the kinsey scale to measure a person’s emotional, romantic, and erotic attractions to other people or no people
Master and Johnson’s research
Observed nearly 700 people in a study of physiological responses during sexual behavior. Included the observation of both people masturbating, having intercourse, having intercourse in a variety of positions, and masturbation with sex toys. Measured physiological variables such as blood pressure, respiration rate, vaginal lubrication, and penile tumescence.
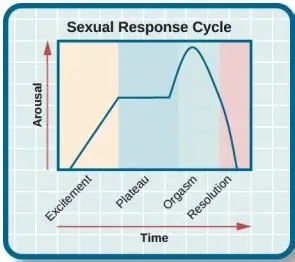
Sexual Response Cycle
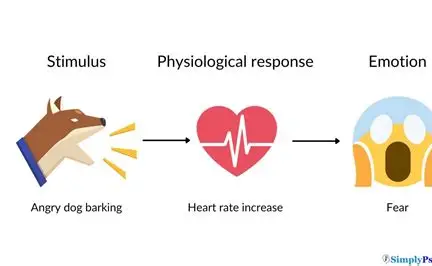
James-Lange Theory
Arousal/Stimulus—→ heart rate increase——> fear
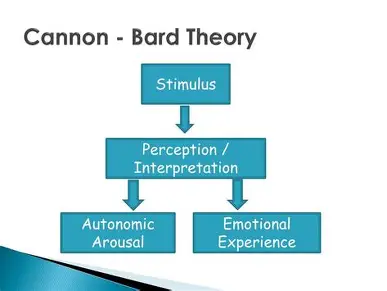
Cannon-Bard theory
Arousal/stimulus elicits both the emotion, fear, and the physical response
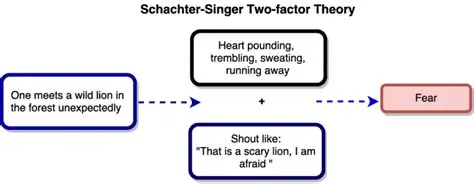
Schacter-Singer two factor theory
Arousal/stimulus elicits in the physical response and the addition of a cognitive label that results in fear
Lazarus' cognitive-mediational theory
arousal—> appraisal——→ fear, heart pounding, sweating

Situationism
The view that our behavior and actions are determined by our immediate environment and surroundings
Dispositionism
The view that our behavior is determined by internal factors, like personality and temperament
Fundamental attribution error-
People’s tendency to over emphasize internal factors as explanations or attributions for the behavior of others. Assumes that behavior is a trait of that person, and under estimates the power of situation. research shows that individualistic cultures are more prone to this than collectivistic ones.
Actor-Observer bias
The phenomenon of attributing other people’s behaviors to internal factors, while attributing our own to situational forces
Self-serving bias
The tendency to explain our successes as the result of internal or dispositional forces, and our failures as a result of situational or external factors
Attribution
A belief about the cause of a result
internal vs external
stable vs unstable
controllable vs uncontrollable
Social role
A pattern of behavior expected of a person in a certain setting or group
Social norms
a groups expectation for what is and is not appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members
Scripts
A script is a person’s knowledge about the sequence of events expected in a specific setting
Attitude
Our evaluation of a person, idea, or object. Can be favorable or unfavorable, positive or negative. Three components-
an effective component, how we feel about it
a behavioral component- effect of the attitude on behavior
cognitive component- beliefs and knowledge
Cognitive dissonance-
Psychological discomfort arising from holding two or more inconsistent attitudes, behaviors, or cognitions. Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance states that when we experience a conflict in our beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors that run counter our positive self-perception, we experience psychological discomfort or dissonance

The effect of initiation-
difficult initiation into a group can influence an individual to like the group more
Justification of effort
suggests that we value goals and achievements we put a lot of effort into
Elaboration Likelihood method
Two routes, central and peripheral.
Central- logic driven and uses data and facts to convince people of an argument. The argument must be strong and if successful, will result in lasting attitude change
Peripheral- Indirect route using peripheral cues to associate positivity with the message

Conformity-
The change in a persons behavior to go along with the group, even if they dont truly agree
Asch Effect-
the influence of the group majority on the individuals judgment
Normative social influence-
Conformity to a group norm to fit in, feel good, and be accepted by the group
Informational social influence-
Conformity to the group norm prompted by the belief that the group is competent and has the correct information
Bystander effect-
Situation in which a witness or bystander does not volunteer to help a victim or person in distress
Aggression
To seek to intentionally harm another person
Prosocial behavior
Voluntary behavior with the intent to help or aid others