Ch 4 Continued Networks
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are the main Types of Networks? (3)
Two sided Markets
Marketplaces
Platforms
Two-sided markets
have two types of members, each creating value for the other (e.g., Free Adobe Reader creates a huge market of users)
Platform is
also a two-sided network with specific members on the two
sides: users and developers (e.g., Windows, iOS, Android)
What is required for the success of digital networks?
The success of these digital networks requires solving the “chicken-or-
the-egg” problem → each side is waiting for the other one to grow
before joining the network
Aka. Deciding which side to monetize and which side to subsidize
(e.g., Free Adobe Reader
Explain the App Store & Their network effect
The App Store for the iPhone is the network effect that fueled its growth
and dominance: The more users, the more Apps, and vice versa.
What are network properties? (4)
Network Properties:
• Network Effect Strength: comes from the strength of positive feedback;
it may vary by network and may vary over time for the same network.
• Network Clustering: The topology of existing members of a network
determines its potential for winner-take-all dynamics to emerge (e.g.,
OpenTable online restaurant reservation, or Uber Eats).
• Disintermediation Risk: Network effects are weaker when participants
can easily transact outside of the network (i.e., disintermediate the
network owner).
• Multihoming Potential: The technical term used to describe the
simultaneous participation of network nodes in multiple competing
networks. (e.g. VOIP)
Implications for managers to harness network economics…(5)
• Network Effects, Not Just Networks: solving the chicken-egg dilemma and
finding a way to trigger positive feedback loops are the precondition for
winner-take-all dynamics (e.g., online dating platforms).
• The Threshold of Significance: for digital products delivered over the Internet,
the market can tip very rapidly (e.g., TikTok). In these markets, being the
innovator and the first mover is critical.
• Users Select a Network: customers will pick a dominant network, not a
product or a service provider (MS. Windows network)
• Controlling the Network Provides Competitive Advantage (iOS and Android)
• The Importance of Mutual Exclusivity: Incompatible standards of two
competing platforms. The higher the cost of multihoming, the more valuable
it is to control ownership of the network.
E.g., VoIP applications are not mutually exclusive
Q: What has led to the unprecedented capture, storage, and processing of data?
A: The expansion of digital networks.
Q: What must be understood to extract value from data and information?
A: The economic characteristics of information.
What is the key distinction between data and information?
A: Information is data in context—data becomes information when given meaning and can be interpreted.
Why are information goods and digital goods purchased?
For gaining access to the information they contain (e.g., software, books, music)
How are information goods characterized?
They are characterized by high fixed costs & very low marginal costs
Economic Characteristics of Information (8)
Information Has High Production Costs: The first copy is very expensive to create (e.g., this textbook)
Information Has Negligible Replication or Marginal Costs
The Information Is Not the Carrier: (movies on VHS tapes and later on DVDs, now streamed on Netflix)
Information Has Negligible Distribution Costs
Costs Are Sunk: the investment cannot be recovered → higher risk
Information Has No Production Capacity Limits: Number of downloads of a song on iTunes
Information Is Not Consumed by Use
Information Goods Are Experience Goods: products or services that need to be tried (i.e., experienced) before their quality can be assessed
Marginal Implications about Information (4)
Information is:
Easily customizable, often modified easily
Reusable (not consumed by use)
often time valued
able to achive significant gross profit margins
due to low replication and distribution costs; firms that produce
successful information goods can enjoy vast profit margins.
What are information-intensive goods?
A: Goods where information is a critical component or necessary resource during the production process, even if customers primarily seek a tangible product or service.
Q: How is information used in industries like restaurant franchising, car manufacturing, cruise ships, or health care?
A: Information supports production, coordination, and service delivery—it’s essential for efficiency, quality, and innovation in these industries.
Why might McDonald’s be considered part of the information business?
A: Because much of what the franchisor provides—like processes, systems, and operational knowledge—is information and expertise, not just food.
How are information and knowledge embedded in production and organization?
A: Through processes, technology, and systems such as automation, design, and data-driven management (e.g., self-driving cars).
How does information play a role in other brands beyond McDonald’s?
It influences design, material selection, production methods, and distribution networks, making it a core element of value creation.
Why does information rely on a physical carrier?
Because information cannot exist or behave independently—it needs a medium like paper, devices, or networks to be transmitted or stored.
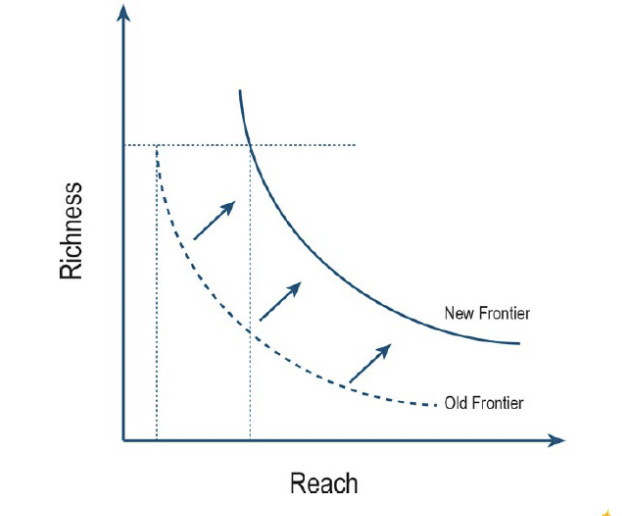
What was the traditional trade-off in information goods?
A trade-off between richness (detail and quality of information) and reach (number of people it could be delivered to).
How has the Internet changed information delivery?
A: It allows firms to reach large audiences with rich, interactive, and personalized information simultaneously.
What have communication networks enabled firms to do?
A: They’ve allowed firms to decouple information from its physical carrier, enabling digital distribution models like Netflix and Spotify.
Explain the difference / Tradeoff between richness & Reach
*Richness represents
the amount of information that can be transmitted,
tailored to individual needs, and
the level of interactivity of the message.
*Reach represents the number of possible recipients of the message
How does Technology effect richness/reach?
This trade-off is fading away with the widespread Internet services and mobile platforms.
There are still compromises to be made between reaching a large audience and offering a very rich exchange (example?)
What does virtual mean?
Something that doesn’t physically exist but is made to appear real through software (e.g., virtual reality).
What else can the term virtual refer to?
Activities performed on a digital platform rather than in a physical space.
What is process virtualizability?
The degree to which a process can be carried out without physical interaction among participants or objects involved.
What is the dominant trend in modern business processes?
Process virtualization
How does online dating illustrate process virtualization?
It shows how traditionally physical interactions can be replaced by digital interactions through software platforms.
What is online shopping an example of?
A: Browsing and evaluating digital representations of products through software or mobile apps—a form of virtualized consumption.
What does process virtualizability theory explain?
A: It identifies which processes can be successfully virtualized and to what extent.
Can all processes be virtualized equally?
No, some processes are more suited to virtualization than others.
Why shouldn’t face-to-face interactions be underestimated?
A: Because personal, in-person communication still holds unique value that digital alternatives can’t fully replace.
Process Virtualization Theory helps…
determine which processes have the potencial to be successfully virtualized
The virtualizability of a process requires 4 elements
sensory requirements (the need for participants to be able to experience
tasting, seeing, hearing, smelling, and touching the other objects).relationship requirements (the need for interaction in a social or professional context, like face-to-face interaction)
synchronism requirements (the degree to which the activities need to occur in real time or with minimal delay)
Identification and control requirements (requiring the unique identification
of all participants and the ability to control their behavior)
Three capabilities of digital technology enable most modern
virtualization initiatives
Representation is the capability of IT to effectively simulate actors, objects, their characteristics, and the user interactions with them.
Reach is the capability of IT to overcome both time and space constraints, allowing the flexible participation of users in processes.
Monitoring and identification is the capability of IT to authenticate process participants and objects and track their activities
Why is airline check-in a good candidate for virtualization?
Because it has low requirements for sensory experience, personal relationships, synchronism, and identification, making it easily performed digitally.
Managerial Implications (4)
Questioning of Traditional Business Models→ (Newspaper classified business is threatened by Craigslist)
Having a direct relationship with the customer is critical → Consider the retail banking industry that is not personal
The Decreasing Value of Asymmetric Information→ Used car dealerships (Lemons and Peaches)
The richness/reach frontier is progressively pushed outward.
Obstacles to realizing virtualization value (5)
New technology must replace all characteristics of the old one.
(e.g., Physical newspapers and books)Human resistance to change
Retaliation from Incumbents
Scarcity of customers’ time and attention leads to a slow adoption rate of the technology.
Adoption rate is a critical success factor
• The largest failure was Webvan, an online grocery shopping
company, which burned $1.2 billion in funding.
• The consumer adoption rate was much slower than the adoption
rates Webvan needed to survive.
What is disruptive innovation?
Innovation enabled by digital technologies that dramatically changes or reshapes entire industries.
What is the difference between sustaining and disruptive technologies?
Sustaining technologies improve existing products and maintain performance, while disruptive technologies fundamentally alter industries and make existing technologies obsolete.
What do sustaining technologies do?
They maintain or revitalize the current rate of performance of existing products or services.
What is the typical performance trajectory of a new product like EV batteries?
A: It usually follows an S-curve growth pattern, with slow initial progress, rapid improvement, and eventual maturity.
What is the impact of disruptive technologies on industries?
They significantly alter or replace established technologies, often transforming or eliminating existing markets.
What this dawg?
S-Curve Behavior of Tech performance
Maintaining technologies
Maintain or revitalize the current rate of performance improvement of the products and services that use them
Sustaining Technologies extend….
the useful life of the product as the market demands further and further improvements
• It will therefore be a good candidate to replace a previous technology because it offers the same set of attributes, but yields superior performance
How do disruptive technologies differ from sustaining technologies?
They can’t be used in mainstream products at first because they initially deliver inferior performance on key dimensions.
What is the first key characteristic of disruptive technologies?
A: They offer a different set of attributes compared to technologies used in the mainstream market.
What is the second key characteristic of disruptive technologies?
Their performance improves faster than the rate of improvement demanded by the market.
Why is it important to understand the dynamics of disruptive technologies?
Because they have the potential to reshape entire industries, as seen with examples like Netflix.
What are two advantages of Disruptive Technologies?
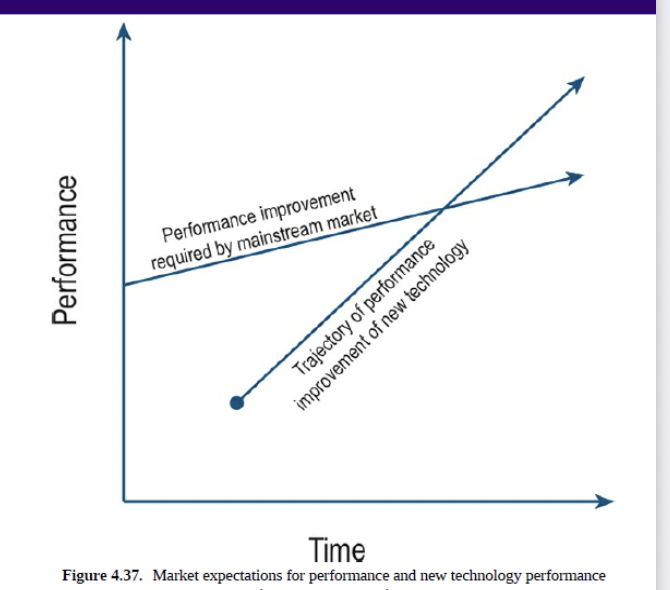
The technology offers a different set of attributes than the technology the firm currently uses in its products.
The rate of performance improvement is higher than the rate of improvement demanded by the market
Example:
In the hard disk industry, disruptive innovation occurred when smaller disk drives emerged. Although early versions had lower storage capacity, they improved rapidly—faster than market demand. Once their capacity met customer needs, mainstream users adopted the new drives, valuing additional benefits like smaller size and lower power consumption.
What are the key implications of disruptive technology for firms?
Disruptive innovations evolve quickly on existing performance metrics and can eventually meet market needs.
Firms focused only on sustaining innovations risk vulnerability, as new technologies introduce appealing attributes that attract customers once the performance gap closes.
By the time customers switch to the new technology, established firms often struggle to adapt and lose their dominant market position.
Where do disruptive technologies usually begin?
They start by serving a small niche market that large companies often overlook.
What is the first step firms should take when a disruptive technology emerges?
Monitor the emergence of new technologies.
What should firms envision regarding disruptive technologies?
The new market that could be created by the technology.
What is a key challenge in adopting disruptive technologies?
Identifying which customers will value the new blend of features and functionalities.
How can firms effectively commercialize disruptive technologies?
By spinning off a new division or separate entity dedicated to the disruptive technology to compete effectively in the emerging market.
What is the value driver in networks?
Larger network size creates value, opposite to scarcity.
What are network effects?
When an individual joins a network, they create value for others; positive feedback loops can lead to market dominance.
What are key characteristics of information in the modern competitive world?
Infinitely reusable, highly customizable, and time-valued.
Why is it important to distinguish information from its carrier?
Because the value and use of information are independent of the medium through which it is transmitted.
How do new technologies affect the richness/reach trade-off?
A: They push the frontier, enabling richer interactions over larger reaches and threatening established business models.
What does process virtualization theory help analyze?
A: The likelihood that an activity can be performed in the digital world.
What is the opportunity in process virtualization?
To anticipate new forms of interaction by leveraging new uses of existing technologies.
How are new technologies classified?
As sustaining (improving existing products) or disruptive (reshaping industries).
Why are disruptive technologies dangerous for established firms?
Firms that underestimate their impact risk losing customers and market position to new entrants.